Japan Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Expected to Reach USD 1,606 Million by 2033 - IMARC Group
Japan Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Statistics, Outlook and Regional Analysis 2025-2033
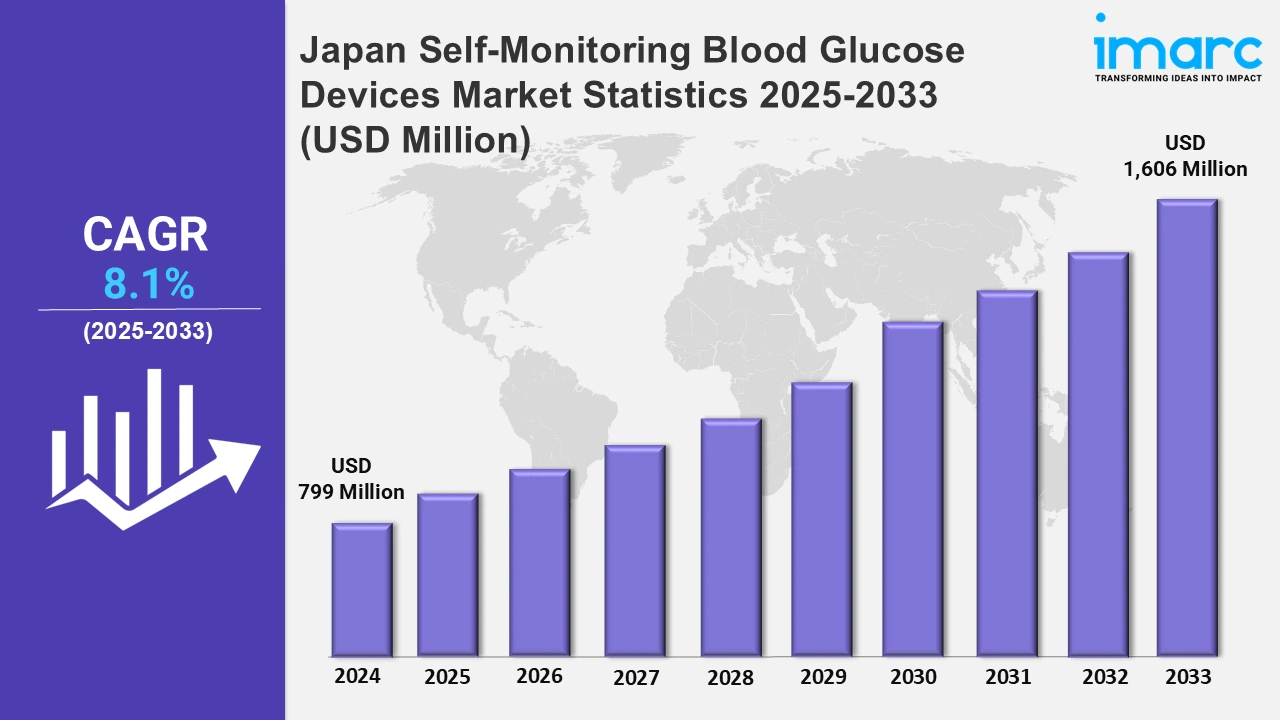
The Japan self-monitoring blood glucose devices market size was valued at USD 799 Million in 2024, and it is expected to reach USD 1,606 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2025 to 2033.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
The availability of non-invasive and wrist-worn devices for continuous glucose monitoring is revolutionizing diabetes treatment. These advancements reduce the need for needle-based sampling, providing increased convenience and comfort for people who manage their blood sugar levels successfully and effortlessly. For example, in March 2022, Tokyo-based healthcare IoT startup Quantum Operation Inc. unveiled a groundbreaking non-invasive device for continuous glucose monitoring. This wrist-worn device allows users to measure blood sugar levels without the need for needle-based sampling.
Moreover, the introduction of colorimetric glucose measuring technologies transformed diabetes care. Continuous improvements in usability and accuracy have resulted in broad acceptance of self-monitoring, establishing it as an essential tool for optimal diabetes care. For instance, Japanese companies invented the first colorimetric glucose measuring meter, which became an international standard. Over decades, they improved user-friendliness and performance, considerably increasing blood glucose self-monitoring and contributing to its broad acceptance around the world, making it a cornerstone of successful diabetes treatment. Furthermore, the market is expanding owing to the elevating prevalence of diabetes and the growing need for efficient self-care solutions. Manufacturers are concentrating on creating compact and user-friendly devices that provide accurate readings and increase patient compliance. Additionally, technology integration, such as Bluetooth-enabled glucose meters, is gaining recognition, allowing for smooth data exchange with healthcare professionals. For example, Abbott Laboratories has increased its presence in Japan with the FreeStyle Libre system, which provides solutions to improve diabetes management. This technology allows users to monitor their glucose levels without the need for traditional finger pricking, thereby making it more convenient and reliable. The Japanese healthcare system's drive for digital health technology encourages the use of such new devices, which contributes to market growth and meets the changing demands of diabetics.
Japan Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Statistics, By Region
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include the Kanto region, Kansai/Kinki region, Central/ Chubu region, Kyushu-Okinawa region, Tohoku region, Chugoku region, Hokkaido region, and Shikoku region. The growing prevalence of diabetes in various regions of Japan is elevating the market.
Kanto Region Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Trends:
In Kanto, upgraded glucose monitoring devices are becoming increasingly popular. Astellas Pharma worked with Roche Diabetes Care Japan to develop the Accu-Chek Guide Me system, which is aimed at metropolitan locations such as Tokyo. This collaboration intends to meet the growing demand for accurate and user-friendly diabetes care solutions, particularly in high-density regions where diabetes is becoming more prevalent.
Kansai/Kinki Region Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Trends:
User-friendly device innovation is an emerging trend in the Kansai/Kinki region. ARKRAY Inc., based in Kyoto, manufactures enhanced glucometers and test strips to fulfill the growing demand in places such as Osaka. These tools are convenient and accurate, allowing people to monitor their blood glucose levels successfully. ARKRAY's innovations contribute to the region's focus on simplifying self-monitoring for diabetes management, ensuring access to high-quality solutions customized to patient requirements.
Central/Chubu Region Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Trends:
