
Australia Consumer Credit Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Credit Type, Service Type, Issuer, Payment Method, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Consumer Credit Market Size and Share:
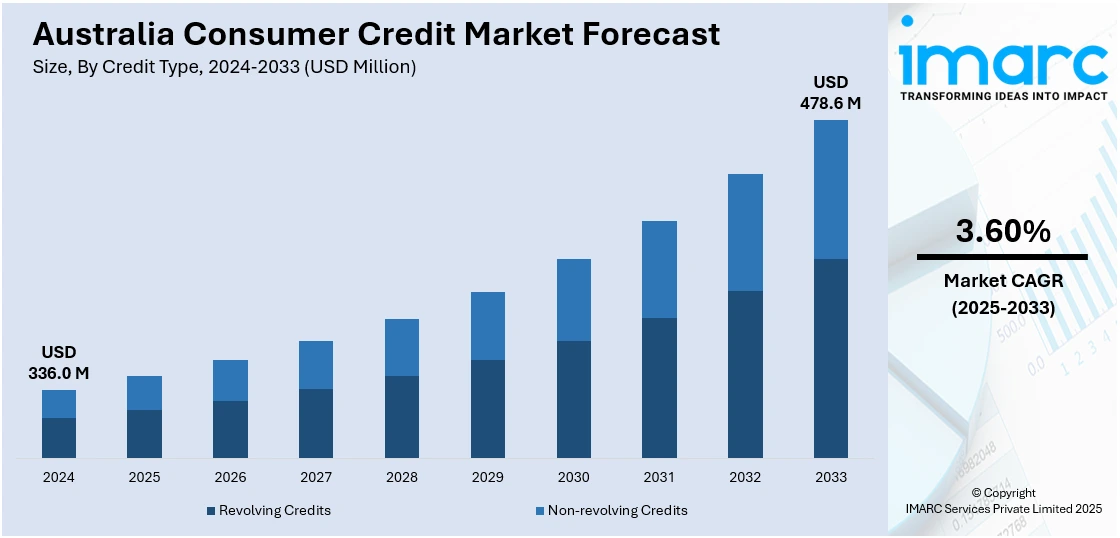
The Australia consumer credit market size reached USD 336.0 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 478.6 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 3.60% during 2025-2033. The market is experiencing growth, driven by increased consumer spending and confidence. The demand for both secured and unsecured credit is rising, influenced by low interest rates and flexible lending policies. However, economic uncertainties and financial pressures on certain sectors may affect credit stability.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 336.0 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 478.6 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 3.60% |
Key Trends of Australia Consumer Credit Market:
Strengthening BNPL Regulations for Consumer Protection
In recent years, the buy now pay later (BNPL) sector has rapidly grown, raising concerns about consumer debt levels and financial vulnerability. To address these concerns, Australia introduced the national consumer credit protection amendment (Low Cost Credit) Regulations in February 2025. This regulation reclassifies BNPL providers as low-cost credit contract (LCCC) providers, subjecting them to stricter oversight. The reforms require BNPL providers to conduct unsuitability assessments, ensuring that credit offerings are appropriate for consumers' financial situations. Additionally, fee caps have been implemented to limit excessive charges, and responsible lending obligations have been modified to enhance borrower protection. The introduction of these reforms in early 2025 marked a significant shift in the regulatory landscape. BNPL providers now face rigorous compliance requirements, including mandatory assessments of borrowers' repayment capacities. This change has led many providers to adjust their business models, focusing on responsible lending practices and transparent fee structures. Some providers have introduced more flexible repayment options and improved disclosure practices to meet regulatory standards. These changes aim to curb risky lending practices, promote responsible borrowing, and safeguard consumers from debt traps. By enhancing consumer protections, the reforms seek to build trust in the BNPL sector and ensure that it remains a safe, sustainable option for credit, which also encourages the growth of the Australia credit market share.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Expanding Consumer Data Rights for Credit Transparency
Australia's consumer data right (CDR) has been pivotal in promoting transparency and competition in the financial sector. In March 2025, the government expanded the CDR to include non-bank lending institutions, effective from mid-2026. This reform is designed to empower consumers with greater access to their financial data, enabling them to compare credit products more effectively. By allowing consumers to share their financial information with different lenders securely, the CDR fosters increased competition and drive better product offerings in the credit market. The expansion of the CDR in 2025 is a key development aimed at transforming the credit market. By including non-bank lenders, the reform broadens the scope of data portability, allowing consumers to access and share their financial information across a wider range of credit providers. This encourages lenders to offer more competitive rates and tailored credit solutions, fostering a more dynamic and consumer-centric market. Financial technology companies (fintech’s) and non-bank lenders are leveraging this data to develop innovative credit products that cater to diverse consumer needs. By reducing compliance costs for lenders, the reform encourages innovation and competition in the credit market. Consumers can now make informed decisions, secure better credit deals, and benefit from tailored financial products. The expansion of the CDR fosters a more dynamic, transparent, and competitive consumer credit environment, ultimately enhancing financial inclusion and literacy.
