
Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Cuisine, Outlet, Location, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market Size and Share:
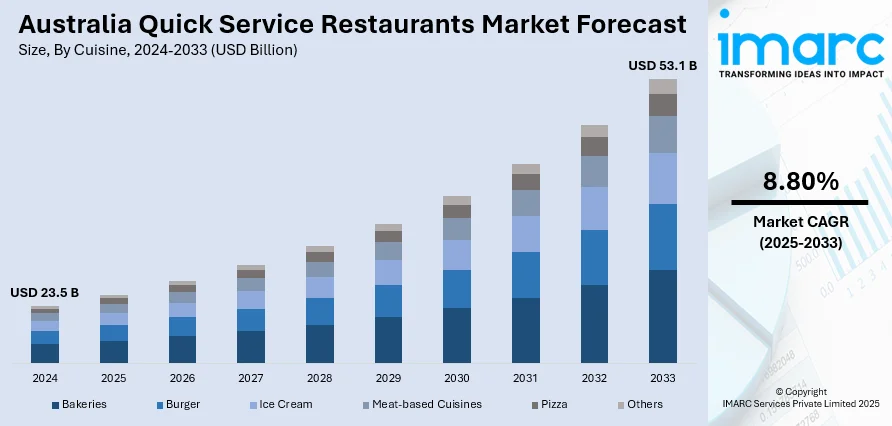
The Australia quick service restaurants market size reached USD 23.5 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 53.1 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 8.80% during 2025-2033. The market is expanding, driven by rising international investments, growing consumer demand for diverse dining options, brand portfolio diversification, and improved operational efficiencies. Increasing competition and evolving food preferences continue to shape the market’s growth trajectory across major cities and regional areas, strengthening the Australia quick service restaurants market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 23.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 53.1 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 8.80% |
Key Trends of Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market:
Growing International Investments Strengthen Local Brands
Australia’s quick service restaurants market has been increasingly influenced by international investors who are aiming to strengthen local brands and accelerate market growth. Global players are seeing Australia as a market with strong potential, driven by changing consumer patterns, growing disposable incomes, and a preference for organized food outlets. International investments bring not only capital but also refined management practices, technology integration, and improved supply chain efficiency. In June 2023, Flynn Restaurant Group, a major US-based operator, announced the acquisition of Pizza Hut Australia, covering approximately 260 outlets. This acquisition marked Flynn’s first major international expansion and introduced new energy into the Australian market. Flynn’s strong track record in operating leading restaurant brands like Applebee’s and Taco Bell is expected to strengthen Pizza Hut Australia's performance, while also raising standards across the quick-service segment. This trend of global investment helps existing brands scale up more rapidly, invest in marketing, modernize operations, and improve consumer experiences. It also puts competitive pressure on domestic operators to innovate and match global standards. Over time, increasing international participation is expected to diversify the market, boost employment, and intensify brand positioning battles, boosting Australia quick service restaurants market growth.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Expanding Brand Portfolios Diversify Market Offerings
The Australia quick service restaurants market is witnessing a clear trend where companies are diversifying their brand portfolios to match evolving consumer demands. There is an increasing shift towards providing new dining formats, expanded menu options, and improved quality, fueled by consumer demand for more variety and unique food experiences. New market entrants are tapping into niche segments to capture emerging demand while offering different dining styles beyond traditional fast food. In February 2025, Firehouse Subs announced its entry into the Australian market through a partnership with Retail Food Group, planning to open 165 restaurants across the country within ten years. Targeting the A USD 1.7 Billion sandwich segment, Firehouse Subs introduced premium, hearty sandwiches made with steamed meats and cheeses, aiming to set a new standard in the category. This development is expected to significantly widen the offerings in the Australian Quick Service Restaurants landscape, challenging existing players and inviting higher innovation across the market. As more brands expand their presence, consumers are gaining access to a broader range of food experiences, pushing the market beyond traditional burger and pizza chains. This diversification of offerings is reshaping the competitive environment, encouraging differentiation, stronger brand engagement, and more tailored food concepts that match Australia's multicultural consumer base, and further accelerates the Australia quick service restaurants market demand.
