
Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type, Battery Capacity, End User, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Overview:
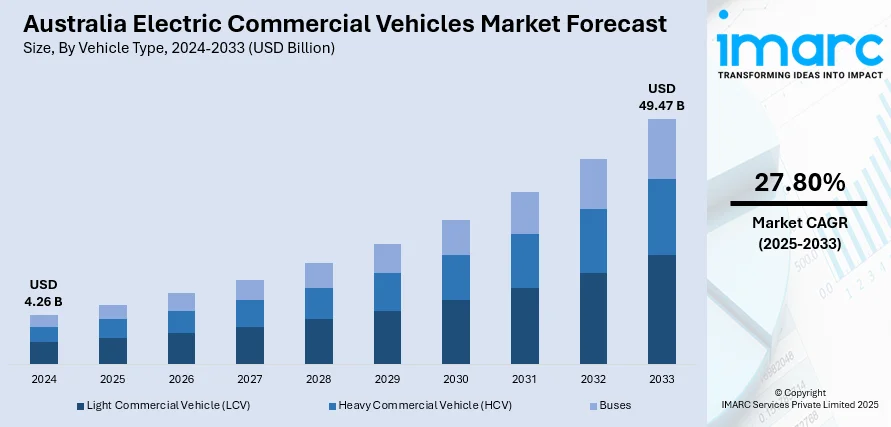
The Australia electric commercial vehicles market size reached USD 4.26 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is projected to reach USD 49.47 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 27.80% during 2025-2033. The Australian government is constantly introducing different incentives and rules to promote the use of electric vehicles (EVs). This, along with the increasing cost of diesel and petrol is driving businesses in Australia to seek more cost-effective transportation alternatives. Apart from this, the heightened focus on maintaining sustainability in business operations is expanding the Australia electric commercial vehicles market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 4.26 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 49.47 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 27.80% |
Key Trends of Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market:
Government Incentives and Rules
The Australian government is constantly introducing different incentives and rules to promote the use of electric commercial vehicles. These incentives are significantly decreasing the capital expenses for businesses and fleet operators, making it relatively cheaper to make the switch to electric versions. Subsidies, grants, and exemptions from taxes are being provided by different states and territories to stimulate the use of electric vehicles (EVs). Additionally, the government is implementing tighter emission norms, which is encouraging companies to move away from conventional internal combustion engine vehicles to more environment friendly electric alternatives. The launch of stringent emission norms and upcoming plans to ban fossil fuel-powered vehicles are also driving the demand for electric commercial vehicles. By introducing policies that support infrastructure development, such as expanding charging networks, the government is laying the groundwork for a more sustainable and electrified commercial vehicle ecosystem across Australia. In 2025, Australia declared a new $50 million program to motivate businesses to shift to EVs and utilize energy-efficient devices such as solar batteries. The financing, provided through a collaboration between the Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC) and Metro Finance, seeks to reduce expenses for small and medium businesses (SMEs), agricultural producers, and transport operators.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Rising Fuel Costs and Operational Efficiency
The increasing cost of diesel and petrol is driving businesses in Australia to seek more cost-effective transportation alternatives, including electric commercial vehicles. Gasoline prices in Australia rose to 1.15 USD per liter in April, up from 1.13 USD per liter in March 2025. Operators of fleets are constantly looking for opportunities to cut fuel expenses, particularly with the volatility in fuel prices cutting into their bottom lines, thereby impelling the Australia electric commercial vehicles market growth. Electric cars, due to their reduced energy usage and lower maintenance costs, are emerging as a cheaper alternative in the long run. Electric commercial vehicles are also providing companies with a means to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, increasingly a necessary consideration with the recent volatility in global fuel prices. Interest in electric vans and trucks is spurred by their potential to reduce operating expenses, especially for urban delivery operations and logistics. As technology improves in EVs, the cost of owning commercial fleets decreases, making EVs increasingly competitive in Australia's commercial market.
