
Australia Waste to Energy Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Waste Type, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Waste to Energy Market Size and Share:
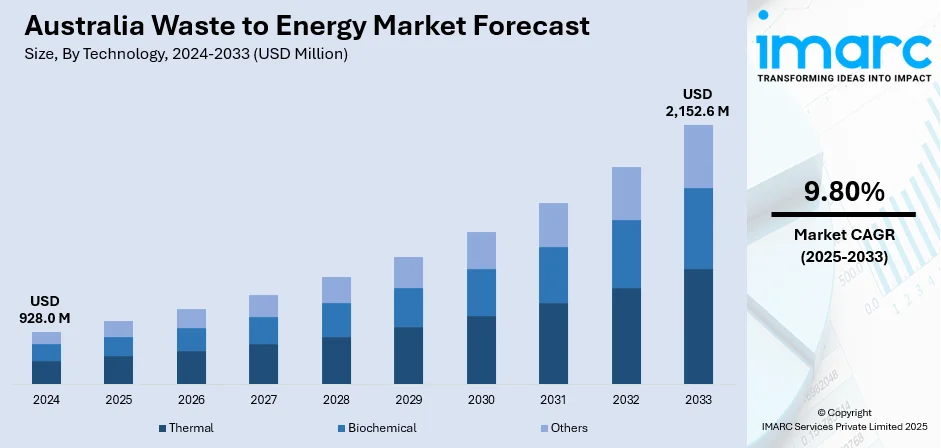
The Australia waste to energy market size reached USD 928.0 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 2,152.6 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 9.80% during 2025-2033. The changing government policies and regulatory reforms that seek to encourage sustainable waste management are impelling the market growth. This trend, along with the constraints on available landfill space and increased environmental pressure, is contributing to the market growth. Additionally, the growing electricity demand is expanding the Australia waste to energy market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 928.0 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 2,152.6 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 9.80% |
Key Trends of Australia Waste to Energy Market:
Addressing Landfill Constraints and Environmental Concerns
The Australia market is growing as the nation is increasingly facing constraints on available landfill space and increased environmental pressure. According to an article published by BDO Australia in 2025, the country produces approximately 75.8 million tons of wastage every year, and this count is increasing every year. As major cities such as Sydney and Melbourne approach landfill capacity, state governments are tightening landfill diversion requirements. As volumes of waste rise from urban developments, conventional methods of disposal become unsustainable. Levies on landfills are increasing, especially in regions such as Victoria and New South Wales, which further discourage waste dumping and encourage energy recovery measures. At the same time, the environmental risks of landfilling, such as methane release, groundwater pollution, and loss of biodiversity, are encouraging environmental authorities to prefer alternatives like incineration with energy recovery.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Increasing Government Policy Support and Regulatory Reforms
The changing government policies and regulatory reforms that seek to encourage sustainable waste management are impelling the Australia waste to energy market growth. State and federal governments are implementing policies that favor cutting-edge thermal treatment technology through financial incentives, transparent permitting procedures, and renewable energy targets. Additionally, the 2024 National Waste Policy Action Plan outlined where Australia needed to concentrate its efforts in order to shift to a safe circular economy. It was prepared in accordance with the 2018 National Waste Policy. Moreover, grant financing and infrastructure assistance are being increased to help accelerate waste to energy (WtE) projects. By coordinating climate action plans with waste reduction objectives, the government is fostering a positive investment environment for public-private partnerships in this area.
Growing Energy Demand and the Need for Diversification
The country’s growing electricity demand and an urgent need to diversify energy sources amid the transition to a low-carbon economy are offering a favorable market outlook. As coal-fired power plants are being phased out and the reliability of renewable sources like wind and solar remains intermittently variable, WtE is emerging as a stable, baseload energy alternative. The integration of WtE into Australia’s energy mix is offering dual benefits like waste reduction and consistent power generation. Municipalities and energy utilities are increasingly partnering on projects that convert municipal solid waste, agricultural residues, and industrial refuse into electricity or heat. This movement is supporting grid stability while aligning with national decarbonization goals. In regional areas, where grid infrastructure is less robust, localized WtE plants are providing reliable energy while simultaneously managing local waste.
