
Australia Telemedicine Market Report by Component (Product, Services), Modality (Real-Time, Store and Forward, and Others), Delivery Mode (Web/Mobile, Call Centers), Facility (Tele-Hospital, Tele-Home), Application (Teledermatology, Teleradiology, Telepsychiatry, Telepathology, Telecardiology, and Others), End User (Providers, Payers, Patients, and Others), and Region 2025-2033
Australia Telemedicine Market Overview:
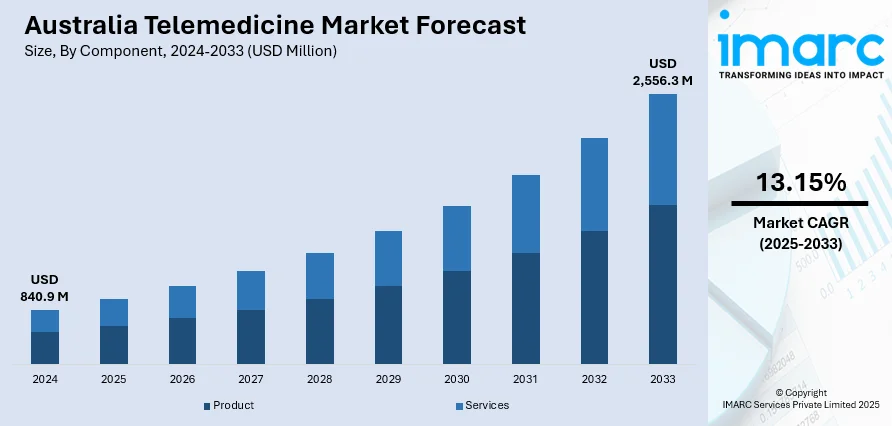
The Australia telemedicine market size reached USD 840.9 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 2,556.3 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 13.15% during 2025-2033. The market is driven by rapid advancements in technology, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, escalating healthcare costs, increasing demand for accessible healthcare, imposition of supportive government policies, and the growing acceptance among patients and providers.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 840.9 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 2,556.3 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 13.15% |
Key Trends of Australia Telemedicine Market:
Rapid Advancements in Technology
Advancements in technology is a major driver in the telemedicine market in Australia. The continuous evolution of digital technologies, including high-speed internet, mobile devices, and telecommunication infrastructure, has made remote healthcare more accessible and efficient. For instance, over 85% of the Australian population enjoys coverage by fifth-generation (5G) networks, and a significant 81% of Australian households have adopted a National Broadband Network (NBN) connection. Moreover, 98% of Australian adults possess internet access at home through fixed or fixed wireless networks. Additionally, innovations in software platforms, such as electronic health records (EHR) and integrated telehealth systems, have facilitated smoother interactions between patients and healthcare providers. Furthermore, telemedicine platforms are increasingly supporting high-definition (HD) video consultations, real-time monitoring, and secure data exchange, which are critical for providing quality remote healthcare services.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Growing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases in the region is a significant driver of the Australia telemedicine market growth. Chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases require ongoing management and regular monitoring, which can be efficiently facilitated through telemedicine. As per industry reports, 1 in 2 Australians (50%) have at least one chronic condition, and 3 in 5 Australians (60%) aged over 65 years have more than one chronic condition. Telemedicine services allow for continuous monitoring of patient's health metrics and facilitate timely interventions, which is crucial for managing chronic conditions. Remote monitoring devices can track vital signs and other health indicators, transmitting data to healthcare providers for review and action. This proactive approach helps in the early detection of potential issues and reduces the need for frequent in-person visits, which can be burdensome for patients.
