
Australia Grid Energy Storage Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Battery Chemistry, Ownership, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Grid Energy Storage Market Overview:
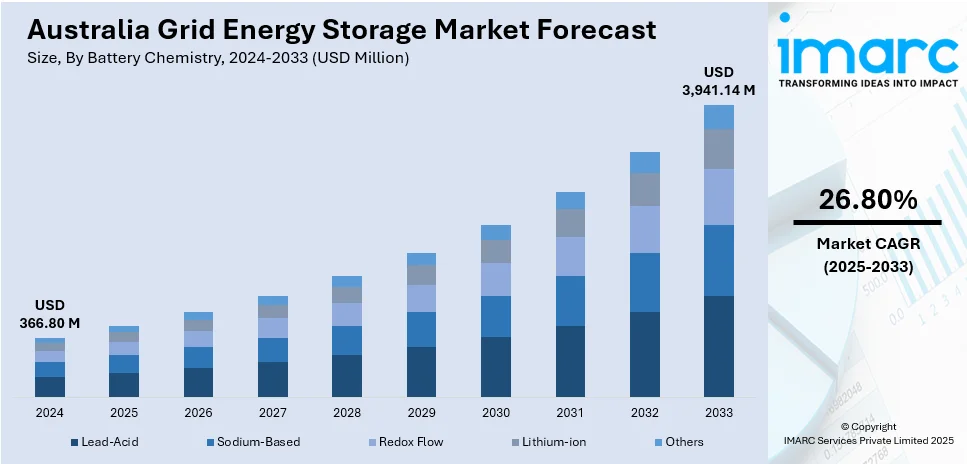
The Australia grid energy storage market size reached USD 366.80 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 3,941.14 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 26.80% during 2025-2033. The demand for renewable energy integration, government incentives, and the growth in storage technologies drive the market. The decarbonization efforts of the country and the grid resilience also support a cleaner energy system. This has contributed positively to the Australia grid energy storage market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 366.80 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 3,941.14 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 26.80% |
Key Trends of Australia Grid Energy Storage Market:
Growing Adoption of Large-Scale Storage Systems
The market demand for large-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS) is increasing in Australia as the nation keeps incorporating renewable energy into its grid. The systems stabilize the grid by holding surplus power produced from solar and wind power during high-demand periods. With the support of incentives from the government and the private sector, utilities are investing in utility-scale BESS projects. For instance, in May 2025, ACE Power submitted plans to develop a large-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) in New South Wales under Australia's EPBC Act. The Eastern Hub Firming Battery will be a 1,000 MW system, with a duration of 4 to 8 hours, totaling up to 8,000 MWh. These facilities also facilitate the shift towards non-coal generation of electricity and clean energy solutions to lower Australia's reliance on fossil fuels and build grid resilience. The Australia grid energy storage market growth, therefore, is anticipated to be strong, backed by a trend towards more efficient and sustainable energy storage technologies.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Energy Storage for Renewable Integration and Grid Stability
Australia's focus on integrating higher levels of renewable energy into its grid has been a significant factor in driving the growth of energy storage. As the country shifts towards renewable sources like solar and wind, energy storage systems provide a necessary solution to manage intermittency and balance supply and demand. For instance, in May 2025, the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) introduced new rules to simplify the connection process for solar PV, wind, and battery energy storage systems (BESS) to the National Electricity Market (NEM). These changes aim to streamline grid integration, reducing costs and time for renewable and storage projects. With increasing renewable energy generation, energy storage becomes essential to store excess energy during periods of high generation and dispatch it during low generation or high demand periods. This capability is crucial for maintaining grid stability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Thus, the development of grid-scale storage solutions is expected to be a key driver in the Australia grid energy storage market growth, contributing to more sustainable energy systems.
Growth Drivers of Australia Grid Energy Storage Market:
Rapid Renewable Energy Expansion and Intermittency Challenges
Australia's speedy shift to renewable energy is a key driver of grid energy storage market expansion. The nation has witnessed a spurt of solar and wind power, especially in states such as South Australia, Queensland, and New South Wales. These renewable sources are, by nature, intermittent and generate grid stability issues, particularly at peak demand or low generation times. Grid-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS) are becoming more and more crucial for managing frequency regulation, storing excess energy for later use, and assisting in supply and demand balance. Australia's geographic spread of renewable resources increases the complexity of managing the grid, making assured energy storage solutions all the more necessary. This dynamic gives utilities, independent power producers, and state governments powerful incentives to invest in storage assets that firm renewables and provide a stable, dispatchable power stream to the National Electricity Market (NEM).