Growth Drivers of Australia Waste to Energy Market:
Rising Waste Generation and Urbanization
Australia’s steadily growing population and accelerating urban development are significantly increasing the amount of waste generated across municipal, commercial, and industrial sectors. This increasing amount of waste creates a huge burden to the current waste management infrastructure, which, in large part, is already at capacity or has a hard time keeping up. Landfill becomes strained, and environmentally conscious hopes are placed on the necessity of a permanent system of waste management. An acceptable solution can be the Waste-to-energy (WtE) technology that transforms waste that is unable to be recycled into power and heat. One of the many benefits of these facilities, besides more efficient handling of waste, is the reduced reliance on landfills and energy generation in the country. WtE plants may also be implemented as a part of more general urban sustainability policies in fast-developing urban districts. They could help to create eco-friendly and stronger communities.
Advancements in Waste Conversion Technologies
Technological innovation is playing a critical role in advancing Australia’s waste-to-energy sector. Modern waste conversion methods such as gasification, pyrolysis, and anaerobic digestion are transforming how waste is processed, enabling more efficient and cleaner energy generation. According to the Australia waste to energy market analysis, these technologies can handle a broader spectrum of waste types, including organic, industrial, and hazardous materials, making WtE solutions more adaptable and cost-effective. Improved emissions control and higher energy recovery rates also enhance environmental performance, making WtE plants more attractive to regulators, investors, and local communities. As these systems become more refined and commercially viable, they support the expansion of decentralized energy production, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon footprints. Continued innovation in this space is key to scaling up sustainable waste management and renewable energy outcomes.
Private Sector Investment and Public-Private Partnerships
Private investment is emerging as a key factor driving the Australia waste-to-energy market demand. Attracted by the long-term profitability and environmental benefits of WtE projects, investors and infrastructure firms are increasingly funding new developments. This interest is complemented by a growing number of public-private partnerships (PPPs), which combine government backing with private sector expertise and capital. Such collaborations help share financial risk, improve project delivery timelines, and ensure regulatory compliance. PPPs are particularly important for large-scale WtE facilities, which require significant upfront investment and long-term operational commitments. These partnerships also support innovation and scalability by leveraging private sector efficiency and government incentives. As Australia moves toward a circular economy, private-public collaboration will be essential in building a resilient, future-ready waste and energy infrastructure.
Government Support of Australia Waste to Energy Market:
Infrastructure Funding and Grant Programs
The Australian government is playing a pivotal role in supporting the growth of the waste-to-energy (WtE) sector by providing dedicated funding at both federal and state levels. Through initiatives like the Recycling Modernisation Fund and financial backing from the Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC), WtE developers gain access to crucial capital for planning, construction, and early-stage project development. These grants and loans help offset high upfront costs and make innovative waste conversion technologies more financially viable. Funding is often tied to clear environmental and operational goals, ensuring that supported projects align with national sustainability targets. By reducing financial barriers and fostering long-term viability, these funding programs are helping to accelerate the transition toward a cleaner, more efficient waste management and renewable energy landscape across the country.
National Waste and Resource Recovery Strategies
Australia’s long-term commitment to environmental sustainability is reflected in national and state-level strategic frameworks that focus on waste reduction, resource recovery, and the transition to a circular economy. The National Waste Policy Action Plan and various state circular economy roadmaps provide structured guidance and measurable goals for waste minimization and energy recovery. These strategies explicitly position waste-to-energy (WtE) as a vital tool for managing non-recyclable waste and reducing landfill reliance. By encouraging the integration of WtE into broader waste management systems, the policies promote innovation, investment, and infrastructure development. They also offer a regulatory foundation that supports consistent planning and operational practices. These coordinated efforts ensure that WtE adoption aligns with environmental goals while creating economic opportunities and addressing long-term waste challenges.
