
Germany Health & Medical Insurance Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Type, Term of Coverage, Channel of Distribution, Income Level, and Region, 2026-2034
Germany Health & Medical Insurance Market Size and Share:
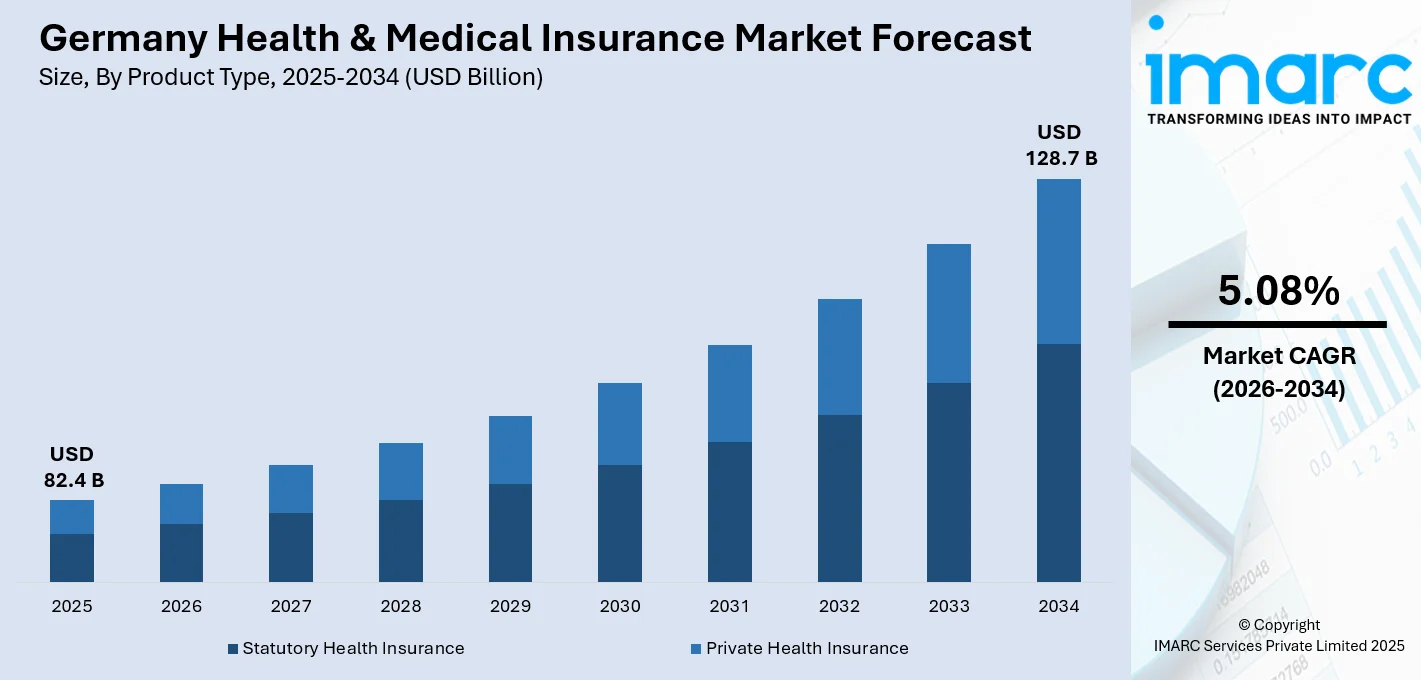
The Germany health & medical insurance market size was valued at USD 82.4 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 128.7 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.08% from 2026-2034. The market is influenced by a well-established regulation and a growing need for specialist coverage, especially in reaction to the demands of the geriatric population. The mandatory health insurance regime provides broad-based coverage, with ongoing adjustments in premiums and benefits to ensure financial viability. Having focused on all-encompassing, custom-tailored insurance offerings, the sector is gradually growing, aiding in the sustained growth of the proportion of Germany health and medical insurance market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 82.4 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 128.7 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 5.08% |
Germany's growing geriatric population is one of the major drivers in the health and medical insurance industry. With more people aged 65 years and above making up a higher percentage of the population, their health needs increase tremendously. Geriatric patients tend to visit hospitals often, with their needs including chronic disease management, long-term care, and rehabilitation. This demographic change is both a challenge and an opportunity for insurers, which has led to the development of specialized health insurance products aimed at meeting the special needs of the elderly. Insurance policies covering long-term care, rehabilitation, and home healthcare are increasingly in demand, as these services become the key to providing the quality of life for the geriatric segment. This expanding need for specialized treatment and lengthening life span have rendered medical and health insurance more crucial than before in guaranteeing ongoing access to healthcare treatments for the elderly, driving the entire industry of health insurance higher.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Strong regulatory system strongly impacts Germany health & medical insurance market growth. With universal coverage of health insurance for all residents, foreigners as well as self-employed individuals, the government guarantees access to the service of healthcare as universal. With this regulatory framework also determining premiums and benefits of the insurers, fairness and transparency are promoted in the system. Recent changes to the statutory health contribution rate are aimed at covering up cost deficits in the system in order to maintain sustainability of the healthcare infrastructure. As per the reports, in 2025, Germany's insurance and healthcare reforms are the implementation of electronic patient files (ePA) on January 15, higher insurance contributions to 2.5%, long-term care insurance premiums up, and new hospital funding reforms from January 1. Moreover, by requiring insurance for all, including those from economically heterogeneous backgrounds, the government reduces risk and provides wide-based coverage. In addition, the regulatory framework promotes insurers to provide extensive products that cater to evolving healthcare needs, including specialized care for the elderly. This policy-led strategy enhances the stability of the market, rendering health insurance a secure way of accessing healthcare for all residents, especially those with growing medical needs.
