
Australia Last Mile Delivery Market Report by Delivery Mode (Regular Delivery, Same-Day Delivery or Express Delivery), Application (E-Commerce, Retail and FMCG, Healthcare, Mails and Packages, and Others), Destination (Domestic, International), Service Type (Business-To-Business (B2B), Business-To-Consumer (B2C), Customer-To-Customer (C2C)), Vehicle Type (Motorcycle, LCV, HCV, Drones), Mode of Operation (Non-Autonomous, Autonomous), and Region 2025-2033
Australia Last Mile Delivery Market Size and Share:
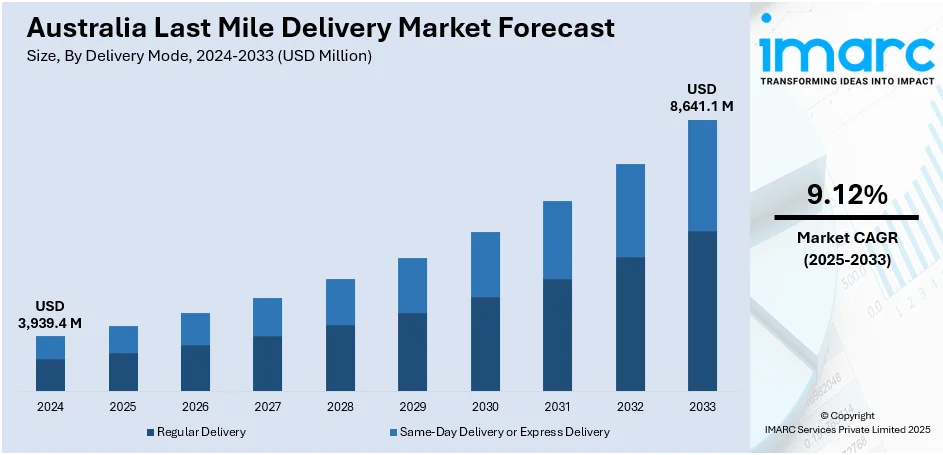
The Australia last mile delivery market size reached USD 3,939.4 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 8,641.1 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 9.12% during 2025-2033. The expansion of e-commerce sector, the increasing consumer demand for fast and convenient delivery services, significant advancements in logistics technology, rapid urbanization, and the rise of innovative delivery solutions like drones and autonomous vehicles are some of the major factors propelling the Australia last mile delivery market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3,939.4 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 8,641.1 Million |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 9.12% |
Australia Last Mile Delivery Market Trends:
Rising E-commerce Sector
The rapid growth of online shopping facilitates the demand for efficient last mile delivery services to meet consumer expectations for quick and reliable deliveries. According to the International Trade Administration, Australia is the eleventh-largest e-commerce market in the world, and revenue is predicted to reach USD 32.3 billion by 2024. This represents a year-on-year increase of 15.5 percent. In comparison, the bricks and mortar retail market grew by 3.4% over the same period to reach USD200 billion. Online commerce represents approximately nine percent of all retail trade in the Australian market. The largest Australian eCommerce platforms/sites are eBay (AU) (69 million monthly visits), Amazon (AU) (22.5 million), Woolworths (20.4 million), JB Hi-Fi ((13.3 million), Big W (11.9 million), Coles (10.7 million), Kogan (10.2 million), Officeworks (9.45 million), Chemist Warehouse (9.1 million), and Catch (8.95 million). According to Australia Post research, 48.8 percent of all online payments are made via PayPal. Credit and debit cards account for 39.9% of online payments. The fastest-growing segment is the buy now pay later market which accounts for 6.7% of online transactions.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Advancements in Logistics Technology
Innovations in logistics, including real-time tracking, route optimization, and the adoption of drones and autonomous vehicles, enhance delivery efficiency and service quality, propelling market growth. For instance, in June 2024, Hort Innovation inked a three-year strategic partnership with multi-award-winning agency, Thinkerbell, in a bid to drive growth in consumption behaviours for the A$16.3bn horticulture sector. The Australian advertising and creative agency won the contract through a competitive pitch process. The agency will deliver innovative multi-platform grower-funded marketing campaigns for 24 different produce categories including Australian bananas, apples, avocados and more. Hort Innovation chief executive Brett Fifield said the agreement, made in consultation with industry, will deliver maximum value for Australian growers and ensure local produce gets the spotlight like never before.
