
Europe Hospital Acquired Disease Testing Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Indication and Country, 2025-2033
Europe Hospital Acquired Disease Testing Market Size and Share:
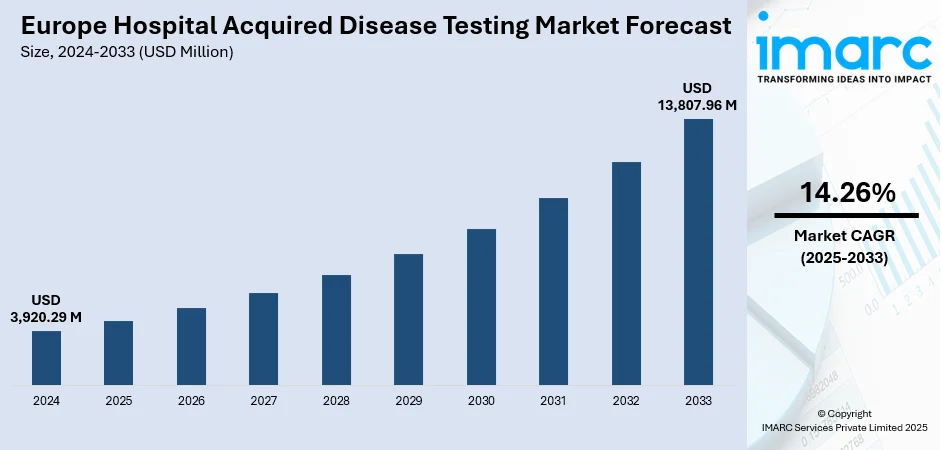
The Europe hospital acquired disease testing market size was valued at USD 3,920.29 Million in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 13,807.96 Million by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 14.26% from 2025-2033. Germany currently dominates the market driven by rising HAIs, stricter EU infection-control regulations, antimicrobial resistance surveillance needs, and post-pandemic emphasis on rapid diagnostics. Aging populations, intensive care unit (ICU) stays, and higher surgical volumes expand testing demand. Adoption of molecular and point-of-care (POC) platforms shortens turnaround time, supporting stewardship and isolation decisions. Reimbursement, laboratory consolidation, and Electronic Health Record (EHR) integration encourage standardized screening. Procurement pressure for cost-effective assays boosts multiplex panels and automation, reducing labor, minimizing errors, and enhancing throughput across centralized and near-patient settings thus surging the Europe hospital acquired disease testing market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3,920.29 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 13,807.96 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 14.26% |
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) estimates that around 4.3 million patients in acute hospitals across the EU/EEA contract at least one healthcare-associated infection (HAI) annually. The rising prevalence of HAIs such as MRSA, Clostridioides difficile, and ventilator-associated pneumonia is a major driver for Europe hospital acquired disease testing market growth. Factors including extended hospital stays, complex surgeries, and greater use of invasive devices heighten infection risks. This growing burden pressures hospitals to adopt faster, more accurate diagnostics particularly molecular and automated platforms to quickly identify pathogens, enable timely treatment and isolation, and ensure regulatory compliance. Such measures improve patient outcomes while reducing healthcare costs from prolonged stays and legal liabilities.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Europe’s healthcare systems operate under strict infection prevention guidelines set by entities such as the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and national health authorities. These regulations require routine screening for high-risk pathogens, mandatory outbreak reporting, and adherence to antimicrobial stewardship programs. Hospitals must adopt advanced testing solutions to meet compliance requirements and avoid penalties. Molecular diagnostics, multiplex PCR panels, and POC tests are increasingly used to detect pathogens rapidly and accurately. Integration of testing systems with electronic health records supports surveillance, trend analysis, and reporting efficiency. These policies not only drive testing adoption but also encourage continuous technological upgrades in laboratories.
Europe Hospital Acquired Disease Testing Market Trends:
Rising Burden of Hospital-Acquired Infections (HAIs)
Hospital-acquired infections remain a significant public health challenge in Europe, with millions of new cases each year affecting patient safety and healthcare costs. Common HAIs, including bloodstream infections, pneumonia, and multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, are linked to longer hospital stays, higher mortality rates, and increased treatment expenses. Aging populations, intensive care unit admissions, and the use of invasive medical devices all contribute to higher infection risks. This growing burden drives demand for advanced, rapid, and accurate testing solutions that can identify pathogens early, guide targeted therapy, and reduce the spread within healthcare settings. Hospitals are increasingly investing in molecular diagnostics, automated systems, and POC devices to enable faster turnaround times, enhance infection control measures, and ensure compliance with stringent European healthcare quality and safety standards.
