
Australia Composite Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product, MGF Process, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Composite Market Overview:
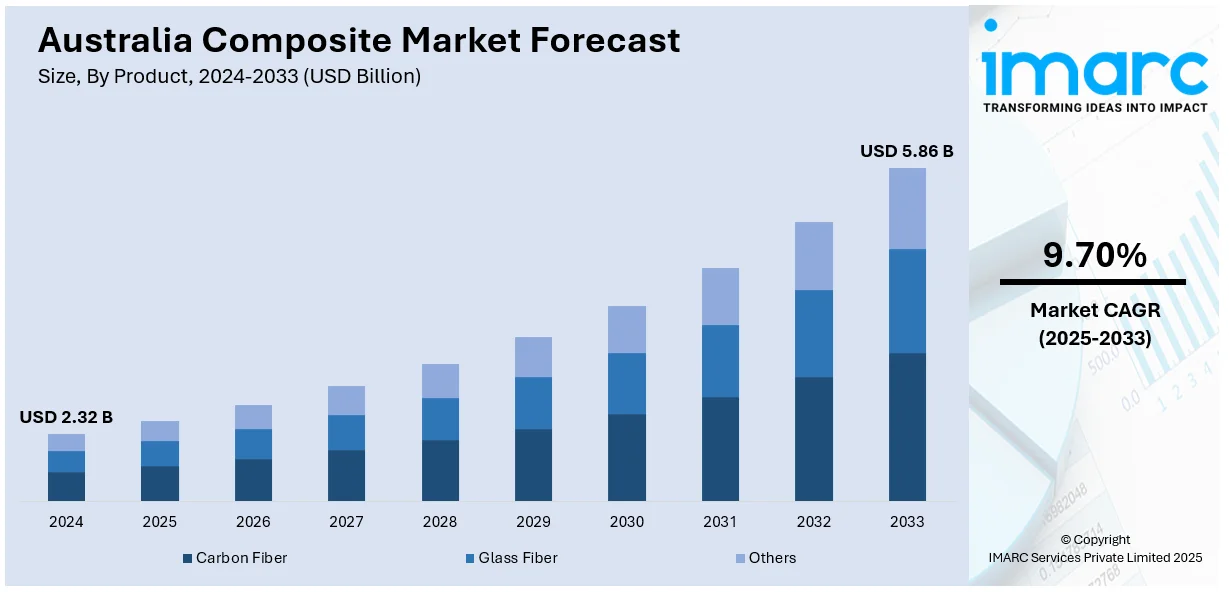
The Australia composite market size reached USD 2.32 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 5.86 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 9.70% during 2025-2033. Market drivers include increasing demand for light, strong, and corrosion-proof material in core sectors of construction, automotive, and aerospace. However, increased infrastructure developments and government initiatives toward green building contribute to composite growth. The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and energy-efficient aircraft drives demand for composites with high performance. Demands from technological advancements in recyclable and bio-based composites also complement environmental compliances and customer demand, thereby contributing to Australia composite market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.32 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 5.86 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 9.70% |
Key Trends of Australia Composite Market:
Increasing Adoption in Construction and Infrastructure
Australian composite market is experiencing high growth with rising usage in construction and infrastructure applications. Composites like FRPs are imparting advantages such as light weight, corrosion resistance, and durability, and are well suited for bridge applications, facades, and building elements. This is spurred by investments by the government in infrastructure modernization and green building constructions. Composites minimize the cost of maintenance and enhance lifespan, which is congruent with the thrust of Australia toward sustainable and robust infrastructure. Furthermore, the flexibility of composites accommodates unique architectural designs, further enhancing the Australia composite market growth. The transition of the industry towards green building certifications also aids composites, as they have a lower carbon footprint than conventional materials such as steel or concrete. With further urbanization and infrastructure renewal, composites are increasingly a part of Australia's construction industry, enabling efficiency, sustainability, and resilience targets.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Advancements in Recycling and Sustainable Composites
Sustainability is one of the main trends influencing the Australia composite market, as there is increased focus on recycling and renewable materials. Recyclable composites are difficult to recycle because thermoset matrices are employed, yet new developments in recyclable thermoplastics and bio-resins are on the rise. Australian industry and researchers are developing closed loop recycling techniques, supporting circular economy objectives and greenhouse gas abatement targets. Bio-composites made from natural fibers and biodegradable polymers are being researched in the construction, automotive, and packaging industries. This green transition is also supported by industry, academia, and government partnerships that are driving commercialization of green composite technologies. Specifically, Australia's recycling industry adds almost USD 19 billion to the economy, and its creation of a job for every 430 tons of recycled material is worth mentioning. This supports sustainability in composites and minimizes environmental footprint while stimulating economic development and innovation, with Australia being at the forefront of green composite development.
