
Canada Electric Vehicle Charging Station Market Report Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Charging Station Type, Vehicle Type, Installation Type, Charging Level, Connector Level, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Canada Electric Vehicle Charging Station Market Size and Share:
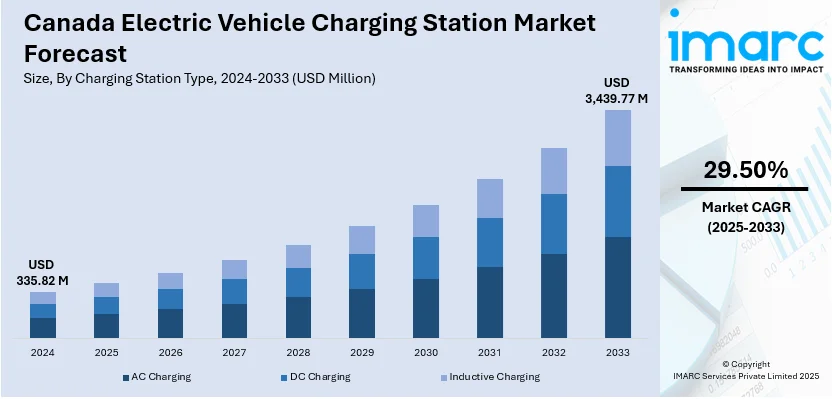
The Canada electric vehicle charging station market size was valued at USD 335.82 Million in 2024. The market is expected to reach USD 3,439.77 Million by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 29.50% during 2025-2033. The market is fueled by the rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), in line with government incentives for sustainable transportation and carbon reduction. In addition, the escalated demand for the infrastructure to accommodate the growing EV fleet, coupled with innovation in charging technologies, further drives the market. Moreover, increased customer awareness of the environment and the shift towards cleaner energy sources are prime drivers of augmenting the Canada electric vehicle charging station market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 335.82 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 3,439.77 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 29.50% |
Canada Electric Vehicle Charging Station Market Analysis:
- Major Drivers: Government incentives and policies supporting zero-emission vehicles, such as the federal iZEV program with up to USD 5,000 rebates, are driving market uptake considerably. Increasing environmental awareness among Canadian consumers is enhancing demand for green transportation solutions. The Canada electric vehicle charging station market growth is supplemented by major infrastructure development investment and strategic public-private collaborations increasing charging availability across the country.
- Key Market Trends: Sophisticated charging technologies, such as ultra-fast charging and wireless charging technologies, are improving user experience and decreasing the time to charge. Integration of clean energy sources, such as solar and wind, into charging facilities supports Canada's goal of clean energy. Smart grid and smart charging technologies are maximizing energy distribution and grid efficiency, which is supporting the Canada electric vehicle charging station market trends.
- Market Challenges: High upfront capital costs of building out infrastructure and difficult installation procedures represent challenges for quick network growth. Consumer range anxiety and lack of charging convenience in rural locations are still notable adoption barriers. Grid limits and the necessity of electrical infrastructure upgrades in some areas demand a lot of investment and planning coordination.
- Market Opportunities: The growing EV market opens up significant opportunities for charging network expansion, especially in underpenetrated areas. Advances in bidirectional charging and vehicle-to-grid technology offer new revenue opportunities. Electrification of corporate fleets and workplace charging installations provide large market growth potential, propelling the Canada electric vehicle charging station market analysis.
The market is largely propelled by the increasing use of electric vehicles (EVs) nationwide, as more individuals and companies turn to greener forms of transportation. Additionally, government incentives and policies in favor of carbon-emission reduction and sustainability are propelling market growth. Notably, the federal iZEV program has offered significant rebates, up to USD 5,000, for certified ZEV purchases, which have facilitated EVs' appeal to a larger population. Aside from this, the enhanced availability of infrastructure development funding also stands in favor of this trend. Moreover, improved charging technology, including the ability to charge vehicles much quicker and the option for wireless charging, is tending to improve the overall experience of EV charging, supporting the Canada electric vehicle charging station market analysis.
