
Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Process, Type, Material, Shelf Life, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market Size and Share:
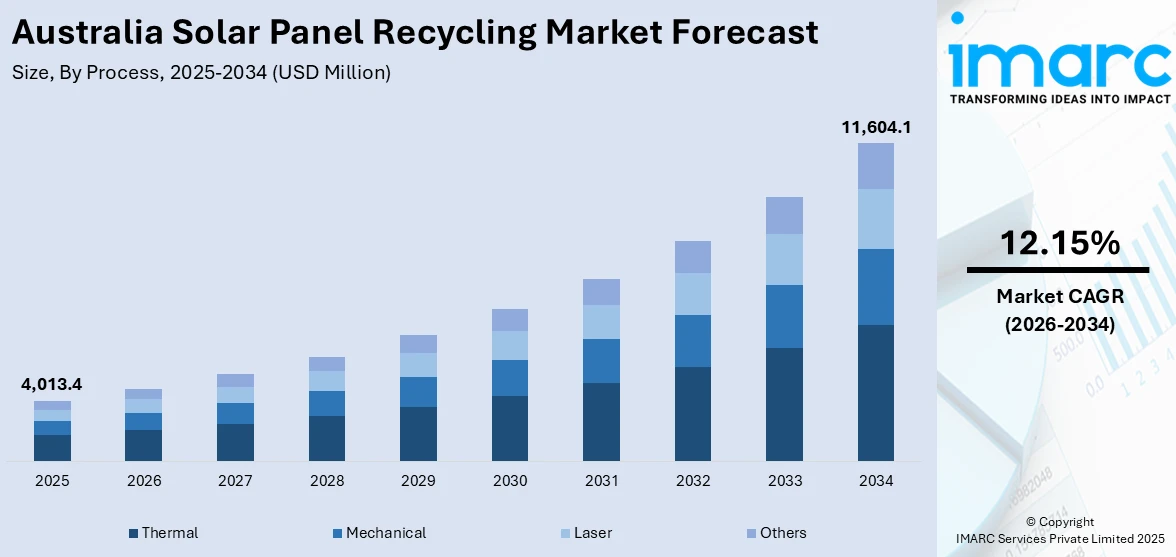
The Australia solar panel recycling market size reached USD 4,013.4 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 11,604.1 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 12.15% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by the rise in end-of-life PV panels, as Australia’s early solar installations reach their 20-25 year lifespan, generating tonnes of waste annually by 2030. Regulatory pressures, such as Victoria’s landfill ban, are accelerating demand for recycling services, prompting companies to expand recovery of silicon, glass, and metals. Additionally, circular economy initiatives and industry partnerships are fostering advanced recycling technologies, further augmenting the Australia solar panel recycling market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 4,013.4 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 11,604.1 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 12.15% |
Key Trends in Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market:
Increasing Demand for Solar Panel Recycling Due to Rising PV Waste
The market is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing volume of end-of-life photovoltaic (PV) panels. With Australia’s rapid adoption of solar energy over the past decade, many early installations are now reaching their 20–25-year lifespan, leading to a rise in PV waste. The country is projected to generate over 100,000 tonnes of solar panel waste annually by 2030, creating a pressing need for efficient recycling solutions. Australia is facing a growing solar waste problem, with estimates suggesting this year the number of end-of-life panels will total 280,000 tonnes and 1.157 million tonnes by 2035. As the recycling industry is not able to catch up, Queensland's first solar panel recycling plant is capable of recycling 240,000 panels annually. However, around 800,000 panels are still in danger of ending up in a landfill. With the National Television and Computer Recycling Scheme set to include solar PV systems by 2025, industry players are advocating for increased investment in circular economy programs. In addition, the market for recycling services is also being driven by government mandates such as Victoria's prohibition on landfill dumping of solar panels. Increasing numbers of companies are entering the business of reclaiming recyclable material, including silicon, glass, and metals. This is a trend that will continue to gain momentum as regional authorities around the nation place tighter waste regulations in place, and as advancements in recycling technologies and sustainable waste disposal practices expand.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Growth in Circular Economy Initiatives and Industry Partnerships
The rise of circular economy models and collaborations between industry stakeholders is also propelling the Australia solar panel recycling market growth. Solar manufacturers, waste management firms, and government bodies are increasingly partnering to develop closed-loop recycling systems that repurpose materials into new panels. For instance, the Australian Council of Recycling (ACOR) has been advocating for standardized recycling processes to improve efficiency. Additionally, companies are investing in advanced separation technologies to enhance material recovery rates, reducing reliance on raw material extraction. Financial incentives, such as grants for recycling infrastructure, are also supporting market expansion. For instance, researchers at UNSW in Australia secured AUD 5 million (approximately USD 3.4 Million) to establish a research hub for solar panel recycling with a view to recycling 99% of photovoltaic materials and re-designing panels for easier recycling. With an estimated over 100,000 tons of photovoltaic waste every year by 2030, the ARC Research Hub will foster innovation across the solar recycling value chain. This project is one of a greater AUD 34.7 million (approximately USD 23.6 Million) research investment that strengthens Australia's focus on sustainable energy solutions. As sustainability becomes a priority for businesses and consumers, the demand for eco-friendly disposal solutions will grow, positioning solar panel recycling as a critical component of Australia’s renewable energy future.
