Disposable Syringe Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Detailed Breakdown of Materials, Machinery & Economics Insights

What is Disposable Syringe?
Disposable syringes are single-use medical devices designed to inject or withdraw fluids from the body in a sterile, safe, and efficient way. They usually consist of three primary parts-a barrel, a plunger, and a needle (in most cases)-made from medical-grade plastics such as polypropylene or polyethylene.
Key Applications Across Industries:
These syringes are manufactured for one-time use to prevent infectious disease transmission and to ensure accuracy and hygiene during the medical procedure. Unlike reusable glass syringes, disposable syringes eliminate the need for sterilization between uses, reducing the risk of cross-contamination in healthcare environments. They are available in various types, including luer-lock, luer-slip, insulin, and prefilled syringes, each tailored for specific medical and pharmaceutical applications. The manufacturing process for disposable syringes includes precision molding, assembly in cleanroom conditions, and sterile packaging to maintain integrity until the point of use. Beyond hospitals, these syringes are widely used in diagnostic centers, vaccination programs, home healthcare, and veterinary applications. The dependence of the global healthcare system on injections for drug delivery-from vaccines and insulin to biologics and antibiotics-underpins continuous demand for disposable syringes. Their ease of use, low cost, and compatibility with automated drug delivery systems have also made them indispensable in modern medicine. Moreover, innovations such as safety syringes with retractable or auto-disable mechanisms have evolved to address needle-stick injuries and enhance patient and clinician safety, reflecting the sector's continuous adaptation to regulatory, safety, and environmental standards in healthcare delivery.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global disposable syringe market reached a value of USD 16.11 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 28.89 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 6.37% during 2025-2033. A blend of healthcare expansion, disease management trends, technological innovation, and safety regulations drives the disposable syringes market around the world. Among them, one of the key demand drivers is the ever-growing focus on infection control and patient safety. While global health systems are forcing down the incidence of hospital-acquired infections and preventing the transmission of blood-borne diseases, single-use syringes are increasingly becoming standard practice in both developed and developing healthcare settings.
The rising immunization programs by governments and international bodies are also major catalysts to demand; billions of vaccine doses are administered each year, especially in public health initiatives and pandemic preparedness. Increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and arthritis, further propels the consumption of syringes since patients need to take injectable therapies or administer insulin quite frequently at home. A trend toward self-administration and home healthcare facilitates demand for easy-to-use, prefilled, safety-enhanced syringes. Meanwhile, advances in syringe design-be it auto-disable mechanisms, retractable needles, or biopolymer alternatives-are extending uses to meet exacting safety and sustainability requirements. Pharmaceutical industry dynamics also play a key role: the rise of biologics and biosimilars, which are mostly administered by injection, drives the adoption of syringes in both clinical and commercial drug delivery. Besides, healthcare infrastructure development in emerging economies, along with increased healthcare spending and public-private manufacturing collaborations, augments local syringe production capabilities and availability. Finally, global regulatory frameworks that champion safe injection practices and sustainable manufacturing-meaning various ISO and WHO standards-continue to reinforce disposable syringe adoption worldwide. Putting all these drivers together means that disposable syringes continue to be an important and growing part of healthcare delivery worldwide.
Case Study on Cost Model of Disposable Syringe Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale disposable syringe manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed disposable syringe manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 200 units of disposable syringe per day.
