
Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Type, Crop Type, Farming System, Formulation, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market Overview:
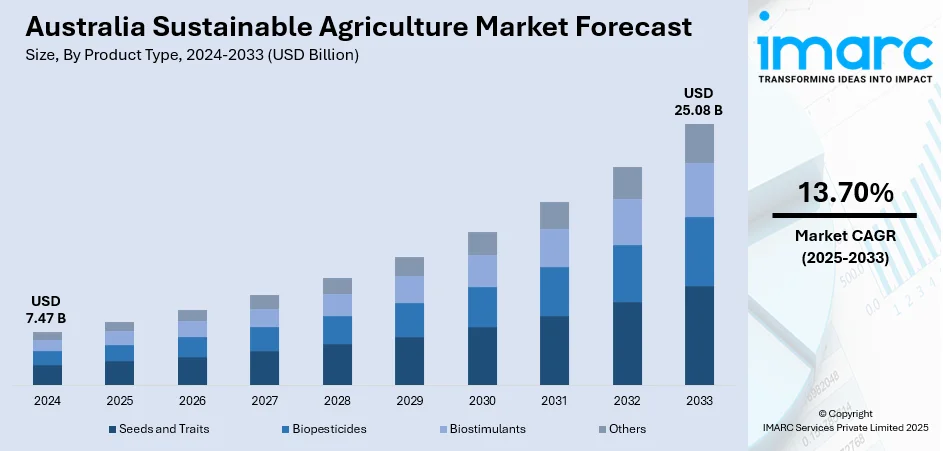
The Australia sustainable agriculture market size reached USD 7.47 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 25.08 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 13.70% during 2025-2033. The Australia sustainable agriculture market is driven by increasing government support through funding and policies, advancements in precision farming and agritech, growing consumer demand for organic produce, climate change adaptation efforts, soil and water conservation initiatives, and the push for carbon-neutral and regenerative farming practices to enhance long-term productivity.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 7.47 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 25.08 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 13.70% |
Key Trends of Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market:
Integration of Advanced Agricultural Technologies
The integration of leading-edge technologies is transforming Australia's farming industry, boosting efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. An important innovation is the creation and release of self-propelled farm equipment. An example is that of SwarmFarm Robotics, which has set up a factory south of Toowoomba, Queensland, making modular robots for farming jobs like fertilizing, spraying herbicides, and weed scouting. Not only are these developing farm practices modernized, but high-tech job creation is now present in areas such as Toowoomba. Yet another important technological advance is the development of a natural feed additive that comes from native Curvularia soil fungi. Australian researchers have created the additive, which has the capacity to cut back livestock methane by as much as 90%, solving a large environmental issue connected with agriculture. This technology presents a sustainable means of curbing greenhouse gas emissions from livestock, supporting the social license and access to markets of the industry. The Government of Australia has seen the value of incorporating technology in agriculture. In 2024, the agricultural sector employed about 257,000 individuals, a growth of 2.4% compared to the previous year. This increase can be explained partially by the sector's modernization and adoption of new technologies, making farming careers more desirable and varied.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Commitment to Environmental Stewardship
Environmental sustainability is a fundamental aspect of agricultural practices and policies in Australia. The Australian Agricultural Sustainability Framework (AASF), advocated by the National Farmers' Federation and supported by the Australian government, exemplifies this dedication. The AASF aims to establish the sustainability principles of Australian agriculture across the country, in alignment with global initiatives such as the Sustainable Development Goals. It highlights environmental care, social responsibility, and economic strength, providing a comprehensive strategy for sustainable farming. Climate change is a major challenge to agriculture, with trends since 2000 reducing average broadacre farm profit by 22% and beef farm profit by 5%. To counter this, Australian farmers are embracing measures to enhance climate resilience, including the quality of feed for livestock and fertilizer use efficiency in cropping. In addition, more than 70% of production is exported from the Australian farm sector, at an estimated USD 75 Billion during 2022–23. This high rate of export places emphasis on having sustainable practices secure international market access and address the environmental expectations of the global consumer base. In conclusion, the convergence of sophisticated technologies and unwavering environmental stewardship are fundamental drivers that spur Australia's sustainable agriculture industry. These drivers improve productivity and efficiency, while also guaranteeing long-term sustainability and global competitiveness of the industry.
