
Australia Higher Education Market Report by Component (Platform, Services), Course Type (Arts, Economics, Engineering, Law, Science, and Others), Learning Type (Online, Offline), End User (State Universities, Community Colleges, Private Colleges), and Region 2025-2033
Australia Higher Education Market Overview:
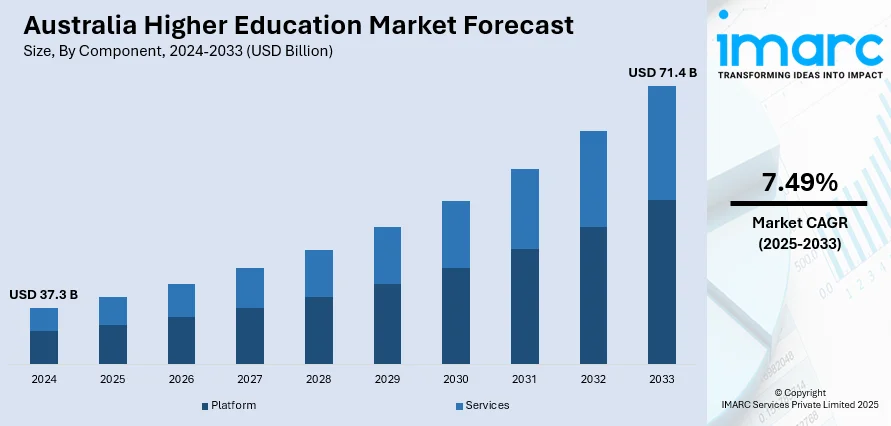
The Australia higher education market size reached USD 37.3 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 71.4 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 7.49% during 2025-2033. The market is propelled by increasing international student enrolment, government investment and support for education, growth in online and distance learning platforms, rising demand for skilled professionals in various sectors, and expansion of research and innovation programs in universities.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 37.3 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 71.4 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 7.49% |
Key Trends of Australia Higher Education Market:
Increasing International Student Enrollment
Australia has become one of the most popular destinations for international students, driven by its high-quality education system, diverse cultural environment, and post-study work opportunities. The presence of world-renowned universities, strong global rankings, and a multicultural society make Australia an attractive option for students from countries such as China, India, and Southeast Asia. Additionally, the geographical proximity of Australia to these regions facilitates easier travel and cultural integration for international students. The robust visa policies of the country, including post-study work visas, allow international graduates to gain work experience in Australia, further enhancing the appeal of its higher education system. As a result, international students form a significant portion of the student population in Australian universities, contributing to the overall growth of the higher education market. According to Gitnux, the higher education sector in Australia possesses the highest number of international student enrollment, accounting for 46% of total international enrollments in 2022. This influx of international students generates revenue for educational institutions and boosts the economy through spending on accommodation, living expenses, and travel.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Government Investment and Support for Education
The Government of Australia is supporting and developing the higher education sector by providing substantial funding to universities, various scholarships to students and enforces numerous regulatory standards. These help in maintaining the high standards of the education system in Australia. For instance, programs such as the Commonwealth Grant Scheme (CGS) provide financial assistance to domestic students. This makes higher education more accessible to Australian citizens. As a result, a sustainable domestic student base is created, which, combined with international students, contributes substantially to the growth of the market. As per a study conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics in 2021, 5.5 million individuals possess a bachelor’s degree or a higher educational qualification, recording a 30.7% rise since 2016. Moreover, the government also promotes research and innovation within universities. This enhances the global reputation of Australia as a leader in education and research. The Parliament of Australia announces the Universities Accord (Student Support and Other Measures) Bill 2024 in response to the Australian Universities Accord Final Report. The Bill includes various amendments made to the Higher Education Support Act 2003 and consists of 5 schedules. Additionally, government policies also focus on ensuring equity in education. This involves providing opportunities for Indigenous students and students from disadvantaged backgrounds to access higher education through specialized support programs. Inclusive approaches such as these drive local enrollment and augment the overall reputation of the Australian education system, contributing to market growth.
Rising Demand for Skilled Professionals
The Australian economy relies immensely on a highly skilled workforce. Sectors such as healthcare, engineering, information technology, and renewable energy particularly require trained professionals. This demand for workers with specialized skills is continuously rising as industries evolve and technologies advance. Due to this, Australian higher education institutions are offering many different programs that have been formulated to meet specific industry needs. Consequently, many courses are gaining popularity in areas such as data science, cybersecurity, and healthcare management. For instance, in 2022, 11% of overseas students are studying health in Australian universities, according to Gitnux. These courses provide a competitive edge in the job market, encouraging students to seek such qualifications. Also, partnerships between universities and industries are creating more opportunities for practical learning and internships. This helps students in gaining real-world experience while pursuing their degrees. Collaborations such as these between education and industry requirements ensure that graduates are well-prepared for the workforce, further augmenting the appeal of Australian higher education.
