
Australia Battery Recycling Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Source, Material, End-Use, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Battery Recycling Market Size and Share:
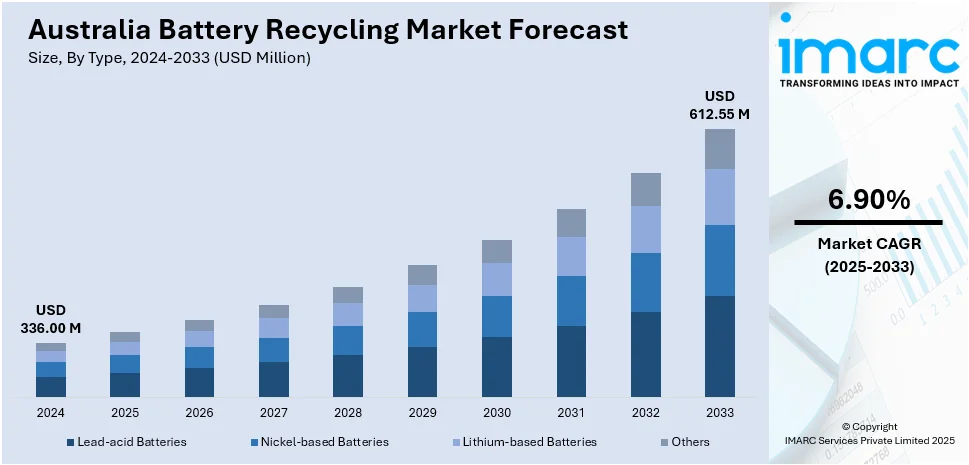
The Australia battery recycling market size reached USD 336.00 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 612.55 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 6.90% during 2025-2033. The surging electric vehicle (EV) adoption, the rollout of residential/commercial energy‐storage generating end-of-life lithium-ion streams, supportive federal and state regulations and incentives for a circular economy, technological advances in hydrometallurgical recovery boosting metal yields, and robust private-public investments in domestic recycling infrastructure are boosting the market expansion.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 336.00 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 612.55 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 6.90% |
Key Trends of Australia Battery Recycling Market:
Explosive Growth in End-of-Life Streams from EV and Grid-Scale Storage Deployments
Australia's rapid electrification of transport and growth in utility-scale energy storage is driving an unprecedented rise in end-of-life lithium-ion batteries, highlighting the need for advanced recycling capabilities. New EV sales reached 114,000 units in 2024, up from the sale of 98,000 units in 2023 and forecasting larger waste streams in the coming years. In parallel, Australia commissioned 4 GW (10 GWh) of grid-scale battery energy storage in 2023 and is set to exceed 5 GW by the end of 2024, making it the fourth-largest utility-storage market globally. These deployments generate over 3,300 tons of lithium-ion battery waste annually, with projections for this figure to grow significantly as passenger EV fleets and stationary storage systems mature. This surge in spent batteries is driving investment in hydrometallurgical and mechanical shredding lines, enabling higher recovery rates of critical metals like cobalt, nickel, and lithium. As recycling infrastructure expands, Australia is positioning itself to capture a larger share of the global circular-economy value chain, transforming waste into a valuable domestic resource.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Robust Policy Support and Mega-Scale Public–Private Investments
Australia's federal and state governments are driving battery recycling growth with strategic funding and regulatory support. In May 2024, the Commonwealth launched an AUD 532 million National Battery Strategy, aimed at bolstering domestic recycling infrastructure, R\&D, and circular-economy efforts, capitalizing on the country's vast reserves of critical minerals like cobalt, nickel, and lithium. At the state level, Western Australia awarded Envirostream AUD 850,000 in late 2024 to develop a dedicated battery sorting and dismantling facility. On the private-sector front, Envirostream’s March 2024 agreements with LG Energy Solution and Hyundai Glovis will inject 6,000 large-format battery packs into Australia's recycling stream, a 140% increase over its 2023 volumes. These partnerships highlight OEMs’ commitment to circular supply chains. Upcoming amendments to the National Waste Policy will introduce Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for lithium-ion batteries and set recycled-content mandates by 2027. These combined policy actions and investments are positioning Australia as a regional leader in battery recycling, reinforcing supply-chain resilience and environmental sustainability.