Advancements in Recycling Technologies
The solar panel recycling sector in Australia is advancing toward more advanced material recovery techniques to handle the increasing number of end-of-life panels. Conventional methods have primarily focused on extracting basic materials like aluminium and glass, often missing out on more valuable elements such as silicon, silver, and copper. Innovative recycling technologies thermal, mechanical, and chemical are being developed to recover these materials more efficiently while minimizing waste. These improvements not only enhance the yield and quality of reclaimed resources but also boost the economic viability of recycling operations. Consequently, these innovations are directly contributing to the rising Australia solar panel recycling market demand, which is driven by sustainability objectives and the necessity for long-term waste management solutions.
Opportunities of Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market:
Increasing Volume of Decommissioned Solar Panels
Australia's substantial growth in rooftop solar installations over the last two decades is now leading to a new challenge: managing the increasing number of decommissioned panels. As earlier systems reach their 25 to 30-year lifespan, there will likely be a significant rise in the volume of panels that need to be retired. This trend will result in a predictable waste stream that could be effectively managed through investments in recycling facilities and collection networks. Establishing efficient processes for the safe disassembly, transportation, and processing of these panels can aid in environmental protection and alleviate pressure on landfills. Companies that venture into the recycling sector at this stage can gain a competitive edge and address the rising demand from manufacturers and governments seeking sustainable disposal methods.
Potential for Resource Recovery
Solar panels are made from various valuable materials, such as silicon, silver, copper, aluminum, and rare trace metals. When these components are properly recovered, they can be reused in new panels or sold to other manufacturing industries, thus minimizing the need for new mining operations. By viewing old panels as a resource rather than waste, recycling can become both a profitable and environmentally sustainable endeavor. Effective resource recovery also enhances supply chain resilience, particularly for materials like silver, which may experience variable global availability and high extraction costs. With the increasing global demand for clean energy solutions, Australia has a unique opportunity to excel in the closed-loop reuse of materials, transforming solar waste into resources for the next generation of energy systems.
Technological Innovation
Advancements in recycling technologies offer a vital opportunity to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of recovering materials from solar panels. Currently, most methods focus on retrieving basic components like aluminum frames and glass, while high-value elements such as silicon, silver, and rare metals are often not fully utilized. New techniques, including thermal processing, chemical separation, and robotic disassembly, could greatly improve recovery rates and reduce processing expenses. By investing in research and development, Australia can promote domestic innovation, bolster local manufacturing, and decrease dependence on foreign recycling methods. By excelling in these areas, Australia can enhance environmental outcomes and increase its solar panel recycling market share, both regionally and globally, by providing scalable solutions ready for export.