Germany Health & Medical Insurance Market Trends:
Growing Geriatric Population and Healthcare Demand
Germany's older population is quickly growing, causing an expanding demand for medical services and health insurance. The number of people 65 years and older is predicted to expand by 41% by the year 2050 to 24 million, or almost one-third of the overall population. This increase in the geriatric population is due to the country's robust healthcare system and high life expectancy, with the super-aged population showing a high level of fitness. Since people in this age group usually need more frequent medical care, the demand for health insurance coverage will be higher, putting pressure on both public and private insurers to respond. On the contrary, the population in the working age is anticipated to decline by 23%, which will contribute less to the healthcare system. Therefore, insurers and the government will have to change their models to provide long-term coverage to an geriatric populace. This changing population underscores the long-term demand for integrated healthcare solutions.
Escalating Government Regulations and Health Insurance Policies
Germany health & medical insurance market forecast is primarily influenced by the government policy and regulation that is focused on providing universal coverage and sustaining a rising healthcare need. Faced with an estimated deficit of €17 billion in 2024, the German government has raised statutory health insurance contribution rates by 0.1 percentage points to 1.7%. This policy shift, as declared by Federal Health Minister Karl Lauterbach, is a part of an overall endeavor to preserve the fiscal soundness of the healthcare sector. The hike allows for continued coverage from healthcare without cutting benefits, showing the government's interest in upholding social security schemes. Health insurance is universal in Germany and covers all inhabitants, including foreigners, to ensure wide coverage. With the increase in healthcare expenses fueled by an geriatric population, these regulatory reforms are necessary to maintaining the system and providing all individuals, especially the elderly, with access to needed care.
Shifting Healthcare Demographics and Financial Sustainability
As Germany's population grows older, both public and private insurance companies are being challenged to meet the higher healthcare demands of the elderly. As the geriatric population needs to visit the doctor more often, there is increased demand for coverage under insurance. This is supported by the obligatory health insurance model in Germany, where everyone living there must participate. Still, the financial sustainability of the scheme is coming under pressure with a declining working population. For this, incremental changes in contribution rates, e.g., 0.1% in 2024, are being attempted in order to narrow the envisaged budget gap. These reforms speak of balancing increased healthcare need and the demands for financial soundness. Insurers are also modifying their contribution patterns to respond to these demographic changes. As the population ages further, Germany health & medical insurance market outlook will have to change, incorporating new solutions to be sustainable and accessible to everyone.
Germany Health & Medical Insurance Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Germany health & medical insurance market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on product type, term of coverage, channel of distribution, and income level.