A desire for low-cost and compact monitoring equipment is shaping the Central/Chubu region. Nipro Corporation, located in Osaka, has produced low-cost glucose monitoring solutions to meet the different demands of patients in cities such as Nagoya. Nipro promotes better diabetes care throughout the region by combining accessibility and innovative functionality, particularly among the elderly and suburban populations that demand dependable and user-friendly devices.
Kyushu-Okinawa Region Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Trends:
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are gaining popularity in Kyushu-Okinawa. Regional hospitals work with local manufacturers to incorporate wearable CGM technology into diabetes care, especially for the elderly population. These devices provide real-time tracking, resulting in better patient outcomes and lifestyle management. The region's emphasis on improved monitoring technologies indicates a growing understanding of the advantages of continuous, non-invasive glucose testing.
Tohoku Region Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Trends:
Improving access to self-monitoring equipment is a popular trend in Tohoku. For example, Terumo Corporation partnered with regional healthcare providers to distribute its glucometers and test strips in Miyagi and Fukushima prefectures. These projects seek to meet the requirements of rural communities by providing dependable monitoring technologies and instructional programs to encourage frequent use, hence assuring optimal diabetes treatment in underserved areas.
Chugoku Region Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Trends:
Chugoku is experiencing an increase in community-based device distribution. Hiroshima hospitals partner with companies like Panasonic Healthcare to provide compact and low-cost glucose monitoring equipment. Subsidies and outreach programs promote wider adoption, particularly among older patients. These collaborations aim to increase self-monitoring behaviors by emphasizing cost and accessibility, which aligns with the region's healthcare priorities for better diabetes management.
Hokkaido Region Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Trends:
Hokkaido healthcare providers collaborate with Abbott Laboratories to deploy continuous glucose monitoring technologies, such as the FreeStyle Libre, which are designed for cold climates. These devices provide constant performance at low temperatures. Clinics in locations, including Sapporo, work closely with Abbott to offer these solutions while also educating individuals on how to manage diabetes in the region's harsh environmental circumstances properly.
Shikoku Region Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Trends:
Shikoku prioritizes boosting access to advanced glucose monitoring devices. Dexcom works with local healthcare groups to offer continuous glucose monitoring solutions. Regional clinics and pharmacies in Takamatsu distribute Dexcom devices while also providing teaching programs to ensure locals understand the benefits of real-time glucose tracking for better diabetes management outcomes in smaller towns.
Top Companies Leading in the Japan Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Industry
Some of the leading Japan self-monitoring blood glucose devices market companies provide leading strategies for success, a competitive overview dashboard, and an evaluation quadrant for assessing company performance. In March 2023, Astellas Pharma signed an agreement with Roche Diabetes Care Japan to commercialize and develop the Accu-Chek Guide Me blood glucose monitoring system with enhanced accuracy as a medical product with BlueStar.
Japan Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market Segmentation Coverage
- Based on the component, the market has been classified into glucometer devices, test strips, and lancets. Glucometer devices are prominent due to their ease of use and extensive features. Test strips are essential for precise results, which fuels demand. Lancets provide minimum pain during blood collection, which complement device use.
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 799 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 1,606 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 8.1% |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Glucometer Devices, Test Strips, Lancets |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Browse IMARC Related Reports on Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices Market:
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.

 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure




.webp)




.webp)