Growth Drivers of Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market:
Changing lifestyles of consumers and urbanization
The key growth driver in Australia's quick service restaurant (QSR) market is the fast, convenience-based lifestyle of city consumers. More Australians live in cities such as Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane, and hence demand for quick, convenient meals keeps on growing. Long working hours, longer commuting times, and rising numbers of dual-income households mean that many Australians have little time to cook at home. QSRs provide an economical substitute, offering low-cost and fast solutions that are suitable for both individuals and families. Urbanization has also prompted the growth of high-footfall locations such as shopping malls, transportation centers, and entertainment zones, which are places where QSRs do well. With cities spreading and lifestyles changing, QSR brands are now more frequently adapting store formats, for instance, smaller stores or kiosk-based models, to suit small urban spaces. This convenience-driven strategy of food service is at the heart of the constant growth of the QSR industry throughout Australia's rapidly growing metropolitan areas.
Varied and Changing Food Choices
Australia's multicultural society is a major driver of growth for the QSR market. With consumers whose populations welcome diverse foods, ranging from Asian, Middle Eastern to Mediterranean and American-style foods, consumers are always on the lookout for variety and novelty in their food choices. Operators in the QSR market have reacted by increasing menu offerings with fusion foods, plant-based foods, and health foods to appeal to a more diversified base. This trend is especially prominent in urban centers such as Perth and Adelaide, with food culture informed by a mix of international influences. Additionally, the younger segment of consumers in Australia is likely to be more adventurous in their eating habits, anticipating both comfort meals of the traditional variety and hip, Instagram-friendly fare. The capacity of QSR brands to move quickly in response to shifting consumer preferences and dietary needs, e.g., gluten-free, vegan, or low-carb options, is now a significant competitive strength. With Australian diners ongoing appreciation for choice and cultural diversity, the QSR industry is well set for steady expansion.
Expansion of Digital Ordering and Delivery Platforms
According to the Australia quick service restaurants market analysis, technological change and the emergence of digital platforms are reshaping the way that Australians use quick service restaurants, making it one of the strongest drivers of market growth. Online ordering, mobile applications, and delivery services such as Menulog, DoorDash, and Uber Eats have increased consumer access to QSRs beyond dine-in models. This transition is particularly pertinent in suburban and rural locations, where proximity to a range of food outlets was previously restricted. QSR brands are also heavily investing in digital infrastructure, providing loyalty schemes, order customization, and contactless payments to enhance customer convenience and experience. In technology-savvy cities such as Canberra and Melbourne, digital-first strategies are helping brands strengthen customer ties while enhancing operational efficiency. Ghost restaurants and delivery-only stores have also become popular, lowering the cost of overheads and increasing delivery scope. With digital convenience emerging as an expected norm, QSR companies that adopt and innovate with technology are poised to drive market growth in Australia.
Opportunities of Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market:
Expansion into Regional and Suburban Markets
One of the greatest opportunities for expansion for Australia's QSR industry is moving into regional and suburban areas. While most QSR brands have long concentrated on high-density urban centers such as Sydney and Melbourne, increased populations in regional towns such as Geelong, Townsville, Ballarat, and the Gold Coast represent untapped markets. All these regions are undergoing continuous infrastructure development, rising migration from capital cities, and expanding tourism activity, which are factors that encourage demand for easy, low-priced dining. Furthermore, low competition in some of the regional towns provides good conditions for QSR chains to develop a loyal customer base. Drive-thru formats and modular stores fit best into these locations, adapting to local practices and mobility by vehicles. As housing development moves further away from city centers, QSR operators can leverage increasing demand for quality foodservice. Penetration into these less saturated markets allows brands to increase market reach, decrease dependency on inner-city traffic, and establish national recognition.