Growth of On-Demand and Same-Day Delivery Services
One major trend shaping the Australia last mile delivery market demand is the surge in on-demand and same-day delivery services, driven by consumers' growing desire for instant gratification. Food delivery platforms, grocery retailers, and pharmacies are increasingly offering rapid delivery options to meet evolving customer expectations. Urban dwellers, in particular, are willing to pay a premium for speed and convenience. Retailers are partnering with third-party logistics providers and leveraging crowdsourced delivery models to extend delivery reach while maintaining flexibility. Additionally, investments in localized micro-fulfillment centers and predictive inventory management are enabling faster dispatch and reduced delivery times. This trend is redefining customer loyalty, with brands that offer reliable, fast delivery gaining a competitive edge in Australia’s retail and service ecosystems.
Growth Drivers of Australia Last Mile Delivery Market:
Surge in E-commerce Activities
The rapid rise of e-commerce in Australia is a key driver of last mile delivery growth. Consumers increasingly expect fast, flexible delivery for online purchases, particularly in fashion, electronics, groceries, and personal care items. The convenience of mobile shopping and digital payment options has accelerated this trend. E-commerce giants and local retailers alike are investing in faster delivery services, including same-day and next-day shipping, to remain competitive. This has boosted demand for last mile logistics providers. In regional areas, growing internet penetration and improved logistics networks are supporting e-commerce expansion. As online shopping continues to grow, particularly post-pandemic, the last mile segment is becoming an essential pillar of the logistics and retail ecosystems across Australia.
Urbanization and Changing Consumer Expectations
Consumer expectations of faster and more predictable delivery are being influenced by the growing urbanization rates in major cities such as Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane. With an increase in population in the urban centers, the need to have goods delivered at high speed has increased particularly food, electronics, and health products. Consumers have come to demand real-time tracking, flexible delivery windows and easy returns, which are challenging logistics companies to update their technology and delivery capabilities. Companies are responding to these demands by deploying intelligent delivery lockers, application-based notifications, as well as regional distribution centers. Moreover, the increasing need in contactless and environmentally friendly delivery services is shaping delivery concepts. According to the Australia last mile delivery market analysis, these shifts in consumer behavior are making last mile delivery a strategic differentiator in Australia’s competitive retail and logistics environment.
Retailers’ Omnichannel Strategies
Australian retailers are increasingly adopting omnichannel strategies to enhance customer experience and boost delivery efficiency. Integrating physical stores with online platforms enables retailers to use stores as mini-distribution hubs, reducing delivery times and costs. This strategy helps in meeting rising expectations for same-day or click-and-collect services. By leveraging inventory data across multiple channels, businesses can fulfill orders faster and closer to the end user. It also helps reduce reliance on centralized warehouses and long-haul transport, which is vital for meeting urban delivery demands. Omnichannel models also support customized delivery schedules and improve returns processing. This trend is propelling investments in last mile technology and infrastructure, strengthening the role of the last mile segment in the broader logistics value chain.
Future Trends of Australia Last Mile Delivery Market:
Expansion of Sustainable Delivery Solutions
Environmental awareness and regulatory pressure are driving the adoption of sustainable last mile delivery practices in Australia. Logistics providers are increasingly using electric delivery vehicles, bicycles, and consolidated delivery models to reduce emissions and traffic congestion in urban areas. Retailers are also exploring carbon-neutral delivery options and recyclable packaging to align with consumer values. Government incentives for green logistics infrastructure further support this shift. As sustainability becomes a market differentiator, companies embracing eco-friendly last mile practices are likely to gain customer loyalty and regulatory favor. This trend is expected to reshape fleet strategies, warehouse planning, and urban delivery networks across Australia in the coming years.