Growth Drivers of Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market:
Water Restriction and New Irrigation Techniques
Australia's unique climate volatility and recurring cycles of drought have resulted in intense emphasis on water-conserving farming techniques, fueling expansion of sustainable agriculture. Being home to vast agricultural regions in regions such as the Murray–Darling Basin and the arid zones of Western Australia, farmers are resorting to precision irrigation methods such as soil moisture sensors and drip irrigation for efficient use of water. These technologies are essential considering water scarcity issues and environmental conservation of river catchments. Farmers are also trying out recycled water and rainwater harvesting systems combined with smart controllers to reduce reliance on unpredictable rainfall. The stress to reconcile farm performance with environmental integrity has triggered the demand for regenerative methods such as cover cropping and perennial pastures, which enhance soil moisture conservation and lower runoff. With an increasing number of farmers acknowledging the importance of climate-resilient systems, sustainable agriculture water management is a key growth driver in the Australian sustainable agriculture industry.
Organic and Traceable Produce Demand
Increased demand for organic, chemical-free, and traceable produce in both domestic and export markets is among the key drivers of growth in sustainable agriculture in Australia. Consumers, especially in urban areas such as Melbourne, Sydney, and Brisbane, are increasingly valuing food safety, environmentalism, and transparency in production processes. This has led farmers to embrace sustainable practices like organic manures, integrated pest management, and non-GMO crop production. Furthermore, Australia's robust export links with markets in Asia and the Middle East have generated demand for premium sustainably produced agricultural crops with full traceability. Technologies including blockchain and QR-coded packaging are being employed to trace produce from farm to shelf, guaranteeing end-users its ethical origins. This change in consumer demand is compelling large and small-scale producers alike to follow sustainability standards, which in turn will fuel the expansion and sophistication of the Australia sustainable agriculture market share.
Technology Adoption and Digital Farm Management
Another key growth driver of Australia's sustainable agriculture sector is technology and data-driven farm management technologies. Large-area livestock farms and broad-acre cropping farms are using drones, satellite imagery, and automated sensors to observe plant health, pasture cover, and soil health. These technologies support precision interventions like targeted fertilizer application or selective pest control with minimal inputs while preserving yield. Robotic reseeding equipment for pasture and autonomous weeders are working across huge areas with minimal disruption, further minimizing the use of herbicides. In grape-growing areas such as South Australia's Barossa and Victoria's Yarra Valley, intelligent sensors and weather stations are employed to schedule sustainable treatments, prevent over spraying, and maintain soil integrity. Together, they allow farmers to measure carbon sequestration, make data-driven decisions, and optimize resource efficiency in real time through farm management software. As digital infrastructure extends even to distant farm regions through rural broadband and satellite infrastructure, more practices become available for sustainability, further propelling the Australia sustainable agriculture market growth.
Opportunities of Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market:
Scaling Up Regenerative Agriculture in the Arid and Semi-Arid Lands
Australia's massive semi-arid and arid regions, traditionally regarded as unsuited to high-output agriculture, hold enormous potential for increasing regenerative farming practices. Rotational grazing, no-till agriculture, and multi-species cover crops are being progressively adopted to meet dryland requirements in areas such as the wheatbelt region of Western Australia and parts of rural Queensland and New South Wales. These practices contribute to the development of soil health, enhance water retention, and restore local biodiversity, transforming marginal land into productive yet sustainable systems. The capacity to rehabilitate degraded soils and reverse desertification processes has long-term economic implications for rural communities. With growing climate pressures, demand for farming systems that build resilience instead of depleting natural resources is increasing. In addition, regenerative agriculture supports Australia's national priorities for carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation, offering the opportunity for farmers to earn revenue through ecosystem service markets and carbon credits while they become more productive.
