
Australia Electric Substation Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Electric Substation Market Overview:
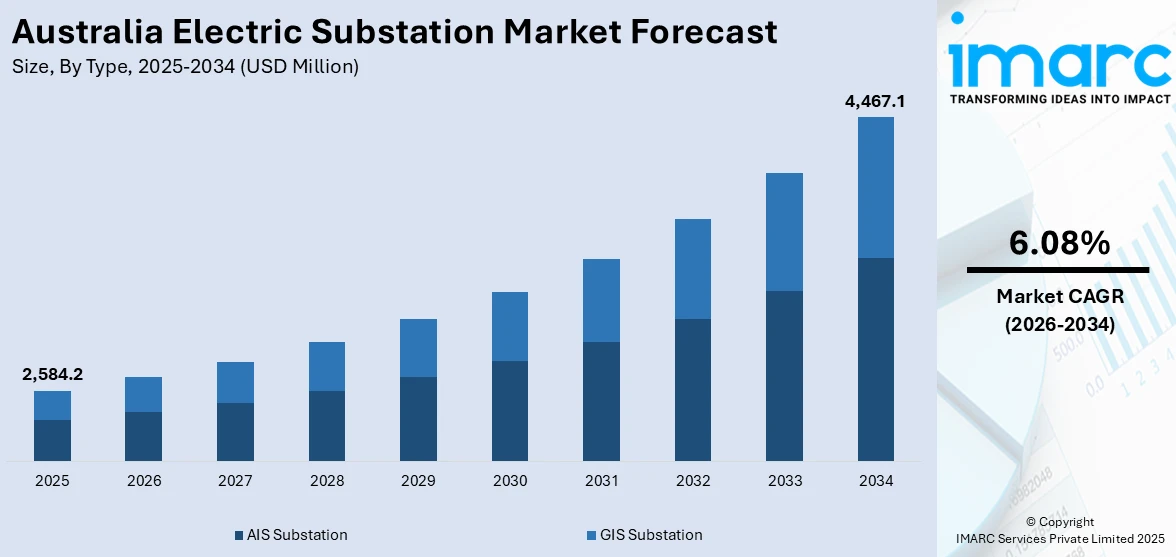
The Australia electric substation market size reached USD 2,584.2 Million in 2025. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 4,467.1 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 6.08% during 2026-2034. The market is undergoing remarkable modernization as a result of digital transformation, renewable energy integration, and development of climate-resilient infrastructure. Utilities are employing intelligent systems, advanced monitoring, and smart grid technologies more and more to enhance reliability and efficiency. The shift towards supporting decentralized and sustainable sources of energy also is speeding up substation upgrades across the country. As investments and policy support for energy transition increase, the industry is expected to witness long-term growth, propelling the Australia electric substation market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2,584.2 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 4,467.1 Million |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 6.08% |
Key Trends of Australia Electric Substation Market:
Integration of Digital Substation Technologies
The Australian electric substation industry is undergoing a strategic transition with the implementation of advanced digital technologies. Substations are becoming increasingly integrated with intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), high-speed communication protocols like IEC 61850, and real-time monitoring systems for data to make the operations more efficient and reliable. These digital technologies enable predictive maintenance, fault diagnosis, and remote monitoring, reducing the requirement for physical checks and lowering system downtime. The automation of critical processes allows quicker decision-making and enhanced response in the event of grid disturbance. Moreover, the digital infrastructure allows for higher flexibility in allowing variable energy sources to be connected and supports decentralized energy generation integration. For instance, in September 2024, Akaysha Energy achieved the initial energization of the 850 MW Waratah Super Battery and 330 kV substation, enhancing New South Wales' electric grid stability amid coal transition. Furthermore, the adoption of cloud-based platforms and advanced analytics is further streamlining asset management and lifecycle planning. Australia electric substation market is experiencing consistent growth as utilities focus on modernization strategies for backing a more intelligent, resilient, and adaptive electricity network against the country's changing energy requirements.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Growth of Renewable Energy Integration Capabilities
Renewable energy integration is playing a leading role in transforming electric substation development in Australia. With a rising installation of large-scale wind and solar farms, substations that can handle variable energy inputs and bidirectional power flows have become the need of the hour. According to the sources, in February 2024, GenusPlus secured a $40 million contract to design and construct a 275kV electric substation on Queensland crown land, supporting the Aldoga Solar Farm and advancing Australia’s renewable grid infrastructure. Moreover, substations today have integrated technologies like dynamic voltage control systems, advanced inverters, and battery storage integration to handle fluctuating renewable supply. In addition, hybrid substations are becoming central infrastructure in markets with high penetration of renewables so that there is seamless coordination between conventional grid sources and decentralized clean energy assets. The installations serve to advance Australia's national goals of lowering carbon emissions and greater dependency on renewable energy sources. Grid operators are using smart control systems to maximize energy dispatch and guarantee grid stability as well. This shift is playing a critical role in driving the Australia electric substation market growth as the country adds strength to its transmission infrastructure to achieve sustainable energy targets.
