
Brazil Agricultural Biotechnology Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Organism Type, Technology, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Brazil Agricultural Biotechnology Market Summary:
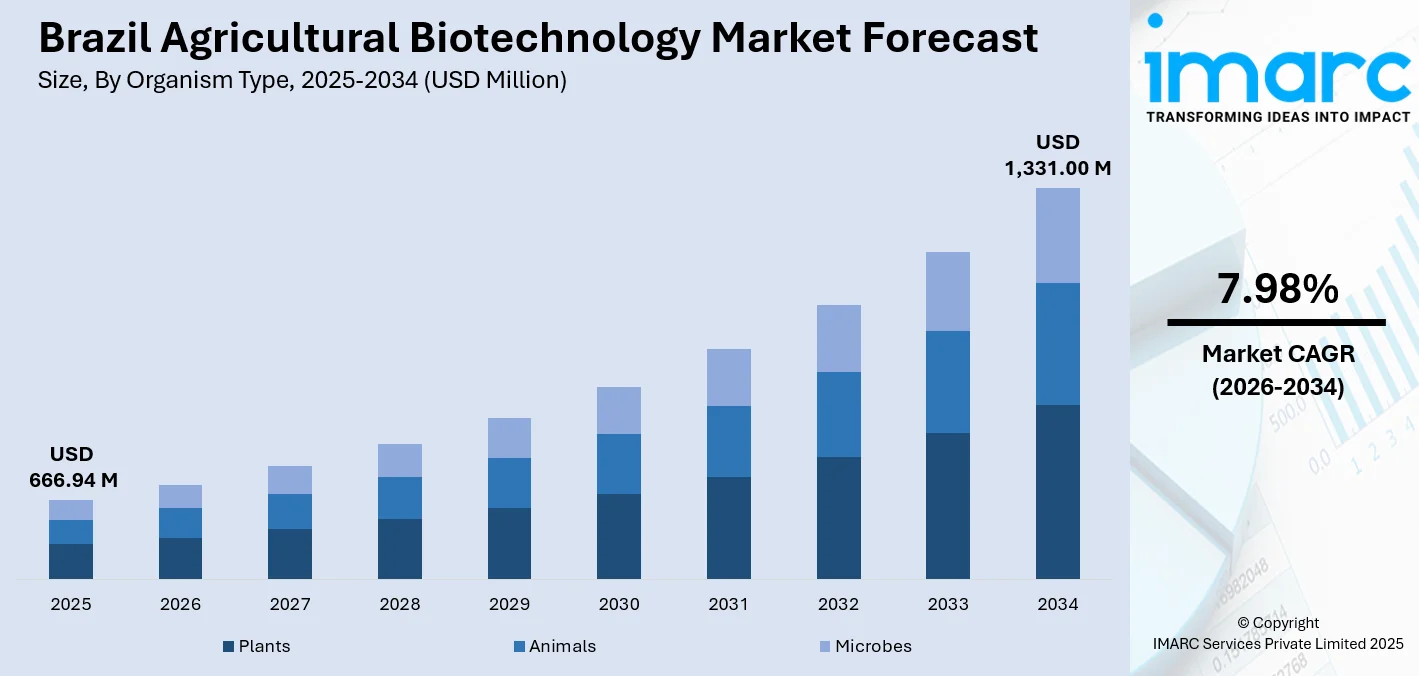
The Brazil agricultural biotechnology market size was valued at USD 666.94 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1,331.00 Million by 2034, growing at a a compound annual growth rate of 7.98% from 2026-2034.
Brazil's agricultural biotechnology sector advances through genomic innovations, precision breeding, and enhanced crop development. The market benefits from extensive agricultural land, favorable climatic conditions, and strong research infrastructure supporting biotechnology adoption. Growing emphasis on sustainable farming practices and food security drives continued investment in biological solutions for agricultural productivity enhancement, expanding the Brazil agricultural biotechnology market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Organism Type: Plants dominate the market with a share of 47% in 2025, owing to extensive cultivation of genetically modified soybeans, corn, and cotton varieties that offer pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, and improved yield characteristics across diverse agroclimatic zones.
- By Technology: Genome editing leads the market with a share of 24% in 2025. This dominance is driven by CRISPR-based precision breeding applications enabling targeted trait modifications, regulatory acceptance for gene-edited crops, and reduced development timelines compared to traditional genetic modification approaches.