Aside from this, growing environmental concerns among consumers in Canada are driving demand for cleaner modes of transportation, which is supporting the Canada electric vehicle charging station market growth. As per industry reports, in 2024, zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs) held a market share of 14.6% of new car registrations, an increase from 11% in 2023, indicating a major shift towards electric mobility. Apart from that, the shift towards cleaner energy sources is increasing demand for green-energy-powered EV charging stations, meeting the country's intentions of reducing its carbon footprint. The growth of the EV market itself is fueling demand for wider and more accessible charging networks. In accordance with this, strategic alliances between public agencies and private firms are making it easier to develop charging infrastructure, paving the way for a smooth transition to a future powered by EVs.
Canada Electric Vehicle Charging Station Market Trends:
Increase in Government Incentives
Government incentives are pivotal in speeding up the development of Canada's electric vehicle (EV) charging station market. Governments at both the federal and provincial levels are providing various monetary assistance initiatives such as installation subsidies for charging stations, tax rebates for individuals purchasing EVs, and infrastructure development grants. The federal government's "Zero Emission Vehicle Infrastructure Program" is funding increased charging network expansion across public, commercial, and residential areas. Also, provinces such as British Columbia and Quebec are taking the lead with dedicated programs for home and workplace charging installations, which is one of the emerging Canada electric vehicle charging station market trends. For example, in September 2024, the Government of Canada committed USD 14.9 Million to 20 projects to install more than 3,000 electric vehicle (EV) chargers nationwide. The projects are designed to promote awareness of the advantages of EVs and facilitate the shift to zero-emission vehicles. The financing will also help in establishing sustainable employment in the EV supply chain. These incentives not only lower the cost hurdle for market players and investors to invest in charging infrastructure but also provide a conducive environment for market players to expand operations, ultimately promoting increased EV uptake throughout the nation.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Expansion of Public Charging Networks
Public charging network expansion is a key trend in Canada's EV market, fueled by heavy investments from government and private sources. Focus is on raising the density of charging points in urban areas, where electric vehicle uptake is increasingly on the rise, and along highways to facilitate long-distance driving. This growth increases accessibility, lowers range anxiety, and makes more consumers opt for electric vehicles. The major efforts involve the installation of rapid-charging stations in strategic areas like shopping malls, offices, and transport hubs. Furthermore, collaboration among municipalities, utilities, and private businesses is driving the establishment of an integrated and efficient charging network. Advanced technologies, such as intelligent charging systems, are being implemented to maximize energy efficiency and provide hassle-free user experiences. Such investments not only reinforce the present demand but also prepare for the growth in the future, making Canada a forerunner in the field of clean transportation. According to this, in April 2024, Aviva Canada revealed the recipients of its Charged for Change program, gifting eight municipalities with electric vehicle charging stations. The initiative, in partnership with Earth Day Canada, is set to counter the absence of public charging stations as a deterrent for Canadians to opt for an EV purchase. Aviva believes to promote further endeavors favoring the transition to EVs.
Integration of Renewable Energy in EV Charging Infrastructure
The incorporation of renewable energy into EV charging infrastructure is picking up speed in Canada as sustainability gains importance in transportation. This trend is positively impacting the Canada electric vehicle charging station market outlook. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power-based charging stations are being established to decrease dependence on conventional electricity grids and lower the carbon footprint of electric vehicle uptake. This is in line with Canada's clean energy objectives and increases the environmental advantages of EVs. As such, in August 2025, Canada announced a CAD 25 Million investment supporting 33 projects to expand EV infrastructure and decarbonize freight transport. The initiative, part of a CAD 1 Billion clean energy strategy, advances national zero-emission goals by funding 850+ chargers, with Quebec receiving major deployments in public, corridor, and airport locations. Companies and cities are increasingly turning to on-site renewable energy systems, including solar and battery storage, to power charging stations. Such systems stabilize peak demand and cut costs by harnessing stored renewable energy during high-demand periods. Smart grid technology is also being incorporated to manage the distribution of renewable energy in a way that maximizes the efficiency of the grid. This transition towards clean-powered charging alternatives not only supports sustainability but also enhances Canada's leadership role in green mobility innovation.