Government Initiatives and Policies of Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market:
Development of a National Product Stewardship Scheme
The Australian Government is moving forward with the establishment of a national product stewardship scheme specifically aimed at solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. This proposed initiative would assign formal responsibility to manufacturers, importers, and distributors for managing solar panels once they reach the end of their life cycle. By enforcing producer responsibility, the scheme promotes sustainable design, bolsters recycling infrastructure, and ensures safer disposal practices. It also seeks to create a cohesive approach to managing solar waste across all states and territories, replacing the current disjointed system. Once in place, the scheme is anticipated to enhance industry accountability, decrease reliance on landfills, and encourage investment in technologies for recovering solar panels. This initiative stands as a crucial step toward achieving a circular economy within Australia's solar sector.
State-Level E-Waste Regulations
Certain Australian states have proactively introduced specific regulations concerning e-waste that encompass solar panels. For instance, Victoria and South Australia have implemented landfill bans on end-of-life solar equipment, urging both residential and commercial users to seek out recycling options. These regulatory actions serve as regional examples in the absence of a national framework. They generate an immediate need for recycling services and stimulate the development of logistics, storage, and dismantling facilities. Although the regulations differ across jurisdictions, the overall impact is a growing compliance landscape that places pressure on solar installers and waste operators to handle disposal responsibly. These state-driven actions also encourage discussions on the harmonization of solar recycling policies at the national level.
Investment in Recycling Infrastructure
Various state governments are backing pilot projects and specific investments aimed at enhancing Australia’s solar panel recycling infrastructure. These efforts include establishing collection hubs, funding trials for material recovery, and creating public-private partnerships to scale recycling operations. In areas like Queensland, pilot programs have been initiated to evaluate the effectiveness of different panel disassembly and recovery methods while increasing awareness among industry stakeholders. Such investments in infrastructure are vital for accommodating the increasing number of end-of-life panels. By ensuring access to proper disposal and processing services, state-level initiatives help bridge the existing infrastructure gap, setting the stage for a more coordinated and comprehensive recycling system nationwide. According to Australia solar panel recycling market analysis, these developments are positioning recycling as a critical component of the country’s long-term clean energy strategy, aligning environmental responsibility with economic opportunity.
Challenges of Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market:
Lack of National Recycling Policy
Australia currently lacks a unified national policy mandating solar panel recycling, resulting in fragmented efforts across states and territories. Without federal legislation or a product stewardship scheme in place, manufacturers, installers, and consumers are not consistently guided or obligated to manage solar waste responsibly. This creates uncertainty for recyclers and limits investment in large-scale processing infrastructure. In some jurisdictions, solar panels are still classified as general waste, further complicating proper disposal. A national framework could set clear standards, drive compliance, and enable coordinated funding or incentives. Until such policy is implemented, recycling efforts remain piecemeal, voluntary, and often insufficient to address the growing volume of retired solar panels entering the waste stream each year.
High Cost of Recycling
Recycling solar panels is a complex and costly process that involves dismantling tightly bonded materials such as tempered glass, silicon wafers, plastics, and metals. These components require specialized equipment and manual labor to separate and recover, significantly increasing operational costs. In contrast, sending panels to landfill is cheaper and more accessible, especially where disposal regulations are lenient. The lack of valuable material yield like small quantities of silver or copper makes it difficult for recyclers to generate profit without subsidies or incentives. This economic imbalance discourages investment in recycling technologies and infrastructure. Without intervention through policy or pricing reforms, the financial burden of recycling remains a major deterrent for the industry.
Limited Recycling Infrastructure
Australia’s current recycling infrastructure is not equipped to handle the rising volume of decommissioned solar panels, especially as early-generation systems begin to reach their end-of-life. Many existing facilities are small-scale or general-purpose recyclers that lack the specialized processes needed for panel disassembly and material recovery. Geographic dispersion also presents challenges; many regions, particularly remote or rural areas, do not have access to appropriate collection or recycling centers. This often results in stockpiling, improper disposal, or long-distance transport, all of which add to costs and emissions. Expanding capacity requires substantial investment, long-term policy support, and collaboration between government, manufacturers, and waste management providers to ensure a reliable national recycling network.
Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on process, type, material, and shelf life.
Process Insights:
- Thermal
- Mechanical
- Laser
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the process. This includes thermal, mechanical, laser, and others.
