
Australia Tea Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Type, Packaging, Distribution Channel, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Tea Market Size and Share:
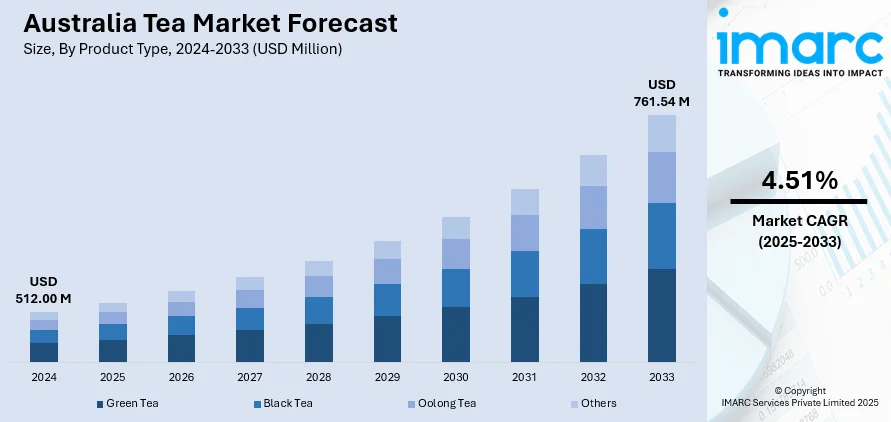
The Australia tea market size reached USD 512.00 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 761.54 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 4.51% during 2025-2033. The rising demand for health-focused beverages, increasing popularity of herbal and specialty teas, growing café culture, expanding retail presence, and heightened consumer awareness of tea’s antioxidant properties are driving the market expansion, supported by product innovation, premiumization trends, and the influence of multicultural preferences on tea consumption habits.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 512.00 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 761.54 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 4.51% |
Key Trends of Australia Tea Market:
Rising Demand for Health and Wellness-Oriented Tea Products
The growing consumer interest in health and wellness is leading to a marked shift toward functional and specialty tea variants, which is positively impacting the Australia tea market outlook. Health consciousness is becoming a major influence on beverage choices, prompting consumers to seek products that offer added nutritional or therapeutic value. According to an industry survey, about 73% (three-quarters) of respondents reported that they put effort into maintaining a healthy diet. This heightened focus on preventive health is directly shaping purchasing behavior in the tea segment. Consumers are becoming more selective, prioritizing teas that align with their wellness goals and contribute to overall health management. Herbal teas, detox blends, immunity-boosting infusions, and products formulated with adaptogenic ingredients such as ashwagandha and turmeric are gaining popularity. In addition to this, brands are responding by launching formulations that promote well-being, with labels emphasizing organic sourcing, non-GMO status, and therapeutic ingredients. As consumers increasingly align their beverage choices with lifestyle goals, functional tea products continue to gain traction in both urban and regional markets, particularly among millennials and health-conscious older demographics.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Premiumization and Expansion of Specialty Tea Offerings
The market is undergoing premiumization, with consumers showing a growing interest in artisanal, single-origin, and boutique tea experiences, which is propelling Australia tea market growth. This trend reflects a broader consumer preference for quality, authenticity, and storytelling behind the product. In line with this, loose-leaf teas, hand-blended infusions, and ethically sourced products are gaining popularity, often commanding higher price points. Boutique tea brands and independent tea houses are capitalizing on this shift by offering curated tasting experiences, tea education workshops, and subscription services. Packaging aesthetics, provenance transparency, and limited-edition releases further enhance the appeal of premium offerings. In urban centers like Melbourne and Sydney, specialty tea cafés mirror the third-wave coffee movement, elevating tea consumption to a craft ritual. This movement towards premiumization is not merely about taste; it encompasses sustainability, ethical labor practices, and a refined lifestyle association that appeals to discerning consumers.