Growth Drivers of Australia Battery Recycling Market:
Increasing Need for Critical Mineral Recovery
The rising global demand for essential materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel is a major factor fueling growth in Australia’s battery recycling market. These minerals are indispensable for manufacturing batteries used in electric vehicles, electronics, and renewable energy storage systems. By recycling end-of-life batteries, Australia can reduce its dependence on environmentally intensive mining practices while securing a stable supply of critical resources. This also supports the creation of a circular economy, where valuable materials are reused rather than discarded, which is further driving the Australia battery recycling market demand. As pressure mounts to meet international clean energy targets, the strategic importance of extracting battery-grade minerals from domestic recycling processes becomes increasingly evident, driving investment and innovation in the sector.
Strengthening Public Awareness and Green Behavior
Australia’s battery recycling market is benefitting from growing societal awareness of environmental responsibility and the impacts of improper waste disposal. As sustainability becomes a mainstream value, individuals and corporations alike are shifting toward eco-conscious behaviors, including proper battery disposal and support for recycling programs. This trend is encouraging producers, retailers, and waste handlers to adopt closed-loop systems and collaborate on take-back schemes. Schools, NGOs, and government campaigns further amplify consumer education and awareness around battery pollution, which is fueling the Australia battery recycling market share. Collectively, this cultural momentum is reinforcing demand for structured battery recycling channels and incentivizing businesses to invest in sustainable operations that align with public expectations and environmental goals.
Development of Domestic Recycling Infrastructure
Australia’s progress in building out its battery recycling infrastructure is significantly boosting the market’s capabilities. New and upgraded facilities are being established in key urban and industrial zones, equipped with advanced technologies for battery dismantling, material separation, and chemical recovery. These developments not only improve operational efficiency but also support localized recycling solutions that reduce transportation costs and carbon footprints. Moreover, these facilities create skilled jobs, contribute to regional economies, and strengthen national supply chains for battery-grade materials. The expansion of physical infrastructure, paired with regulatory support and increased battery waste volumes, is positioning Australia to handle growing demand and become a leader in responsible battery recycling practices.
Opportunities of Australia Battery Recycling Market:
Expanding E-Waste and Consumer Battery Recycling
With the increasing adoption of electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and wearables, Australia is witnessing a surge in small-format battery waste. This trend presents a valuable opportunity for battery recyclers to diversify their operations beyond large-format batteries from electric vehicles and grid storage. Companies are now investing in technologies and systems specifically designed to process compact, portable battery types efficiently and safely. The growing awareness among consumers about the proper disposal of electronic waste further supports collection initiatives. As product lifecycles shorten and device usage intensifies, specialized recycling services for consumer electronics are poised to become a critical segment of the broader battery recycling market, contributing significantly to resource recovery, landfill diversion, and overall environmental sustainability in Australia.
Global Demand for Recovered Battery Materials
Australia has a strategic opportunity to become a key exporter of refined battery-grade materials sourced through domestic recycling efforts, thereby driving the Australia battery recycling market growth. As demand for critical raw materials grows in battery-producing nations, such as China, South Korea, and the US, recycled outputs like lithium, nickel, and cobalt present high-value export prospects. These secondary materials can command premium pricing in international markets due to their lower environmental footprint and compliance with ethical sourcing standards. With increasing pressure on global supply chains to reduce reliance on virgin mining, Australian firms can scale recycling operations to serve overseas manufacturers. This not only boosts economic returns but also aligns with global climate commitments, positioning Australia as a sustainable, responsible supplier in the international battery value chain.
Industry Collaboration Driving Innovation
The Australian battery recycling market is being shaped by growing cross-industry collaboration that spans recyclers, automotive manufacturers, technology innovators, and energy providers. According to the Australia battery recycling market analysis, these partnerships are accelerating advancements in automated battery disassembly, chemical recovery methods, and second-life energy applications. Joint research and development (R&D) initiatives and pilot projects are producing scalable technologies that improve efficiency and cost-effectiveness while also enabling the reuse of battery components. Some firms are exploring business models centered on battery refurbishment, where used batteries are repurposed for non-automotive uses such as stationary energy storage. These synergies are transforming recycling from a linear waste solution into a dynamic circular economy driver, broadening value capture across the battery lifecycle and unlocking long-term growth potential for all stakeholders involved.