Growth in Automotive and Aerospace Applications
In Australia, the market for composites is growing strongly across automotive and aerospace applications. Composites such as carbon fiber and glass fiber reinforced plastics are being used to enhance fuel efficiency and performance by minimizing vehicle weight. This is particularly important in the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) in the automotive industry, where lightweighting increases battery range and efficiency. In the same vein, aerospace industries use composites in aircraft components, improving strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Increased emphasis on innovation, safety, and sustainability drives the trend. Australia's expanding aerospace industry, encouraged by government policies and research partnerships, also stimulates composite demand. Additionally, composites provide design flexibility, enabling manufacturers to create more aerodynamic and efficient cars and airplanes. Since both the automotive and aerospace sectors prioritize performance and sustainability, composites are increasingly important materials in manufacturing in Australia.
Growth Drivers of Australia Composite Market:
Strategic Demand from Mining, Rail and Automotive Sectors
Australia's composite materials industry is underpinned by robust sectoral demand—especially from mining, rail, and automotive sectors—that are advantaged by lightweight, high-strength, and corrosion-resistant attributes. In remote mining operations in the Pilbara and Bowen Basin, operators increasingly rely on tough but light composite structures for equipment panels, enclosures, and protection housing, lowering logistics weights and improving durability in outback environments. In the same way, the nation's vast rail system, linking large ports and inland freight routes, hunts composite parts like fiber-reinforced panels and couplings that provide longer life and enhanced energy efficiency through lighter train weight. In Melbourne and Adelaide automotive production and bespoke coachwork businesses, engineers and craftsmen are integrating composites into specialty vehicles and EV panels, weighing structural needs against green, lighter designs. These sector-specific needs, ranging from the Outback's red dust to rail-served corridors and manufacturing centers, develop localized, high-value uses that support composites as a must-have in diverse industries throughout the Australian economy.
Marine and Renewable Energy Applications Drive Composite Adoption
Another strong driver of Australia's composites market is growing adoption within marine and renewable energy applications—arenas where corrosion resistance, strength-to-weight ratio, and durability are at a premium. Along the long shoreline—from the Great Barrier Reef area to the gulfs in the south—ship builders of marine vessels are opting for composite hulls, boardwalk construction, and superyacht parts that withstand saltwater corrosion and provide easier maintenance. Concurrently, the offshore renewables industry—wave energy, tidal pilot schemes, and coastal wind facilities—utilizes composite blades, mooring cables, and buoy elements that withstand hostile marine environments while minimizing weight while maximizing performance in assemblies. The trends are particularly evident in markets like South Australia's Spencer Gulf and Western Australia's coastal innovation districts, where industry clusters are investigating local composite manufacture for marine technology. By complimenting national clean energy goals and serving Australia's strong maritime industries, composite materials find favor in their singular capacity to prosper in the conditions set by salt, wind, and water—yet provide structural benefits that conventional materials cannot rival.
Innovation Through Research‑Industry Partnerships and Localized Production
One of the major growth drivers according to the Australia composite market analysis, is the interplay among research centers, industrial clusters, and local manufacturing for localized innovation and capacity. Organizations such as New South Wales and Queensland specialized materials research centers work closely with manufacturers and native land-based producers to create composites specifically designed for specific regional requirements—like bushfire-affected areas, UV-stable coverings for high-sunlight regions, and abrasion-resistance surfaces appropriate to desert-bordering infrastructure. Concurrently, local production centers facilitate fast prototyping, batched advanced composites, and design-to-production loops that are prohibitively expensive with off‑shore sourcing. The environment promotes testing for bio-based resins from sustainable local forestry waste products, bespoke fiber blends of imported and Australian-grown fibers, and modular panel arrays optimized for shipping across outlying territories. Co-innovation, built on locally based manufacturing capabilities, allows composite suppliers to address the diverse performance requirements of Australian markets while creating regional manufacturing toughness and supply chain flexibility.