Rising Healthcare Costs
The rising healthcare costs are a significant driver of the Australia telemedicine market share. Moreover, traditional healthcare services involve high expenses related to in-person consultations, hospital visits, and administrative costs. On the other hand, telemedicine offers a cost-effective alternative by reducing the need for physical infrastructure and allowing for more efficient use of healthcare resources. It reduces overhead costs associated with maintaining physical facilities and staff. Additionally, telemedicine also decreases the frequency of unnecessary in-person visits, which can help lower operational costs. Furthermore, it eliminates travel expenses and reduces the financial burden for patients associated with traditional healthcare visits. The overall efficiency of telemedicine services helps healthcare system to save overall cost by streamlining processes and reducing the strain on emergency services and hospitals.
Growth Drivers of Australia Telemedicine Market:
Geographic Disparities and Rural Healthcare Needs
One of the most significant drivers of telemedicine growth in Australia is the nation's huge geography and the consequent disparity of healthcare accessibility between rural and urban regions. With much of the population residing in rural or inaccessible areas, health care services in a face-to-face format may prove logistically cumbersome and frequently delayed. Telemedicine offers a swift and effective means of overcoming this deficiency, enabling patients to seek opinion from general practitioners and specialists without having to undertake a journey of lengthy distance. Unique to the Australian situation is the long-running conflict of ensuring equal access to healthcare throughout regions such as the Northern Territory and Western Australia, where Indigenous people generally have difficulties accessing regular medical care. The Australian government has moved to ensure its support for telehealth systems in an attempt to overcome these challenges, adopting telemedicine as part of rural health policy. With increasing awareness and infrastructure of digital services, especially in remote areas, telemedicine is emerging as an essential means of delivering equitable healthcare across the country.
Government Policy Support and Medicare Integration
Government support has played a crucial role in the expansion of the Australia telemedicine market demand. An important milestone was reached with the inclusion of telehealth services in the Medicare Benefits Schedule, enabling patients to be subsidized for virtual consultation. This policy changes not only legitimated telemedicine as a common healthcare service but also led to the adoption by both providers and consumers. In contrast to some nations where telehealth is mostly in the private sector, Australia's public healthcare system facilitates and champions virtual care. Another distinctly Australian aspect is the federal government's initiative to integrate telemedicine into aged care services and mental health services, seeing its utility in chronic disease management as well as enhancing mental health access. The pandemic had initially catalyzed the accelerated growth of telehealth, but continued government support has assisted in firmly establishing it as a long-term feature. Continued investment and policy experimentation are making telemedicine a viable, long-term element of Australia's healthcare system.
High Mobile Penetration and Digital Literacy
Australia's digital literacy and broad access to smartphones and internet connectivity have offered rich soil for telemedicine growth. Australians are generally at ease with using digital interfaces for banking, shopping, and learning, so it has been relatively easy to transfer to virtual health. The nation's robust telecommunication network, especially in urban and regional spaces, has facilitated excellent-quality video consultations and secure data transfer. One distinctive strength in the Australian context is the continued investment by the government in national broadband programs, focused on narrowing coverage disparities in rural and Indigenous communities. The multicultural character of Australia has also led telemedicine platforms to provide multilingual services and culturally adapted care, creating even wider appeal. With tech-savvy consumers increasingly seeking convenience, telemedicine aligns well with evolving patient expectations. This digital readiness, combined with the increasing use of wearable health devices and integrated patient portals, is accelerating adoption and enabling a more proactive and connected healthcare experience.
Opportunities of Australia Telemedicine Market:
Improving Indigenous and Remote Community Healthcare
There is a prime opportunity in the telemedicine market in Australia to improve healthcare provision to Indigenous and remote communities. Often, these communities experience specialized barriers in the form of differences in language, cultural sensitivities, and fewer opportunities for receiving regular medical services. Telemedicine can address this by providing regular consultations, follow-up sessions, and specialist consultations without needing patients to physically make long trips. What is special about this potential in Australia is the wide and largely empty interior, termed the Outback, housed by several indigenous people. Adapting telehealth systems with culturally sensitive user interfaces, multilingual languages, and integration with Aboriginal health workers can enhance interaction and results. Furthermore, mobile health vans that are satellite-connected can push telemedicine even farther. This strategy not only solves centuries-long health disparities but also creates possibilities for public-private collaboration and mobile connectivity innovation. Telemedicine, by matching community demand, has the potential to significantly remake Australia's healthcare for its most vulnerable groups.