Government Initiatives of Australia Battery Recycling Market:
National Strategy and Policy Alignment
Australia’s National Battery Strategy lays the foundation for a sustainable and competitive battery industry, emphasizing a full lifecycle approach, including robust recycling systems. The strategy reflects the government's commitment to circular economy principles by encouraging material reuse, minimizing environmental harm, and supporting industry-wide accountability. It provides regulatory consistency for stakeholders, helping recyclers, manufacturers, and investors make long-term decisions. Complementary policies at federal and state levels further align with this vision, promoting standardized waste classification, safe transport protocols, and end-of-life handling of batteries. By embedding recycling into broader energy and manufacturing goals, the strategy ensures that resource recovery plays a central role in Australia’s transition to clean technologies, making battery recycling an integral part of the national energy, industry, and environmental policy landscape.
Collaborative Product Stewardship Initiatives
Government-backed programs like B-cycle exemplify Australia’s push for extended producer responsibility through product stewardship. These schemes involve manufacturers, importers, retailers, and consumers in the shared management of batteries throughout their lifecycle, from purchase to safe disposal. B-cycle funds the establishment of accessible drop-off points nationwide, enhances consumer education, and certifies recyclers to ensure environmentally sound practices. By driving collaboration across the supply chain, such initiatives encourage transparency, create more efficient collection systems, and reduce the environmental footprint of batteries. Product stewardship frameworks also help standardize battery waste handling, bridging the gap between regulation and practice. These efforts significantly contribute to the development of a cohesive battery recycling ecosystem, enabling higher recovery rates and reinforcing Australia's shift toward a more circular and sustainable economy.
Government Funding and Innovation Support
Australia’s federal and state governments actively support the growth of battery recycling through targeted grants and research incentives. Programs such as the Modern Manufacturing Initiative and state-level innovation funds offer financial assistance to develop advanced recycling infrastructure, pilot new technologies, and boost research and development (R&D) in sustainable processing methods. These funding mechanisms lower entry barriers for emerging recyclers and help established players upgrade their capabilities. By supporting projects focused on materials recovery, emissions reduction, and closed-loop recycling, the government fosters innovation across the sector. Additionally, funding often encourages public–private partnerships and accelerates the commercialization of novel techniques. This financial backing not only drives technological progress but also ensures that Australia remains competitive in the global battery value chain while aligning economic growth with environmental stewardship.
Challenges of Australia Battery Recycling Market:
Disjointed Collection and Transportation Systems
Australia’s battery recycling sector struggles with a fragmented collection and logistics framework that hinders efficiency and accessibility. The country’s vast geography, coupled with a dispersed population and remote communities, poses significant transportation and collection challenges. Many rural and regional areas lack proper battery drop-off points, limiting consumer participation and leading to low recovery rates, especially for household and small-format batteries. Without a standardized national collection infrastructure or streamlined coordination among stakeholders, batteries often end up in landfills or storage, rather than recycling streams. These inefficiencies not only affect recycling volumes but also raise operational costs. Establishing an integrated, nationwide system that combines public awareness, policy mandates, and logistical innovation is critical for boosting participation and improving recycling performance across all regions.
Financial Constraints in Recycling Business Models
Battery recycling in Australia is often challenged by cost-intensive operations that hinder commercial viability. The high expense of transporting hazardous battery waste, combined with labor-intensive disassembly processes and expensive processing equipment, drives up overheads for recyclers. For smaller facilities or those handling low-margin, non-EV batteries, profitability remains elusive without steady input volumes or government incentives. Moreover, fluctuating global prices for recovered materials like lithium or cobalt impact revenue stability. Inconsistent supply chains and the lack of robust reverse logistics networks further exacerbate financial strain. To overcome this, Australia’s recycling sector requires strategic investment, public-private partnerships, and supportive policy frameworks that ensure long-term economic sustainability and enable smaller players to compete and scale within an increasingly complex materials recovery landscape.
Technological Gaps and Innovation Barriers
Despite growing interest in battery recycling, Australia still faces key technological limitations that constrain efficiency and scalability. Existing processes for dismantling and recovering valuable materials, particularly from lithium-ion batteries, often lag global benchmarks. The country’s reliance on imported machinery and limited local research and development restricts innovation in recycling methods and equipment. As battery chemistries evolve, recyclers must continually adapt, but the current domestic capabilities fall short of handling newer, more complex battery types in an environmentally sound manner. Furthermore, inadequate investment in pilot programs and next-gen processing technologies delays the sector’s ability to scale sustainably. Closing this innovation gap through localized R&D, international collaboration, and tech transfer will be vital to strengthening Australia’s position in the circular battery economy.