Growth of Online Retail and Direct-to-Consumer Channels
Digitalization is a significant factor augmenting Australia tea market share. Online retail and direct-to-consumer (DTC) models are witnessing substantial growth. According to an industry report, approximately 63.94% of Australia’s 26.714 Million population are active eCommerce shoppers. The shift toward digital platforms gained momentum in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, which prompted widespread changes in shopping behavior. With lockdowns limiting access to physical stores, consumers increasingly turned to e-commerce for their everyday needs, including tea. Moreover, brands are increasingly investing in robust online storefronts, user-friendly mobile apps, and subscription models that ensure regular customer engagement and loyalty. Social media marketing, influencer collaborations, and targeted advertising are becoming key tools for customer acquisition, particularly for niche and specialty tea brands. Consumers also benefit from transparent ingredient sourcing, customer reviews, and educational content online. The convenience of home delivery, coupled with flexible packaging options and exclusive digital discounts, continues to drive momentum for DTC and e-commerce-led growth in the Australian tea segment.
Growth Drivers of Australia Tea Market:
Growing Health Awareness and Consumer Trends
One of the significant growth drivers for the Australian tea market is growing health awareness among consumers. Australians are becoming increasingly discerning about what they eat and drink, with a strong desire for natural, organic, and wellness-driven beverages. The changing lifestyle and eating pattern have made tea—especially herbal and green tea—a popular choice over sugary drinks and coffee. Local brands are fighting back with blends that support digestive health, immunity, relaxation, and detoxification. To the region, a special advantage lies in using indigenous botanicals such as lemon myrtle, eucalyptus, and wattle seed, which are being included in tea blends due to their health properties and local popularity. Not only does this addition of indigenous ingredients improve product differentiation, but it also endorses sustainability and cultural attachment that appeals to environmentally and socially aware consumers. The market for tea therefore continues to develop beyond the conventional black tea towards a broader range of wellness-oriented products which address Australia's health-conscious, multicultural population.
Multicultural Influence and Widening Taste Profiles
Australia's affluent multicultural nation heavily influences its tea market, with the availability of a broad range of taste profiles and consumption patterns to reflect diverse ethnic groups. Immigrant populations from nations such as China, India, Sri Lanka, and Japan have imported traditional tea-bibbing practices, which have helped to foster a greater appreciation for specialty teas including oolong, chai, matcha, and Ceylon blends. These immigrant groups have not only grown demand for imported and specialty teas but have challenged domestic producers to create fusion products. With Australians venturing more into food and drink experience, there is a discernible trend towards exploring world tea varieties. This trend is also complemented by Australia's intense Asian trade connections and cultural exchange through travel, education, and immigration. Tea houses and specialty cafes providing ceremonial-style or regional-style service, or regional brewing have become popular, further increasing consumer familiarity and acceptance. This multicultural environment is rich in context for promoting market expansion based on diversity and ongoing innovation.
Sustainable Practices and Local Production
Growing concern for environmental sustainability and local production are emerging as imperative drivers in the Australian tea industry, both of which are actively fueling expansion. Consumers are increasingly looking for environmentally friendly products, leading brands to invest in sustainable packaging, ethically sourced ingredients, and organic cultivation. In return, various Australian tea producers are growing tea in areas such as Victoria and Tasmania, which have climates conducive to producing high-grade leaves. Not only do such local efforts minimize dependence on imports but also facilitate traceability and transparency—qualities highly appealing to contemporary Australian consumers. Increased popularity of community-supported agriculture and farmer's markets has further contributed to fostering locally grown and artisan tea brands. Besides, partnerships with Indigenous communities for native plant harvesting encourage sustainable practices while respecting ancient knowledge. Support from the government for agricultural innovation and clean modes of production further enhances this industry.
Opportunities of Australia Tea Market:
Growth of Specialty and Premium Tea Segments
The tea market in Australia offers good opportunities in the specialty and premium tea segments, fueled by consumer interest in high-quality, artisanal products. As Australians shift away from bland supermarket tea bags in increasing numbers, there is an escalating appreciation for loose-leaf teas, single-origin teas, and handcrafted blends. This transition provides an opportunity for boutique brands to succeed through distinctive flavor blends and narratives about the sourcing and creation of their products. Adding native Australian ingredients like lemon myrtle, aniseed myrtle, and finger lime provides a competitive advantage by imbuing teas with an unmistakably earthy local character. These products resonate with local consumers and provide the opportunity for export, especially in Europe and Asia, where there is increased interest in Australian-harvested botanicals. With a sophisticated consumer base and high environmental concerns, Australia provides fertile ground for high-end tea brands that focus on authenticity, traceability, and sensory experience.