Opportunities of Australia Composite Market:
Shaping New Directions in Transport and Resource Industries
The Australia composite market demand offers significant opportunities in the country's transport and resource industries, an alignment that is based on the country's expansive land mass, scattered population hubs, and strong extractive industries. In far-flung mining areas like the Pilbara, composites provide massive benefits to modular infrastructure, including light-weight shelters, access tunnels, and vehicle body panels that withstand tough, abrasive conditions. Portability and resistance to corrosion are especially advantageous in mining camps and mobile processing plants, where constant movement and maintenance difficulties are the norm. Rail lines running across the wide interior like the Perth freight routes to Queensland mineral lines, are also ideal places for the introduction of composite sleepers, overhead lines, and vibration-damping panels to enhance durability without increasing weight. In coastal environments, ocean boats in use by fishery fleets or tourist charters can convert to composite cabins and hull modules, taking advantage of salt‑resistant durability. At the same time, the automobile industry, with its increasing focus on lightweight construction for electric and specialty cars, treats composites as a test bed for interior panels and light frameworks to minimize energy use. By linking these opportunities with domestic infrastructure needs and mobility issues, Australia is able to extend composite applications to important national industries.
Tidal and Solar Energy Infrastructure: Green Horizon
Australia's international leadership of renewable energy presents major opportunities for composites in tidal, offshore wind, and solar markets, particularly in coastal states such as South Australia, Victoria, and Tasmania. Composite materials have the potential to be crucial for the manufacturing of strong, corrosion-resistant parts in floating solar farms, wave energy converters, and offshore turbine blades. Floating solar farms on sea water bays and reservoirs are enhanced by composite pontoons that are resistant to saline degradation and guarantee long-term functionality. In the marine renewable projects along the rocky southern shores, where sea winds and sea waves are persistent, the composites provide light yet strong options for mooring systems, protective buoys, and support pylons. The composite design flexibility makes custom forms and smooth adaptation to marine environments possible, with less ecological footprint than metal structures. Since Australia has an ample supply of sunlight, wind, and ocean energies, composite producers can take advantage by aligning with new clean energy industry markets. Through the creation of environmentally friendly composite products tailored to renewable environments, players can support decarbonization as they unlock innovation-driven growth in regional energy systems.
Architecture, Building, and Fire‑Resistant Urban Planning
As Australia's thriving cities and growing regional urbanization grow, the building industry presents intriguing opportunities for composites, particularly for applications that call for light, long-lasting, and fire‑resistant materials. Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane, as well as bushfire‑exposed areas in New South Wales and Victoria, urgently require facade panels, cladding systems, and architectural features that balance low weight and high thermal resistance. Fire-resistant resins impregnated composites can yield protective coatings that withstand intense heat without sacrificing structural performance or architectural appearance. Aside from building cladding in cities, composite formwork systems with lightweight, reusable, and multi-geometry adaptability could be adopted—a perfect fit for contemporary building fashion that calls for dynamic form and energy-efficient envelopes. Likewise, in regional infrastructure and housing schemes, such as remote community buildings or coastal protection structures, composites bring resistance to salt spray, sunlight, and moisture. Local developers and builders value their simplicity of transport, quick assembly, and low maintenance requirements. Through the promotion of local composite manufacturing specific to these construction issues, Australia's building sector can improve safety, design freedom, and environmental tolerance across urban and regional projects.