Growth Drivers of Australia Consumer Credit Market:
Digital Financial Services and Fintech Innovation
Rapid development of fintech and digital financial services is among the most important drivers of growth in Australia's consumer credit market. As a technologically advanced population with highly connected individuals and tech-savvy consumers, Australia offers ground for new credit solutions presented through mobile and digital channels. Fintech firms have brought new lending products, simplified loan application procedures, and customized credit products that are appealing particularly to the younger population. Such digital lenders mainly rely on unconventional sources of data to determine creditworthiness, making credit more accessible to people who might lack a decent track record with conventional financial institutions. In addition, Australia's open regulatory framework has facilitated the development of open banking, which makes it possible for consumers to provide lenders with financial information securely for improved credit evaluation. Such openness has brought more competitive credit products and enhanced consumer power. The emergence of such digital platforms is transforming the way Australians borrow and utilize credit.
Changes in Consumer Expenditures and Lifestyle Habits
According to the Australia consume credit market analysis, shifting lifestyles and consumption patterns among consumers are also driving growth in the market. With increasing cost of living in Sydney and Melbourne, among other cities, several Australians have opted to rely on credit products to fund day-to-day expenditures, purchases, or sustain lifestyle levels. The demand for flexible spending instruments such as Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) products has grown, especially among millennials and Gen Z shoppers who like installment plans lasting shorter periods compared to conventional credit cards. Australians also increasingly use credit to finance travel, education, and home renovation, indicating a cultural trend towards paying for experiences and personal enrichment over necessities. This trend is also underpinned by the high degree of confidence in financial institutions, combined with the prevalent provision of secured and unsecured credit facilities. With increasing consumer confidence comes a heightened demand for affordable, customized credit products that reflect changing financial practices and aspirations.
Real Estate and Housing Market Impact
Australia's vibrant real estate market remains a significant driver of consumer credit expansion. Since property is expensive in city areas such as Brisbane, Perth, and Canberra, consumers may need to take large credit facilities for home purchases, refurbishments, and allied expenses. Mortgage-linked credit, home equity loans, and personal lines of credit are usually availed by homeowners to fund renovations or consolidate debt. In addition, first-time homebuyers will tend to require bridging loans and other products to access the housing market, particularly where government schemes offer inducements to ownership. The boom in construction and housing in regional markets, fueled in part by remote working trends and regional migration, also drives borrowing. This sustained demand for property finance has a spillover impact on other consumer credit as people spend on furnishing, landscaping, and other related property costs. The core position of the real estate sector in Australian wealth creation guarantees that it will be a support pillar for the overall growth of the Australia consumer credit market demand.