Analysis by Product Type:
- Statutory Health Insurance
- Private Health Insurance
Statutory Health Insurance is compulsory health insurance for people with incomes below a certain level, offering full coverage at relatively low premiums. It is financed by employees' and employers' contributions and provides access to the most important healthcare services such as hospital care, physician visits, and drugs. This scheme is highly prevalent among Germany's general population, especially those in lower-income groups.
Private Health Insurance can be purchased by those with more income, freelancers, and government officials. It provides greater individualized and comprehensive coverage than statutory health insurance, such as private hospital accommodations, reduced waiting periods, and greater access to specialists. The premiums are charged based on aspects such as age, health, and coverage level, and so it is flexible but more costly for those eligible.
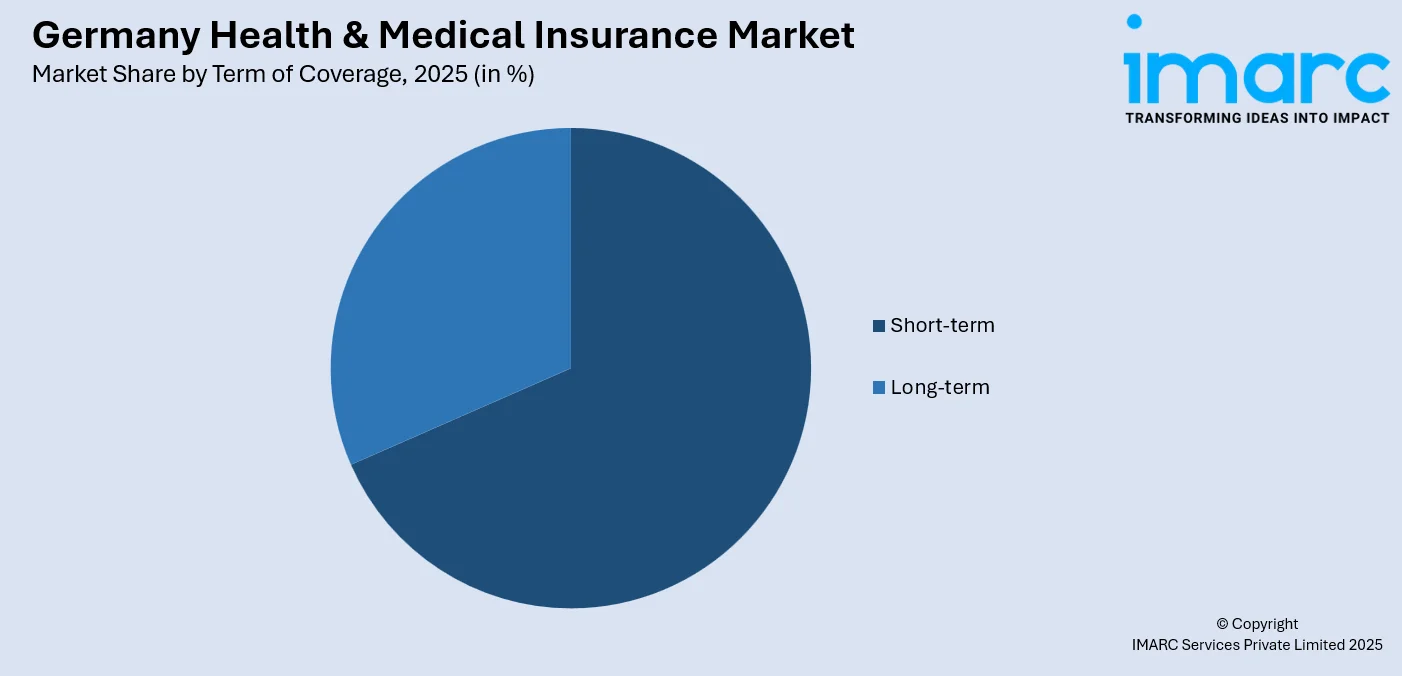
Analysis by Term of Coverage:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Short-term
- Long-term
Short-term health insurance offers coverage for short-term medical requirements or unforeseen accidents and, therefore, is best for people who require health cover for a short time. It offers basic healthcare services at a lower premium than long-term insurance but with less coverage. Used mostly by tourists or those between health covers, it caters to short-term healthcare needs.