Canada Electric Vehicle Charging Station Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Canada electric vehicle charging station market, along with forecasts at the country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on charging station type, vehicle type, installation type, charging level, connector level, and application.
Analysis by Charging Station Type:
- AC Charging
- DC Charging
- Inductive Charging
Alternating Current (AC) charging is the most prevalent method of electric vehicle charging in Canada, especially in workplace and home settings. AC chargers, which normally work at Level 1 or Level 2, provide an affordable and suitable solution for everyday vehicle recharging. Their availability enables EV drivers to charge vehicles at night or while at the workplace, minimizing reliance on public charging stations. AC charging is the backbone of Canada's EV network, facilitating mass adoption of electric cars. Its ease of use, low cost, and compatibility with established electrical grids make it a critical element in the nation's move to cleaner transportation.
Direct Current (DC) fast charging plays a crucial role in quick recharging of electric cars, especially along highways and in congested urban centers. DC chargers deliver high-voltage electricity directly to the battery, significantly reducing charging times compared to AC systems. This capability is crucial for enabling long-distance travel and minimizing range anxiety among EV users. In Canada, DC charging stations represent strategic investments in the national EV network, facilitating the adoption of battery electric vehicles. Their speed and efficiency render them unavoidable for commercial fleets, public buildings, and commuters who need fast, convenient charging options.
Inductive charging, also known as wireless charging, is a new technology in Canada's electric vehicle market. Energy from a charging pad is wirelessly transferred to a vehicle through electromagnetic fields. Although still in nascent stages, inductive charging also brings greater convenience and potentially could be incorporated into public roads, parking lots, and fleet depots. It has the potential to deliver smooth charging experiences with less need for cables and user intervention. With increasing adoption of EVs, inductive technology can supplement AC and DC stations, diversifying Canada's charging network.
Analysis by Vehicle Type:
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are pure electric vehicles that draw power exclusively from the battery, the main drivers of charging infrastructure expansion in Canada. Their uptake highlights the importance of convenient and fast-charging points throughout urban and rural settings. BEVs generally utilize AC charging in home and work contexts and DC fast charging for long-distance driving, minimizing range anxiety. The rising popularity of BEVs has also led to strategic investments in public charging networks, emphasizing their pivotal position in enabling Canada's low-emission transportation system.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) have a conventional internal combustion engine combined with an electric motor powered by a battery, enabling operators to toggle between fuel and electricity. In Canada, PHEVs play a crucial role in phasing in consumers to electric mobility, particularly in areas where the charging infrastructure is yet to be established. Consumers can recharge PHEVs using typical AC charging at home or in the office, offering convenience for users. The availability of PHEVs contributes to an expansion of the market for public charging points, as well as decreasing dependency on fossil fuels and closing the gap between conventional cars and purely electric BEVs in the transportation market.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) employ a mix of an internal combustion engine and regenerative braking to power an electric motor, without external charging. HEVs do not directly stimulate demand for charging stations but contribute heavily to making the public comfortable with electrified powertrains and fuel efficiency. Their existence facilitates a gradual transition to electric mobility by being less emission-intensive than traditional vehicles. HEVs serve as a bridging technology, supplementing BEVs and PHEVs, whereas the most prominent objective of charging infrastructure growth in Canada is for vehicles needing external electricity sources.
Analysis by Installation Type:
- Portable Charger
- Fixed Charger
Portable chargers are versatile charging solutions that enable electric vehicle users in Canada to charge their cars anywhere a suitable electrical socket can be found. They are particularly useful for homeowners with no installed home charging infrastructure or for road travelers who need to recharge while on the move. Portable chargers offer convenience, mobility, and cost-effectiveness since they do not need to be permanently installed. Although they tend to provide slower charging rates than fixed stations, they serve a critical role in facilitating early EV uptake, emergency charging cases, and flexible usage patterns, and therefore are a valuable addition to Canada's expanding EV charging network.
