
Australia Vaccine Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Patient Type, Indication, Route of Administration, Product Type, Treatment Type, Distribution Channel, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Vaccine Market Summary:
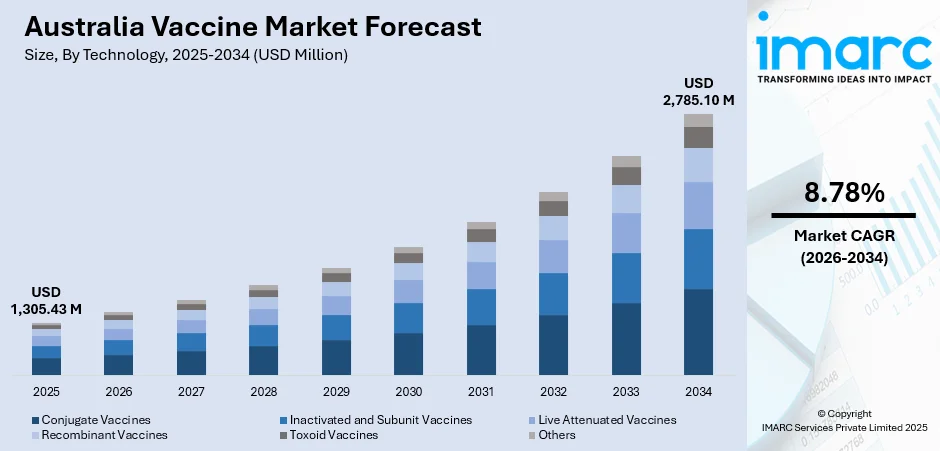
The Australia vaccine market size was valued at USD 1,305.43 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2,785.10 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.78% from 2026-2034.
The Australian vaccine market is experiencing robust expansion driven by the nation's comprehensive National Immunisation Program, increasing infectious disease prevalence, technological innovations in vaccine development, and substantial government investment in pandemic preparedness. The convergence of demographic aging, heightened public health awareness, and strategic infrastructure investments is fundamentally reshaping the competitive landscape, creating substantial opportunities for market participants across the pharmaceutical value chain and positioning Australia as a regional leader in vaccine manufacturing and distribution.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Technology: Inactivated and subunit vaccines dominate the market with a share of 30% in 2025, driven by their proven safety profile, established manufacturing infrastructure, and widespread application across influenza and bacterial disease prevention programs.
- By Patient Type: Paediatric segment leads the market with a share of 60% in 2025, supported by Australia's comprehensive childhood immunization schedule and government-funded vaccination programs targeting infants and children.
- By Indication: Bacterial diseases represent the largest segment with a market share of 55% in 2025, owing to the inclusion of pneumococcal, meningococcal, and pertussis vaccines in the National Immunization Program schedule.
- By Route of Administration: Intramuscular and subcutaneous administration leads the market with 70% market share in 2025, reflecting the predominant delivery method for most NIP-funded vaccines including influenza, pneumococcal, and childhood immunizations.
- By Product Type: Multivalent vaccines dominate with 65% market share in 2025, driven by combination vaccines that protect against multiple diseases in single administrations, improving compliance and reducing healthcare visits.
- By Treatment Type: Preventive vaccines hold 80% of the market in 2025, reflecting Australia's strong focus on prophylactic immunization programs and disease prevention strategies.
- By Distribution Channel: Hospital pharmacies lead with 35% market share in 2025, supported by their role in administering specialized vaccines and serving as primary immunization points for inpatients and high-risk populations.
- By End User: Hospitals represent the largest end-user segment with 40% market share in 2025, driven by their comprehensive immunization services, specialized vaccine storage capabilities, and role in administering vaccines to vulnerable populations.