Long-term insurance offers uninterrupted cover for a longer duration, encompassing wide-range healthcare services like preventive care, hospitalization, and specialist advice. It is favored by individuals who desire security in their medical expenses and ongoing access to needed medical services. Long-term covers usually serve persons with chronic illness or old-aged persons who need ongoing health supervision and care.
Analysis by Channel of Distribution:
- Single Tied or Insurance Group Intermediaries
- Broker and Multiple Agents
- Credit Institutions
- Direct Selling
- Others
Single Tied or Insurance Group Intermediaries concentrate on providing coverage from one insurer. These intermediaries excel at offering specialized, expert knowledge regarding their insurer's products and ensuring customers are personally recommended. They simplify the buying process, providing an easy-to-use experience, and regularly help with claims handling and policy renewal.
Brokers and Multiple Agents provide diverse products from numerous insurers, presenting independent advice specifically tailored to the customer's requirement. The channel provides an opportunity for consumers to compare multiple policies and select one according to their suitability. Brokers also provide advice on intricately written policy conditions, allowing customers to better navigate the world of insurance.
Credit Institutions sell health insurance as part of other financial services. Credit Institutions, like banks, can package insurance as one of a collection of financial services, allowing the customer to centralize their finances. The comfort and familiarity of the bank mean that customers often find the process easier to deal with.
Direct Selling enables insurers to access customers directly without middlemen. Direct selling is now more commonly utilized via online platforms, telephone services, and personal consultations. Direct selling offers a more personalized relationship between insurers and customers, typically leading to more favorable pricing, transparency, and assistance for consumers seeking simple insurance solutions.
Other distribution channels are digital platforms and niche-intermediaries that cater to niche markets. Digital platforms enable customers to easily compare, buy, and administer insurance policies at their fingertips. Niche-intermediaries can specialize in particular consumer requirements, such as expat or chronic-illness coverage, and provide customized expertise to help customers navigate the choice process.
Analysis by Income Level:
- Employed Annual Income < EUR 64,350
- Employed Annual Income > EUR 64,350
- Self-employed
- Civil Servants
Those with less than an annual income of EUR 64,350 usually rely more on statutory health insurance since it is obligatory for lower incomes. Affordability and extensive coverage are the most important factors when selecting health insurance for this demographic, since it will be less likely for them to use private insurance due to the higher cost.
Working persons who earn above EUR 64,350 qualify for both private and statutory health insurance. This category is most likely to opt for private health insurance because of its additional benefits, including having lesser waiting times for treatment and the use of private healthcare centers. They tend to opt for more individualized treatment and the freedom that comes with private insurance.
Self-employed people have the freedom to opt for private and statutory health insurance. Nevertheless, self-employed people tend to have more expensive private insurance premiums. In most cases, they base their choice on the necessity for full coverage and whether they can efficiently cover their medical expenses.
German civil servants can receive special public health insurance benefits in relation to their occupation. The benefits, however, come at lower premiums and more services, and so statutory health insurance becomes highly desirable among civil servants. Sometimes, they prefer to choose private insurance, but most hold on to the statutory option as much as they do because of the favored conditions that come their way with regards to their field.
Regional Analysis:
- Western Germany
- Southern Germany
- Eastern Germany
- Northern Germany
Western Germany has a higher proportion of both employed and self-employed, which creates a greater need for health insurance coverage. The area also has a highly developed healthcare system, which makes people want to invest in full-coverage health plans, particularly private health insurance. Private insurance is highly preferred in urban areas such as Cologne and Düsseldorf.
Southern Germany, especially areas such as Bavaria, enjoys higher income levels and a more prosperous population. The region enjoys a greater level of private health insurance uptake since people tend to look for better healthcare services and more customized policies. The robust economic performance of the region supports a greater percentage of the population in being able to afford private health insurance options, with statutory health insurance acting as a fall-back option for lower-income individuals.