Increased Use of Automation and AI
The integration of robotics, automation, and artificial intelligence is transforming the future of last mile delivery in Australia. Companies are adopting AI for optimized route planning, predictive delivery windows, and real-time demand forecasting. Autonomous delivery vehicles and drones are also undergoing trials, especially in regional and hard-to-access areas. Smart lockers and automated hubs enable 24/7 parcel access while reducing human dependency. AI-driven chatbots and delivery apps improve customer interaction and issue resolution. These technologies not only enhance efficiency but also reduce labor costs and human error. As labor shortages persist and consumer demand for speed intensifies, automation will become central to meeting Australia’s evolving last mile delivery expectations and logistics scalability.
Growth of Micro-Fulfillment Centers
To meet the rising demand for same-day delivery and reduce logistics costs, companies in Australia are investing in micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs). These small-scale warehouses, located closer to urban customers, speed up last mile operations and allow faster replenishment. MFCs integrate automation and inventory management technologies to support efficient picking and packing of orders. Retailers, especially in groceries and fast-moving consumer goods, use these hubs to decentralize fulfillment and improve delivery reliability. By placing MFCs in city outskirts or within existing stores, businesses optimize real estate costs while boosting service levels. This trend is expected to expand, enhancing last mile efficiency and supporting the dynamic needs of Australia’s digitally driven consumer base.
Challenges of Australia Last Mile Delivery Market:
High Delivery Costs and Operational Inefficiency
One of the primary challenges in Australia’s last mile delivery market is the high cost associated with final-leg logistics. The country’s vast geography, low population density in rural regions, and traffic congestion in cities contribute to inefficiencies. Fuel prices, labor shortages, and increased consumer expectations for faster delivery add financial pressure. Many logistics providers operate with thin margins, and the cost of failed or delayed deliveries further impacts profitability. Additionally, achieving scale in remote areas requires significant infrastructure investment. These challenges make balancing cost-efficiency with customer satisfaction difficult. Companies must optimize delivery networks, adopt technology for smarter routing, and rethink warehousing strategies to mitigate these issues while ensuring timely and cost-effective delivery.
Infrastructure and Traffic Constraints
Australia’s urban infrastructure is often ill-equipped to handle the rising volume of last mile deliveries, especially in congested city centers. Narrow roads, limited parking space, and delivery time restrictions complicate timely drop-offs. In regional and rural areas, inadequate road connectivity and limited logistics facilities slow down delivery operations. The lack of standardized logistics infrastructure across different states also affects scalability and consistency in service. These infrastructure gaps hinder delivery optimization and customer experience, particularly during peak shopping seasons. To overcome this, stakeholders must collaborate with urban planners and local councils to create delivery-friendly zones, expand smart locker networks, and promote infrastructure upgrades aligned with the growth of e-commerce and digital retail.
Rising Consumer Expectations and Delivery Failures
Modern Australian consumers expect seamless and transparent delivery experiences, including precise tracking, flexible timing, and fast service. These rising expectations put immense pressure on last mile delivery systems. Any delay, miscommunication, or failure in delivery impacts customer trust and brand reputation. Delivery issues such as missed drop-offs, damaged goods, or failed address attempts are common pain points, particularly in suburban and rural deliveries. High expectations also drive demand for customization, such as rescheduling or rerouting, adding complexity to operations. As competition intensifies, logistics providers must improve service accuracy and invest in real-time communication technologies. Failure to adapt could result in customer churn, negative reviews, and loss of market share in Australia’s competitive logistics landscape.
Australia Last Mile Delivery Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on delivery mode, application, destination, service type, vehicle type, and mode of operation.
Delivery Mode Insights:
- Regular Delivery
- Same-Day Delivery or Express Delivery
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the delivery mode. This includes regular delivery and same-day delivery or express delivery.