Fixed chargers are fixed installations, typically at homes, workplaces, and public stations, constituting the core of Canada's EV infrastructure. They offer consistent, high-capacity charging and can serve both AC and DC systems, allowing for quicker and more efficient charging of vehicles. Fixed chargers are made for repeated, frequent use and help achieve predictability and stability in EV operations. Strategically placed in cities, highways, and commercial areas, they make charging accessible and promote mass use of electric vehicles. Through providing reliable performance and connectivity with smart charging networks, fixed chargers are instrumental in furthering Canada's greener transportation objectives.
Analysis by Charging Level:
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
Level 1 charging employs common household outlets and offers the slowest type of electric vehicle charging. Level 1 charging is mostly utilized in Canada for overnight or emergency charging purposes, which renders it appropriate for domestic environments with low energy demands. Although Level 1 chargers offer less power output, they are inexpensive, simple to install, and available to almost all EV owners. Their lack of complexity means that even those who lack special infrastructure can have vehicles ready. While sluggish, Level 1 charging has a significant supporting role to play in Canada's EV infrastructure by providing a cheap and reliable means of daily, low-need charging.
Level 2 is the most prevalent level of charging used in Canada for residential, commercial, and public spaces. Higher than Level 1 voltage greatly cuts down charging time to the point where it is reasonable for daily driving and fleet applications. Level 2 charging delivers a compromise between speed, efficiency, and convenience that allows both residential and commercial use of electric vehicles. Widespread implementation assuages range anxiety and prompts repeated use of EVs. By providing speedier, dependable charging without the infrastructure requirements of Level 3 systems, Level 2 chargers are a key part of Canada's expanding EV charging infrastructure.
Level 3 charging applies high-voltage current directly to the vehicle battery, allowing for fast recharging in a matter of minutes compared to Levels 1 and 2. In Canada, Level 3 stations are essential for long-distance travel and high-traffic city centers and service both private and commercial EV fleets. They mitigate range anxiety and maximize the usability of battery electric vehicles for daily and long-term use. As EV adoption grows, Level 3 chargers are strategic investments in infrastructure that guarantee quick, efficient, and dependable charging, propelling Canada's shift towards sustainable transportation.
Analysis by Connector Type:
- Combines Charging Station (CCS)
- CHAdeMO
- Normal Charging
- Tesla Supercharger
- Type-2 (IEC 621196)
- Others
The Combined Charging System (CCS) is on the verge of becoming the new norm connector type for electric vehicles in Canada, which will facilitate both AC and DC charging using one interface. Its adaptability enables vehicles to make use of fast-charging networks while still being compatible with slower Level 1 or Level 2 stations. CCS enables quick energy transfer, lowering charging time and making long-distance travel possible for battery electric vehicles. With more automakers using CCS, its prevalence makes Canada's charging infrastructure more robust, with uniformity, efficiency, and reliability.
CHAdeMO is a DC fast-charging plug that has been extensively utilized by first-generation electric vehicles in Canada. It facilitates fast charging, especially for road trips and fleet urban applications, minimizing downtime for users. CHAdeMO plugs are still significant in ensuring compatibility with past EV models, providing a variety of vehicles access to Canada's fast-charging network. Even though newer standards such as CCS are becoming popular, CHAdeMO facilitates network diversity and interoperability. Its availability in prime public and commercial locations assists in bridging historic and contemporary EV technologies, for a smooth charging process.
Normal charging connectors, most commonly employed for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging, play a vital role in everyday vehicle charging at home, work, and in public places. These connectors are straightforward, secure, and useable for most electric vehicles, which enables continuous energy refilling without having to install specialized infrastructure. Standard connectors are the backbone of Canada's EV charging infrastructure, providing convenience for novice EV drivers and occasional users. Although slower than fast-charging connectors, their cost-effectiveness and ease of fitting make them essential to the mass adoption of EVs.