Strengthening Substation Resilience and Climate Adaptability
With rising climate risks, the Australian electric substation market is focusing more on resilience and climate adaptability. Substations are designed to withstand severe weather events, such as bushfires, flooding, and excessive heat, which are highly common due to global climate change. Improvements in infrastructure involve raising key equipment, application of fire-resistant materials, waterproofing of units, and the adoption of mobile or modular substations that can be quickly installed or moved in case of a crisis. In addition, the installation of microgrid-compatible substations and the integration of distributed energy resources add to system flexibility and localized resilience. Cybersecurity modernization is also being focused on in order to defend infrastructure from mounting digital threats. All these measures combined provide stronger operational continuity and shorter recovery times during disruptive events. This strategic bolstering is fueling quantifiable expansion in the Australia electric substation market, aiding countrywide grid stability in a world of uncertainty around climate and changing energy environments.
Growth Drivers of Australia Electric Substation Market:
Renewable Energy Transition and Grid Modernization Requirements
Australia's aggressive renewable energy transition targets, aiming for net-zero emissions by 2050, are driving massive investments in electric substation infrastructure. The integration of variable renewable sources like solar and wind requires sophisticated substations capable of handling bidirectional power flows and grid stability services. Government initiatives, including the Rewiring the Nation program with AU$20 billion in transmission investment commitments, are accelerating substation deployment nationwide. Major projects such as HumeLink, EnergyConnect, and VNI West necessitate new high-voltage substations and upgrades to existing facilities to accommodate renewable energy zones. The phase-out of coal-fired power plants requires replacement infrastructure that can provide system services previously delivered by thermal generators. Smart grid technologies and digital automation are essential for managing increasingly complex energy flows, creating sustained market opportunities for advanced substation solutions across transmission and distribution networks.
Energy Security and Grid Reliability Imperatives
Australia's growing electricity demand, coupled with extreme weather events and aging infrastructure, necessitates robust substation investments for energy security. System integrity protection schemes (SIPS) require sophisticated substation control systems to prevent cascading blackouts during grid disturbances. Battery energy storage integration at the substation level provides essential grid services, including frequency regulation, voltage support, and emergency power reserves. Mining sector expansion in remote areas drives demand for specialized high-voltage substations to support industrial operations and export infrastructure. Interstate interconnection projects require major substation developments to enable power sharing between states and improve system reliability. Climate resilience initiatives mandate hardened substation designs capable of withstanding bushfires, floods, and extreme temperatures, driving replacement and upgrade cycles. These reliability imperatives fuel consistent market growth as utilities prioritize system security and operational continuity.
Distributed Energy Resources Integration and Electrification Trends
The proliferation of distributed energy resources, including rooftop solar, residential batteries, and electric vehicles, is transforming substation requirements across Australia. Two-way power flows from prosumers necessitate advanced substation controls and monitoring systems to maintain grid stability and power quality. Electric vehicle charging infrastructure demands substantial substation capacity upgrades in urban and highway corridor locations. Industrial electrification trends, particularly in manufacturing and transport sectors, require specialized substation solutions to handle increased electrical loads. Microgrid developments at commercial, industrial, and community scales need dedicated substation infrastructure for islanding capabilities and grid interconnection. Smart city initiatives incorporate advanced substation technologies for optimized energy management and real-time grid operations. Regional development programs drive substation construction to support population growth and economic expansion in previously underserved areas, creating sustained market demand for scalable and flexible substation solutions.