Green Awareness and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Green awareness is becoming a growing concern among companies in Australia, with more companies now focusing on environmental friendliness in their business operations, pushing commercial vehicles to go electric. Companies are becoming increasingly conscious of their carbon footprint and actively looking at opportunities to lower greenhouse gas emissions within their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. The market for electric commercial vehicles is driven by high demand and keeping pace with international sustainability measures. Businesses in different industries, ranging from logistics to retail and public transport, are seeing the environmental advantages of using commercial EVs, which emit zero tailpipe emissions and have a lesser overall environmental footprint than conventional diesel-powered vehicles. In their fleets, businesses are not only complying with rules but also promoting their public image as green organizations through the use of EVs.
Growth Drivers of Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market:
Advancements in Battery Technology
Innovations in battery technology are greatly improving the efficiency and performance of electric commercial vehicles in Australia. Enhancements in both lithium-ion and solid-state batteries are allowing for longer driving ranges, minimizing downtime, and providing quicker charging options. This increases the reliability of electric vans, buses, and trucks for both long-haul logistics and urban transport. Additionally, decreasing battery costs are contributing to a lower total cost of ownership, making electric fleets more financially feasible for businesses. These developments address range anxiety while also boosting fleet productivity and operational planning. As technology progresses, an increase in adoption rates is expected, directly enhancing Australia electric commercial vehicles market demand.
Urban Emission Regulations
Strict emission regulations in significant Australian cities are encouraging transport operators to transition to cleaner, more sustainable fleets. Urban regions are facing heightened concerns regarding air quality, carbon emissions, and noise pollution, making diesel-powered commercial vehicles less appealing. Local authorities are introducing policies that promote replacing high-emission vehicles with electric options to achieve sustainability goals. This regulatory impetus is driving logistics companies, public transport providers, and delivery fleets to turn toward electric commercial vehicles. With cities pursuing net-zero objectives, early adopters can gain a competitive edge by reducing penalties, conforming to eco-friendly regulations, and enhancing their corporate reputation in an increasingly green economy.
Growing E-commerce and Logistics Demand
The fast expansion of Australia’s e-commerce sector has heightened the demand for effective last-mile delivery solutions. Electric commercial vehicles present cost-effective and environmentally friendly choices for frequent, short-distance urban deliveries. Businesses in retail, food delivery, and logistics are progressively incorporating electric vans and trucks to satisfy growing consumer expectations while lowering fuel and maintenance expenses. The move toward quicker delivery timelines makes electric vehicles particularly suitable due to their reduced operational costs and efficiency in city travel. Moreover, companies are integrating EVs into their fleets to fulfill sustainability pledges and attract eco-conscious consumers. According to Australia electric commercial vehicles market analysis, the growth of e-commerce is poised to be a significant catalyst for long-term adoption.
Opportunities of Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market:
Expansion of Charging Infrastructure
The growth of charging infrastructure offers significant opportunities within Australia’s electric commercial vehicles sector. As the demand for electric buses, trucks, and vans continues to rise, both public and private entities are prioritizing the installation of efficient and rapid charging stations. Logistics companies, fleet operators, and last-mile delivery services require convenient access to charging points to maintain operational efficiency. This situation provides opportunities for investments in ultra-fast chargers, depot-based charging hubs, and renewable-powered charging stations. Furthermore, collaborations between energy firms and automotive manufacturers can lead to comprehensive solutions for extensive fleet charging. A strong infrastructure network will speed up adoption and boost confidence in long-distance operations throughout urban and regional Australia.
Fleet Electrification for Corporates
The electrification of corporate fleets is becoming a game-changing opportunity in Australia’s electric commercial vehicles market. Large companies, particularly in logistics, e-commerce, and retail, are increasingly tasked with meeting sustainability goals while minimizing operational costs. Transitioning entire fleets to electric vehicles enables firms to reduce fuel costs, enjoy lower maintenance requirements, and adhere to stricter emissions regulations. Public transport entities also hold great potential for adoption, as electric buses align with government initiatives for clean mobility. This transition opens avenues for collaborations with vehicle manufacturers, leasing firms, and charging infrastructure providers. Organizations that take the lead in electrification enhance their operational efficiency and improve their eco-friendly image, gaining a competitive advantage in terms of customer perception and regulatory adherence.