Eastern Germany, traditionally less advanced economically, also has a higher percentage of its population covered under statutory health insurance. With generally lower incomes than other areas, residents in this region are not as likely to be able to pay for private health insurance, leaving a larger market share to statutory coverage.
Northern Germany reveals an uneven insurance profile, with equilibrium between private and statutory health insurance schemes. Coastal cities such as Hamburg and Bremen have a mixed profile of affluent individuals who choose private insurance, but in the rural settings, there is greater dependence on statutory health insurance because of lower income levels. The region also has sound healthcare infrastructure, promoting extensive coverage.
Competitive Landscape:
Germany health & medical insurance market outlook is highly competitive and has a wide variety of providers, both public and private. The market is led by public insurers, providing wide coverage with emphasis on availability and affordability to the masses. Public insurers have the advantages of robust government support and a huge client base. Private insurers service the more affluent population, with a variety of flexible and individualized policies and usually additional privileges like quicker access to healthcare benefits and wider therapeutic options. Both public and private insurers compete in terms of cost, quality of services, and level of coverages, and each segment tends to target serving the unique requirements of their chosen groups. The regulatory environment of the market guarantees that all insurers are subject to stringent rules, creating a competitive but stable environment. This competition encourages ongoing improvements in service provision and the creation of innovative insurance products.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Germany health & medical insurance market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- March 2025: BlackRock, Allianz, and T&D Holdings agreed to buy Viridium Group from Cinven for EUR 3.5 billion. Viridium has expertise in closed life insurance portfolios management, mangeriatric EUR 67 billion in assets of 3.4 million policyholders. The deal, set to close during the second half of 2025, will further enhance Allianz's position in Germany's health and medical insurance business.
- February 2025: The German National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Funds (GKV-SV) signed an agreement with Santhera Pharmaceuticals on the reimbursement of treatment with AGAMREE (vamorolone) for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). With this achievement, AGAMREE was the first medicine in Germany to be granted a government price for the treatment of DMD in patients 4 years and older.
- September 2024: ERGO Group's subsidiary DKV Deutsche Krankenversicherung AG (DKV) has announced that it will introduce a new supplementary dental insurance product to the German market. The new plan is intended to improve protection of dental health through the introduction of contemporary benefits and flexible variants.
- August 2024: ERGO, O2 Telefónica, and Telefónica Insurance formed an alliance for the introduction of embedded insurance services in Germany. Through this alliance, the companies will introduce the O2 Care Travel, which will include international health insurance with repatriation, rescue, and recovery costs along with hassle-free travel and emergency assistance. Individuals and families are eligible to buy this insurance plan.
- July 2024: Fintiba collaborated with BARMER to provide all-round health insurance for international students and professionals. With this partnership, Fintiba combines BARMER's medical services such as visits to doctors, dental consultations, hospitalization, and preventive checks into their repertoire.
- January 2024: Allianz Partners has announced the release of the Allyz mobile app, a digital solution offering travelers trusted guidance and expertise along with access to the entire range of insurance benefits offered to customers. The release of the mobile app in France, Germany, and the Netherlands is a significant step in the growth of Allianz Partners' digital platform.
Germany Health & Medical Insurance Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered | Statutory Health Insurance, Private Health Insurance |
| Terms of Coverage Covered | Short-term, Long-term |
| Channel of Distributions Covered | Single Tied or Insurance Group Intermediaries, Broker and Multiple Agents, Credit Institutions, Direct Selling, Others |
| Income Levels Covered | Employed Annual Income < EUR 64,350, Employed Annual Income > EUR 64,350, Self-employed, Civil Servants |
| Regions Covered | Western Germany, Southern Germany, Eastern Germany, Northern Germany |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Germany health & medical insurance market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Germany health & medical insurance market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Germany health & medical insurance industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The health & medical insurance market in the Germany was valued at USD 82.4 Billion in 2025.
The Germany health & medical insurance market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 5.08% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 128.7 Billion by 2034.
Major drivers in the Germany health and medical insurance market are rising demand for health services as a result of the geriatric population, government policies enforcing health coverage, healthcare technology progress, and improved public awareness concerning the need to have health insurance for financial stability and quality access to care.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