- Key Players: The Australia vaccine market exhibits competitive intensity, with major multinational pharmaceutical corporations competing across product segments. The market is characterized by ongoing technological innovation, strategic government partnerships, and significant infrastructure investments in domestic manufacturing capabilities.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Australian vaccine market demonstrates remarkable momentum, driven by growing public health awareness, rising infectious disease prevalence, and comprehensive national immunization programs targeting populations across the lifespan. Strategic government support through robust policy frameworks provides comprehensive guidance for vaccine access, establishing a vision for a healthier Australia through immunization and reducing the impact of vaccine-preventable diseases through high uptake of safe, effective, and equitable programs. The convergence of technological innovation expanded domestic manufacturing capabilities, and public-private research collaborations is fundamentally reshaping the competitive landscape and creating substantial opportunities for market participants across the pharmaceutical value chain. In June 2025, the Australian Government launched the National Immunization Strategy for Australia 2025-2030, setting out six key priority areas to increase and sustain immunization uptake, strengthen trust in vaccines, and improve equitable access particularly for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
Australia Vaccine Market Trends:
Expansion of Domestic Vaccine Manufacturing Infrastructure
Australia is witnessing significant expansion in domestic vaccine manufacturing capabilities, with substantial investments in advanced production facilities. The CSL Seqirus facility in Tullamarine represents the only cell-based influenza vaccine manufacturing facility in the Southern Hemisphere, creating a supply chain worth more than AUD 300 Million annually to the Australian economy. Additionally, Moderna's agreement with the Australian Government to build an mRNA vaccine manufacturing facility in Victoria, expected to produce up to 100 million vaccine doses annually, further strengthens the nation's sovereign manufacturing capabilities and pandemic preparedness infrastructure.
Introduction of Novel RSV Prevention Programs
The landscape of respiratory syncytial virus prevention in Australia evolved significantly with the introduction of maternal RSV vaccination and infant monoclonal antibody programs. The National RSV Mother and Infant Protection Program commenced, providing pregnant women with free access to the Abrysvo vaccine under the National Immunisation Program. Complementary state-funded programs provide nirsevimab to eligible infants, with early real-world data demonstrating substantial effectiveness against RSV-associated hospitalisation, resulting in significantly fewer RSV-related hospital admissions than initially forecast during the initial rollout season.
Expansion of Pharmacy Vaccination Services
The Australian Government's implementation of the National Immunisation Program Vaccinations in Pharmacy (NIPVIP) Program from January 2024 has transformed vaccine accessibility across the nation. Participating pharmacies can receive payments for administering NIP vaccines, enabling eligible individuals aged five years and over to access free vaccinations at community pharmacies. This expansion has been accompanied by broadening pharmacist vaccination scopes across states and territories, with Victorian intern pharmacists now authorised to administer vaccines under supervision, significantly expanding the immunisation workforce capacity.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Australia vaccine market demonstrates robust growth potential throughout the forecast period, underpinned by strategic government initiatives, expanding immunisation schedules, and ongoing investment in domestic manufacturing infrastructure. In June 2025, the Australian government has unveiled its new National Immunization Strategy in order to direct Australia's battle against diseases that can be prevented by vaccination during the next five years. The market generated a revenue of USD 1,305.43 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 2,785.10 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.78% from 2026-2034.
Australia Vaccine Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Inactivated and Subunit Vaccines | 30% |
| Patient Type | Paediatric | 60% |
| Indication | Bacterial Diseases | 55% |
| Route of Administration | Intramuscular and Subcutaneous | 70% |
| Product Type | Multivalent Vaccine | 65% |
| Treatment Type | Preventive Vaccine | 80% |
| Distribution Channel | Hospital Pharmacies | 35% |
| End User | Hospitals | 40% |
Technology Insights:
- Conjugate Vaccines
- Inactivated and Subunit Vaccines
- Live Attenuated Vaccines
- Recombinant Vaccines
- Toxoid Vaccines
- Others
The inactivated and subunit vaccines segment dominates with a market share of 30% of the total Australia vaccine market in 2025.
Inactivated and subunit vaccines represent the cornerstone of Australia's immunization landscape, encompassing seasonal influenza vaccines, pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, and hepatitis vaccines that form integral components of the National Immunization Program. These vaccine technologies utilize killed or fragmented pathogen components to stimulate immune responses without causing disease, offering favorable safety profiles particularly suitable for immunocompromised individuals and elderly populations. The December 2024 opening of CSL Seqirus' AUD 800 Million cell-based influenza vaccine manufacturing facility in Tullamarine represents a transformative development, establishing the Southern Hemisphere's first cell-based production capability with capacity to manufacture seasonal and pandemic influenza vaccines under a long-term agreement with the Australian Government.
The segment benefits from established manufacturing infrastructure, extensive clinical evidence supporting efficacy and safety, and broad applicability across diverse indication categories from respiratory infections to bacterial diseases. Cell-based manufacturing technology offers significant advantages over traditional egg-based production, including faster scale-up capabilities for pandemic response, reduced production timelines, and elimination of egg-related allergen concerns that restrict vaccine access for certain populations. The Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration has registered multiple inactivated vaccine formulations for the 2025 influenza season, including both egg-based and cell culture-based quadrivalent vaccines, reflecting the technology's continued evolution and market relevance.