Local Manufacturing and Assembly
Local manufacturing and assembly present significant opportunities to bolster Australia’s role in the electric commercial vehicles landscape. By promoting the domestic production of electric vans, trucks, buses, and essential components such as batteries and powertrains, Australia can lessen its dependence on imports while creating jobs and enhancing technological expertise. Establishing local assembly plants also allows for vehicle customization to suit Australian road conditions and specific industry requirements, such as those in mining or regional logistics. Additionally, government initiatives like grants and incentives can accelerate investment in battery production facilities and the supply chain for components. Developing a strong domestic foundation will reduce costs for fleet operators and may also position Australia as a potential exporter in the Asia-Pacific electric vehicle market.
Government Support for Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market:
Purchase Incentives and Rebates
Government-supported purchase incentives and rebates are vital in mitigating the significant initial costs associated with electric commercial vehicles in Australia. By providing direct financial support such as subsidies, grants, or discounts right at the time of purchase, authorities enhance the accessibility of EVs for logistics operators, public transport agencies, and small enterprises. These initiatives help to lessen the financial disparity between traditional diesel vehicles and electric options, promoting quicker adoption. Fleet owners gain considerable advantages from these programs since reduced acquisition expenses enhance return on investment timelines. Ultimately, such financial initiatives foster market confidence, stimulate demand, and facilitate the shift toward sustainable mobility, making electrification a more practical choice for commercial transport operators in both urban and regional settings.
Tax Benefits and Exemptions
Tax incentives serve as another crucial factor propelling the expansion of Australia's electric commercial vehicle market. By lowering registration costs, import tariffs, and fringe benefits tax for electric fleets, the government decreases ownership expenses, making the adoption of EVs more appealing to businesses. These exemptions yield significant savings for logistics operators, fleet managers, and companies focused on sustainable practices. Additionally, favorable tax conditions motivate corporate buyers to convert a substantial portion of their fleets to electric options, thus contributing to emission reductions. These measures provide financial advantages and align with the nation’s sustainability goals. Over time, consistent tax incentives create a more stable and supportive regulatory landscape, aiding in the faster integration of commercial EVs across various sectors.
Infrastructure Investments
The development of infrastructure is one of the most essential types of governmental support for the electric commercial vehicles market in Australia. Both federal and state authorities are working toward enlarging the network of fast-charging stations along major roads, in urban areas, and across regional paths to facilitate efficient fleet operations. For logistics and freight businesses, having access to dependable charging infrastructure is crucial to addressing range constraints and enhancing productivity. Public-private collaborations are becoming key drivers in this area, with joint efforts to establish charging stations that cater to both light and heavy-duty vehicles. These infrastructure investments alleviate operational difficulties and boost confidence among businesses contemplating fleet electrification. A solid infrastructure framework is essential for scalability, laying the groundwork for sustained market expansion and greater adoption of electric commercial vehicles.
Challenges of Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market:
High Upfront Costs
A significant obstacle in Australia’s electric commercial vehicles sector is the substantial initial investment needed to acquire these vehicles. When compared to diesel or petrol alternatives, electric vans, trucks, and buses have a higher price tag due to costly battery packs and sophisticated components. This poses challenges for small and medium-sized logistics companies, which often operate with narrow profit margins. Although there are long-term advantages, such as lower fuel and maintenance expenses, the lengthy payback period deters many from making the switch. Without enhanced financial incentives or reduced manufacturing costs, numerous operators remain hesitant, which slows the transition to electric fleets throughout Australia.
Battery Supply Constraints
The availability of batteries presents a significant hurdle for the electric commercial vehicles market in Australia. The country relies largely on imports for lithium-ion batteries and related materials, which makes the market susceptible to fluctuations in global prices and disruptions in supply chains. Furthermore, the limited domestic production capabilities increase reliance on external suppliers, raising sustainability and long-term cost concerns. Additionally, the demand for raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel puts extra pressure on battery prices, making electric commercial vehicles more expensive and less accessible for smaller enterprises. To tackle this issue, investments in local battery assembly, recycling facilities, and diverse supply sources are crucial to ensure reliable and cost-effective access to essential components.