Stringent Regulatory Framework and Compliance Requirements
One of the significant Europe hospital acquired disease testing market trend is the rising influence by strict infection prevention and control regulations set by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines, and national health ministries. These frameworks mandate routine pathogen surveillance, outbreak notification, and adherence to antimicrobial stewardship programs. Non-compliance can result in financial penalties, reputational damage, and even operational restrictions for healthcare facilities. This regulatory pressure encourages hospitals to adopt advanced diagnostic technologies capable of delivering precise and timely results. Integration with electronic health record systems supports automated reporting, epidemiological tracking, and compliance audits. Furthermore, government-backed initiatives and funding programs are incentivizing the adoption of next-generation molecular and multiplex testing platforms, ensuring hospitals maintain the highest infection control standards while optimizing resource use and reducing preventable patient harm.
Technological Advancements in Diagnostic Testing
Rapid advancements in diagnostic technologies are transforming Europe hospital acquired disease testing market outlook. Molecular diagnostics, real-time PCR, next-generation sequencing (NGS), and multiplex PCR panels are enabling faster, more sensitive, and more accurate pathogen detection compared to traditional culture methods. Multiplex PCR panels can identify up to 20 pathogens simultaneously, reducing diagnosis time by up to 70 %, which is vital for timely treatment decisions and isolation measures during outbreaks. Automated laboratory systems minimize human error, enhance workflow efficiency, and support high-throughput testing during peak demand. POC devices are gaining adoption for bedside diagnostics, delivering immediate results without relying on central labs. AI-driven analytics integrated with digital health platforms strengthen predictive surveillance and infection trend monitoring. These innovations not only ensure compliance with stringent European infection control policies but also improve patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for healthcare providers.
Europe Hospital Acquired Disease Testing Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Europe hospital acquired disease testing market, along with forecast at the regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on indication.
Analysis by Indication:
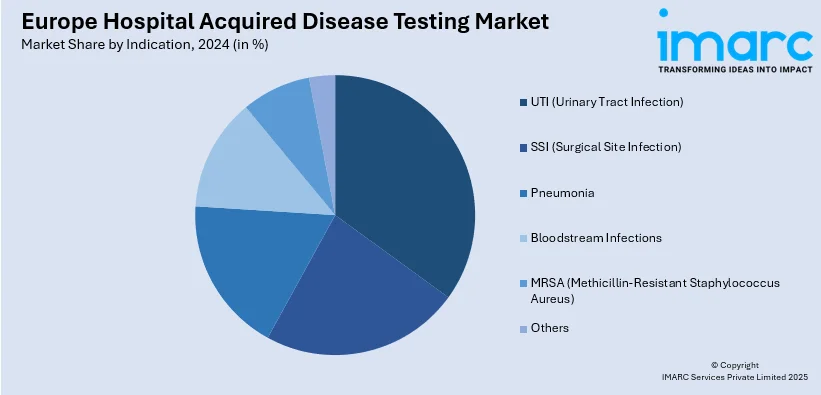
- UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
- SSI (Surgical Site Infection)
- Pneumonia
- Bloodstream Infections
- MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus)
- Others
Based on the Europe hospital acquired disease testing market forecast, the Urinary tract infections (UTIs) account for a total share of 22.7% in Europe’s hospital-acquired disease testing market due to their high prevalence among hospitalized patients, especially those with indwelling urinary catheters or undergoing prolonged stays. Catheter-associated UTIs (CAUTIs) are one of the most common healthcare-associated infections, driven by factors such as aging populations, increased surgical interventions, and chronic disease management. UTIs can lead to serious complications like sepsis if undiagnosed or untreated, creating strong demand for rapid and accurate diagnostic testing. Hospitals prioritize UTI detection to improve patient outcomes, reduce length of stay, and comply with infection control protocols. The availability of advanced molecular diagnostics and automated urine culture systems further supports their dominant market position.