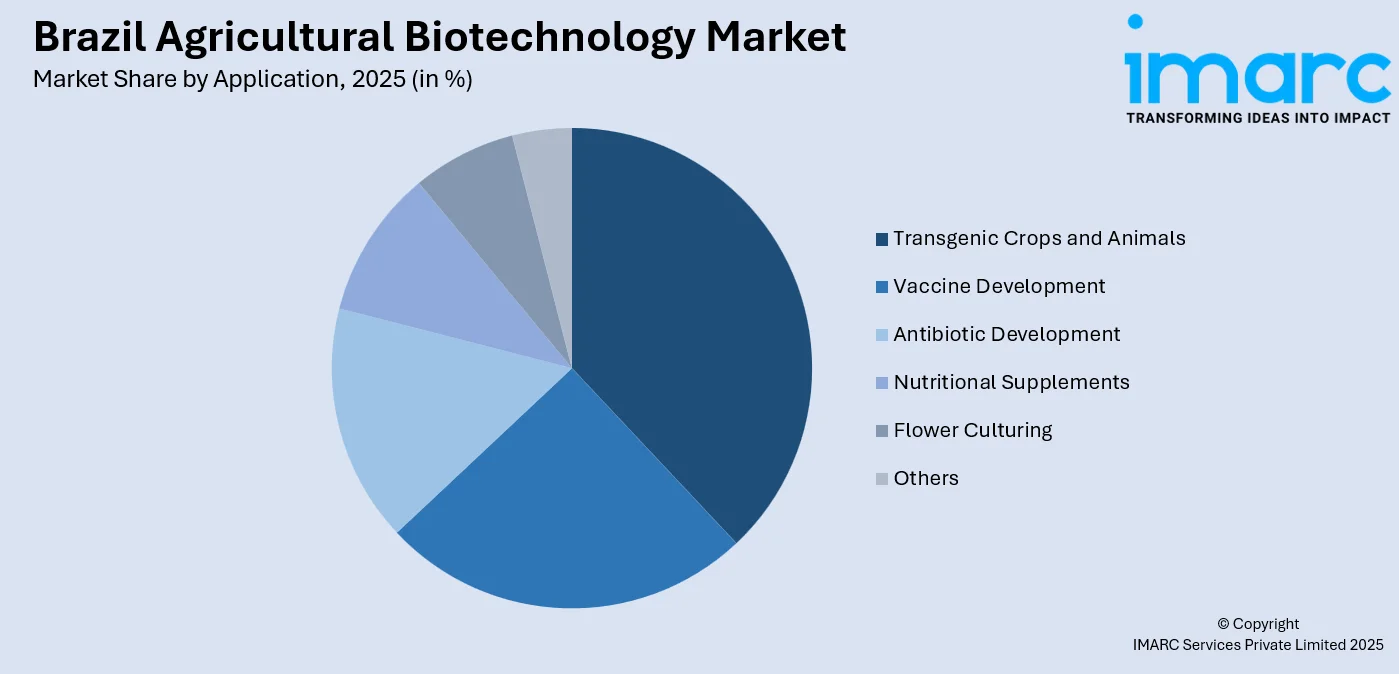
- By Application: Transgenic crops and animals hold the largest segment with a market share of 38% in 2025, reflecting widespread commercial adoption of biotech-enhanced agricultural commodities that address pest management challenges, reduce chemical input requirements, and enhance overall farm productivity.
- By Region: Southeast represents the largest region with 29% share in 2025, driven by concentration of agricultural research institutions in São Paulo, proximity to major grain-producing areas, established biotechnology companies, and robust infrastructure supporting field trials and commercial cultivation.
- Key Players: Key players drive the Brazil agricultural biotechnology market by expanding genomic research capabilities, developing climate-resilient crop varieties, and strengthening partnerships with agricultural cooperatives. Their investments in regulatory compliance, farmer education programs, and seed distribution networks boost adoption rates, accelerate technology deployment, and ensure consistent product availability across diverse agricultural segments.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Brazil's agricultural biotechnology market experiences robust expansion driven by increasing demand for sustainable crop protection solutions and enhanced agricultural productivity. The country's position as a global agricultural powerhouse creates substantial opportunities for biotechnology integration across major commodity crops. Rising farmer awareness regarding biotechnology benefits, coupled with supportive regulatory frameworks, accelerates technology adoption rates. Government initiatives promoting agricultural modernization and food security strengthen market foundations. Growing environmental consciousness drives preference for biological pest control methods and reduced chemical dependency. Investment in research infrastructure and public-private partnerships enhances innovation capabilities. The sector benefits from Brazil's extensive biodiversity resources providing valuable genetic material for crop improvement programs. Expanding export markets for biotech commodities create additional revenue streams for producers. Climate change adaptation requirements increase relevance of drought-resistant and stress-tolerant crop varieties. Digital agriculture integration with biotechnology solutions enables precision farming applications, optimizing resource utilization and maximizing yields across diverse production systems.