Opportunity of Australia Electric Substation Market:
Digital Transformation and Smart Grid Technology Adoption
The transition towards intelligent grid infrastructure presents significant opportunities for advanced digital substation technologies in Australia. Deployment of artificial intelligence and machine learning in substation operations enables predictive maintenance, automated fault detection, and optimized asset performance management. Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and edge computing solutions facilitate real-time monitoring and control of substation equipment, reducing operational costs and improving reliability. Cybersecurity solutions specifically designed for critical infrastructure protection create new market segments as utilities prioritize grid security. Digital twin technology for substation modeling and simulation offers enhanced planning and operational optimization capabilities. Advanced analytics platforms for grid optimization and energy forecasting represent emerging opportunities as Australia moves towards a more complex, decentralized energy system. These digital innovations drive Australia electric substation market demand expansion as utilities seek competitive advantages through technological advancement and operational excellence.
Energy Storage Integration and Hybrid Infrastructure Development
The growing deployment of battery energy storage systems co-located with substations creates substantial market opportunities for hybrid infrastructure solutions. Grid-scale batteries require specialized substation equipment, including transformers, switchgear, and control systems capable of rapid response and bidirectional power flow management. Virtual power plant aggregation services need sophisticated substation controls to coordinate multiple distributed resources and provide grid services. Pumped hydro storage projects, particularly Snowy 2.0, require major substation infrastructure investments to connect large-scale storage to the transmission network. Hydrogen production facilities powered by renewable energy need dedicated high-voltage substations to support electrolysis operations and grid interconnection. Community battery programs drive demand for distribution-level substation upgrades and specialized equipment for local energy storage deployment. According to the Australia electric substation market analysis, these storage integration requirements fuel sustained market growth as energy storage becomes essential for grid stability and renewable energy utilization.
Export Infrastructure and Critical Minerals Processing Expansion
Australia's role as a global critical minerals supplier creates opportunities for specialized substation infrastructure supporting mining operations and processing facilities. Green hydrogen export projects require massive electrical infrastructure including high-voltage substations to power electrolysis plants and liquefaction facilities. Critical minerals processing for battery supply chains demands reliable, high-capacity electrical infrastructure with specialized substation solutions for smelting and refining operations. Port electrification initiatives for zero-emission shipping require substantial substation capacity to support electric cargo handling and vessel charging infrastructure. Data center expansion driven by artificial intelligence and cloud computing demands ultra-reliable substation infrastructure with backup power and cooling systems. Defense infrastructure modernization programs create opportunities for hardened substation solutions meeting military specifications and security requirements. These industrial developments generate significant market demand for specialized, high-capacity substation solutions supporting Australia's economic diversification and export competitiveness.
Challenges of Australia Electric Substation Market:
Supply Chain Disruptions and Equipment Procurement Delays
The Australia electric substation market faces significant challenges from global supply chain disruptions affecting critical equipment procurement and project timelines. Specialized high-voltage transformers, switchgear, and digital control systems require long lead times, often extending 12-18 months, creating project scheduling complexities. International trade tensions and shipping constraints have increased equipment costs and delivery uncertainties, particularly for components manufactured in Europe and Asia. Local manufacturing capacity limitations necessitate heavy reliance on imported equipment, exposing projects to currency fluctuations and geopolitical risks. Skilled technician shortages for specialized equipment installation and commissioning further compound delivery challenges. These supply chain constraints impact the market growth as utilities face cost overruns and delayed infrastructure deployment, potentially affecting renewable energy transition timelines and grid reliability objectives.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Approval Complexities
Complex regulatory frameworks across different Australian states create significant challenges for substation development projects, particularly for interstate transmission infrastructure. Environmental impact assessments require extensive consultation with indigenous communities, ecological surveys, and heritage protection measures, often extending approval timelines by years. Land acquisition processes face increasing community opposition and legal challenges, particularly in densely populated areas or environmentally sensitive locations. Compliance with evolving safety standards, cybersecurity regulations, and grid codes requires continuous technical updates and additional certification processes. Planning approval coordination between federal, state, and local authorities creates bureaucratic complexities and potential conflicts in jurisdiction requirements. These regulatory challenges constrain market opportunities as developers face increased development costs, extended project timelines, and uncertainty in approval outcomes, deterring investment in critical grid infrastructure.
Aging Infrastructure and Asset Management Complexities
Australia's aging substation infrastructure, with many assets approaching end-of-life, presents significant challenges for utilities managing replacement cycles and maintenance requirements. Legacy equipment compatibility issues complicate the integration of modern digital technologies and smart grid capabilities, requiring costly retrofitting or complete system replacements. Asset condition monitoring and predictive maintenance programs demand substantial investments in new technologies and skilled personnel to prevent unexpected failures. Coordination of planned outages for major substation upgrades requires complex scheduling to minimize grid disruption and maintain system reliability. Skills shortage in specialized substation engineering and maintenance creates workforce capacity constraints for managing increasingly complex infrastructure portfolios. These asset management challenges impact market demand as utilities balance capital expenditure requirements with operational costs while maintaining service reliability standards across diverse geographic and climatic conditions.