Increasing Export Demand for Sustainably Certified Produce
According to the Australia sustainable agriculture market analysis, the region’s international reputation as a producer of clean, safe, and quality agricultural products positions it to supply the increased demand on the world market for sustainably certified food and fiber. With consumers in Asia-Pacific, Europe, and the Middle East becoming more environmentally aware, there is growing demand for organic, non-GMO, low-carbon, and animal welfare-compliant agricultural produce. Major export opportunities exist for Australian farmers who are able to respond to these sustainability demands. Areas such as Tasmania and Victoria have already proven themselves as authorities in traceable premium food production, and this is a model that can be emulated throughout the rest of the nation. The creation of certification schemes and supply chain transparency instruments adds to the strength of Australia's position within the international market. Moreover, free trade agreements and bilateral relationships are also capable of facilitating the export of sustainably grown commodities, especially from industries such as horticulture, viticulture, and grass-fed beef. Taking up sustainability not just enhances the value addition to Australia's exports but also ensures long-term market loyalty.
Integration of Renewable Energy in Agricultural Operations
The incorporation of renewable energy into farming activities is a fast-growing prospect in Australia's sustainable agriculture sector. With the high solar radiation and extensive rural landholdings of the country, farms are gradually well-suited to install solar panels, wind turbines, and storage batteries to provide energy for irrigation, cold storage, and processing plants. States like South Australia and the Northern Territory are already witnessing agricultural businesses turning to off-grid options to minimize diesel reliance and decrease operation expenses. Solar-powered irrigation pumps and automated irrigation systems are being tested in water-short regions to maximize efficiency and minimize emissions. Additionally, combining renewables with smart farm technology enables facile energy management, again in line with national and regional targets for sustainability. Government subsidies and clean energy financing programs also give the use of these technologies’ economic incentives. With increasing energy prices, and emissions reduction more critical, renewable energy implementation in agriculture presents a double benefit of productivity, profitability, and environmental management.
Government Support of Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market:
Climate-Smart Agriculture Policy Frameworks
The Australian government has made significant strides in supporting sustainable agriculture through incorporating climate resilience into national farm policies. Through targeted strategies that complement the nation's wider climate action and environmental ambitions, authorities are persuading farmers to undertake practices that reduce emissions, build healthier soils, and promote biodiversity. Initiatives within national agricultural ministries have established roadmaps for low-carbon agriculture, climate-resilient grazing, and regenerative land management. They work to minimize agriculture's carbon footprint and ready the industry to cope with mounting climate stressors. Regional plans in New South Wales and Victoria, for example, facilitate soil carbon actions and water efficiency to safeguard critical river basins like the Murray–Darling Basin. In addition, First Nations land management strategies are also being incorporated into sustainability policies, recognizing the extensive ecological understanding that First Nations peoples possess. Such holistic policies provide a robust cornerstone which further increases the Australia sustainable agriculture market demand throughout varied agricultural regions.
Economic Incentives and Sustainability Grants
To help mitigate the cost of adopting sustainable agriculture, the Australian government has implemented a variety of grants, rebates, and low-interest loan programs. These state and federal funding aids aim to incentivize farmers to embrace green technologies, invest in soil rejuvenation, and utilize better water and energy consumption systems. Some state programs, like Queensland and South Australia, also offer specific funding for drought resilience, carbon farming, and integrated pest management. Farmers may also obtain funding to take up environmental stewardship programs, which remunerate activities that enhance biodiversity or conserve natural resources. Notably, a number of grants are now linked to quantifiable environmental results, including the enhancement of soil carbon or the restoration of habitats, underpinning accountability as well as fueling sustainability. This outcome-based funding strategy not only incentivizes adoption but also innovation, as farmers are encouraged to seek out innovative tools and techniques congruent with government targets. These monetary measures are key to reducing barriers to sustainable agriculture throughout Australia's agricultural heartland.