Growth Drivers of Australia Higher Education Market:
Decentralized Education and Regional Campus Development
One of the emergent trends in the Australian higher education scene is the development and expansion of regional campuses. Universities increasingly open or develop facilities outside metropolitan areas to provide access to rural and distant communities. The decentralization drive is especially important in a nation where geographical distances may restrict access to quality education for wide parts of the population. Government incentives and local development programs have stimulated universities to provide a broader spectrum of full-degree courses and vocational streams beyond the traditional urban hub. These satellite campuses decrease educational disparities and assist in alleviating regional skills shortages by ensuring course programs suit local industry requirements. For instance, courses in agriculture, environmental science, and rural health tend to be more developed in regional institutions. Widening regional access also generates new streams of revenue and increases community participation, so this is an important contributor to the Australia higher education market growth for institutions looking to diversify their presence and contribution.
Emergence of Transnational Education and Offshore Collaborations
Australia's higher education providers are making more use of transnational education (TNE) models to reach out further internationally. By collaborating with foreign universities, establishing overseas campuses, or providing joint degrees, Australian institutions are accessing demand from students who cannot move but are looking for a Western-style education. Southeast Asian and Middle Eastern countries have expressed special interest in these collaborations, driven by the reputation of Australia's education and cultural compatibility. Such TNE arrangements permit institutions to construct international brand recognition and diversify revenue streams, as well as promote research and exchange of faculty. Additionally, Australian universities are less vulnerable to domestic enrollment volatility by creating a wider pool of international students. The adaptability of these arrangements also permits universities to customize programs according to local market demand, increasing relevance and intake. As demand for high-quality and accessible education increases across the world, transnational models provide an education system with a scalable and sustainable growth model.
Indigenous Knowledge Integration and Cultural Curriculum
According to the Australia higher education market analysis, a new and distinctive growth impetus is the embedding of Indigenous knowledge systems and perspectives into mainstream academic curricula. Universities nationwide are embracing initiatives to integrate Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander material into fields like environmental science, law, health, and education. This is part of more general national reconciliation and recognition efforts, and it presents institutions with the opportunity to create unique academic programs that cannot be found elsewhere. The concept of incorporating Indigenous studies draws in domestic students committed to social justice and cultural education, along with international students looking to gain an enhanced sense of Australia's identity and heritage as well as its Indigenous cultures. Universities are also forming collaborations with Indigenous communities for research, curriculum design, and cultural immersion experiences. These programs enhance the student experience, increase institutional diversity, and make Australian universities leaders in inclusive and culturally responsive education, enabling them to drive enrolments and meet wider social impact mandates.
Opportunities of Australia Higher Education Market:
Growth in International Student Demand
Australia continues to be a top global destination for international students, offering a major opportunity for higher education providers. Its strong academic reputation, multicultural environment, and high quality of life attract students from Asia, the Middle East, and beyond. Cities such as Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, and Perth host world-accredited universities that are broadening their reach and courses to respond to the interests of the world. Post-study work rights, migration access, and English-medium experience make Australia particularly attractive to students who wish to establish themselves outside of their countries of origin. Institutions can take advantage by investing in international marketing, establishing offshore alliances, and developing dual-degree or exchange arrangements. Moreover, the increasing demand for study areas like technology, health sciences, and sustainability opens up room for customization of curricula for emerging skills. These trends offer long-term expansion opportunities, particularly for universities that frame themselves as globally competitive and culturally diverse education centers, which further increases the Australia higher education market share.
Growth of Online and Blended Learning Models
The rising acceptance and popularity of flexible learning modes have created new opportunities for higher education institutions in Australia. The widespread enrollment of pandemic-driven online and blended learning demonstrated the sustainability of digital delivery of education, with institutions now committed to ongoing investment in high-quality online programs. This offers a special opportunity to entice domestic and international students preferring or needing remote study options as a result of work, location, or personal reasons. Australian regional and rural students, who frequently experience logistics hindering campus access to study, benefit too. Additionally, the provision of short-term certificates, micro credentials, and stackable degrees allows universities to accommodate professionals demanding upskilling on a non-long-term basis. Integrating academic content with technological advancement allows Australian universities to reach more students, diversify their income streams, and address changing needs of today's learners both locally and internationally.