Analysis by Application:
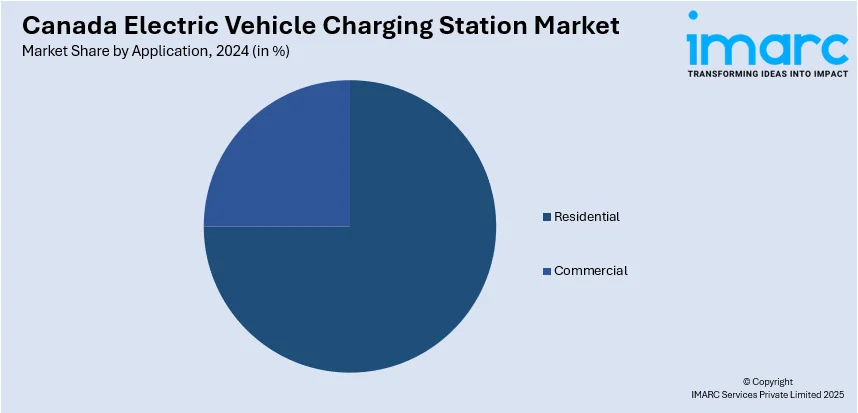
- Residential
- Commercial
Ontario is a prominent market for electric vehicle charging infrastructure in Canada due to its high population density, large urban areas, and forward-thinking EV adoption policies. The province is home to a high percentage of residential, commercial, and public charging points, supporting both commuter and long-distance travel. Urban centers such as Toronto and Ottawa lead the demand for speedy, reliable charging, while suburban and rural areas are augmented by strategically located Level 2 and Level 3 stations. Ontario's proactive promotion of electric mobility and investments in the charging network position it at the forefront of pushing Canada toward sustainable transport.
Quebec has become a robust market for EV adoption and charging infrastructure, fostered by governmental incentives and an increasing EV-conducive environment. The province is aided by high-density urban regions like Montreal and Quebec City, which promote residential and business charging options. Quebec's climate also highlights the need for dependable, efficient charging networks in order to uphold battery performance. Public and workplace chargers are essential to enabling everyday mobility, with DC fast chargers supporting long-distance driving throughout the province. Quebec's emphasis on sustainability and infrastructure building solidifies its position as a top region for EV development in Canada.
Alberta is a significant region in the market, especially along highways and in major cities such as Calgary and Edmonton. The province's vast geography and oil-based economy render the shift to electric mobility both difficult and strategically important. Alberta's charging ecosystem prioritizes fast-charging facilities to enable long-distance travel and minimize range anxiety among EV owners. Household and business charging continues to grow in urban agglomerations, ensuring convenience and accessibility. Alberta's investment in diverse EV applications demonstrates the potential of the province to balance energy transition efforts with practical mobility solutions, in support of Canada's nationwide adoption of electric vehicles.
British Columbia leads Canada in electric vehicle adoption due to robust environmental policies, incentives, and public consciousness. Cities such as Vancouver and Victoria have dense grids of residential, commercial, and public charging points to support high penetrations of EVs. The province has deployed strategically DC fast chargers along major routes to support intercity travel and long-distance mobility. BC's coastal climate and environmentally conscious citizenry are driving private and commercial investment in EV infrastructure. The province's comprehensive approach to charging networks makes it a model for integrating sustainable transportation solutions, ensuring accessibility, reliability, and convenience for electric vehicle users across the region.
Competitive Landscape:
The market maintains intense competition among the players based on technological development, network growth, and alliances. There is tremendous investment in fast-charging, intelligent payment systems, and interoperable platforms by the companies to improve user experience and gain a competitive edge in a fast-expanding market. Cooperative ventures among government agencies, utility companies, and commercial property developers are becoming more widespread to increase infrastructure and facilitate accessibility. Market players are also focusing on environmentally friendly solutions, incorporating renewable energy sources, and providing value-added services like real-time charging monitoring and maintenance assistance. Pricing mechanisms and service reliability continue to be central drivers of customer preference and retention. As per the Canada electric vehicle charging station market forecast, the market is poised to experience strong growth in the next half a decade, with new entrants and technological innovations fueling competition. At large, the landscape is that of a dynamic, innovation-driven ecosystem with a focus on efficiency, scalability, and customer-centric solutions.,
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Canada electric vehicle charging station market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Canada Electric Vehicle Charging Station Market News:
- In July 2025, A new public Level 3 electric vehicle (EV) charging station launched at Toyota Canada’s headquarters in Scarborough, Ontario, developed by Mitsui Canada and powered by Jule’s battery-supported charging technology. The station features four fast-charging pedestals, enhancing accessibility and grid efficiency. This pilot project aims to strengthen Canada’s EV charging network, support sustainable transportation, and address key barriers to EV adoption, providing reliable, community-focused fast-charging infrastructure.