Research, Innovation, and Regional Capacity Building Support
The Australian government also promotes sustainable agriculture with substantial investments in agricultural research, technology development, and farmer training. Financing is channeled to universities, innovation centers, and public-private collaborations involved in regenerative farm systems, carbon-free animal production, and climate-tolerant crop varieties. Research institutions in states such as Western Australia and Tasmania are searching for region-based solutions to sustainability, assisting in the specific adaptation of approaches to local soil conditions, climatic conditions, and agricultural systems. Additionally, regional capacity-building initiatives are assisting farmers with the tools and information necessary to effectively implement these innovations. Extension services, demonstration farms, and online learning sites are being increased so practical know-how can be extended to producers in remote locations. Support for community-driven projects, such as Indigenous-led sustainability initiatives, is also picking up pace, making the effort more inclusive and integrated. Through promoting research and knowledge sharing, the government is building the foundation of long-term sustainable farming in Australia and enabling farmers to be active guardians of land.
Challenges of Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market:
Climate Variability and Rising Weather Extremes
Australia's high climate variability and rising occurrence of extreme weather conditions are the greatest challenge that sustainable farming in Australia must address. Large sections of the continent have been witnessing cycles of extended droughts, severe heatwaves, and irregular rainfall, and with this, it becomes challenging to achieve consistent yields using sustainable methods. Farmers in areas such as New South Wales and Western Australia are frequently compelled to adjust to varying planting and harvest windows, which can interfere with the timing of regenerative strategies like cover cropping or rotational grazing. Tropical storms and flooding in northern parts of the country can reverse years' worth of work building up soils in one season. Such extremes inhibit long-term planning necessary for sustainable agriculture and render it impossible to be dependent only on nature-based systems without the intervention of technology. Although sustainable farming is engineered to be resilient, the severity and variability of Australia's climate remain a serious threat for both new adopters and established practitioners.
High Transition Costs and Limited Access to Capital
Shifting to sustainable agriculture in Australia sometimes demands high initial investment, which poses a fundamental obstacle to farmers, especially small to medium-sized businesses. Techniques like regenerative grazing, organic certification, and integrated pest management sometimes necessitate buying new machinery, training workers, modifying infrastructure, or resting and regrowing land, all of which cost money. Many rural areas, especially in inland regions of Queensland and South Australia, face limited access to financial services or tailored sustainability grants. Without adequate financial support or incentives, many producers are hesitant to shift from conventional high-input farming systems that deliver short-term returns. Moreover, uncertainty about the payback period and lack of region-specific financial modeling tools further complicate decision-making. Even as farmers are committed to sustainable practices, the absence of scalable financial support mechanisms through banks, co-ops, or government initiatives can slow down or limit the rate of change throughout the agricultural sector.
Knowledge Gaps and Regional Disparities in Support Services
Another significant issue confronting Australian sustainable agriculture is uneven regional access to knowledge, extension services, and technical support throughout the country. While producers in areas with prominent agricultural universities or government-funded innovation centers such as Victoria or some parts of New South Wales, will likely have access to current research and advice, numerous remote or less affluent areas do not benefit from adequate access to specialized advice. In the Northern Territory or western Queensland, growers can end up using practices that are antiquated or passed down through informal channels, a process that can be impeded by the adoption of efficient sustainable methods. Moreover, the absence of standardized guidelines and customized advisory services for various farming systems renders it difficult for producers to assess which sustainable practices are most appropriate for their particular soil conditions, climate, and markets. Without focused education, field demonstrations, and peer-to-peer learning forums, the adoption of sustainable practices may be piecemeal. Closing this knowledge gap is essential to providing a unified, national approach to sustainable agriculture.
Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the region/country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on product type, crop type, farming system, formulation, and application.
Product Type Insights:
- Seeds and Traits
- Biopesticides
- Biostimulants
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the product type. This includes seeds and traits, biopesticides, biostimulants, and others.
Crop Type Insights:
- Cereals and Grains
- Oilseeds and Pulses
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the crop type have also been provided in the report. This includes cereals and grains, oilseeds and pulses, fruits and vegetables, and others.
Farming System Insights:
- Organic Farming
- Conservation Agriculture
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Precision Agriculture
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the farming system. This includes organic farming, conservation agriculture, integrated pest management (IPM), and precision agriculture.
Formulation Insights:
- Liquid
- Dry
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the formulation. This includes liquid and dry.