Decentralized Energy Systems and Community Resilience
Australia's grid energy storage expansion is also driven by the transition towards decentralized energy frameworks and community energy resilience programs. Remote and off-grid areas such as Northern Territory or Western Australia's mining regions need energy autonomy because of limited grid connection. In these areas, isolated microgrids and hybrid renewable systems are increasingly combined with battery storage to minimize diesel use and provide uninterrupted power. Even in cities, neighbourhoods and councils are investing in community storage schemes to enable solar take-up at neighbourhood level and peak-shaving. Initiatives such as community batteries enable residents to store surplus rooftop solar, which is plentiful because of the high residential solar penetration in Australia. Such innovations are transforming the conventional centralised utility model and giving local energy management control. Storage systems not only enhance grid resilience but also act as a buffer in the event of extreme weather conditions like bushfires and heatwaves, that are increasingly frequent and intense, making the case for robust, distributed energy infrastructure.
Government Policy, Market Reforms, and Private Investment
Encouraging government policy and electricity market reform are at the forefront of pushing Australia's grid energy storage industry forward. Federal and state government programs are providing grants, low-interest finance, and planning assistance to storage projects related to renewable regions and infrastructure of national interest. South Australia and Victoria, for instance, have put in place targets and funding arrangements specifically designed to increase large-scale battery installation. The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) is also developing rules to better place storage in the electricity market, enabling batteries to engage in services such as frequency regulation, arbitrage, and network support. Private investors and international energy players are also deeply interested in Australia's storage market because it has clear regulatory frameworks and high levels of renewable potential. The synergy of public backing, access to markets, and increasing investor confidence is racing ahead with the commercialization and scale-up of grid storage projects. With clean, reliable electricity becoming increasingly in demand, energy storage will continue to be one of the pillars of Australia's transforming power system.
Government Support of Australia Grid Energy Storage Market:
Federal Strategic Prioritization of Clean Energy and Storage
The Australian federal government has recognized energy storage as a crucial part of its future energy transition strategy. Through initiatives such as the National Battery Strategy and the Critical Minerals Strategy, the federal government is attempting to make Australia not only a user but also a provider of storage technology. This comprises the development of upstream battery material supply chains and deployment of grid-scale energy storage systems. Active roles are undertaken by government-sponsored bodies like the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), and the Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC) which offer concessional finance and grants for Australia-wide large-scale battery projects. The funds aim to de-risk private investment and drive commercial deployment. The federal government further collaborates with the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) to improve regulatory settings to allow energy storage assets to engage more actively in wholesale markets. Together, these are part of a coordinated federal push to integrate storage into the national energy mix.
State-Level Incentives and Regional Storage Initiatives
Australian state governments have also led the charge in promoting grid energy storage adoption, with regional needs and energy usage profiles frequently informing the support they provide. South Australia, for instance, is at the forefront of large-scale battery deployment, with robust state government backing for leading-edge initiatives such as the Hornsdale Power Reserve. The Victorian government has initiated standalone programs to co-finance storage projects associated with its renewable energy zones, assisting in reducing grid congestion and enhancing reliability. New South Wales has proposed grid-scale storage as part of its Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap, providing long-term financial instruments and accelerated development processes for battery developers. Such state policies tend to incorporate accelerated planning approvals, capital cost-sharing, and coordination with renewable procurement auctions. Western Australia, which has an isolated grid system, is conducive to storage solutions appropriate for remote conditions, such as distributed energy storage and hybrid microgrids. The regionalized model enables customized policy structures that match each state's energy issues and grid structures.
Community Batteries, Microgrids, and Local Empowerment Programs
Besides major utility-scale ventures, Australian governments are increasingly promoting distributed energy storage at the household and community levels. Initiatives like community battery trials, which are funded by partnerships between state and local councils and energy retailers, allow communities to store extra solar power together. It is particularly pertinent to suburbs with high rates of rooftop solar adoption, such as found in Perth, Adelaide, and Brisbane. Pilot schemes, technical reports, and upgrades to support local energy hubs are financed by governments. In remote and regional communities, particularly in Northern Territory and Indigenous communities, microgrid projects with storage are being focused assistance to decrease diesel reliance and boost energy self-reliance. In addition to enhancing energy access and affordability, these initiatives are also creating local employment and building capacities. By encouraging a bottom-up approach to energy resilience, Australian governments are expanding the scope of storage beyond the central utilities to empower local communities.
Australia Grid Energy Storage Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country/regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on battery chemistry, ownership, and application.