Manufacturing Process: Manufacture of disposable syringes involves a series of precisely controlled mechanical and sterile operations designed to guarantee accuracy, reliability, and safety for usage in medical environments. Processing starts with raw material preparation, involving mainly medical-grade polypropylene and polyethylene, selected for their chemical resistance, biocompatibility, and transparency. These are melted and injection molded into two key components of the syringe-the barrel and the plunger-by high-precision molds under cleanroom conditions. The barrel, which holds fluid, is formed with clear volume markings that are in place to ensure dosing accuracy, and the plunger is molded to fit snugly inside the barrel, maintaining smooth movement and leak-proof performance. After molding, components are trimmed, inspected, and cooled, then move to the assembly phase in which the rubber gasket or piston tip attaches to the plunger to ensure an airtight seal. The next stage in the process involves needle manufacturing and attachment. Stainless steel is drawn into fine tubes, cut to size, and ground to produce sharp, beveled tips. Needles are then cleaned, sterilized, and attached to the syringe body, either permanently or via detachable luer-lock fittings. The assembled syringes then undergo leakage, alignment, and function testing for quality and accuracy. Once verified, they are automatically packed in sterile blisters or sealed pouches, often under ISO Class 8 cleanroom conditions. The final step in the process is sterilization, usually via ethylene oxide gas or gamma radiation, which assures complete microbial elimination. Following sterilization, products are labeled, batch-coded, and packed for distribution, ready for safe, single-use medical applications.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
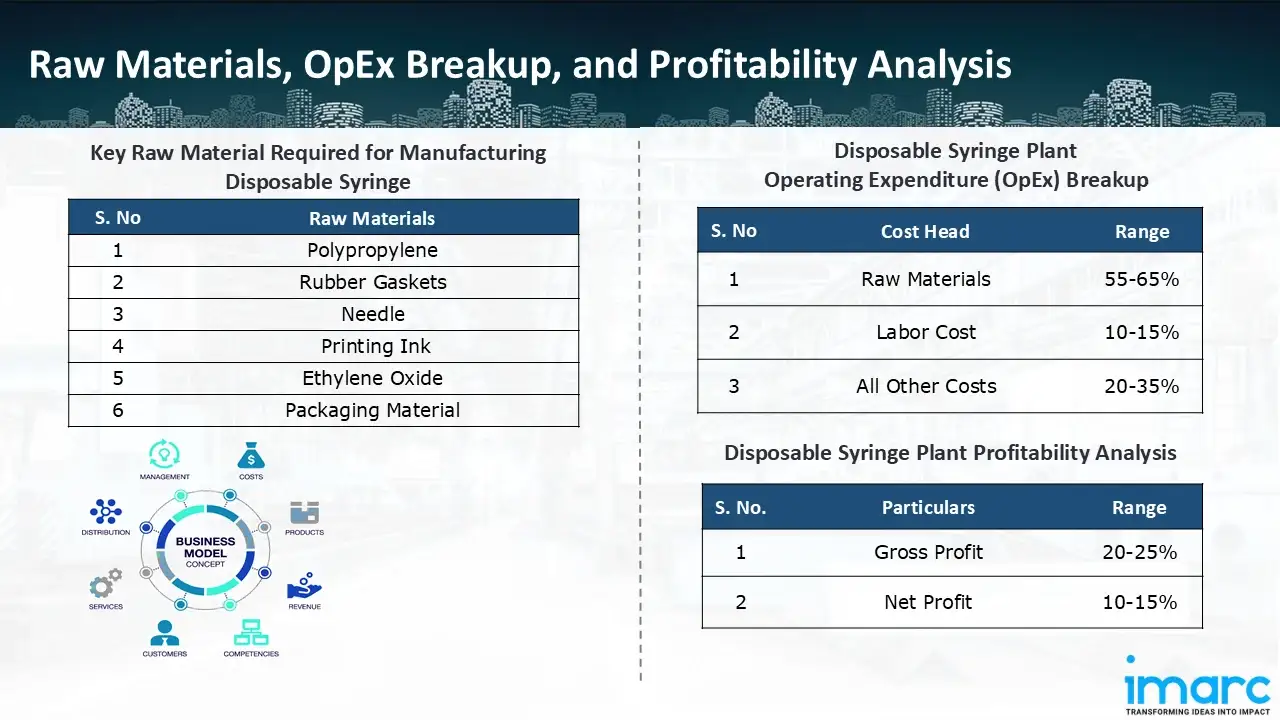
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for disposable syringe manufacturing include:
- Polypropylene
- Rubber Gaskets
- Needle
- Printing Ink
- Ethylene Oxide
- Packaging Material
Machineries Required:
- Plastic Granule Hopper / Dryer
- Conveyor / Loader System
- Injection Molding Machine (Barrel & Plunger)
- Mold Temperature Controller / Chiller
- Wire Drawing Machine
- Needle Cutting & Point Grinding Machine
- Needle Beveling Machine
- Needle Polishing / Cleaning Unit
- Injection Molding Machine (Tip/Hub)
- Ultrasonic Welding Machine
- Automatic Syringe Assembly Line
- Conveyor System / Automation Robotics
- Vision Inspection System
- Silicone Oil Sprayer / Lubrication System
- Autoclave / Steam Sterilizer
- Gamma Radiation Chamber
- Ethylene Oxide (EO) Sterilizer
- Blister Packing Machine
- Sealing Machine
- Cartoning / Boxing Machine
- Labeling Machine
- Leak Test Machine
- Vision Inspection / Microscope System
- Plunger Force Tester
- Needle Gauge Measurement Device
- Moisture / Contaminant Detector
- Compressed Air System
- Deionized Water System
- Cleanroom HVAC System
- Vacuum Conveyor
- Chillers
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in a disposable syringe manufacturing plant ranges between 55-65%, labor cost ranges between 10% to 15%, and all other costs ranges between 20-35% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 20-25%, and net profit lie between the range of 10-15% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the disposable syringe manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 200 units of disposable syringe per day, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In January 2025, BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company) announced further investments in its U.S. manufacturing network to boost capacity for vital medical devices, such as syringes, needles, and IV catheters to fulfil the continuous demands of the country's healthcare system. New needle and syringe production lines have been constructed at the BD factories in Connecticut and Nebraska as part of the company's 2024 investment of more than US$ 10 million to increase manufacturing capacity.
- In July 2024, Nipro Medical Corporation, a prominent player in the global healthcare and medical device industries, is pleased to announce the opening of its first North American production plant in Greenville, North Carolina, as part of a major expansion in the US. Over the next five years, an estimated US$ 398 million will be invested in this strategic initiative, which is expected to create 232 new jobs.
- In March 2024, SCHOTT Pharma, a leader in pharmaceutical drug delivery systems and containment solutions, will construct the first facility in the United States to produce the prefillable polymer syringes needed to fulfil the demand for deep-cold storage and transportation of mRNA drugs. Furthermore, the facility will be able to manufacture glass prefillable syringes for GLP-1 treatments, such as those used to treat obesity or diabetes. The project, which would require a US$ 371 million total investment and is scheduled to begin operations in 2027 after groundbreaking is anticipated by the end of 2024.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.