
Australia Microgrid Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Energy Source, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Microgrid Market Overview:
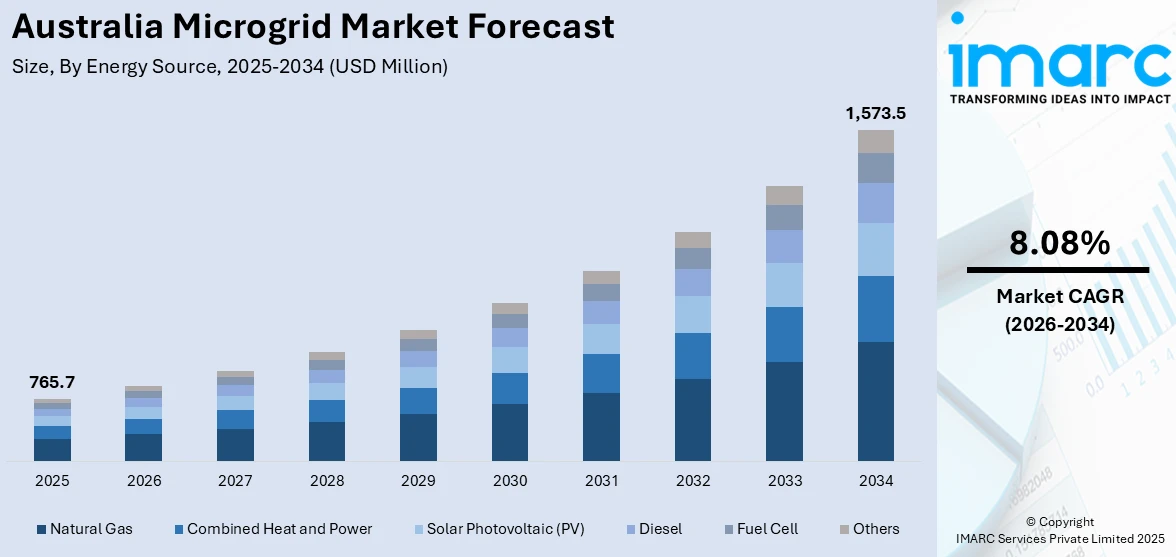
The Australia microgrid market size reached USD 765.7 Million in 2025. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 1,573.5 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 8.08% during 2026-2034. The market is expanding due to rising energy costs, grid instability, and government support for renewables. Declining battery prices and abundant solar/wind resources enhance feasibility, while remote industries and communities seek energy independence. Policies such as ARENA funding and the SRES accelerate adoption, and extreme weather events drive demand for resilient power solutions. Corporate sustainability goals in commercial and industrial microgrid deployments are further augmenting the Australia microgrid market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 765.7 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 1,573.5 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 8.08% |
Key Trends of Australia Microgrid Market:
Increasing Adoption of Renewable Energy Integration in Australian Microgrids
The market is witnessing a significant shift toward renewable energy integration, driven by the country’s abundant solar and wind resources. With rising energy costs and growing environmental concerns, businesses, remote communities, and utilities are increasingly adopting microgrids powered by solar PV, wind, and battery storage. As of 2022, Australia's energy mix was still heavily dependent on fossil fuels at 90% of the total, where natural gas supplied 27% of the supply and 34% of power generation. At the same time, renewable sources expanded to 9.5%, led mainly by solar and biomass. Bioenergy accounted for 5% of the final consumption, supported by major projects, including the Malabar Biomethane Injection and Kwinana Waste-to-Energy. These projects demonstrate significant shifts towards more energy-efficient and grid-integrated infrastructure. The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) has funded numerous projects to demonstrate the viability of hybrid renewable microgrids, particularly in off-grid and regional areas. Additionally, government incentives, such as the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES), are accelerating the deployment of distributed energy resources (DERs). As battery storage costs decline, more microgrids are incorporating advanced energy management systems to optimize renewable generation and ensure grid stability. This trend is expected to continue, with Australia aiming to achieve 82% renewable electricity by 2030, further enhancing microgrid development as a key solution for energy resilience and decarbonization.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Growth of Commercial and Industrial (C&I) Microgrids for Energy Resilience
The rising demand from commercial and industrial (C&I) sectors seeking energy resilience and cost savings is also supporting the Australia microgrid market growth. During the fiscal year 2022–23, Australia's net energy use grew 2% to 23,294 PJ, with residential and industrial consumption growing 3% and 4%, respectively. At the same time, renewable sources grew by 12% to 325 PJ or 33% of the nation's electricity supply. Energy use from the transport sector jumped by 19% and agriculture by 12%, while manufacturing fell by 4%. With increasing energy intensity and demand in other sectors, the use of microgrid systems has become more important within the industrial setup of Australia. Industries such as mining, agriculture, and manufacturing are investing in microgrids to reduce reliance on the main grid, mitigate power outages, and lower operational expenses. Mining companies, in particular, are deploying hybrid microgrids combining diesel, solar, and storage to cut fuel costs and meet sustainability targets. Furthermore, grid instability due to extreme weather events has pushed businesses to adopt microgrids for uninterrupted power supply. Advanced control technologies and AI-driven energy management systems are enhancing the efficiency of C&I microgrids, enabling real-time load balancing and demand response. With Australia’s energy market becoming more volatile, the C&I segment is expected to drive substantial growth in the microgrid sector, supported by favorable policies and corporate sustainability commitments.