Employability-Centric Curriculum and Industry Partnership
Australia's emphasis on industry-based education and employability offers one of the key opportunities for higher education institutions. The nation possesses a developed system of incorporating work-integrated learning, internships, and industry partnerships into the university curriculum. This opens the avenue for institutions to create curriculums based on workforce requirements, especially in high-growth fields like healthcare, engineering, IT, and green energy. Australian universities can have the opportunity to enhance partnerships with local and global businesses, government agencies, and start-ups to co-develop courses, facilitate research commercialization, and enhance graduate employment outcomes. Regional economic development initiatives, especially in regions such as Western Australia and the Northern Territory, provide opportunities for universities to be aligned with local workforce strategy and community needs. By branding themselves as talent developers and innovation collaborators, institutions can entice students as well as investments and become a meaningful contributor to national economic aspirations. Such industry alignment provides a competitive advantage and propels long-term institutional salience in an increasingly dynamic education environment.
Government Initiatives of Australia Higher Education Market:
Emphasis on Regional and Equity Access Expansion
Increased access to higher education by students from regional, rural, and remote communities has been a top priority by the Australian government through a variety of specific policies and funding initiatives. In consideration of the educational gap between non-metropolitan and metropolitan regions, programs have been established with the aim of inducing universities to develop or enhance regional campuses, as well as offering support services aligned to local requirements. Initiatives to provide financial incentives, accommodation support, and other learning materials have assisted in enhancing student participation rates from disadvantaged groups. Indigenous students are also the focus of special consideration, with encouragement for universities to include culturally relevant curricula and support arrangements. Such initiatives cater to social and geographical inequalities and assist in enhancing national workforce development in general through alignment of regional education streams with local needs in the labor market. The focus of the government on inclusiveness and access highlights its dedication to making higher education a fairer and regionally accountable system throughout Australia.
Investment in Innovation and Research through National Initiatives
Australia's federal government keeps nurturing the nation's competitiveness on a global level in innovation and research through significant investments in university-driven initiatives. Universities may conduct advanced research in a wide range of areas, from health and climate science to quantum computing and clean energy, thanks to programs like the Australian Research Council funding programs and the National Collaborative Research Infrastructure Strategy. The aim of these programs is to build the knowledge economy in Australia and make its universities a positive force for addressing local and global problems. Furthermore, government-sponsored partnerships with industry sectors and universities are positively encouraged, opening doors to research commercialization and field applications. Regional universities are also encouraged to set up innovation centers driving local growth and knowledge transfer. These investments in infrastructure and retaining talent over the long-term position Australian universities to be central to national policy agendas while allowing them to attract foreign researchers, collaborators, and sponsors.
International Education Strategy and Global Engagement
As a response to the significance of international students to the university industry and economy, the Australian government has come up with a far-reaching international education strategy with the objective of enhancing global connection. This encompasses financing transnational education, global marketing campaigns, and diversification of source nations for international students. There are also schemes to encourage Australian students abroad to move around through scholarships and bilateral exchange arrangements to enhance educational links with priority areas like Southeast Asia and the Pacific. It also offers regulatory frameworks to facilitate quality standards for international partnerships and protect the well-being of international students studying in Australia. Through strategies such as expedited visa processing and post-study work rights, the government promotes the competitiveness of Australian universities in the international education market. The measures are part of a more comprehensive national approach to making higher education an asset for diplomacy and an important service export industry, and one that is long-term sustainable and relevant internationally.
Challenges of Australia Higher Education Market:
Dependence on International Student Revenue
One of the most pressing challenges facing Australia’s higher education sector is its heavy reliance on international student fees as a primary source of revenue. This model, while rewarding in periods of steady global mobility, leaves universities vulnerable to large financial losses during global crises like pandemics, geopolitical conflict, or shifts in visa regulations. Metropolitan areas such as Melbourne and Sydney, which welcome high numbers of international students, were hardest hit by border shutdowns and enrolment drops in recent history. Dependence on too few countries, with China and India in particular, also leaves institutions open to changes in diplomatic ties or student popularity. International students finance research and campus infrastructure while international enrollment, although providing assistance, does not diversify financing streams and hence poses a concern regarding long-term financial viability. Australian universities are now being called to rebalance their revenue models, invest more in local student participation, and lower reliance on a single group of students, to support the increasing Australia higher education market demand.