Integration with Mental Health and Aged Care Services
According to the Australia telemedicine market analysis, increased demand for mental health and aged care services represents a significant opportunity for the expansion of telemedicine. The nation has witnessed growing mental health issues among young and older populations, especially in rural regions where there is limited access to psychiatrists and psychologists. Telehealth facilitates routine mental health checks and therapy sessions, which enable timely intervention free of stigma that at times is connected with face-to-face visits. Australia's health system has already begun integrating virtual care in national mental health programs, and there is also more scope to broaden these services with increased personalization and accessibility. Aged care too is an area in which telemedicine has the potential to revolutionize care delivery. Elderly Australians can be treated virtually via consultations from home or residential aged care facilities, minimizing hospital visits and enhancing chronic disease management. With an ageing population and policy reforms favoring home-based care, telemedicine presents scalable, cost-saving solutions responsive to changing demographic needs in both urban and regional environments.
Innovation in Personalized and Preventative Healthcare
Telemedicine in Australia also stands poised to drive innovations in personalized and preventative healthcare. With digital health technologies like wearable sensors, mobile applications, and remote monitoring devices becoming increasingly prevalent, there is a potential to develop comprehensive telehealth platforms that enable continuous care. Such platforms can offer real-time tracking of health, warning signals early, and treatment modification based on data, transforming healthcare from a reactive to proactive model. Australia's populace, which is highly digitally active, is growing more receptive to the use of technology for managing personal health. In addition, support by the government for electronic health records (in the form of the My Health Record system) gives rise to a central data repository that can facilitate more customized care by telemedicine. Healthcare companies and startups can partner to develop AI-based solutions that suggest lifestyle modifications, drug regime changes, or referrals to specialists based on continuous data. This intersection of technology and care is a bright growth prospect for Australia's telemedicine industry, especially as more patients want control over their health experience.
Government Support of Australia Telemedicine Market:
Medicare Reforms and Telehealth Funding Initiatives
One key element of government patronage that is propelling Australia's telemedicine industry is the coverage of telehealth services under the Medicare Benefits Schedule. This reform constituted a historic policy change, with patients being able to receive subsidized virtual consultations via the public healthcare system. Contrary to most nations where telemedicine is a specialty or privately sponsored service, Australia's strategy incorporates telehealth within general healthcare coverage, which lessens the burden and makes it more accessible to a large population. Accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic, the policy has been adopted as a standard feature, testifying to the government's support for virtual care. The Australian government has also intermittently added to the list of telehealth services and providers eligible for funding, acknowledging its ability to defuse pressure off hospitals and enhance rural healthcare provision. Such continuing funding and regulation has provided a stable background for telemedicine service providers and technology firms to innovate and grow telemedicine services across the country.
Targeted Programs for Rural and Indigenous Health Access
The government of Australia has put specific focus on utilizing telemedicine in enhancing healthcare outcomes within remote, rural, and Indigenous communities. Traditionally, such areas experience immense healthcare access issues because of distance and limited resources. The federal and state governments have taken specific initiatives to provide funding for telehealth infrastructure, such as subsidization of internet connectivity upgrades and telemedicine equipment in regional health clinics. This focused assistance is vital because of Australia's vast geography and the circumstance that Indigenous groups tend to experience higher incidences of chronic illness and fewer accesses to health care services than the national average. There are combined efforts across government health departments, Indigenous groups, and technology solution providers to make telemedicine platforms culturally sensitive and community oriented. While this multi-pronged government strategy encourages fairness in access to healthcare, it also assists in establishing trust and participation in telehealth services within these underprivileged populations.