Growth Drivers of Australia Microgrid Market:
Energy Resilience in Remote and Off-Grid Communities
One of the major drivers for microgrid market expansion in Australia is the demand for resilient and reliable energy solutions in off-grid and remote communities. Due to the country's large geography and sparse population outside urban cities, most regions, especially in Northern Territory, Western Australia, and rural Queensland, lack access to stable electricity from the national grid. Microgrids provide a customized solution by allowing these communities to produce, store, and control their own power through an interconnection of solar, wind, battery storage, and backup generation. The use of microgrids minimizes dependence on distant power transmission lines, which are exposed to weather interference, bushfires, and technical outages. Moreover, Indigenous and rural communities are contributing directly to microgrid projects that enhance energy autonomy and sustainability. The reliability and flexibility provided by microgrids make them suitable for energizing critical infrastructure like schools, clinics, and water utilities in remote areas, which in turn drives the steady Australia microgrid market demand and technology development within this space.
Government Support and Policy Frameworks for Clean Energy
Australia's microgrid market is being driven by encouraging government policies and nation-level commitments to clean energy transformation. State and federal initiatives have progressively put more emphasis on decentralized power systems as part of overall sustainability and climate resilience plans. States such as Victoria and South Australia have established pilot schemes and funding programs to explore the viability of renewable energy-based community-scale microgrids. These endeavors are supported by research collaborations with universities and technology suppliers to provide a sound support ecosystem for innovation. The emphasis on cutting carbon emissions and ensuring renewable energy goals has further spurred the rollout of microgrids in the urban fringe projects and agricultural areas. Besides, regulatory adaptability in Australia supports trials with energy sharing, peer-to-peer trading, and grid-connected microgrid models. The synergistic effects of public investment, enabling regulation, and increasing national recognition of energy transition form a solid policy foundation that continues to accelerate microgrid use throughout various parts of the country.
Industrial Sector Demand for Energy Autonomy and Sustainability
According to the Australia microgrid market analysis, increasing numbers of businesses are looking to microgrids as a solution to growing energy reliability, reduce costs, and achieve sustainability goals. In agriculture, mining, and manufacturing sectors, particularly in regions like Western Australia and Queensland that are rich in resources, companies have operations where grid availability is unreliable or nonexistent. Microgrids allow these facilities to generate their own power using renewable sources like solar and biomass, while incorporating battery storage and backup systems to maintain consistent operations. Energy autonomy is particularly valuable for mining operations that require 24/7 power in isolated locations. In agriculture, microgrids help power irrigation, cold storage, and processing facilities, enhancing productivity and climate resilience. On top of this, corporate sustainability targets and investor pressure are compelling businesses to lower carbon footprints, and renewable-powered microgrids become a strategic choice. As industries place a growing focus on operational efficiency and green responsibility, their demand is becoming a solid and persistent growth driver for the microgrid market in Australia.