Brazil Agricultural Biotechnology Market Trends:
Integration of Digital Agriculture with Biotechnology Solutions
Agricultural biotechnology increasingly converges with digital farming technologies, creating integrated platforms combining genomic data with precision agriculture tools. This integration enables real-time monitoring of crop performance, predictive analytics for trait expression, and data-driven decision-making for seed selection. Farmers utilize smartphone applications accessing biotechnology databases to optimize planting strategies based on soil conditions, weather patterns, and pest pressure forecasts. The combination of biotechnology-enhanced seeds with IoT sensors and satellite imagery maximizes resource efficiency while reducing environmental impact. This trend accelerates as agricultural producers recognize synergies between genetic improvements and digital management systems for comprehensive farm optimization.
Expansion of Genome Editing Applications Beyond Traditional Crops
Genome editing technologies extend beyond conventional commodity crops to encompass specialty crops, horticultural products, and livestock applications. For instance, CRISPR technique reduced development time from 10-12 years using classical breeding to just 6 months for genome-edited soybeans. Brazilian researchers develop gene-edited varieties of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants addressing specific market demands for improved shelf life, nutritional content, and disease resistance. Livestock biotechnology advances focus on animal health improvements, feed efficiency enhancements, and production trait optimization. This diversification reflects maturation of genome editing platforms and regulatory clarity regarding gene-edited organisms. The trend creates new market opportunities while addressing broader agricultural challenges including nutritional security, animal welfare concerns, and sustainable intensification of diverse agricultural systems.
Strengthening of Public-Private Research Partnerships
Collaborative research models between government institutions, universities, and private biotechnology companies intensify to accelerate innovation and technology transfer. These partnerships pool resources, share intellectual property, and distribute development risks across multiple stakeholders. Joint ventures focus on addressing uniquely Brazilian agricultural challenges including tropical disease management, adaptation to diverse climatic conditions, and development of locally relevant crop varieties. Public institutions contribute fundamental research capabilities and germplasm resources while private partners provide commercialization expertise and market access. This collaborative approach shortens development timelines, reduces costs, and ensures biotechnology solutions address practical farming needs while maintaining scientific rigor and regulatory compliance standards. The Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation currently supervises 480 public and private institutions conducting biotechnology research across Brazil.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Brazil agricultural biotechnology market demonstrates strong growth potential driven by expanding agricultural production demands and increasing technology adoption rates. Continuous advancements in genome editing techniques, synthetic biology applications, and precision breeding methodologies enhance product development capabilities. Growing emphasis on sustainable agricultural intensification creates favorable conditions for biotechnology integration across production systems. Rising investment in agricultural research infrastructure and favorable regulatory developments support market expansion. Climate adaptation requirements and food security imperatives strengthen demand for biotechnology solutions addressing environmental stresses and productivity enhancement needs across diverse agricultural segments. The market generated a revenue of USD 666.94 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 1,331.00 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 7.98% from 2026-2034.
Brazil Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Organism Type |
Plants |
47% |
|
Technology |
Genome Editing |
24% |
|
Application |
Transgenic Crops and Animals |
38% |
|
Region |
Southeast |
29% |
Organism Type Insights:
- Plants
- Conventional Techniques
- Established Genetic Modification
- New Breeding Techniques
- Animals
- Conventional Techniques
- Established Genetic Modification
- New Breeding Techniques
- Microbes
- Conventional Techniques
- Established Genetic Modification
- New Breeding Techniques
Plants dominate with a market share of 47% of the total Brazil agricultural biotechnology market in 2025.
Plant-based biotechnology applications maintain market leadership through extensive deployment across Brazil's major agricultural commodities including soybeans, corn, cotton, and sugarcane. The segment benefits from established regulatory pathways, farmer familiarity with transgenic crop management, and proven economic benefits including reduced pesticide costs and increased yields. Brazilian agricultural producers demonstrate strong acceptance of biotech plant varieties addressing specific regional challenges such as tropical pest pressures, fungal diseases, and herbicide-resistant weed management. Recent developments in genome-edited plant varieties expand application possibilities while potentially simplifying regulatory requirements compared to traditional transgenic approaches.