Growth Opportunity in the Ready-to-Drink and Functional Beverage Segment
The functional beverage and ready-to-drink (RTD) tea markets present significant scope for growth in Australia's tea industry. With lifestyles becoming increasingly hectic, consumers are looking for convenient but healthy beverages, which tea-based beverages perfectly address. Local companies are already starting to capitalize on this trend with packaged herbal infusions, fizzy teas, and kombucha-style drinks produced from Australian-grown tea and herbs. Functional gains like hydration, energy, relaxation, or digestive health are all more in demand now, and thus teas with vitamins, adaptogens, or probiotics are especially appealing. Hot weather in much of Australia also encourages the kind of robust demand for cold, refreshing beverages that places RTD tea in a strong position as an alternative to sparkling soft drinks. Furthermore, Australia's sophisticated food manufacturing capacity and focus on clean labeling offer perfect circumstances for creating innovative, health-related beverages. This sector coincides with existing wellness themes, and promotes the creation of niche, value-added drinks that can access both domestic and foreign markets.
Tourism, Cultural Experiences, and Tea-Based Hospitality
Australia's robust tourism market and increasing experiential consumption drive offer a further valuable opportunity for the tea industry. With millions of foreign visitors and a strong domestic tourist economy, there is plenty of scope to integrate tea into culture and hospitality experiences. High tea offerings, tea tasting workshops, and farm-to-cup experiences in destinations such as the Dandenong Ranges or Tasmania provide immersive options to connect consumers. Native Australian ingredients used in tea ceremonies also bring a cultural narrative layer that resonates with locals as well as tourists looking for genuine and memorable experiences. Tea can further find application in wellness retreats, spa, and gourmet food pairings, making it more relevant outside conventional consumption. With governmental and local council backing for agritourism and rural development, tea producers can work with the hospitality industry to develop niche products. These getaways not only enhance brand presence but also raise the status of tea as a lifestyle product in Australia.
Challenges of Australia Tea Market:
Limited Domestic Production and Climate Constraints
Among the major issues confronting the Australian tea market is the constrained level of domestic tea production that limits the possibility of responding to increasing consumer demand locally. In contrast to established tea-producing nations, Australia has comparatively few areas where the best climate and soil conditions exist for extensive commercial tea cultivation. Whereas regions such as Victoria and Tasmanian regions have had success in boutique tea cultivation, overall yields are limited and tend to be directed to the high-end market. This indicates that much of the tea is imported, mainly from nations such as India, China, and Sri Lanka. Such reliance on imports exposes the market to global supply chain interruption, foreign exchange rate volatility, and varying international trade regulations. Moreover, climate change-driven unpredictable weather conditions also affect the predictability of local crops, and it becomes challenging for Australian farmers to increase scale or match imported tea price-wise and volume wise.
Market Competition and Consumer Brand Loyalty
Another significant challenge in the Australian tea industry is stiff competition, both from established multinational players and increasing demand for substitute beverages. Supermarkets are controlled by giant, established tea companies with deep marketing budgets, powerful distribution networks, and economies of scale. It is thereby challenging for small or new entrants to secure shelf space and consumer access. Also, consumers in Australia tend to be highly loyal to their favorite brands, especially for day-to-day tea products, which poses a challenge for local manufacturers to bring in new varieties or high-end substitutes. Coffee culture also presents competition, especially in larger cities where culture surrounding coffee bars is prevalent. Consumers are still greatly attracted to coffee as their daily dose of caffeine, which constrains the development possibility of traditional black tea. In order to thrive, smaller tea companies have to come up with innovative means to stand out based on niche marketing, special ingredients, or health positioning, which will further contribute to the Australia tea market demand.