Opportunities of Australia Microgrid Market:
Regional Australian Community-Led Energy Projects
Australia offers a special case for community-driven microgrid projects, particularly in regional and rural Australia where centralized grid systems are either unreliable or economically not feasible. Tasmania, Northern Queensland, and remote areas of South Australia's communities are taking charge of the energy future by working with local councils, utilities, and renewable energy businesses to build independent microgrids. These systems improve energy security while also promoting local ownership and participation, which enhances long-term participation and success. Most projects combine solar panels, battery storage, and sometimes even small wind turbines, making a clean and resilient power source specific to the community's needs. Moreover, some of these regions host Indigenous populations who view microgrids as the means to regain sovereignty over key services while also embracing sustainability. With rising awareness and technical assistance, additional areas are likely to pursue microgrid opportunities as the means to localized energy self-reliance and empowerment.
Integration with Disaster Resilience and Emergency Preparedness
The high frequency of natural hazards in the form of bushfires, floods, and cyclones in Australia provides a strong case for microgrids to become a key player in disaster resilience and preparedness. Conventional power infrastructure is prone to destruction during natural hazards, typically leaving an entire community in darkness for an extended duration. Microgrids, particularly those intended to function independently of the central grid, can supply power continuously during outages, keeping important infrastructure like hospitals, emergency centers, communications networks, and water treatment plants running. Utility companies and government agencies in bushfire regions of Victoria and New South Wales, for instance, are investigating microgrid technologies to minimize the chances of outages due to fire. These microgrids can be designed to island from the larger grid in the event of emergencies and keep on supplying electricity locally, greatly enhancing the region's capacity for disaster response and recovery. The increasing recognition of climate risk will increasingly promote both public and private financing of microgrid-enabled solutions to resilience strategies over the long term.
Decentralized Energy Systems for Urban Sustainability Goals
Urban hubs throughout Australia are turning toward decentralized energy systems, such as microgrids, as they shift toward a greater effort to be more sustainable and decrease emissions. Melbourne, Sydney, and Brisbane have made significant climate change targets and are busy seeking ways to drop their reliance on fossil fuels. Microgrids offer a scalable solution to power residential developments, commercial developments, and mixed-use precincts using renewable energy and improving energy efficiency. Urban microgrid initiatives usually involve solar PV, battery storage, and intelligent energy management systems that maximize power consumption across a metropolitan district. These systems are being integrated into new developments and smart city schemes from the outset, and hence they are becoming an integral element of green urban planning. Microgrids also provide the ability to share energy between buildings through peer-to-peer trading and community-based energy markets. With local governments and real estate developers increasingly coming into line with green building codes and consumer demand for sustainable lifestyles, urban microgrids are a forward-thinking option in Australia's changing energy picture.
Government Support of Australia Microgrid Market:
Federal Government Assistance for Decentralized Energy Systems
The federal government of Australia has increasingly seen the potential in microgrids to address energy access, particularly for remote communities and disaster-affected areas. Through a series of funding schemes and programs, the government is promoting the installation of microgrids as part of the wider transition towards decentralized and renewable-based energy systems. Much emphasis has been placed on funding feasibility studies and pilot initiatives in regions where classical grid extension would prove to be technologically infeasible or economically non-viable. Many such projects are centered on Indigenous communities and off-grid areas with a view to enhancing energy autonomy and minimizing diesel generation dependency. Government-sponsored research and development grants are also facilitating partnerships between energy providers, academia, and technology companies to lead innovation within the microgrid sector. The focus on emissions reduction and energy resilience by the federal government is in line with the functionality microgrids provide, making them a key component in Australia's long-term energy planning. These initiatives are also facilitating the creation of a policy framework more supportive of microgrid expansion across the country.
State-Level Microgrid Trials and Clean Energy Policies
State governments in Australia are proactive in driving microgrid development through programs and energy transition policies. Victoria, for instance, has a targeted microgrid program that finances community-based energy projects and experiments with renewables and battery storage technologies. Decentralization is part of the state's energy transformation agenda and is a key driver towards transitioning away from coal-based generation. Likewise, South Australia, which is at the forefront of integrating renewables into the system, also encourages microgrid installation in residential and agricultural settings. These state programs usually involve fiscal incentives, technical assistance, and stakeholder outreach programs with the aim of speeding up community involvement in local energy production. Queensland and Western Australia have also started investing in microgrid approaches for island and rural communities, citing the contribution of localized energy towards enhancing system robustness. These state initiatives mirror the varying energy requirements of different regions and illustrate how customized policy support is assisting in microgrid application scaling as per regional plans of sustainability and economic development.