Streamlined Regulatory Pathways and Approvals
To enhance the scalability and attractiveness of waste-to-energy (WtE) projects, Australian governments are actively working to simplify the regulatory landscape. Efforts are being made to streamline approval processes for zoning, environmental assessments, and energy integration, which are traditionally time-consuming and complex. This regulatory reform is especially beneficial for developers, reducing delays, lowering compliance burdens, and facilitating faster project deployment. A more predictable and transparent approval system increases investor confidence, encouraging both domestic and international participation in the market. These changes also ensure that WtE initiatives meet strict environmental standards without being hindered by bureaucratic inefficiencies. By refining administrative pathways, government authorities are helping accelerate the growth of the WtE sector, making it a more viable and competitive component of Australia’s clean energy and waste management strategy.
Australia Waste to Energy Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on technology and waste type.
Technology Insights:
- Thermal
- Incineration
- Pyrolysis
- Gasification
- Biochemical
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology. This includes thermal (incineration, pyrolysis, and gasification), biochemical, and others.
Waste Type Insights:
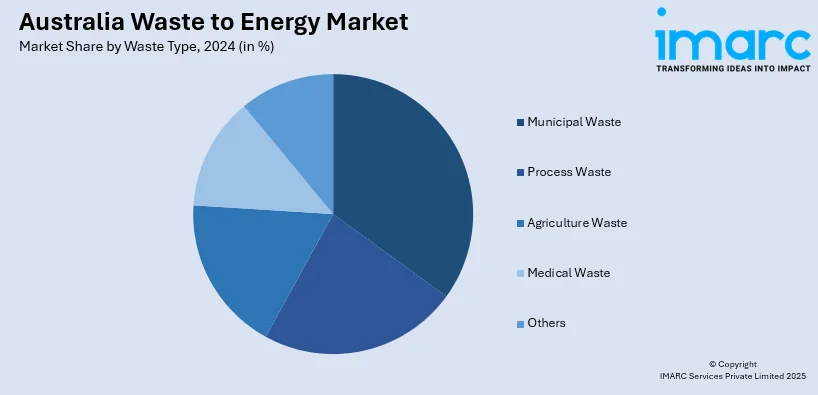
- Municipal Waste
- Process Waste
- Agriculture Waste
- Medical Waste
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the waste type have also been provided in the report. This includes municipal waste, process waste, agriculture waste, medical waste, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Waste to Energy Market Report News:
- In July 2025, the ACCC raised initial competition concerns regarding Acciona’s proposed acquisition of the East Rockingham Waste-to-Energy Project, which is presently under administration and receivership. Acciona currently holds a 10% ownership stake in the project, serves as a creditor, and acts as its engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) contractor.
- In April 2025, Australia moved closer to establishing its first major advanced soft plastics recycling facility, as Cleanaway and Viva Energy have finalized a pre-feasibility study for the project. This collaboration seeks to transform soft plastic waste into food-grade recycled products by combining Cleanaway’s extensive national waste collection infrastructure with Viva Energy’s capabilities in refining and polymerization processes.
- In October 2024, Australia entered a new phase in waste management with the launch of its first large-scale waste-to-energy power plant. This milestone signals a shift toward incinerating household waste to generate electricity, rather than relying on traditional landfilling. Several similar projects are now in development across the country, aiming to curb landfill use and harness energy from waste. While this approach offers potential environmental benefits by reducing landfill dependency, it has also sparked concerns among environmental advocates.
Australia Waste to Energy Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered |
|
| Waste Types Covered | Municipal Waste, Process Waste, Agriculture Waste, Medical Waste, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia waste to energy market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia waste to energy market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia waste to energy industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The waste to energy market in Australia was valued at USD 928.0 Million in 2024.
The Australia waste to energy market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.80% during 2025-2033.
The Australia waste to energy market is projected to reach a value of USD 2,152.6 Million by 2033.
Australia’s waste-to-energy market is characterized by rapid adoption of advanced technologies such as incineration, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. Circular economy integration is central, combining recycling and energy recovery across municipal and industrial waste.
The market growth is propelled by national landfill constraints and stricter regulatory mandates to divert waste. Government policies, including the National Waste Policy and financial incentives, also support WtE adoption. Rising electricity demand and the desire for energy diversification amid decarbonization efforts further accelerate investment in waste-to-energy solutions.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