Opportunities of Australia Consumer Credit Market:
Potential in Regional and Remote Areas
One of the most promising opportunities in Australia's consumer credit space is more effectively serving regional and remote communities, which are underbanked or lack access to mainstream financial services. In Western Australia, Queensland, and the Northern Territory it is common for most towns not to have a physical presence of mainline banks, thus complicating access to credit. This gap creates an opportunity for fintechs and credit unions to provide online-first lending products specially designed for these communities. The increasing adoption of mobile connectivity in rural areas, along with enhanced internet penetration through government programs such as the National Broadband Network (NBN), enables the growth of online credit platforms. Additionally, local economic activity like agriculture, mining, and tourism create distinctive credit demands that are frequently underserved by mainstream institutions. Banks that have the ability to offer flexible repayment schedules, seasonal loan products, and culturally appropriate services, specifically for Indigenous clients, have the potential to establish long-term, repeat customer bases in such high-potential markets.
Sustainable Finance and Green Credit Products
The increased emphasis on environmental sustainability in Australia offers a special opportunity for green credit product development. Consumers in states such as Victoria and the Australian Capital Territory, where climate-related policies are comparatively more progressive, are increasingly seeking financing for environmentally friendly products and services. Lenders can exploit this trend by providing green personal loans, energy-efficient home improvement loans, and electric vehicle credit products. These products can also be linked with state government incentives or rebates, which can make them more appealing and affordable for borrowers. Additionally, environmentally conscious consumers will most likely react favorably towards lenders that embed environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles into their credit products. This offers an opportunity for creative collaboration among financial institutions, green technology firms, and public authorities. By linking product development to Australia's climate targets and regional clean energy capabilities, credit providers can reach an emerging market segment that appreciates both financial choice and sustainability, which leads to the Australia consumer credit market growth.
Credit Inclusion Via Open Banking and Alternative Data
Australia's open banking reforms are introducing new possibilities for credit inclusion by enabling consumers to share their financial data securely with lenders. This structure, governed by the Consumer Data Right (CDR), enables lenders to better evaluate a borrower's financial conduct, something that extends beyond mere credit scores. Consequently, those with short credit histories, eg, young people, migrants, or someone coming out of a period of past financial difficulty, can have access to customized credit products. Furthermore, the inclusion of alternative data, including utility bills, rent payments, and digital transactions, supports a broader assessment of creditworthiness. Such change is especially valuable in multiculturally diverse cities such as Sydney and Melbourne, where non-traditional lending communities may be hindered by access to mainstream lending. By taking advantage of these new streams of data and building the AI-driven risk models, financial institutions could expand the customer base in a responsible, technology-enabled manner by reducing defaults.
Regulation and Oversight of Australia Consumer Credit Market:
Part of ASIC and the National Consumer Credit Protection Framework
Australia's consumer credit market is regulated by a robust regulatory framework mainly managed by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC). Lenders and brokers are, in accordance with the National Consumer Credit Protection Act, under obligation to have an Australian Credit License and to also comply with responsible lending obligations. This ensures that they evaluate whether a credit product is appropriate for a consumer considering their financial circumstances, needs, and goals. These laws aim to avoid predatory lending to ensure that lending is only done when the borrowers could realistically repay their obligation. Australia's regulatory approach is proactive: It emphasizes educating customers, is accountable to the lenders, and there must be open disclosure. ASIC also performs periodic audits, investigations, and public enforcement action to ensure market integrity. Special to Australia is the focus on suitability tests and the explicit distinction between regulated and unregulated credit, which offers structure and flexibility to market participants and ensures borrower protection at the same time.
Targeted Reforms for Emerging Credit Products
Australia's regulatory landscape is constantly adapting to respond to shifts in consumer trends and the development of new credit products, specifically Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) schemes. The platforms initially existed in a legality grey area since they did not fall under the classical frameworks of credit under current legislation. But as over-indebtedness fears and financial damage grew, the government moved to implement bespoke regulatory changes to place these services into ASIC's jurisdiction. This is an example of the Australian response to financial innovation, to add proportionate measures to protect consumers while fostering competition and innovation. Short-term, high-cost lenders, commonly known as payday lenders, have also come under scrutiny for their operations, which have disproportionately affected low-income and regional communities. Australia's response is to make sure that new credit models are exposed to conduct and disclosure obligations, shutting loopholes while retaining the merits of access to alternative credit.