Challenges of Australia Composite Market:
Geographic Isolation and Excessive Logistics Costs
One of the biggest hurdles in Australia's composite industry originates from the nation's wide geography and scattered population centers. Its manufacturers eyeing clients in distant mining areas like the Pilbara, or infrastructure-related projects in outback terminals, confront expensive logistics and transport costs that undercut competitive prices and margins. Composite parts which are typically large even if lightweight, present the shipping difficulty of substantial weight per unit when being transported from coastal production bases in Brisbane, Melbourne, or Perth to inland locations. Special handling or protection packaging requirements also add to the expense. Meanwhile, international rivals based closer to the shipping lanes affiliated with regional construction or mining centers are able to provide quicker delivery at reduced expense. These supply chain challenges also impact supply chain reliability: interruptions in overseas supply of inbound fiber, resin, or tooling can halt local production timelines. As a result, the geographical remoteness of key Australian industries both increases demand for composites and hinders effective, affordable delivery, arising as an ongoing tension within the market's operating dynamics.
Talent Shortage and Innovation Traps
One other critical challenge is talent shortages and barriers to innovation diffusion throughout Australia's composite materials industry. While there are research specialist institutions and universities developing composite science in provinces such as Victoria and Queensland, the application of research advances to practical, large-scale manufacturing is uneven. Numerous regional fabricators and small-to-medium-sized industries have difficulty finding employees with extensive experience in composite design, mold tooling, and advanced processing methods. Consequently, companies may be limited to low-end uses instead of venturing into high-value markets such as aerospace-grade panels, high-performance marine composites, or building structures optimized for bushfire resistance. Furthermore, the lack of broad national apprenticeship programs or specialized composite technology training institutions translates into innovative best practices, such as bio-based resin use or automated layup processes—being in many cases confined to prestige urban labs. Unless the gap is bridged between pioneer research, qualified production personnel, and local manufacturing centers, Australia may fall behind in both innovation adoption and quality consistency in composite products, restricting the industry's capacity to scale and dynamically respond to various domestic demands.
Material Cost Volatility and Competition from Alternatives
The other challenge is the uncertainty of material costs and the competition from established materials such as steel, aluminum, or engineered wood, particularly with imported composites having price links to international resin and fiber markets. Composite manufacturers must deal with changing raw material prices that can critically affect bid projects for sectors such as rail, construction, or marine. When raw material prices rise, customers working on slim budgets will revert to tried and tested alternatives, even if composites hold long-term performance benefits. Furthermore, there is limited availability of a significant domestic supply base for niche fibers or resins, so Australia tends to rely on imported intermediates. This exposure boosts foreign currency fluctuations, while also raising the possibility of supply disturbances, especially amidst times of global market instability. Concurrently, long-established materials producers have entrenched supply chains and historical relationships with local infrastructure industries, providing them with price stability and procurement experience that composites suppliers find difficult to replicate. These economic pressures force composites companies to articulate their value proposition and wrest share from traditional materials backed by ingrained procurement habits.
Australia Composite Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on product, MGF process, and application.
Product Insights:
- Carbon Fiber
- Glass Fiber
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the product. This includes carbon fiber, glass fiber, and others.
MFG Process Insights:
- Layup
- Filament
- Injection Molding
- Pultrusion
- Compression Molding
- RTM
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the MGF process have also been provided in the report. This includes layup, filament, injection molding, pultrusion, compression molding, RTM, and others.