Coordination with Local Governments and Councils
Local councils and governments in Australia are becoming key stakeholders in the microgrid industry, especially in enabling on-ground deployments of energy projects. With increasing numbers of councils embracing climate action plans and net-zero emissions goals, microgrids are being mainstreamed into urban design and local community resilience planning. Local governments are partnering with utilities, property developers, and technology companies to establish microgrid-capable precincts and buildings that enhance renewable energy self-sufficiency. For example, certain councils in New South Wales and Victoria are integrating microgrids into the design of smart cities or retrofitting public buildings with solar-powered microgrid systems to maintain consistency during grid disruptions. These endeavors support local environmental policies while also encouraging increased public participation in energy consumption and sustainability efforts. Councils also play a key role in procuring state and federal funding, obtaining permits, and making sure community consultation is incorporated into the project development process. This strategy improves the social acceptance and long-term sustainability of microgrid projects throughout heterogenous communities.
Challenges of Australia Microgrid Market:
High Initial Investment
One of the biggest problems that Australia's microgrid sector faces is the large amount of capital needed for an initial investment. Even though microgrids translate into long-term cost savings and energy resiliency, the engineering, procurement, installation, and integration costs are still high barriers to overcome, particularly for smaller councils, communities, or organizations that lack solid financial support. In areas such as Western Australia and the Northern Territory, where microgrids may bring significant advantages, restricted access to funding sources tends to impede project roll-out. Large-scale energy project finance models are not necessarily applicable to decentralized systems, and the return on investment can be highly variable depending upon location, technology options, and local energy requirements. Moreover, insurance and maintenance expenses are also greater owing to the intricacy of integrating various technologies such as solar, batteries, and control systems. Such a financial risk dissuades certain stakeholders from investing in microgrid infrastructure, particularly when less sustainable but cheaper alternatives like diesel generators continue to be dominantly utilized in remote regions.
Regulatory Complexity and Grid Integration
Australia's disunited energy regulations among states and territories are another challenge for uniform deployment of microgrids. Different jurisdictions have their own regulations on energy licensing, grid connection, and power distribution, thus introducing uncertainty and bureaucratic slowness for developers. Microgrid operators must deal with national as well as local regulations, which can be tedious and complicated. This is especially burdensome for hybrid microgrids that are tied to the primary grid for a portion of the time and standalone during power outages. Coordination with utilities for load management, feed-in tariffs, and grid synchronization complicates the deployment. Microgrids can also be seen by some grid operators as competitors instead of partners and hence may be hesitant or even resist approving deployments. Regulatory clarity in states where microgrids remain a niche technology also takes a hit, making the scaling up of successful pilot projects challenging. Without coordinated, nationally harmonized policies, the potential of microgrids to enable a decentralized and renewable energy future is still held back.
Technical and Operational Challenges in Remote Areas
Running microgrids in Australia's remote and geographically complex regions presents technical challenges of its own. Hostile environmental conditions like high temperatures, dust, cyclones, or restricted access to skilled labor, can impact the reliability and lifespan of microgrid components such as batteries, inverters, and control systems. In places such as central Queensland or the Pilbara, maintenance and technical support are frequently delayed because of logistical limitations, potentially leading to system downtimes or poor performance. Access to replacement parts, service engineers, and software expertise is usually limited in areas outside large urban centers, placing an additional operational burden. Moreover, the interconnection of variable renewable sources such as solar or wind to a firm microgrid necessitates sophisticated energy management systems, which can be difficult to use by local personnel without specific expertise. These issues underscore the need to create robust, easy-to-use systems and enhance local capacity to maintain them effectively, albeit one requiring time, effort, and sustained investment.
Australia Microgrid Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on energy source and application.