Consumer Protections and Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Consumer protection is key to the credit regulation regime of Australia, with various channels available to assist borrowers in case of disputes or financial difficulties. The Australian Financial Complaints Authority (AFCA) is an impartial authority that addresses complaints between consumers and financial service providers, with a free and binding dispute resolution process. This provides consumers with a trustworthy and unbiased process to obtain redress without going to court. Further, credit providers are bound by law to provide hardship support and flexibility in repayments to financially distressed borrowers, particularly when the borrower is unemployed, ill, facing an economic downturn, or in any other state of financial distress. Australia also heavily focuses on data privacy and ethical consumer information use, especially in the Consumer Data Right and credit reporting regimes. Such protections are particularly critical in a multicultural and diverse society where vulnerability may be heightened by language constraints or unfamiliarity with financial systems. By infusing regulation with fairness, accessibility, and openness, Australia develops a credit market that synthesizes innovation and responsibility.
Challenges of Australia Consumer Credit Market:
Soaring Household Debt and Cost-of-Living Issues
Most critically for Australia's consumer credit sector is the extent of household debt paired with increasing living costs. With several Australians making use of credit to cover everyday expenses, particularly in the key metropolitan cities of Sydney and Melbourne, there is increasing concern at the prospect of over-indebtedness. The expense of housing, utilities, and staples keeps on increasing, causing strains on household budgets and an over-reliance on short-term credit arrangements. This can create a debt trap whereby consumers balance multiple lines of credit, ranging from personal loans to credit cards and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) arrangements. In the regional markets, where pay is generally less and job opportunities fewer, the burden of finance is more severe. These financial pressures also affect credit performance, as more borrowers become unable to service their payments. This poses a threat to the consumer and the lenders, who have to tighten lending evaluations in order to limit defaults.
Limited Financial Literacy and Credit Awareness
The lack of financial literacy and knowledge about credit products is another persistent problem in the Australian consumer credit industry. In spite of the prevalent accessibility of financial services, several Australians, especially young consumers and people from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds, are not fully aware of how credit operates, what it involves in terms of commitments, and how to use it in a responsible manner. In Indigenous and rural communities, exposure to impartial financial education is still uneven, which means they are more susceptible to high-cost lenders or unbecoming credit contracts. Additionally, the rapid development of fintech products such as BNPL has brought newer types of credit that may seem interest-free but have hidden charges or fees consumers might not pay attention to. This ignorance can lead to inaccurate money management, default on payments, and long-term impairment of credit ratings. To bridge this divide, efforts by lenders, regulators, and educators need to be concerted in nature to ensure that credit literacy is accessible, culturally responsive, and relevant.
Compliance with Regulation and Technological Transformation
Reshaping to meet Australia's changing regulatory landscape while accepting digital change poses a twin challenge for most credit providers. As laws tighten up to safeguard consumers, particularly with reforms regarding responsible lending, data sharing, and new products—lenders have to keep investing in compliance systems, staff training, and oversight. Fintechs and smaller lenders can often struggle especially to achieve a balance between innovation and regulatory requirements, particularly when scaling up operations or launching new products. At the same time, the transformation to digital credit products requires huge investment in secure infrastructure technology, AI-based credit evaluations, and intuitive platforms. Cybersecurity assurance and protection of customer information, particularly under the Consumer Data Right regime, create an additional complexity. For lenders serving multiple states or aiming at various market segments, adapting credit offerings and digital interfaces while complying with regulatory requirements creates an expensive and resource-consuming problem. In this environment, only the institutions that can respond rapidly and responsibly will be able to sustain competitiveness as well as consumer confidence.
Australia Consumer Credit Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on credit type, service type, issuer, and payment method.
Credit Type Insights:
- Revolving Credits
- Non-revolving Credits
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the credit type. This includes revolving credits and non-revolving credits.