The plant biotechnology segment continues evolving through development of stacked trait varieties combining multiple beneficial characteristics within single crop platforms. In November 2025, Bayer launched the Intacta 5+ soybean trait in Brazil, representing the first technology offering tolerance to five herbicides: mesotrione, dicamba, glyphosate, glufosinate, and 2,4-D, while providing protection against caterpillar pests. Innovations focus on incorporating drought tolerance mechanisms, enhanced nitrogen use efficiency, and improved nutritional profiles alongside existing pest resistance traits. Brazil's diverse agroclimatic zones create demand for regionally adapted varieties optimized for specific environmental conditions. For example, biotech soybean varieties developed specifically for Cerrado region conditions demonstrate superior performance compared to varieties designed for southern production areas. This geographic specialization drives continued research investment and product diversification within the plant biotechnology segment.
Technology Insights:
- Genome Editing
- Synthetic Biology
- Genetic Engineering
- Marker-Assisted Breeding
- Plant Breeding
- Germplasm
- Others
Genome editing leads with a share of 24% of the total Brazil agricultural biotechnology market in 2025.
Genome editing technologies, particularly CRISPR-Cas systems, gain prominence through their precision, efficiency, and potential regulatory advantages over traditional genetic modification approaches. Brazilian researchers leverage these tools for targeted trait improvements without introducing foreign genetic material, potentially qualifying edited varieties as non-transgenic under certain regulatory frameworks. Applications span development of disease-resistant varieties, nutritional enhancement, and adaptation to environmental stresses. The technology's versatility enables rapid iteration and trait stacking while reducing development timelines compared to conventional breeding. Academic institutions and research centers across Brazil establish genome editing facilities, building domestic capacity and reducing dependency on international technology providers.
The genome editing segment attracts substantial investment from both public research institutions and private biotechnology companies recognizing the technology's transformative potential. Collaborative projects between Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation and international partners advance genome editing applications for tropical crops underrepresented in global research portfolios. Recent successes include development of citrus varieties with enhanced resistance to greening disease and cassava varieties with improved nutritional content and disease tolerance. These achievements demonstrate genome editing's practical utility for addressing critical agricultural challenges while establishing Brazil's position in the global agricultural biotechnology innovation landscape.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Vaccine Development
- Transgenic Crops and Animals
- Antibiotic Development
- Nutritional Supplements
- Flower Culturing
- Others
Transgenic crops and animals represent the leading segment with a 38% share of the total Brazil agricultural biotechnology market in 2025.
Transgenic crop applications dominate commercial agricultural biotechnology deployment throughout Brazil, with genetically modified soybeans, corn, and cotton varieties occupying substantial production acreage. These crops incorporate traits including insect resistance through Bacillus thuringiensis expression, herbicide tolerance enabling simplified weed management, and increasingly, stacked traits combining multiple beneficial characteristics. Brazilian farmers demonstrate strong adoption rates driven by economic benefits including reduced input costs, simplified crop management, and improved yields. The regulatory environment supporting transgenic crop commercialization, combined with extensive experience managing these varieties, reinforces market leadership. Animal biotechnology applications remain more limited but show growth potential in livestock improvement programs.
The transgenic segment continues expanding through introduction of next-generation varieties addressing emerging challenges and market demands. Recent developments include drought-tolerant corn varieties incorporating water-use efficiency genes, relevant for production areas experiencing increased climate variability. Insect-resistant traits evolve to address emerging pest pressures and manage resistance development through trait rotation strategies. For instance, In August 2025, BASF, Corteva Agriscience, and M.S. Technologies announced a trait licensing agreement to bring BASF's novel nematode resistant soybean trait combined with Enlist E3 and Conkesta E3 soybeans to Brazilian farmers. These continuous improvements maintain transgenic crop competitiveness while addressing sustainability concerns through reduced insecticide applications and enhanced environmental compatibility.
Regional Insights:
- Southeast
- South
- Northeast
- North
- Central-West
Southeast represents the largest region with 29% share of the total Brazil agricultural biotechnology market in 2025.