Patient Type Insights:
- Paediatric
- Adult
The paediatric segment leads the market with a share of 60% of the total Australia vaccine market in 2025.
Australia's paediatric vaccination segment encompasses comprehensive immunization programs targeting infants, children, and adolescents through scheduled vaccinations administered at specific developmental milestones. The National Immunization Program provides free vaccines at scheduled ages from birth through adolescence, including protection against diseases such as diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, pneumococcal disease, meningococcal disease, measles, mumps, rubella, and human papillomavirus. According to the National Centre for Immunization Research and Surveillance, childhood vaccination coverage rates in 2024 stood at 91.6% for one-year-olds, 89.4% for two-year-olds, and 92.7% for five-year-olds, though these rates represent concerning declines from pre-pandemic levels.
The segment's dominance reflects the intensive immunization schedule during early childhood years and strong government incentive programs linking vaccination status to family tax benefits, creating structural demand drivers that underpin market growth. From September 2025, the National Immunization Program transitioned from Prevenar 13 to Prevenar 20 (20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine) for children, expected to prevent more cases of invasive pneumococcal disease compared to the previous formulation. Adolescent vaccination programs targeting HPV and meningococcal ACWY disease continue through school-based delivery models, though coverage rates have declined, with HPV vaccination coverage dropping below 80% in boys during 2024, prompting renewed focus on strategies to address vaccine hesitancy and access barriers.
Indication Insights:
- Bacterial Diseases
- Meningococcal Disease
- Pneumococcal Disease
- Diphtheria/Tetanus/Pertussis (DPT)
- Tuberculosis
- Haemophilus Influenzae (Hib)
- Typhoid
- Others
- Viral Diseases
- Hepatitis
- Influenza
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- Measles/Mumps/Rubella (MMR)
- Rotavirus
- Herpes Zoster
- Varicella
- Japanese Encephalitis
- Rubella
- Polio
- Rabies
- Dengue
- Others
The bacterial diseases segment holds the largest share of 55% of the total Australia vaccine market in 2025.
Bacterial disease vaccines constitute the largest indication segment within Australia's vaccine market, encompassing pneumococcal, meningococcal, pertussis, and other bacterial pathogen vaccines integrated throughout the National Immunization Program schedule. The severity of bacterial infections, especially in susceptible groups including newborns, the elderly, and immunocompromised people, is reflected in the segment's predominance, driving comprehensive vaccination strategies across multiple life stages.
The segment experienced significant evolution with the introduction of Prevenar 20 replacing Prevenar 13 on the childhood National Immunisation Program schedule, providing protection against additional pneumococcal serotypes beyond the previous formulation. Real-world data demonstrate that pneumococcal conjugate vaccines achieve strong effectiveness at preventing invasive pneumococcal disease from targeted strains in Australian children, reducing disease burden and hospitalisations across paediatric populations. From July 2024, the meningococcal ACWY vaccine MenQuadfi was funded on the National Immunisation Program, replacing Nimenrix for the adolescent age group, while state-funded meningococcal B vaccination programs continue in South Australia and Queensland, reflecting ongoing expansion of bacterial disease prevention strategies.
Route of Administration Insights:
- Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Administration
- Oral Administration
- Others
The intramuscular and subcutaneous administration segment accounts for 70% of the total Australia vaccine market in 2025.
Intramuscular and subcutaneous injection routes represent the predominant vaccine delivery methods in Australia, reflecting the immunological advantages of parenteral administration for most vaccine formulations currently available on the National Immunization Program. These routes enable direct delivery of antigenic components to immune-responsive tissues, facilitating robust and durable immune responses across diverse vaccine types including inactivated, subunit, conjugate, and mRNA formulations. The expansion of immunization workforce capacity through programs enabling pharmacist and intern pharmacist vaccination services has strengthened delivery infrastructure for injectable vaccines across community settings.
The segment encompasses the vast majority of NIP-funded vaccines including influenza, pneumococcal, meningococcal, pertussis-containing combinations, and the newly introduced RSV vaccines. The maternal RSV vaccination program, which commenced in February 2025, provides Abrysvo vaccine via intramuscular injection to pregnant women from 28 weeks gestation, while nirsevimab monoclonal antibody is administered intramuscularly to eligible infants. The Australian Immunisation Handbook provides comprehensive guidance on injection techniques, site selection, and co-administration protocols, supporting standardised delivery across the diverse network of vaccination providers including general practitioners, hospitals, community health centres, and community pharmacies.