Increasing Cost of Living and Issues of Student Affordability
The high cost of living in Australia, especially in capital cities such as Sydney and Melbourne, is creating an increasing impediment to access to higher education for both domestic and international students. Affordability of housing, transport, and day-to-day living frequently discourages potential students, particularly from regional areas or lower socio-economic groups. International students have the additional problem of financing visa applications and supporting themselves while in education, frequently without proper access to support mechanisms. Although scholarships and subsidies may be available, they are not always plentiful or extensive enough, with associated questions around equity and inclusion. The financial burden is also likely to affect student performance and welfare, leading institutions to increase welfare services and emergency assistance. These are nevertheless reactive and not structural measures. Long-term affordability issues are likely to affect Australia's status as a global education center of excellence, which is likely to demand government and institutional efforts to make education financially accessible and not exacerbate socioeconomic gaps.
Balancing Research Excellence with Teaching Quality
Australian universities are internationally renowned for research productivity, but the intense focus on research quality can at times be at the cost of good teaching and student interaction. Most academic staff feel pressured to gain research grants and publish their work, which can decrease their time for teaching tasks or restrict their interest in pedagogy. This problem is especially evident in research-heavy institutions, where teaching can be regarded as a secondary role. For students, it can result in inconsistencies in teaching quality, restricted academic assistance, and less access to experienced staff. More importantly, the increasing use of casual or sessional teachers, in many cases with non-permanent contracts, introduces uncertainty in the teaching environment and impacts continuity among students. While the research outputs of Australian universities contribute to their international rankings, balancing strong research with excellent teaching is a multifaceted task. Achieving it calls for systemic reform of funding models, performance measurements, and institutional culture.
Australia Higher Education Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on component, course type, learning type, and end user.
Component Insights:
- Platform
- Services
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the component. This includes platform and services.
Course Type Insights:
- Arts
- Economics
- Engineering
- Law
- Science
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the course type have also been provided in the report. This includes arts, economics, engineering, law, science, and others.
Learning Type Insights:
- Online
- Offline
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the learning type. This includes online and offline.
End User Insights:
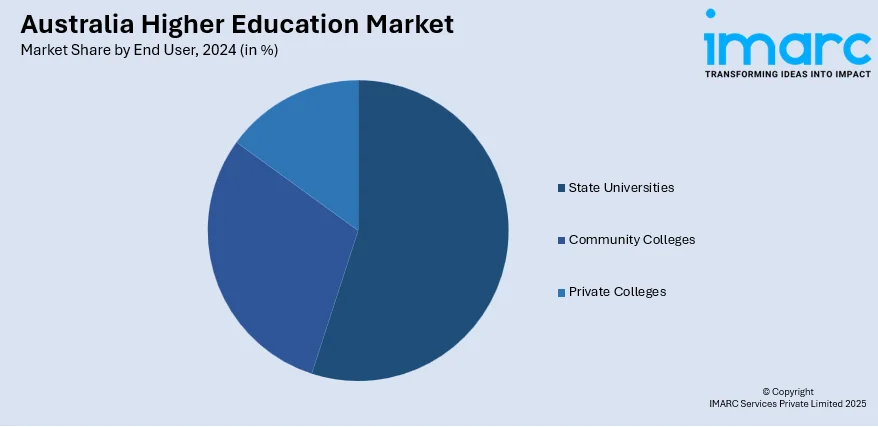
- State Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Colleges
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes state universities, community colleges, and private colleges.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Higher Education Market News:
- August 9, 2024: The education sector of Australia has invested $175 million in advertising between May and June this year. The investment in advertising increased by 19% as the Australian higher education institutions are spending more money on advertisement and marketing, to attract more students to university.
Australia Higher Education Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Platform, Services |
| Course Types Covered | Arts, Economics, Engineering, Law, Science, Others |
| Learning Types Covered | Online, Offline |
| End Users Covered | State Universities, Community Colleges, Private Colleges |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia higher education market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia higher education market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia higher education industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia higher education market was valued at USD 37.3 Billion in 2024.
The Australia higher education market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 7.49% during 2025-2033.
The Australia higher education market is expected to reach a value of USD 71.4 Billion by 2033.
The Australia higher education market is advancing through a shift toward hybrid and online learning models, catering to both domestic and global learners. There is growing interest in micro credentials and lifelong learning driven by career-focused upskilling. Institutions are also emphasizing international partnerships and regional campus expansion, reflecting Australia’s global reach and national equity priorities.
The Australia higher education market is driven by strong international student demand, government investment in research and innovation, and expanding regional education access. Policies supporting global engagement and lifelong learning also contribute to growth. Universities benefit from Australia's reputation for academic excellence, multicultural environment, and strategic ties to Asia-Pacific education markets.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