Application Insights:
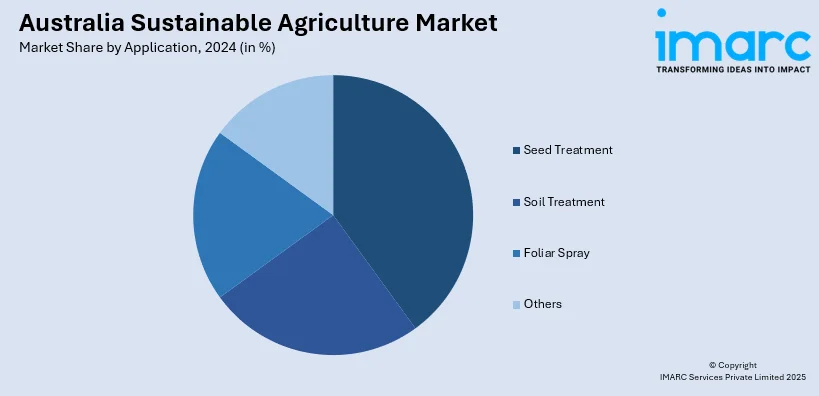
- Seed Treatment
- Soil Treatment
- Foliar Spray
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application. This includes seed treatment, soil treatment, foliar spray, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market News:
- October 2024: The Queensland Government announced the four winners of the fertilizer project under the Backing Business in the Bush Fund (BBBF) and the Regional Economic Futures Fund (REFF). The BBBF offered financial assistance between USD 500,000 and USD 2 Million for every project, whereas grants via REFF ranged from USD 50,000 to USD 12.75 Million. Mort & Co is set to receive an unspecified amount to boost its existing organic fertilizer production near its Grassdale feedlot south of Dalby by incorporating additional granulators and an automated batching system. Another beneficiary is the precision agriculture company, DataFarming, which intends to use its funding to create digital systems that link fertilizer producers directly with farmers.
- October 2024: Flamingro, an excellent certified organic biostimulant based on chitin for optimal plant growth and a stronger root system, was featured in Good Fruit & Vegetables magazine. The article named “Bio-Stimulant Ticks Aussie Organic Box” explored its introduction into the Australian market. It is available to farmers across Australia, having shown a 26% increase in root mass in experiments. With 70-80% of modern wine grape vines established, it intends to offer crucial protection that could significantly reduce losses across the industry.
- September 2023: High Valley Dawn Permaculture in Rosslyn Bay, Queensland announced the start of building a facility for processing and packaging in order to enhance the production of organic fruits and vegetables for local markets, enterprises, and the farm's paddock-to-plate restaurant, Beaches Rosslyn Bay.
Australia Sustainable Agriculture Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered | Seeds and Traits, Biopesticides, Biostimulants, Others |
| Crop Types Covered | Cereals and Grains, Oilseeds and Pulses, Fruits And Vegetables, Others |
| Farming Systems Covered | Organic Farming, Conservation Agriculture, Integrated Pest Management (IPM), Precision Agriculture |
| Formulations Covered | Liquid, Dry |
| Applications Covered | Seed Treatment, Soil Treatment, Foliar Spray, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia sustainable agriculture market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia sustainable agriculture market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia sustainable agriculture industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia sustainable agriculture market was valued at USD 7.47 Billion in 2024.
The Australia sustainable agriculture market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 13.70% during 2025-2033.
The Australia sustainable agriculture market is expected to reach a value of USD 25.08 Billion by 2033.
The Australia sustainable agriculture market is seeing rising adoption of regenerative practices, integration of agri-tech solutions like precision irrigation and drones, and growing demand for organic, traceable produce. Government support, consumer awareness, and climate challenges are driving innovation, while regions embrace eco-friendly methods tailored to local soil and climate conditions.
Key drivers of Australia sustainable agriculture market include increasing climate variability, water scarcity, rising consumer demand for organic and eco-friendly produce, and strong government support. Technological advancements, such as precision farming and renewable energy integration, also encourage adoption of sustainable practices, particularly across arid and resource-constrained farming regions.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