Energy Source Insights:
- Natural Gas
- Combined Heat and Power
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV)
- Diesel
- Fuel Cell
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the energy source. This includes natural gas, combined heat and power, solar photovoltaic (PV), diesel, fuel cell, and others.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
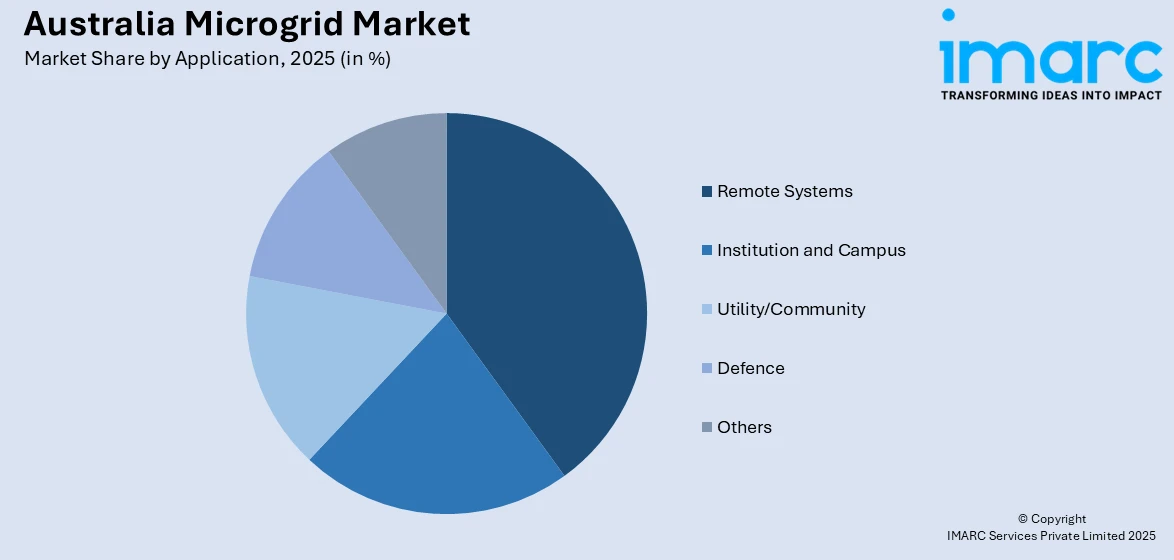
- Remote Systems
- Institution and Campus
- Utility/Community
- Defence
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application have also been provided in the report. This includes remote systems, institution and campus, utility/community, defence, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Microgrid Market News:
- February 4, 2025: Ocean Sun and Canopy Power collaborated to introduce floating solar technology in Australia through Ocean Sun's 700 kWp membrane-based system that also features rainwater harvesting. This scalable and modular solution integrates renewable microgrids, battery storage, photovoltaic systems, and wind energy to address water and land scarcity challenges. The project aims to introduce sustainable energy solutions for energy producers, agricultural activities, and hydrogen facilities across the country.
- October 21, 2024: Aspen Technology announced its Microgrid Management System (MMS) for industries that have high energy demands, such as refining, chemicals, and mining. It is built upon the OSI monarch SCADA platform. It effortlessly integrates renewable energy resources, load control, and storage functions, hence increasing operation efficiency and contributing to the goal of net zero. The MMS provides real-time management, advanced forecasting, and enhanced security, offering Australian industries a trusted solution for the reliability and sustainability of energy.
Australia Microgrid Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Energy Sources Covered | Natural Gas, Combined Heat and Power, Solar Photovoltaic (PV), Diesel, Fuel Cell, Others |
| Applications Covered | Remote Systems, Institution and Campus, Utility/Community, Defence, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia microgrid market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia microgrid market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia microgrid industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia microgrid market was valued at USD 765.7 Million in 2025.
The Australia microgrid market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 8.08% during 2026-2034.
The Australia microgrid market is expected to reach a value of USD 1,573.5 Million by 2034.
The Australia microgrid market trends include rising deployment of hybrid systems combining solar, wind, and battery storage in off-grid and regional zones. There is also a shift toward community-driven energy models and peer-to-peer energy trading initiatives. Urban precincts integrate smart microgrids into new developments, and businesses are increasingly investing in energy autonomy solutions, which further fuels the market share.
The Australia microgrid market is driven by the need for energy resilience in remote areas, increasing reliance on renewable energy, and government support for decentralized power systems. Rising electricity costs and climate-related disruptions further encourage communities and industries to adopt microgrids for reliable, sustainable, and independent energy solutions across diverse regions.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