Regulatory Frameworks and Digital Health Strategy
In addition to funding, Australia's government fosters the telemedicine industry through wide-ranging regulatory frameworks and a national digital health strategy aimed at encouraging innovation while maintaining patient safety and data protection. The Australian Digital Health Agency has the central role of coordinating telehealth services and overseeing digital health infrastructure, such as the My Health Record systema federal, which is an electronic health record platform. The infrastructure enables easy sharing of patient data among healthcare providers during telemedicine visits, ensuring continuity of care. The government's regulatory framework weighs promoting telemedicine innovation against rigorous compliance requirements, especially those concerning patient confidentiality and clinical governance. Australia is the only country that has the participation of several layers of government from federal to state and territory in regulation of telehealth, which involves coordinated policy formulation and implementation. Such regulatory support guarantees telemedicine services of high quality, which generates consumer confidence and promotes adoption in various sectors of healthcare.
Challenges of Australia Telemedicine Market:
Infrastructure Shortfalls in Rural and Remote Regions
Despite Australia's impressive advances in telemedicine uptake, the greatest challenge continues to be Australia's uneven digital infrastructure, especially in rural and remote areas. While major cities boast high-speed internet and extensive mobile coverage, much of rural Australia continues to struggle with connectivity, which can strongly undermine the efficacy of telehealth services. This is compounded by Australia's enormous geographical size, which makes deploying infrastructure costly and logistically challenging in remote regions such as the Outback. In Indigenous communities, this issue is even more significant since limited internet availability directly limits them from reaping the benefits of telemedicine innovation. Governments have invested in initiatives to help improve connectivity, but these are in progress and take time to close the digital gap completely. In the absence of trustworthy internet, telemedicine consultations can be interrupted or out of the question, restricting healthcare equity and virtual care's complete potential in such populations.
Regulatory Difficulty and Disjointed Health Systems
Australia's regulatory environment offers a challenging complexity for telemedicine practitioners, with the country's healthcare system being multi-jurisdictional in nature. Australia's federal framework translates to the national government's control of Medicare and general health funding, with states and territories in charge of licensing, privacy legislation, and delivery of services regulations. Fragmentation creates inconsistencies in telemedicine rollout and compliance needs, making it more complex for providers to deliver seamless, borderless virtual care. Moreover, the regulatory landscape requires much to maintain compliance with standards of privacy, clinical governance, and professional licensure, the cost of which may be particularly prohibitive for small telehealth ventures. The continuous development of telemedicine-specific regulation also requires providers to be highly responsive in order to continue complying. This regulatory intricacy is distinguishable from more centralized healthcare models in other parts of the world and is an uncommon hurdle that will need to be overcome to facilitate more integrated telemedicine growth throughout Australia.
Patient Acceptance and Digital Literacy Barriers
Whereas telemedicine holds tremendous potential, patient acceptance and digital literacy are still strong challenges in the context of Australia. Some population groups like older adults and Indigenous people, for example, are less at ease with digital technologies or more hesitant about online consultations versus conventional face-to-face care. In the most rural areas, where telemedicine would be most valuable, decreased digital proficiency and reduced exposure to telehealth platforms tend to discourage utilization. In addition, cultural issues, language differences, and privacy and quality of care trust factors may dictate whether patients are willing to use telemedicine. To overcome this, healthcare providers need to invest in cultural competency training, education, and communication strategies attuned to diverse populations to build patient confidence and utilization. The problem is special in Australia because of the country's multicultural composition and large number of remote Aboriginal communities with special healthcare needs and health beliefs. Overcoming these barriers is essential to ensuring telemedicine delivers equitable and effective healthcare solutions nationwide.
Australia Telemedicine Market News:
- In October 2023, Vitura Health Limited announced that it has entered into a binding agreement to acquire the entire issued capital of Doctors on Demand (DoD). DoD is a private Australian company that operates a leading digital platform to facilitate the treatment of patients and the provision of telehealth, healthcare and related services via videoconference.