- In April 2025, Tim Hortons is partnering with FLO to install electric vehicle (EV) fast chargers at 100 restaurants across Canada by 2028, making it the largest restaurant EV charging provider in the country. The first charger is operational in Regina, with 14 more by the end of 2025 and 50 by 2026. FLO Ultra™ chargers provide up to 120 km of range in 10 minutes, offering reliable, fast charging at popular, accessible locations nationwide.
- July 2025: United Chargers introduced Canada’s first EV charging subscription, the Grizzl-E Power Subscription. Priced at CAD 29.99 monthly, it includes a free smart charger, installation, app-based control, and USD 10 monthly cashback for five years, reducing upfront costs and supporting Canada’s clean transport transition.
- July 2025: Saskatchewan launched the Municipal Electric Vehicle Initiative (MEVi), offering USD 850,000 in funding to expand EV charging infrastructure. Municipalities, businesses, and community groups can receive rebates up to 75% for Indigenous applicants, supporting Level 2 and DC fast chargers, with projects required to be completed by December 2026.
- May 2025: Nissan Canada partnered with Wallbox and RocketEV Charging Solutions to launch a seamless home charging program. EV owners can acquire Wallbox’s Pulsar Plus Level 2 charger and arrange installation through authorized dealers or via nissan.ca, streamlining access to dependable charging solutions and contributing to Canada’s transition toward sustainable electric mobility.
- May 2025: ChargePoint partnered with Eaton to deliver a full EV charging ecosystem across the US, Canada, and Europe. The collaboration integrates chargers, infrastructure, and engineering services, with joint development of bidirectional power transfer and V2X technologies, aiming to streamline deployment, reduce costs, and accelerate large-scale electrification.
- March 2025: The Canada Infrastructure Bank announced a CAD 194 Million loan to Jolt for installing up to 1,500 curbside EV chargers in urban areas. The advertiser-supported network offers drivers 7 kWh of free daily charging, aiming to cut emissions, augment EV adoption, and expand clean transport infrastructure.
- July 2024: Canada announced a USD 3.1 Million investment to install 660 Level 2 EV charging stations in Nova Scotia. This initiative supports the country's goal of 100% zero-emission vehicles by 2035, contributing to emissions reduction and advancing sustainable mobility through federal and provincial funding.
Canada Electric Vehicle Charging Station Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Charging Station Types Covered | AC charging, DC charging, Inductive charging |
| Vehicle Type Covered | Battery electric vehicle (BEV), Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), Hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) |
| Installations Covered | Portable charger, Fixed charger |
| Levels Covered | Level 1, Level 2, Level 3 |
| Connector Types Covered | Combined charging station (CCS), CHAdeMO, Normal charging, Tesla Supercharger, Type-2 (IEC 621196), Others |
| Applications Covered | Residential, Commercial |
| Regions Covered | Ontario, Quebec, Alberta, British Columbia, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Canada electric vehicle charging station market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Canada electric vehicle charging station market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the cement industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The electric vehicle charging station market in Canada was valued at USD 335.82 Million in 2024.
The Canada electric vehicle charging station market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 29.50% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 3,439.77 Million by 2033.
The market is driven by government incentives including the federal iZEV program offering up to USD 5,000 rebates, rising environmental consciousness among consumers, substantial infrastructure development funding, and strategic public-private partnerships. Additionally, technological innovations in fast-charging and wireless charging systems are enhancing user experience and supporting market growth.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