Leverage of Health and Wellness Trends
Australia's increasing emphasis on health and wellness offers QSR operators a considerable opportunity to diversify their portfolios. As consumers increasingly make nutrition more of a priority, they are actively looking for foods that are lower in calories, fat, and sugar without sacrificing taste or convenience. This movement has created an opportunity for QSR brands to launch healthier food options, including fresh vegetables, whole foods, plant-based proteins, and food with clear nutritional labelling. Australia's robust fitness culture, particularly in urban centers like Brisbane and Perth, makes health-conscious consumers more likely to favor brands that fit their lifestyle. QSRs offering local, organic, or sustainable ingredients on their menus also have the potential to gain from favorable consumer attitudes. School children, students at universities, and young professionals increasingly demand fast, yet healthy meals. With changing food tastes, brands that break new ground in this area and promote products competently will emerge as market leaders in Australia.
Using Technology for Personalization and Loyalty
Australian foodservice digitalization provides a significant chance for QSR brands to build more tailored customer experiences and deepen loyalty. The country boasts high smartphone penetration, and hence mobile apps present a prime touchpoint for interacting with customers. QSR chains can leverage data analytics to personalize promotions, monitor preferences, and provide personalized offers, thus driving repeat business. Integration with digital wallets, rewards schemes, and gamified app functionality is also becoming popular, particularly among younger diners in high-tech cities such as Canberra and Sydney. In addition, AI-enabled kiosks and dynamic menu boards in-store provide quicker service while allowing upselling and effective queue management. Brands that put investments in frictionless omnichannel experiences, integrating physical and digital interactions, which can foster better consumer connections and grow market share. As digital behavior increasingly impacts eating habits, technology-enabled personalization is a powerful growth driver for the QSR sector in Australia.
Challenges of Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market:
Rising Operating Costs and Labor Shortages
One of the most urgent problems faced by the Australia quick service restaurants is escalating cost of doing business, most notably labor and rent. Australia's minimum wage is one of the highest in the world, which drives up the cost of staffing QSR outlets, especially in Sydney and Melbourne. This problem is exacerbated by ongoing labor shortages in the hospitality industry, exacerbated by a shortage of temporary foreign workers and backpackers who previously accounted for casual QSR positions. Regional locations have even more severe challenges in finding skilled and trustworthy personnel, often resulting in shorter operating hours or restrictions on services. High rents in high-quality retail sites and city shopping precincts also put pressure on margins. Most QSR operators are compelled to either pass on these increasing costs or raise prices, which can affect customer retention. These cost pressures further complicate it for smaller or independent QSR brands to face competition from larger franchises with greater financial and logistical leeway.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Ingredient Sourcing
Supply chain reliability has become an acute issue in Australia's QSR market. The nation's geographic remoteness, dependence on imported inputs, and exposure to harsh climate conditions have exposed vulnerabilities in food distribution channels. Bushfires, floods, and droughts have caused volatile availability and prices of major ingredients ranging from fresh produce to dairy and meat. Import delays and higher freight prices have also contributed to making it more difficult for QSRs to be able to provide consistent menu items. Smaller or specialty QSRs, especially those serving international food, tend to have difficulty sourcing certain items because of regulatory restrictions and dependence on imports. In places such as Northern Territory or remote North Queensland, logistics problems are also exacerbated by long transport distances and sparse supplier bases. These disrupt day-to-day operations yet also constrain menu innovation and forward planning. Creating more stable, localized supply chains is increasingly necessary but this means a huge investment of time and coordination that many operators struggle with.
Changing Consumer Expectations and Sustainability Pressures
With Australian consumers increasingly health-aware, sustainable, and ethical in their sourcing, QSR operators are under mounting pressure to reformulate their business models. Consumers no longer want merely fast service, as today, they demand food sourcing transparency, environmentally friendly packaging, and healthier meals. In an environmentally conscious nation, especially in urban centers such as Hobart and Adelaide, businesses are under the spotlight regarding waste reduction and carbon emissions. QSRs with high-volume plastic packaging or heavy dependence on processed foods tend to get criticized on social media, which hurts brand image. Becoming sustainable in practices like compostable packaging, energy-conscious kitchens, or sustainably sourced ingredients is expensive and operationally intensive, particularly for smaller players. Balancing these increasing expectations with being price-competitive is a tightrope act. Moreover, quickly changing consumer tastes such as the adoption of plant-based diets or allergen-free meals need to be continuously adapting. Not adapting to these expectations has the potential to result in customer loss and diminished market responsiveness.
Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on cuisine, outlet, and location.
Cuisine Insights:
- Bakeries
- Burger
- Ice Cream
- Meat-based Cuisines
- Pizza
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the cuisine. This includes bakeries, burger, ice cream, meat-based cuisines, pizza, and others.
Outlet Insights:
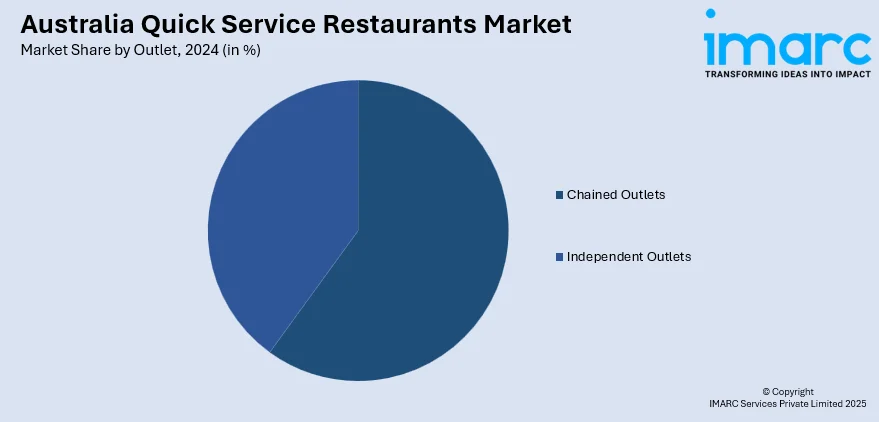
- Chained Outlets
- Independent Outlets
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the outlet have also been provided in the report. This includes chained outlets and independent outlets.
Location Insights:
- Leisure
- Lodging
- Retail
- Standalone
- Travel
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the location have also been provided in the report. This includes leisure, lodging, retail, standalone, and travel.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market News:
- April 2025: Collins Foods exited Taco Bell operations in Australia, transferring 27 outlets, and shifted focus to expanding its KFC footprint in Germany by opening 40–70 new stores over five years. The move reflected shifting dynamics in Australia's quick service restaurants market, impacting brand competition.
- February 2025: Firehouse Subs announced its entry into Australia's quick service restaurants market through a partnership with Retail Food Group. The plan aimed to open 165 outlets over 10 years, strengthening competition in the AUSD 1.7 Billion sandwich segment and boosting employment opportunities nationwide.
Australia Quick Service Restaurants Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Cuisines Covered | Bakeries, Burger, Ice Cream, Meat-based Cuisines, Pizza, Others |
| Outlets Covered | Chained Outlets, Independent Outlets |
| Locations Covered | Leisure, Lodging, Retail, Standalone, Travel |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia quick service restaurants market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia quick service restaurants market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia quick service restaurants industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia quick service restaurants market was valued at USD 23.5 Billion in 2024.
The Australia quick service restaurants market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 8.80% during 2025-2033.
The Australia quick service restaurants market is expected to reach a value of USD 53.1 Billion by 2033.
Australia quick service restaurants market trends include rising demand for plant-based and health-focused menu options, expansion into regional areas, and increased use of digital ordering and delivery platforms. Sustainability initiatives, tech-driven personalization, and fusion cuisines are also shaping consumer expectations, encouraging brands to innovate and adapt to evolving dining habits.
Australia quick service restaurants market is driven by changing consumer lifestyles, urbanization, and growing demand for convenient, affordable meals. Rising digital adoption, multicultural food preferences, and a strong focus on health-conscious options also support expansion. These factors encourage innovation and geographic diversification across both metropolitan and regional parts of the country.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












