
Australia Power Grids Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Energy Source, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Power Grids Market Overview:
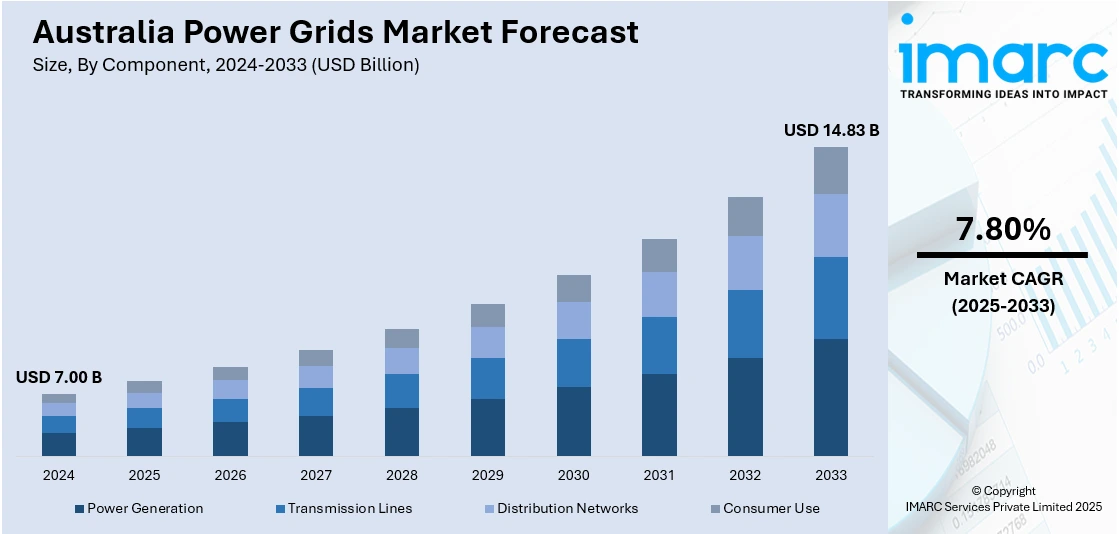
The Australia power grids market size reached USD 7.00 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 14.83 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 7.80% during 2025-2033. The increasing renewable energy integration, grid modernization, government support, demand for energy resilience, and digitalization of grid management are supporting the market growth. Moreover, growing energy consumption, technological advancements in storage, regulatory push for sustainability, and need for disaster-resistant infrastructure are stimulating the market growth. Furthermore, investment in smart grids, competitive energy pricing, rising electric vehicle adoption, and urbanization are contributing to the Australia power grids market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 7.00 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 14.83 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 7.80% |
Key Trends of Australia Power Grids Market:
Growing Demand for Integration of Renewable Energy
Australia's power grids market is undergoing a significant shift due to the increasing demand for incorporating renewable energy. Australia has gradually phased out fossil fuels and focused on cleaner, greener sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. This shift has occurred due to both environmental concerns and a requirement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in compliance with global climate agreements. With Australia focusing on achieving its renewable energy targets, the power grid infrastructures are being restructuring to accommodate the growing stream of renewable energy. Unlike the traditional forms of energy, solar and wind renewables are random in nature and do not offer a constant energy output. This requires the power grids to be more efficient and robust enough to balance energy that changes over a day based on weather patterns, thereby driving the Australia power grids market growth.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Grid Modernization and Infrastructure Improvements
Grid modernization remains a major propeller of the Australian power grids market. With the growing need for energy and the growing diversification of the sources of generation, the current grid infrastructure in Australia must be upgraded to ensure its reliability and efficiency. There is aging infrastructure, as well as the requirement of integration of renewable energy sources, so there is massive investment to be made to modernize the power grid. The smart grid system incorporates the adoption of advanced technologies such as smart meters, real-time monitoring, and automated control systems. They enhance the accuracy of demand forecasting, increase response rates, and maximize power distribution, reducing waste and minimizing energy losses. Additionally, smart grids help balance supply and demand for energy, especially with the incorporation of renewable sources of energy such as wind and solar, which produce fluctuations in the production of energy. Through the deployment of these technologies, grid managers are better able to control and fine-tune the grid in real-time, making the grid more adaptive and flexible. In line with these efforts, in March 2024, the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) unveiled its 'Integrated System Plan 2024', outlining a $12.7 billion roadmap to transition the national grid toward more decentralized, renewable-powered infrastructure over the next decade, reinforcing the country's push toward a modern, resilient energy system, which further contributes to the Australia power grids market demand.