Australia Battery Recycling Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the region/country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on type, source, material, and end-use.
Type Insights:
- Lead-acid Batteries
- Nickel-based Batteries
- Lithium-based Batteries
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes lead-acid batteries, nickel-based batteries, lithium-based batteries, and others.
Source Insights:
- Industrial
- Automotive
- Consumer Products
- Electronic Appliances
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the source have also been provided in the report. This includes industrial, automotive, consumer products, electronic appliances, and others.
Material Insights:
- Manganese
- Iron
- Lithium
- Nickel
- Cobalt
- Lead
- Aluminum
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the material have also been provided in the report. This includes manganese, iron, lithium, nickel, cobalt, lead, aluminum, and others.
End-Use Insights:
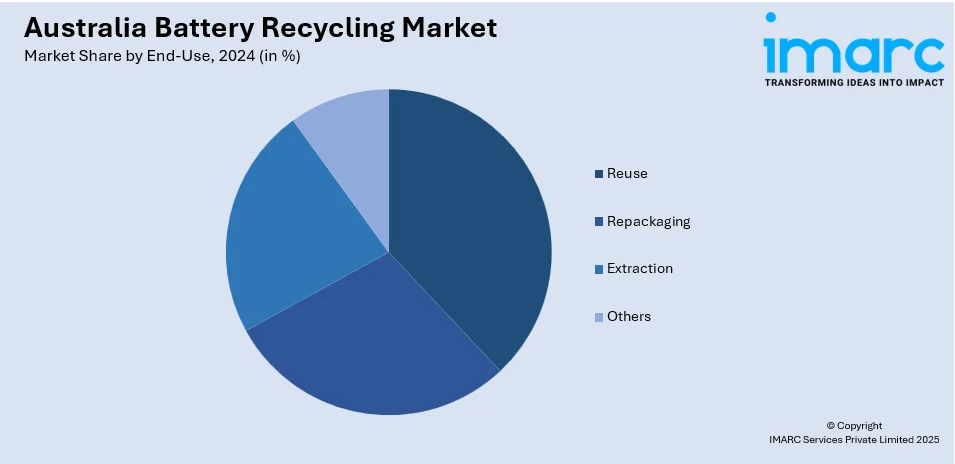
- Reuse
- Repackaging
- Extraction
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end-use. This includes reuse, repackaging, extraction, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Battery Recycling Market News:
- December 2024: Australia-based Iondrive raised AUD 6.1 million to fund its lithium-ion battery recycling pilot plant and commercialization efforts. The company uses a deep eutectic solvent-based technology to recycle batteries more efficiently and sustainably.
- September 2024: Western Australian start-up Renewable Metals raised an additional AUD 8.1 million in a seed extension, bringing total funding to about AUD 16.1 million, to scale up its innovative alkali‑based lithium‑ion battery recycling technology. Their process recovers nickel, cobalt, lithium, manganese and copper from end‑of‑life batteries, avoids harmful sodium sulfate byproducts, and cuts costs.
Australia Battery Recycling Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Lead-acid Batteries, Nickel-based Batteries, Lithium-based Batteries, Others |
| Sources Covered | Industrial, Automotive, Consumer Products, Electronic Appliances, Others |
| Materials Covered | Manganese, Iron, Lithium, Nickel, Cobalt, Lead, Aluminum, Others |
| End-Uses Covered | Reuse, Repackaging, Extraction, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia battery recycling market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia battery recycling market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia battery recycling industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The battery recycling market in Australia was valued at USD 336.00 Million in 2024.
The Australia battery recycling market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.90% during 2025-2033.
The Australia battery recycling market is projected to reach a value of USD 612.55 Million by 2033.
The major key trend of the Australia battery recycling market includes advanced recycling technologies, such as hydrometallurgical and mechanical processes, which are improving the recovery of valuable battery metals. Meanwhile, growing end-of-life streams from EV fleets and stationary energy storage systems are pushing up recycling volumes, thus contributing to the market growth.
The growth of Australia’s battery recycling market is fueled by rising electric vehicle ownership and energy storage deployments that generate increasing lithium-ion waste streams, strong government backing through policies like the National Battery Strategy and circular-economy mandates, and investment in advanced recycling technologies to reclaim critical minerals and boost resource security.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