Product Type Insights:
- Multivalent Vaccine
- Monovalent Vaccine
The multivalent vaccine segment dominates with a market share of 65% of the total Australia vaccine market in 2025.
Multivalent vaccines represent the predominant product category within Australia's immunization landscape, combining protection against multiple pathogens or pathogen strains within single formulations to optimize immunization efficiency and patient compliance. These combination products reduce the number of healthcare visits and injections required, particularly important for paediatric populations where comprehensive protection must be achieved through multiple vaccine administrations during early childhood.
The segment's growth trajectory is supported by ongoing development of expanded-valency formulations offering broader protection against pathogen diversity. Quadrivalent influenza vaccines have become standard for seasonal immunization programs, with the 2025 season offering multiple quadrivalent options including both egg-based and cell-based formulations. In September 2025, the National Immunisation Program transitioned from Prevenar 13 to Prevenar 20 (20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine) for childhood vaccination, providing protection against seven additional pneumococcal serotypes including 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 22F, and 33F, with clinical trials demonstrating the expanded formulation is expected to prevent 25-30% more cases of invasive pneumococcal disease in children compared to the previous vaccine.
Treatment Type Insights:
- Preventive Vaccine
- Therapeutic Vaccine
The preventive vaccine segment holds 80% of the total Australia vaccine market in 2025.
Preventive vaccines constitute the overwhelming majority of Australia's vaccine market, reflecting the nation's public health focus on disease prevention through prophylactic immunization strategies. The National Immunization Program centers on preventing vaccine-preventable diseases before exposure occurs, with scheduled vaccinations targeting populations at specific life stages when disease risk is elevated or before anticipated exposure through school attendance, travel, or occupational activities. The National Immunization Strategy for Australia 2025-2030, launched in June 2025, establishes a framework for reducing the impact of vaccine-preventable diseases through high uptake of safe, effective, and equitable immunization programs.
The preventive focus extends across all age groups, from infant immunization schedules through adolescent vaccination programs and adult immunization recommendations for seasonal influenza, pneumococcal disease, and herpes zoster. The introduction of the National RSV Mother and Infant Protection Program in February 2025 represents the latest expansion of preventive immunization, with maternal vaccination transferring protective antibodies to infants and monoclonal antibody prophylaxis providing direct protection for vulnerable newborns.
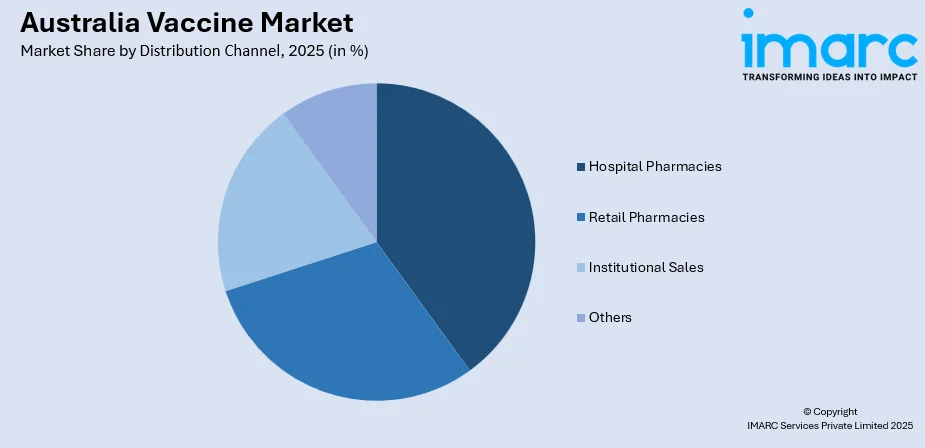
Distribution Channel Insights:
Access the Comprehensive Market Breakdown Request Sample
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Institutional Sales
- Others
The hospital pharmacies segment leads with a share of 35% of the total Australia vaccine market in 2025.
Hospital pharmacies represent the largest distribution channel for vaccines in Australia, serving as critical supply points for inpatient immunization services, specialist vaccination programs, and vaccines requiring specialized storage or administration protocols. Hospital-based vaccination services are particularly important for high-risk populations including immunocompromised patients, pregnant women receiving maternal vaccines, and newborns eligible for RSV prophylaxis through nirsevimab administration. The distribution infrastructure benefits from established cold chain capabilities, quality assurance protocols, and integration with clinical care pathways that ensure appropriate patient selection and adverse event monitoring.