Application Insights:
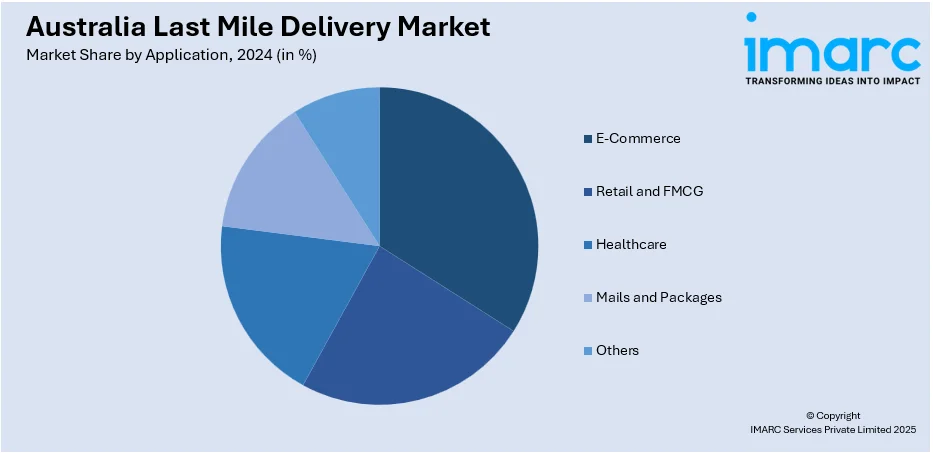
- E-Commerce
- Retail and FMCG
- Healthcare
- Mails and Packages
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application have also been provided in the report. This includes e-commerce, retail and FMCG, healthcare, mails and packages, and others.
Destination Insights:
- Domestic
- International
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the destination. This includes domestic and international.
Service Type Insights:
- Business-To-Business (B2B)
- Business-To-Consumer (B2C)
- Customer-To-Customer (C2C)
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the service type have also been provided in the report. This includes business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), and customer-to-customer (C2C).
Vehicle Type Insights:
- Motorcycle
- LCV
- HCV
- Drones
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the vehicle type. This includes motorcycle, LCV, HCV, and drones.
Mode of Operation Insights:
- Non-Autonomous
- Autonomous
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the mode of operation have also been provided in the report. This includes non-autonomous and autonomous.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Last Mile Delivery Market News:
- In March 2023, DHL Global Forwarding, the freight specialist arm of Deutsche Post DHL Group, opened its newest facility in Brisbane to meet the surging demand for Australian perishable goods export, with an investment of AU$17 million (11 million EUR) over ten years.
- In June 2024, Australia Post introduced major upgrades to its services, including a next-day delivery option - the Australia Post Metro service catering specifically to businesses delivering in the same city, to meet the growing demand for fast and convenient parcel delivery. With customers’ increasing expectations in mind, Australia Post introduced their Metro service last year, and combined with the existing Express Post and StarTrack Premium services, they have both business to business, and consumer deliveries covered.
- In June 2024, ANC, a prominent last mile delivery provider for some of Australia's most well-known brands, unveiled a $45.5 million initiative aimed at encouraging owner-drivers to transition to electric trucks and vans across the country. Named Project Spark, the initiative is supported by a $12.8 million grant from the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA). The program focuses on overcoming key obstacles to electrifying the owner-driver trucking sector. It offers solutions such as subsidized lease arrangements and enhanced access to charging infrastructure.
Australia Last Mile Delivery Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Delivery Modes Covered | Regular Delivery, Same-Day Delivery or Express Delivery |
| Applications Covered | E-Commerce, Retail and FMCG, Healthcare, Mails and Packages, Others |
| Destinations Covered | Domestic, International |
| Service Types Covered | Business-To-Business (B2B), Business-To-Consumer (B2C), Customer-To-Customer (C2C) |
| Vehicle Types Covered | Motorcycle, LCV, HCV, Drones |
| Mode of Operations Covered | Non-Autonomous, Autonomous |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia last mile delivery market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia last mile delivery market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia last mile delivery industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The last mile delivery market in Australia was valued at USD 3,939.4 Million in 2024.
The Australia last mile delivery market is projected to reach a value of USD 8,641.1 Million by 2033.
The Australia last mile delivery market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.12% during 2025-2033.
Australia's last-mile delivery market is driven by booming e-commerce growth, consumer demand for fast and convenient deliveries (including same-day), rapid urbanization, and significant advancements in logistics technology like AI-powered route optimization and autonomous delivery solutions.
Key trends in Australia's last-mile delivery market include the significant impact of booming e-commerce, driving demand for faster and more convenient services like same-day delivery. There's a strong shift towards automation and innovative technologies such as AI-powered route optimization, real-time tracking, and the increasing piloting and adoption of drones and autonomous vehicles. Sustainability is also a growing focus, with a rise in electric vehicle fleets and eco-friendly practices.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