The Southeast region maintains market leadership through concentration of agricultural biotechnology research institutions, seed companies, and supporting infrastructure. São Paulo hosts numerous biotechnology research centers, universities, and private sector facilities conducting foundational research and product development activities. The region's proximity to major agricultural production areas facilitates field testing, regulatory trials, and technology transfer activities. Established transportation networks and port facilities support seed distribution and agricultural commodity exports. Additionally, the Southeast benefits from higher agricultural technology adoption rates, sophisticated farmer networks, and stronger linkages between research institutions and commercial agriculture. Government research funding and private sector investment concentrate in the region, reinforcing its competitive advantages.
The Southeast's biotechnology ecosystem encompasses the entire value chain from fundamental research through commercial deployment. Campinas region emerges as a biotechnology hub with research universities, startup incubators, and established companies creating innovation clusters. These concentrations facilitate knowledge transfer, talent mobility, and collaborative projects accelerating technology development. The region also hosts regulatory agencies overseeing biotechnology approvals, streamlining communication between developers and authorities. Financial services supporting agricultural investments and technology adoption concentrate in Southeast urban centers, providing capital access for biotechnology commercialization initiatives and farm-level technology implementation across the broader agricultural sector.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Brazil Agricultural Biotechnology Market Growing?
Favorable Regulatory Framework Accelerating Innovation and Commercialization
Brazil's progressive biosafety regulatory framework has created an enabling environment for agricultural biotechnology development. The Biosafety Law of 2005 established CTNBio as the competent authority for evaluating and approving biotechnology products, with decisions that are sovereign and legally binding. The publication of Normative Resolution No. 16 in 2018 adapted regulations to accommodate new breeding techniques, allowing gene-edited products to be classified as conventional when no foreign DNA is introduced. In December 2024, Law No. 15.070/2024 established a dedicated regulatory framework for bioinputs, streamlining approval procedures and reducing registration timelines for biological products. In June 2024, Brazil established the International Biosafety Network of Products generated from Modern Biotechnology along with Uruguay, Argentina, and Paraguay to enable coordinated approvals throughout the region.
Climate Change Adaptation and Environmental Sustainability Requirements
Increasing climate variability and extreme weather events create urgent needs for crop varieties demonstrating resilience to environmental stresses including drought, heat, and changing pest pressures. Biotechnology provides tools for accelerating development of climate-adapted varieties incorporating stress tolerance mechanisms through genetic modification or genome editing approaches. Traditional breeding timelines prove insufficient for rapid adaptation required under accelerating climate change scenarios. Agricultural producers face increasing production risks from weather unpredictability, making investment in resilient crop varieties essential for farm viability. According to the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service report on Sustainable Agriculture Programs in Brazil, during the ABC Plan implementation period, 613 Technological Reference Units were established nationwide to demonstrate and disseminate climate-smart agricultural technologies. Environmental sustainability concerns drive demand for biotechnology solutions reducing chemical input requirements through enhanced pest resistance and improved nutrient use efficiency. Regulatory pressures to minimize environmental impacts from agricultural production support biotechnology adoption as alternatives to conventional chemical-intensive approaches. Consumer preferences for sustainably produced agricultural products create market incentives for environmental performance improvements. Biotechnology enables productivity maintenance or enhancement while reducing environmental footprints through decreased pesticide applications, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and improved resource utilization. Government environmental policies increasingly recognize biotechnology's potential contributions to sustainable intensification objectives. These converging pressures establish biotechnology as essential component of agricultural adaptation strategies addressing climate and environmental challenges.
Strengthening Research Infrastructure and Intellectual Property Frameworks
Brazil's substantial investments in agricultural research infrastructure and human capital development create strong foundations for biotechnology innovation and commercialization. Public research institutions including Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation maintain extensive biotechnology research programs spanning fundamental science through applied product development. University systems produce significant numbers of trained biotechnology professionals ensuring adequate talent pipelines for research and commercial activities. Intellectual property protection frameworks strengthen, providing security for biotechnology investments and encouraging technology transfer between research institutions and commercial entities. Patent systems recognize biotechnology innovations, enabling return capture from research investments and stimulating continued innovation activities. Public-private partnership models distribute development risks while leveraging complementary capabilities of different stakeholders. Government funding programs specifically target biotechnology research addressing national agricultural priorities and strategic crop improvement objectives. These investments accelerate technology development timelines while ensuring alignment with Brazilian agricultural needs. International research collaborations bring advanced technologies and methodologies to Brazilian institutions, enhancing domestic capabilities. Regulatory frameworks for biotechnology continue maturing, providing clearer pathways for product approval and commercialization. This institutional strengthening across research, intellectual property, and regulatory dimensions creates favorable conditions for sustained biotechnology sector growth and development.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Brazil Agricultural Biotechnology Market is Facing?