Country Analysis:
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Others
According to the Europe hospital acquired disease testing market analysis the Germany leads the Europe hospital-acquired disease testing market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high hospital density, and strong emphasis on infection prevention and control. The country’s strict regulatory framework mandates routine surveillance, rapid pathogen identification, and reporting of healthcare-associated infections, encouraging widespread adoption of advanced diagnostic technologies. Significant investment in laboratory automation, molecular diagnostics, and point-of-care testing supports faster turnaround times and improved clinical outcomes. Germany’s aging population and high rates of complex surgical procedures further increase the incidence of hospital-acquired infections, driving testing demand. Additionally, strong public health initiatives, well-funded research programs, and collaboration between hospitals and diagnostic developers reinforce Germany’s position as a frontrunner in implementing cutting-edge testing solutions and infection control strategies.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established diagnostic solution providers, specialized molecular testing companies, and emerging innovators in rapid point-of-care technologies. Competition is driven by the need for faster turnaround times, higher sensitivity, and compliance with strict European infection control regulations. Players differentiate through technological innovation, such as multiplex PCR panels, automation, and integration with digital health platforms for real-time surveillance. Strategic collaborations with healthcare institutions, government agencies, and research organizations are common to expand testing capabilities and market reach. Pricing competitiveness and cost-effectiveness are crucial due to budget constraints in public healthcare systems. Additionally, the market is seeing increasing focus on AI-powered analytics and portable testing devices, intensifying competition between centralized laboratory-focused solutions and near-patient testing platforms. Overall, the environment is highly dynamic, shaped by innovation, regulatory demands, and growing awareness of hospital-acquired infection risks.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Europe hospital acquired disease testing market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- July 2025: Sandoz expanded its biosimilar production in Slovenia with a new USD 440 Million facility, enhancing injectable supply for hospitals, thereby supporting safer and more reliable drug availability across Europe.
- June 2025: Llusern Scientific received ISO 13485 certification for its Lodestar DX, a rapid molecular point-of-care test for UTIs. The device enabled single-visit diagnosis and antibiotic stewardship, helping reduce overtreatment in hospitals. This development supported precision diagnostics in European healthcare facilities dealing with high rates of hospital-acquired urinary tract infections.
- May 2025: Roche planned a Phase 3 trial for zosurabalpin, a novel antibiotic targeting carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, a critical hospital-acquired pathogen. The trial involved 400 patients across Europe and other continents, addressing urgent treatment gaps in ICUs and offering hope for controlling resistant infections threatening European hospital environments.
- February 2025: AbbVie’s Emblaveo, a new combination antibiotic for complicated intra-abdominal infections, received FDA approval for use in critical care settings. The REVISIT Phase 3 trial showed strong efficacy against Gram-negative pathogens. Previously authorised in the EU, the drug offered European hospitals an effective option against resistant infections in high-risk patients.
Europe Hospital Acquired Disease Testing Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Indications Covered | UTI (Urinary Tract Infection), SSI (Surgical Site Infection), Pneumonia, Bloodstream Infections, MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus), Others |
| Countries Covered | Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Europe hospital acquired disease testing market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Europe hospital acquired disease testing market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Europe hospital acquired disease testing industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The hospital acquired disease testing market in Europe was valued at USD 3,920.29 Million in 2024.
The Europe hospital acquired disease testing market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 14.26% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 13,807.96 Million by 2033.
Key factors driving the Europe hospital-acquired disease testing market include rising incidence of HAIs, strict infection control regulations, and growing antimicrobial resistance. Technological advancements in molecular diagnostics, increased adoption of rapid and point-of-care testing, and aging populations requiring intensive care also fuel demand, improving detection speed, accuracy, and patient outcomes.
Urinary tract infections hold the largest share of 22.7% in Europe’s hospital-acquired disease testing market due to their high occurrence in hospitalized patients, particularly those with catheters or extended stays. Their risk of severe complications drives demand for rapid, accurate diagnostics to enable timely treatment and compliance with infection control protocols.
Germany leads the Europe hospital-acquired disease testing market due to its robust healthcare infrastructure, dense hospital network, and stringent infection control policies. High adoption of advanced diagnostics, significant investment in laboratory automation, and an aging population with greater infection risk further strengthen its market dominance and testing capacity.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