Government Policies and Support
Government policies and initiatives are crucial factors in deciding the growth of Australia's power grids market. The Australian government has been actively working towards creating a policy framework that supports the advent of a low-carbon energy system and encourages investment in clean energy infrastructure. Governments and state governments are implementing different incentives and programs that are driving the market growth. One of the most important drivers of grid expansion is the government's commitment to achieve its renewable energy target. The Renewable Energy Target (RET) scheme, for instance, is one of the central acts that seek to ensure that the electricity supply in the country is predominantly from renewable energy. This has necessitated the establishment of renewable power infrastructure, including power cables that have capacity for adjustment to accommodate changes in renewable energy production.
Growth Drivers of Australia Power Grids Market:
Growth of Urban Population and City Energy Demand
Australia's power grids market has a key growth driver in the form of rapid urbanization. Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, and Perth are some of the cities that are still adding to population numbers, putting growing pressure on current electricity infrastructure. As these residential and commercial areas grow, the need for efficient, high-capacity power delivery increases. Aged grid networks in these city centers are being pushed beyond their design capacity, leading to upgrades and expansions to prevent blackouts and accommodate changing energy usage patterns. In addition, the emergence of high-density apartments, electric vehicle charging points, and smart building technologies has changed the nature of energy consumption in urban settings. Grid operators have reacted by investing in infrastructure capable of managing more dynamic loads and varied sources of energy. These investments are frequently found in underground cabling, city substations, and sophisticated control systems to provide reliable service to expanding metropolitan regions. Mitigating the distinct challenges of Australia's expanding cities is an integral part of long-term power grid development.
Decentralized Energy and Community-Led Projects
Decentralized power generation is increasingly shaping the future of Australia's power networks. In suburban and regional towns, there is growing enthusiasm for community-based energy initiatives, such as cooperative solar farms, microgrids, and peer-to-peer energy trading schemes. These arrangements allow individuals and businesses to produce, store, and share their own electricity, minimizing dependence upon centralized utility companies. This pattern is most prevalent in areas of high solar potential, for example, in Queensland and Western Australia. The more consumers engage with producing their own electricity, the more essential power grids capable of withstanding two-way flow of electricity and decentralized sources of input become. The old grid system, designed for unidirectional supply, needs to change to facilitate real-time balancing, storage integration, and local energy exchange. Grid managers are spending money on new technologies and reconfiguring infrastructure to address these decentralization challenges. Models of community energy are also consistent with increasing public interest in sustainability and energy independence.
Climate and Disaster Preparedness Resilience Planning
According to the Australia power grids market analysis, the region’s experience with climate-related events like bushfires, floods, and severe heat has accelerated the demand for more resilient power grid infrastructure. The last few years have exposed legacy systems to weather disruptions and emphasized the need for increased grid resilience, particularly following widespread outages during natural disasters. Governments and utilities are therefore placing a high priority on investments in technologies and approaches that can protect energy delivery during emergencies. This encompasses building fire-resistant transmission lines, deploying mobile substations, and developing predictive analytics for disaster response. In regions at risk of bushfire events, such as regional New South Wales and Victoria, grid hardening projects are being sped up to safeguard assets and continue service. Resilience planning also includes distributed energy resources and microgrids, which can be made to stay on in emergency situations, support critical services. This proactive approach toward disaster preparedness offers safety while playing into long-term growth drivers in infrastructure upgrades and innovation across Australia's power grid sector.