Regulation and Sustainability Pressures
Australia's high level of regulatory stringency is both a strength and a weakness for the tea market. On one hand, exacting standards regarding food safety and labeling enhance consumer trust. On the other hand, such standards create compliance costs that are cumbersome for small and medium-sized businesses. Import regulations, quarantine demands, and biosecurity legislation are particularly challenging when sourcing herbal and botanical ingredients, potentially making it harder to source and raising operational costs. In addition, sustainability is now a prime concern for both regulators and consumers, necessitating businesses having to use environmentally friendly packaging, sustainable sourcing procedures, and open supply chains. Compliance with these expectations requires further investment in certifications, audits, and green logistics, which may be beyond local producers. As consumers become increasingly aware of environment and social concerns, deviation from these values may result in reputational damage or loss of market share. Ensuring compliance with these regulatory and sustainability requirements is critical for tea businesses wanting to operate effectively in Australia's competitive and socially conscious market.
Australia Tea Market Consumption:
Changing Consumer Attitudes and Lifestyle Trends
Tea drinking in Australia is facing a perceptible shift, driven by changed lifestyle patterns and increasing emphasis on health and wellbeing. While traditional black tea still maintains its position in many Australian homes, over time there has been a consistent move towards a more fragmented range of tea offerings. Herbal teas, green teas, and caffeine-free infusions are becoming more popular among healthy consumers looking for natural substitutes for sweet drinks or coffee. Australian consumers also become more educated about the functional effects of various types of tea, including relaxing properties, digestive function, or detoxification. This trend in taste is driven by greater exposure to international tea cultures, particularly from travel and the multicultural society of Australia. Consequently, the patterns of consumption are growing beyond the traditional morning or afternoon tea to encompass wellness routines, relaxation habits, and hydration related to fitness. This new connection with tea is transforming it from an elementary drink into a lifestyle companion.
Effect of Multiculturalism on Tea Trends
According to the Australia tea market analysis, the multicultural nature of the population greatly influences tea drinking habits throughout the nation. With large communities from Asia, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent, traditional tea customs from these regions have become increasingly mainstream. It is hence common to find Australians enjoying chai, matcha, oolong, or Turkish apple tea as part of their daily routines. These multicultural influences have also led to the proliferation of specialty tea houses and ethnic grocery stores that offer a wide selection of global tea varieties. It contributes to richness and sophistication in the national tea culture, enabling both contemporary and traditional approaches to tea drinking. Australian consumers are also adopting tea ceremonies, loose-leaf infusions, and premium teaware, drawing inspiration from Japanese, Chinese, and Indian cultural customs. The outcome is a tea market in which tea consumption is no longer monolithic but instead is a synthesis of international tastes and local appropriation, promoting experimentation and increased tolerance of non-Western tea cultures.
Tea within the Australian Café Culture
The lively café culture of Australia, historically based on coffee, is slowly embracing tea as a refined and adaptive product. In city centers such as Melbourne and Sydney, tea menus at cafés and specialty stores are being widened to incorporate cold brews, tea lattes, and artisanal infusions that resonate with younger, trend-oriented buyers. These outlets tend to offer tea brewed using native ingredients or organic mixtures that correspond with the wider push for sustainability and conscious consumption. The growing popularity of boutique and hotel high tea experiences also points to the extent to which tea is being reimagined as a social and indulgent experience. In contrast to more traditional patterns of home consumption, today's consumption increasingly involves tea consumed in public, experiential environments. This is serving to raise tea's profile within Australia's beverage culture and expose it to new markets. As tea continues to gain ground in a coffee-driven society, its visibility in hospitality and social venues speaks to the increasing popularity among demographics and age groups.
Australia Tea Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on product type, packaging, distribution channel, and application.
Product Type Insights:
- Green Tea
- Black Tea
- Oolong Tea
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the product type. This includes green tea, black tea, oolong tea, and others.
Packaging Insights:
- Plastic Containers
- Loose Tea
- Paper Boards
- Aluminium Tin
- Tea Bags
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the packaging have also been provided in the report. This includes plastic containers, loose tea, paper boards, aluminium tin, tea bags, and others.