The January 2024 implementation of the National Immunization Program Vaccinations in Pharmacy (NIPVIP) Program has enhanced the role of community pharmacies in vaccine distribution, with participating pharmacies receiving payments of AUD 18.85 per vaccination for administering NIP vaccines to eligible individuals aged five years and over. This program expansion has diversified distribution channels while maintaining hospital pharmacies' critical role for specialized vaccines, maternal immunization programs, and services to vulnerable populations. The expansion of pharmacist vaccination scope across Australian states and territories, including authorization for travel vaccines, meningococcal B, and RSV vaccines in some jurisdictions, continues to reshape distribution channel dynamics.
End User Insights:
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Vaccination Centers
- Academic and Research Institutes
- Others
The hospitals segment represents the largest end user category with 40% of the total Australia vaccine market in 2025.
Hospitals constitute the primary end-user segment for vaccines in Australia, encompassing public and private hospital networks that deliver comprehensive immunization services across inpatient, outpatient, and emergency department settings. Hospital-based vaccination services are essential for maternal immunization programs, neonatal vaccines, and immunization of high-risk patients including those with immunocompromising conditions, chronic diseases, or advanced age. The infrastructure advantages of hospital settings, including established cold chain systems, clinical expertise, and adverse event management capabilities, position hospitals as critical vaccination delivery points.
The 2025 RSV Mother and Infant Protection Program has strengthened hospitals' role in vaccine delivery, with maternity hospitals serving as primary administration points for both maternal Abrysvo vaccination and nirsevimab monoclonal antibody administration to eligible newborns. On 24 November 2023, In Australia, nirsevimab was approved for the prevention of RSV lower respiratory tract disease in newborns and infants born during or beginning their first RSV season, as well as in children up to 24 months old who are still susceptible to severe RSV disease during their second RSV season. Hospital-based specialist immunization services also support vaccination of complex patients requiring individualized assessment, including those with previous adverse events, immunocompromising conditions, or contraindications requiring specialist review before vaccination.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria and Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales dominates the Australia vaccine market, driven by the largest population base concentrated in Sydney metropolitan area, extensive healthcare infrastructure, leading research institutions, and comprehensive immunization service networks across urban and regional communities.
Victoria and Tasmania represent a significant market share, supported by Melbourne's advanced healthcare ecosystem, presence of major vaccine manufacturing facilities including CSL Seqirus operations, strong pharmaceutical research capabilities, and well-established immunization delivery networks.
Queensland holds substantial market presence, driven by tropical disease vaccination requirements, state-funded meningococcal B programs, growing population demographics, expanding healthcare infrastructure across coastal regions, and proactive public health immunization initiatives targeting diverse communities.
Northern Territory & South Australia region demonstrates steady growth, characterized by targeted vaccination programs for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities, remote area immunization services, South Australia's state-funded meningococcal B program, and specialized tropical disease prevention initiatives.
Western Australia exhibits notable market growth, supported by pioneering RSV immunization programs demonstrating strong effectiveness outcomes, expanding pharmacy vaccination services, robust cold chain infrastructure across remote regions, and innovative public health delivery models.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Australia Vaccine Market Growing?
Rising Infectious Disease Burden Driving Immunization Demand
Australia experienced unprecedented infectious disease activity during 2024, with record-breaking respiratory illness seasons fundamentally reshaping vaccine demand patterns and public health priorities. Between January 1 and October 2024, 349,728 influenza alerts were registered, making the 2024 flu season the worst since 2019. This dramatic disease burden has heightened awareness of vaccine importance among healthcare providers, policymakers, and the general population, driving increased investment in immunization infrastructure and expanded vaccination programs. The ongoing global resurgence of measles across all regions, including countries in the Asia-Pacific region, has prompted additional vigilance and catch-up vaccination initiatives to protect Australian populations against importation risks.
Strategic Government Investment in Domestic Manufacturing Capabilities
The Australian Government has made substantial investments to strengthen sovereign vaccine manufacturing capabilities, enhancing pandemic preparedness and reducing reliance on international supply chains. Moderna's partnership with the Australian Government to establish mRNA vaccine manufacturing in Victoria further expands domestic production capabilities, with expected capacity to produce up to 100 million vaccine doses annually. These investments create structural market growth drivers through expanded local production capacity, reduced import dependency, and enhanced ability to respond rapidly to emerging health threats.