Battery Chemistry Insights:
- Lead-Acid
- Sodium-Based
- Redox Flow
- Lithium-ion
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the battery chemistry. This includes lead-acid, sodium-based, redox flow, lithium-ion, and others.
Ownership Insights:
- Third-party Owned
- Utility Owned
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the ownership have also been provided in the report. This includes third-party owned and utility owned.
Application Insights:
- Renewables
- Peak Shifting
- Ancillary Services
- Backup Power
- Others
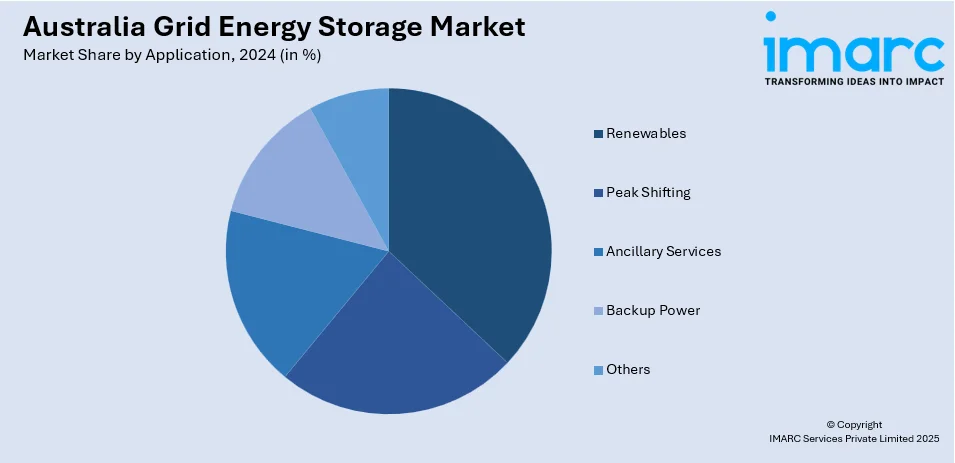
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application. This includes renewables, peak shifting, ancillary services, backup power, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Grid Energy Storage Market News:
- In May 2025, Elements Green, a UK-based renewable energy developer, received grid connection approval for a 1.3GWh solar-plus-storage facility in Queensland, Australia. The Eurimbula Hybrid Facility, located in the Central Queensland renewable energy zone, is set to enhance energy integration and contribute to Australia's clean energy goals.
- In May 2025, BYD Australia and Livium, through its subsidiary Envirostream Australia, expanded their existing battery recycling deal to include Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS). This new three-year agreement aims to enhance the recycling of BESS, contributing to a more sustainable energy storage ecosystem in Australia.
- In April 2025, Wärtsilä announced that it will supply a 64 MW / 128 MWh energy storage system for Octopus Australia’s Fulham Solar Battery Hybrid project, one of Australia’s first large-scale DC-coupled hybrid systems. The system will enhance renewable energy efficiency, integrating a solar farm with advanced energy storage, contributing to Victoria's net zero emissions goal by 2045.
- In December 2024, Fluence Energy, in partnership with Eku Energy, Shell Energy, and Perfection Private, officially opened the 200 MW / 400 MWh Rangebank Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) in Cranbourne, Melbourne, Australia. The system, Victoria's second-largest BESS, is designed to support grid stability and can power 80,000 homes for one hour during peak demand. It uses Fluence's Gridstack™ technology and will be operated under a tolling agreement with Shell Energy, which has access to the system’s full capacity for the next 20 years.
Australia Grid Energy Storage Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Battery Chemistries Covered | Lead-Acid, Sodium-Based, Redox Flow, Lithium-ion, Others |
| Ownerships Covered | Third-party Owned, Utility Owned |
| Applications Covered | Renewables, Peak Shifting, Ancillary Services, Backup Power, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia grid energy storage market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia grid energy storage market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia grid energy storage industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia grid energy storage market was valued at USD 366.80 Million in 2024.
The Australia grid energy storage market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 26.80% during 2025-2033.
The Australia grid energy storage market is expected to reach a value of USD 3,941.14 Million by 2033.
The Australia grid energy storage market is witnessing trends like expanding utility-scale battery projects, increased investment in long-duration storage, and integration with renewable energy hubs. Community and virtual power plant models are gaining traction, while regulatory updates and digital grid technologies are also shaping a more flexible, decentralized, and resilient energy network.
The Australia grid energy storage market is driven by rapid renewable energy adoption, grid stability needs, and rising electricity demand. Government incentives, market reforms, and declining battery costs further support growth. Storage systems are essential for balancing supply, reducing outages, and enabling clean energy integration across urban, regional, and remote areas.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