Australia Power Grids Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on component and energy source.
Component Insights:
- Power Generation
- Transmission Lines
- Distribution Networks
- Consumer Use
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the component. This includes power generation, transmission lines, distribution networks, and consumer use.
Energy Source Insights:
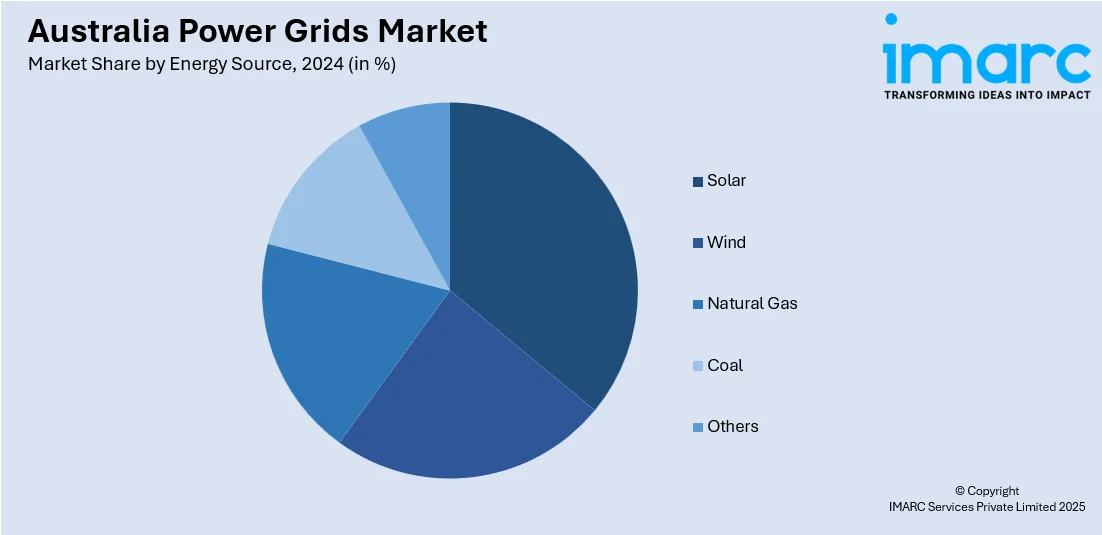
- Solar
- Wind
- Natural Gas
- Coal
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the energy source have also been provided in the report. This includes solar, wind, natural gas, coal, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Power Grids Market News:
- In 2024, VicGrid unveiled a USD 4 billion plan to expand Victoria’s transmission network, adding 380 km of new lines and upgrading 430 km. This supports seven renewable energy zones, aiming to integrate more wind and solar power as coal plants retire.
Australia Power Grids Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Power Generation, Transmission Lines, Distribution Networks, Consumer Use |
| Energy Sources Covered | Solar, Wind, Natural Gas, Coal, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia power grids market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia power grids market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia power grids industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia power grids market was valued at USD 7.00 Billion in 2024.
The Australia power grids market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 7.80% during 2025-2033.
The Australia power grids market is expected to reach a value of USD 14.83 Billion by 2033.
The Australia power grids market trends include growing use of microgrids for remote locations, integrating renewable energy sources, and using smart grid technologies. There is also a shift toward decentralized systems, real-time energy monitoring, and infrastructure upgrades to support electric vehicles and improve resilience against climate-related disruptions and extreme weather events, which propel market share.
The Australia power grids market is driven by urban expansion, decentralized energy generation, and the need for climate-resilient infrastructure. Growing electricity demand, rising rooftop solar adoption, and increased focus on disaster preparedness are pushing investments in modern, flexible, and smart grid systems across both urban and regional parts of the country.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