Service Type Insights:
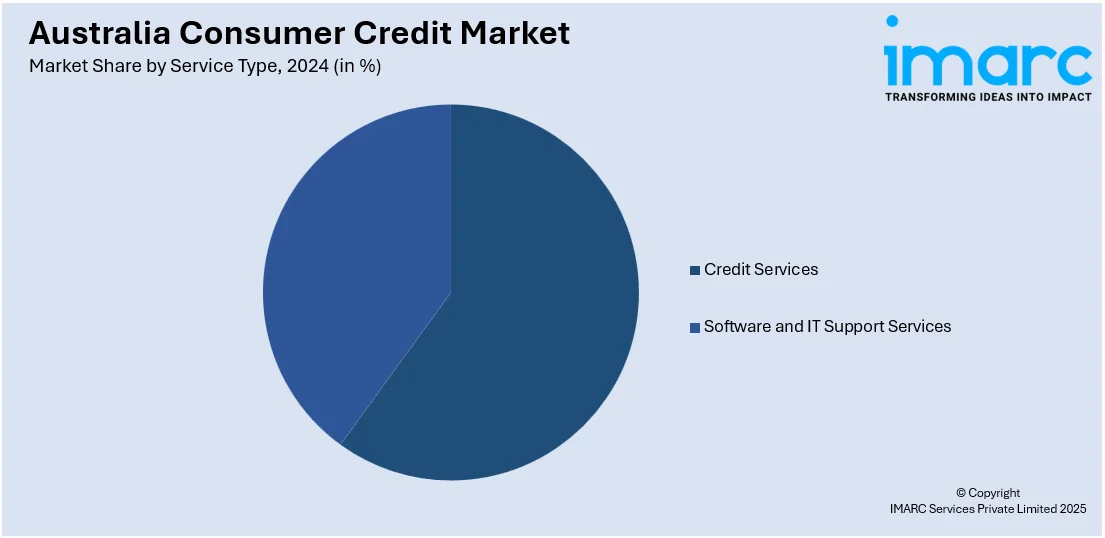
- Credit Services
- Software and IT Support Services
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the service type have also been provided in the report. This includes credit services and software and IT support services.
Issuer Insights:
- Banks and Finance Companies
- Credit Unions
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the issuer have also been provided in the report. This includes banks and finance companies, credit unions, and others.
Payment Method Insights:
- Direct Deposit
- Debit Card
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the payment method have also been provided in the report. This includes direct deposit, debit card, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Consumer Credit Market News:
- February 2025: ASIC launched a consultation on new regulatory guidance for Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) providers, effective June 2025. The reforms, under the Treasury Laws Amendment Act 2024, required credit licenses, modified lending obligations, and electronic disclosure, enhancing consumer protection in Australia’s consumer credit market.
- October 2024: Beforepay Group launched its first regulated personal loan under the National Consumer Credit Protection Act, offering loans of USD 2,001–USD 3,000 for up to 3 months. This expansion enhanced credit access, leveraging AI-driven risk models, and strengthened Australia’s consumer credit offerings.
Australia Consumer Credit Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Credit Types Covered | Revolving Credits, Non-revolving Credits |
| Service Types Covered | Credit Services, Software and IT Support Services |
| Issuers Covered | Banks and Finance Companies, Credit Unions, Others |
| Payment Methods Covered | Direct Deposit, Debit Card, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia consumer credit market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia consumer credit market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia consumer credit industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia consumer credit market was valued at USD 336.0 Million in 2024.
The Australia consumer credit market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 3.60% during 2025-2033.
The Australia consumer credit market is expected to reach a value of USD 478.6 Million by 2033.
The Australia consumer credit market is shifting toward digital lending, with fintech platforms offering faster, more personalized services. Open banking is enhancing credit accessibility, while green financing and ethical lending practices are gaining traction amid growing demand for sustainability and financial transparency.
Key drivers of the Australia consumer credit market include digital innovation, rising cost-of-living pressures, and shifting lifestyle preferences. Growing fintech services and a greater emphasis on flexible finance solutions like Buy Now, Pay Later and supportive open banking policies, are encouraging broader access to credit across diverse consumer segments.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