Distribution Channel Insights:
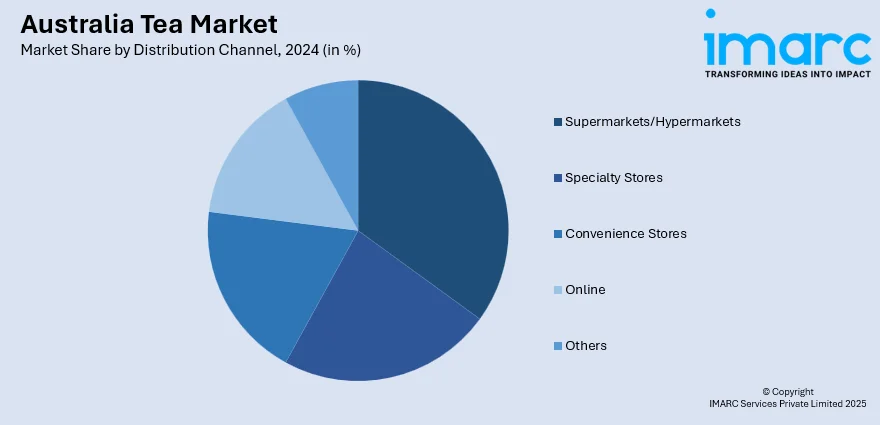
- Supermarkets/Hypermarkets
- Specialty Stores
- Convenience Stores
- Online
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the distribution channel. This includes supermarkets/hypermarkets, specialty stores, convenience stores, online, and others.
Application Insights:
- Residential
- Commercial
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application have also been provided in the report. This includes residential and commercial.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided, including:
- Adore Tea
- Byron Bay Tea Company
- Daintree Tea Company
- Infuse Tea Company
- Nerada Tea
- T Bar Tea
- Tavalon Tea Australia & New Zealand
- The Australian Tea Company
- The Tea Centre
- Yarra Valley Tea Co.
Australia Tea Market News:
- June 2024: Gotcha Fresh Tea increased its footprint in Australia by setting a shop in World Square in Sydney, Waverley Garden and Doncaster, Victoria, the Adelaide Myer Centre Rundle Mall, and a flagship store at the Sydney Fish Market. Along with opening a new store in Mexico, the brand also wants to open ten more there and has set a strategic goal of opening 100 outlets throughout the Mexican market. With more than 200 locations worldwide and more than 50 in Australia, Gotcha hopes to open 100 more in the country in the upcoming three years.
- August 16, 2024: Lipton Teas and Infusions introduced its European premium tea collection, the Lipton Exclusive Selection, to the Australian market. This range, already available in over 24 countries, features high-quality blends such as English Breakfast, Earl Grey, Green Tea Sencha, Delicate Mint, and Chamomile Linden, all packaged in plastic-free, high-infusion pyramid teabags. The teas are sourced from Rainforest Alliance-certified farms, emphasizing sustainable and ethical production practices.
Australia Tea Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered | Green Tea, Black Tea, Oolong Tea, Others |
| Packagings Covered | Plastic Containers, Loose Tea, Paper Boards, Aluminium Tin, Tea Bags, Others |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Supermarkets/Hypermarkets, Specialty Stores, Convenience Stores, Online, Others |
| Applications Covered | Residential, Commercial |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Companies Covered | Adore Tea, Byron Bay Tea Company, Daintree Tea Company, Infuse Tea Company, Nerada Tea, T Bar Tea, Tavalon Tea Australia & New Zealand, The Australian Tea Company, The Tea Centre, Yarra Valley Tea Co., etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia tea market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia tea market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia tea industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia tea market was valued at USD 512.00 Million in 2024.
The Australia tea market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 4.51% during 2025-2033.
The Australia tea market is expected to reach a value of USD 761.54 Million by 2033.
Australia's market trends for tea reflects a shift from conventional black blends toward diversified wellness-oriented offerings, such as herbal, green, and caffeine-free infusions. Demand grows for native botanicals and top-shelf estates, with cafes featuring cold-brew and ceremonial teas. Multicultural influence also broadens taste and occasions of consumption.
The Australia tea industry is fueled by increasing health awareness, multiculturalism, and increasing demand for specialty and premium blends. Indigenous production with local ingredients, government assistance in agribusiness, and sustainability also enhance demand. Inclusion of tea in wellness routines and café lifestyles is also a contributing factor to consumption growth.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