Range Anxiety for Long-Distance Fleets
Range issues are a principal challenge for heavy-duty and intercity transport fleets within Australia’s electric commercial vehicles market. While shorter-range EVs are often sufficient for urban deliveries, long-haul trucking demands vehicles that can cover extended distances without needing frequent recharges. The current limitations of battery technology do not effectively support these requirements, particularly for freight operatives traveling on regional and interstate routes. The lack of fast-charging stations along highways exacerbates this problem, causing caution among operators regarding large-scale adoption. Range anxiety adversely affects reliability, productivity, and fleet scheduling. Until more advanced battery technologies and a wider network of charging stations are developed, this challenge will persist in hindering the shift to electric heavy-duty transport in Australia.
Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on vehicle type, propulsion type, battery capacity, and end user.
Vehicle Type Insights:
- Light Commercial Vehicle (LCV)
- Heavy Commercial Vehicle (HCV)
- Buses
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the vehicle type. This includes light commercial vehicle (LCV), heavy commercial vehicle (HCV), and buses.
Propulsion Type Insights:
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug in Hybrid Vehicle (PHEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the propulsion type. This includes battery electric vehicle (BEV), plug in hybrid vehicle (PHEV), and fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV).
Battery Capacity Insights:
- <50kwh
- 50-150 kwh
- >150kwh
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the battery capacity. This includes <50kwh, 50-150 kwh, and >150kwh.
End User Insights:

- Logistics
- Last Mile Delivery
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes logistics and last mile delivery.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Recent News and Developments:
- In May 2025, Volvo Trucks secured a historic order for 30 battery-electric trucks from Linfox in Australia, marking the largest order of its kind in the country. Production of these electric trucks will begin at Volvo’s Brisbane facility in 2026, enhancing the company's commitment to zero-emissions transport solutions.
- In May 2025, Kimberly-Clark Australia launched its first electric truck in collaboration with TR Group, Volvo Group, Brisbane Transport, and Ofload, signifying an important advancement in sustainable freight. This initiative focuses on lowering emissions while showcasing the practicality of electric trucks in actual operations.
- In April 2025, Jameel Motors Australia launched Farizon, a Geely Commercial Vehicle brand, offering innovative electric commercial vehicles. The lineup includes the Farizon SV, a versatile van with an exceptional range, and the H9E truck series, designed for urban logistics, emphasizing sustainability and advanced technology for Australian businesses.
- In November 2024, Western Australia welcomed its first fully electric OEM heavy-duty truck, a Volvo FM Electric, delivered to CD Dodd. This milestone supports decarbonisation efforts in the transport and mining sectors. The truck can carry 50 tonnes, highlighting the industry's move towards sustainable transportation solutions.
Australia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Vehicle Types Covered | Light Commercial Vehicle (LCV), Heavy Commercial Vehicle (HCV), Buses |
| Propulsion Types Covered | Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), Plug in Hybrid Vehicle (PHEV), Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) |
| Battery Capacities Covered | <50kwh, 50-150 kwh, >150kwh |
| End Users Covered | Logistics, Last Mile Delivery |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia electric commercial vehicles market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia electric commercial vehicles market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia electric commercial vehicles industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The electric commercial vehicles market in Australia was valued at USD 4.26 Billion in 2024.
The Australia electric commercial vehicles market is projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.80% during 2025-2033.
The Australia electric commercial vehicles market is expected to reach a value of USD 49.47 Billion by 2033.
Australia is witnessing increasing adoption of electric commercial vehicles due to advancements in battery technology, fleet electrification by logistics firms, and government-backed charging infrastructure expansion. Growing interest in hydrogen fuel-cell trucks and digital fleet management integration further highlights the evolving landscape of sustainable transport solutions.
Rising fuel costs, stricter emission regulations, and growing corporate sustainability commitments are driving demand for electric commercial vehicles in Australia. Supportive government incentives, coupled with long-term cost savings from reduced maintenance and energy use, further make electrification an attractive option for logistics, retail, and public transport operators.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