Type Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
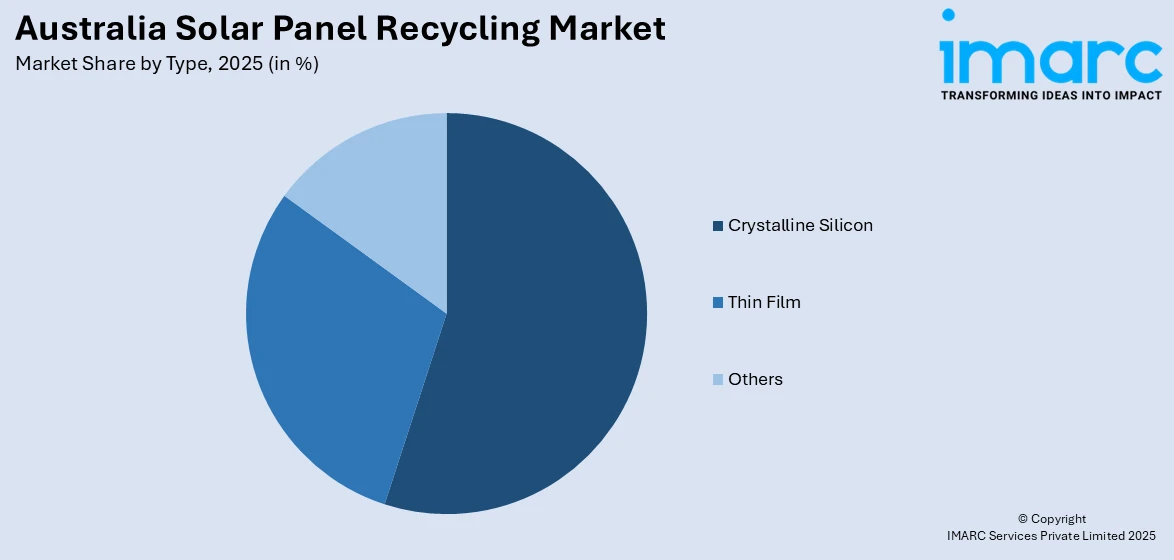
- Crystalline Silicon
- Thin Film
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type have also been provided in the report. This includes crystalline silicon, thin film, and others.
Material Insights:
- Metal
- Glass
- Aluminum
- Silicon
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the material. This includes metal, glass, aluminum, silicon, and others.
Shelf Life Insights:
- Normal Loss
- Early Loss
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the shelf life have also been provided in the report. This includes normal loss and early loss.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market News:
- November 24, 2024: Sircel Pty Ltd launched its most advanced solar panel recycling facility in Parkes, NSW, marking a major step toward sustainability. With over 1.3 million tonnes of solar panels nationwide and only 15% currently recycled, the new plant aims to recover valuable materials, including aluminum, glass, copper, and silver. Funded by the NSW Environmental Protection Authority’s Circular Solar Phase 2 grants program, the initiative will help redirect end-of-life panels back into the circular economy.
Australia Solar Panel Recycling Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Processes Covered | Thermal, Mechanical, Laser, Others |
| Types Covered | Crystalline Silicon, Thin Film, Others |
| Materials Covered | Metal, Glass, Aluminum, Silicon, Others |
| Shelf Lives Covered | Normal Loss, Early Loss |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia solar panel recycling market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia solar panel recycling market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia solar panel recycling industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The solar panel recycling market in the Australia was valued at USD 4,013.4 Million in 2025.
The Australia solar panel recycling market is projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.15% during 2026-2034.
The Australia solar panel recycling market is expected to reach a value of USD 11,604.1 Million by 2034.
Rising volumes of decommissioned panels, increasing environmental regulations, and a push toward zero-waste energy systems are driving market demand. Government pilot programs and industry support for closed-loop supply chains are encouraging infrastructure investment. Public concern over landfill impact is also prompting stronger action from solar manufacturers and policymakers.
Australia is witnessing a shift from informal disposal to structured recycling processes, driven by increased awareness and emerging local recycling capabilities. Innovation in material separation and circular design principles is gaining momentum. There's also rising interest in integrating recycling within broader renewable energy transition planning.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