Expansion of National Immunization Program Coverage
Continuous expansion of the National Immunization Program to incorporate new vaccines and extend eligibility criteria drives sustained market growth across multiple disease categories. The February 2025 introduction of the National RSV Mother and Infant Protection Program provides free maternal RSV vaccination to all eligible pregnant women under the NIP, complemented by state-funded nirsevimab programs for infants. The September 2025 transition to Prevenar 20 on the childhood schedule expands pneumococcal protection to additional serotypes. From January 2024, the NIPVIP Program extended free National Immunisation Program (NIP) vaccine access through community pharmacies, improving convenience and accessibility. The National Immunization Strategy 2025-2030 establishes a comprehensive framework for sustained program evolution, with priorities including strengthening trust in vaccines, improving equitable access for priority populations, and enhancing immunization data systems.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Australia Vaccine Market is Facing?
Declining Vaccination Coverage Rates Across Age Groups
Australia has experienced concerning and sustained declines in vaccination coverage rates since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, with childhood vaccination coverage at all age milestones falling below the aspirational target of 95%. Coverage at 24 months dropped below 90% in 2024 for the first time since 2016, while adolescent HPV vaccination rates fell below 80% in boys during 2024, representing the greatest declines observed between 2023 and 2024. These coverage gaps reflect complex challenges including vaccine hesitancy, access barriers, and competing healthcare priorities.
Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation Challenges
Vaccine hesitancy and misinformation continue to present significant challenges to immunization program effectiveness, with low levels of trust associated with vaccine skepticism and refusal. The pandemic period left some individuals with lingering questions and misperceptions about vaccines, supercharged by misinformation and increasing political polarization of vaccination issues. These attitudinal barriers particularly affect uptake of discretionary vaccines and timely completion of childhood vaccination schedules.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and International Dependencies
Despite significant investments in domestic manufacturing, Australia remains partially dependent on international vaccine supply chains for certain products, creating vulnerability to global supply disruptions, manufacturing delays, and competing international demand during pandemic situations. The complexity of vaccine production processes, stringent quality requirements, and specialized cold chain logistics create supply constraints that can delay program implementation and limit market expansion.
Competitive Landscape:
The Australia vaccine market exhibits competitive intensity characterized by the presence of multinational pharmaceutical corporations alongside domestic manufacturers competing across technology platforms, indication categories, and distribution channels. Market dynamics reflect strategic positioning across mRNA, protein-based, and traditional vaccine technologies, with leading companies maintaining significant market presence. The competitive landscape is increasingly shaped by domestic manufacturing capabilities, government partnership arrangements, and technological innovation in areas including cell-based production, mRNA platforms, and expanded-valency formulations.
Recent Developments:
- February 2025: The National RSV Mother and Infant Protection Program commenced, providing pregnant women free access to Abrysvo vaccine under the National Immunisation Program, with early real-world data from Western Australia demonstrating nirsevimab effectiveness of 88.2% against RSV-associated hospitalization, corresponding to 57% fewer hospitalisations than forecast predictions.
Australia Vaccine Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Conjugate Vaccines, Inactivated And Subunit Vaccines, Live Attenuated Vaccines, Recombinant Vaccines, Toxoid Vaccines, Others |
| Patient Types Covered | Paediatric, Adult |
| Indications Covered |
|
| Route of Administrations Covered | Intramuscular and subcutaneous administration, Oral administration, Others |
| Product Types Covered | Multivalent vaccine, Monovalent vaccine |
| Treatment Types Covered | Preventive vaccine, Therapeutic vaccine |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Hospital pharmacies, Retail pharmacies, Institutional sales, Others |
| End Users Covered | Hospitals, Clinics, Vaccination centers, Academic and research institutes, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia vaccine market size was valued at USD 1,305.43 Million in 2025.
The Australia vaccine market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.78% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 2,785.10 Million by 2034.
Multivalent vaccinations are the most popular due to combination vaccines, which provide protection against several diseases in a single dose, increasing compliance and lowering medical visits.
Key factors driving the Australia Vaccine market include rising infectious disease prevalence with 2024 recording Australia's highest influenza season, strategic government investment in domestic manufacturing infrastructure, expansion of the National Immunisation Program to include RSV vaccines, and implementation of the National Immunisation Strategy 2025-2030.
Major challenges include declining vaccination coverage rates with childhood immunisation falling below 95% targets, vaccine hesitancy and misinformation affecting uptake, supply chain vulnerabilities for certain products, and the need to address equity gaps in vaccination access for priority populations including Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