Australia Electric Substation Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on type and application.
Type Insights:
- AIS Substation
- GIS Substation
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes AIS substation and GIS substation.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
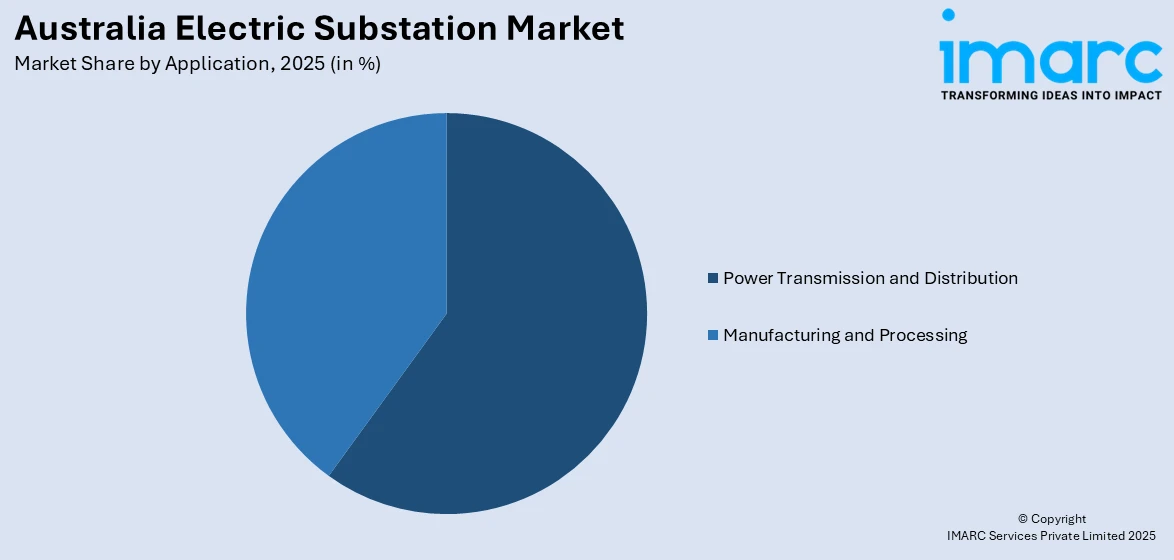
- Power Transmission and Distribution
- Manufacturing and Processing
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application have also been provided in the report. This includes power transmission and distribution and manufacturing and processing.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Electric Substation Market News:
- In January 2025, Hitachi Energy collaborated with Transgrid to deliver high-voltage substation gear for Australia's HumeLink project. The significant enhancement of the electric substation system will boost grid reliability and facilitate increased transmission of renewable energy throughout New South Wales, further consolidating the nation's shift toward a low-carbon electricity grid.
- In August 2024, the EnergyConnect project attained a major milestone with the energization of the initial 220 kV section at Buronga substation in New South Wales. This highlight reflects the growth and upgrading of Australia's electric substation infrastructure, improving grid reliability and enabling renewable energy interconnection in multiple states.
Australia Electric Substation Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | AIS Substation, GIS Substation |
| Applications Covered | Power Transmission and Distribution, Manufacturing and Processing |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia electric substation market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia electric substation market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia electric substation industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The electric substation market in Australia was valued at USD 2,584.2 Million in 2025.
The Australia electric substation market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.08% during 2026-2034.
The Australia electric substation market is projected to reach a value of USD 4,467.1 Million by 2034.
The market experiences an accelerating digital transformation through intelligent electronic devices and real-time monitoring systems. Renewable energy integration capabilities drive hybrid substation development for variable power flows. Climate resilience measures include fire-resistant materials and cybersecurity modernization to withstand extreme weather events and digital threats.
The Australia electric substation market is driven by renewable energy transition mandates, grid modernization requirements, and energy security imperatives. Government infrastructure investments, distributed resource integration, and industrial electrification trends accelerate demand across transmission and distribution networks nationwide.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