- In March 2023, Woolworths-owned HealthyLife launched telehealth service for its Australian users. It has tapped a third-party virtual platform provider, ASX-listed Global Health, to help connect patients with general practitioners (GPs), dietitians, and nutritionists who can provide health consultations, medical certificates, e-scripts and referrals.
Australia Telemedicine Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on component, modality, delivery mode, facility, application, and end user.
Component Insights:
- Product
- Hardware
- Software
- Others
- Services
- Tele-Consulting
- Tele-Monitoring
- Tele-Education
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the component. This includes product (hardware, software, and others) and services (tele-consulting, tele-monitoring, and tele-education).
Modality Insights:
- Real-Time
- Store and Forward
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the modality have also been provided in the report. This includes real-time, store and forward, and others.
Delivery Mode Insights:
- Web/Mobile
- Audio/Text-based
- Visualized
- Call Centers
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the delivery mode. This includes web/mobile (audio/text-based, visualized), and call centers.
Facility Insights:
- Tele-Hospital
- Tele-Home
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the facility have also been provided in the report. This includes tele-hospital and tele-home.
Application Insights:
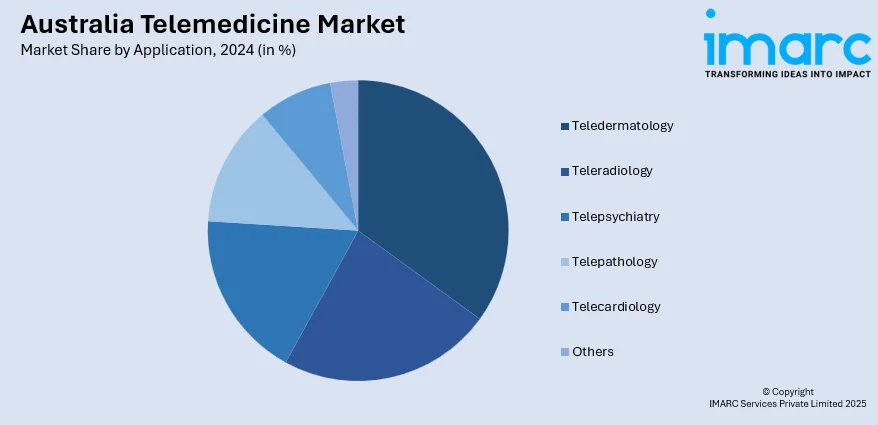
- Teledermatology
- Teleradiology
- Telepsychiatry
- Telepathology
- Telecardiology
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application. This includes teledermatology, teleradiology, telepsychiatry, telepathology, telecardiology, and others.
End User Insights:
- Providers
- Payers
- Patients
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes providers, payers, patients, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Telemedicine Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered |
|
| Modalities Covered | Real-Time, Store and Forward, Others |
| Delivery Modes Covered |
|
| Facilities Covered | Tele-hospital, Tele-home |
| Applications Covered | Teledermatology, Teleradiology, Telepsychiatry, Telepathology, Telecardiology, Others |
| End Users Covered | Providers, Payers, Patients, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia telemedicine market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia telemedicine market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia telemedicine industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia telemedicine market was valued at USD 840.9 Million in 2024.
The Australia telemedicine market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 13.15% during 2025-2033.
The Australia telemedicine market is expected to reach a value of USD 2,556.3 Million by 2033.
The Australia telemedicine market trends include increased integration with public healthcare, growing use in mental health and aged care, and expansion in rural and Indigenous communities. Advances in digital infrastructure and patient acceptance, combined with government support, are fueling a shift toward hybrid models blending virtual and in-person healthcare services nationwide.
The Australia telemedicine market is driven by government Medicare support, the need to improve healthcare access in remote and Indigenous communities, rising digital adoption, and growing demand for mental health and aged care services. These factors collectively boost telehealth’s role in providing timely, accessible, and cost-effective healthcare nationwide.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