Regulatory Complexity and Approval Timeline Uncertainties
Biotechnology product commercialization requires navigating complex regulatory frameworks involving multiple government agencies assessing environmental safety, food safety, and agricultural impacts. Approval processes extend over multiple years, creating uncertainty regarding commercialization timelines and investment returns. Regulatory requirements for extensive field testing, environmental impact assessments, and safety documentation impose significant development costs. Changing regulatory interpretations and evolving biosafety protocols create compliance challenges for developers. Public sector regulatory capacity limitations sometimes delay application processing and approval decisions. These regulatory uncertainties discourage smaller companies from entering the biotechnology sector while imposing planning challenges for established developers managing product development pipelines.
Public Perception Challenges and Consumer Acceptance Issues
Despite widespread commercial adoption, segments of Brazilian society maintain concerns regarding agricultural biotechnology safety, environmental impacts, and corporate control over agricultural systems. Consumer advocacy groups campaign against transgenic crop cultivation, creating periodic political pressures affecting regulatory policies. Media coverage often emphasizes potential risks while underrepresenting established safety evidence and economic benefits. Lack of public understanding regarding biotechnology mechanisms and safety assessment procedures contributes to skepticism. International market concerns about genetically modified organisms occasionally affect Brazilian agricultural exports despite regulatory approvals. These perception challenges create political uncertainties affecting long-term policy stability and potentially constraining technology deployment in specific crops or regions.
High Development Costs and Intellectual Property Concentration
Biotechnology product development requires substantial capital investments spanning years before generating commercial returns. Regulatory compliance costs, extensive field-testing requirements, and intellectual property licensing expenses create high barriers to entry. Concentration of foundational biotechnology patents among multinational corporations creates dependency relationships and profit distribution challenges. Smaller Brazilian companies and public research institutions face difficulties accessing proprietary technologies necessary for competitive product development. Licensing costs for essential technologies consume significant portions of development budgets. This intellectual property concentration limits domestic biotechnology sector diversification while creating concerns about foreign control over critical agricultural technologies essential for national food security objectives.
Competitive Landscape:
The Brazil agricultural biotechnology market demonstrates moderate concentration with multinational corporations maintaining significant market presence alongside growing domestic companies and public research institutions. Competition centers on trait innovation, regulatory approval success, seed distribution network strength, and farmer relationship management. Companies invest heavily in research and development activities, field testing infrastructure, and regulatory compliance capabilities. Strategic partnerships between international technology providers and Brazilian seed companies facilitate market access and local adaptation. Competitive dynamics increasingly emphasize digital agriculture integration, precision farming applications, and comprehensive agronomic support services beyond seed sales. Market participants differentiate through regional adaptation, customer service quality, and agricultural productivity solutions.
Recent Developments:
- In June 2025: Symbiomics, a Brazilian biotechnology company developing microbiome solutions for sustainable agriculture, successfully closed its Series A funding round with an equity investment led by Corteva through its Corteva Catalyst platform. The companies will collaborate to discover novel microbial solutions for crop health and increased yields.
Brazil Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Organism Types Covered | Plants, Animals, Microbes |
| Technologies Covered | Genome Editing, Synthetic Biology, Genetic Engineering, Marker-Assisted Breeding, Plant Breeding, Germplasm, Others |
| Applications Covered | Vaccine Development, Transgenic Crops and Animals, Antibiotic Development, Nutritional Supplements, Flower Culturing, Others |
| Regions Covered | Southeast, South, Northeast, North, Central-West |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Brazil agricultural biotechnology market size was valued at USD 666.94 Million in 2025.
The Brazil agricultural biotechnology market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.98% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 1,331.00 Million by 2034.
Plants dominated the market with a share of 47%, driven by extensive deployment across major agricultural commodities including soybeans, corn, and cotton with proven economic benefits and established farmer acceptance.
Key factors driving the Brazil agricultural biotechnology market include expanding agricultural production demands for export markets, climate change adaptation requirements necessitating stress-tolerant crop varieties, and strengthening research infrastructure supporting innovation capabilities.
Major challenges include regulatory complexity with extended approval timelines, public perception issues affecting consumer acceptance and policy stability, high development costs limiting market entry, intellectual property concentration among multinational corporations, and periodic political uncertainties affecting long-term policy frameworks.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