Application Insights:
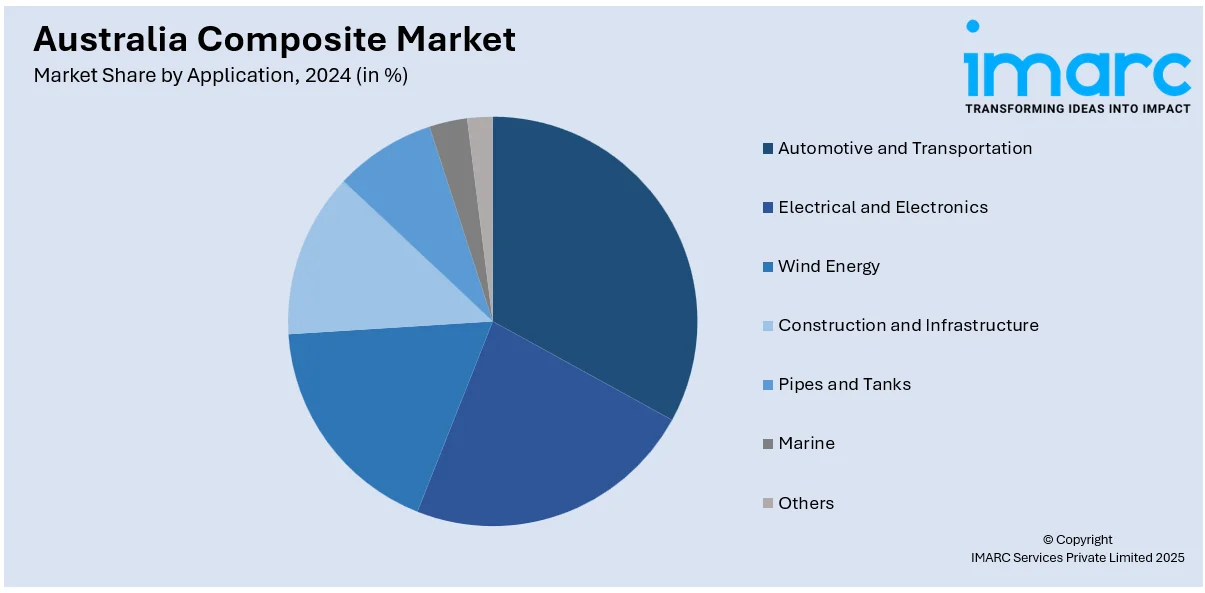
- Automotive and Transportation
- Electrical and Electronics
- Wind Energy
- Construction and Infrastructure
- Pipes and Tanks
- Marine
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application. This includes automotive and transportation, electrical and electronics, wind energy, construction and infrastructure, pipes and tanks, marine, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Composite Market News:
- In May 2025, Australia’s first home-grown orbital rocket, Eris, by Gilmour Space Technologies, is set to launch from a new pad in Bowen, North Queensland. The test flight, lasting about eight minutes over the Coral Sea, may carry a ceremonial jar of Vegemite into orbit. The rocket is expected to crash into the ocean post-launch. Flight clearance is granted from Thursday 7:30 am to 5:30 pm, with the launch window open until Monday.
- In September 2024, Intercontinental Exchange (ICE) has launched a new suite of indices for the Australian residential mortgage-backed securities (RMBS) market. These indices provide transparent benchmarks to track AUD-denominated RMBS performance across various credit ratings. The indices support research, benchmarking, and new financial product design. This launch enhances market transparency and helps investors evaluate performance amid the resilient Australian residential MBS market, backed by ICE’s global fixed income expertise.
- In April 2024, Wagners launched a new 356mm Fibre Reinforced Polymer (FRP) utility pole to address timber shortages in electricity networks. Manufactured in Queensland, these FRP poles offer high strength, lasting 80 years, and resist rot, corrosion, termites, and acid soils. Weighing a quarter of timber poles, they reduce transport and installation risks. This locally made solution provides durable, low-maintenance alternatives ideal for sensitive environments like wetlands.
Australia Composite Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Products Covered | Carbon Fiber, Glass Fiber, Others |
| MRF Processes Covered | Layup, Filament, Injection Molding, Pultrusion, Compression Molding, RTM, Others |
| Applications Covered | Automotive and Transportation, Electrical and Electronics, Wind Energy, Construction and Infrastructure, Pipes and Tanks, Marine, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia composite market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia composite market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia composite industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia composite market was valued at USD 2.32 Billion in 2024.
The Australia composite market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.70% during 2025-2033.
The Australia composite market is expected to reach a value of USD 5.86 Billion by 2033.
The Australia composite market trends include increased use of bio-based resins, fire-resistant materials for construction, and advanced composites in marine and renewable energy sectors. Local manufacturing is expanding through research-industry partnerships, while demand for lightweight, sustainable solutions grows across transport, infrastructure, and remote industrial applications in Australia’s diverse environments.
The Australia composite market is driven by rising demand from mining, transport, marine, and renewable energy sectors. The need for lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant materials suits the country’s harsh environments. Local innovation, sustainability goals, and regional infrastructure projects further support the growing use of composites across various Australian industries.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












