
India Carbon Credit Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Project Type, End-Use Industry, and Region, 2026-2034
India Carbon Credit Market Summary:
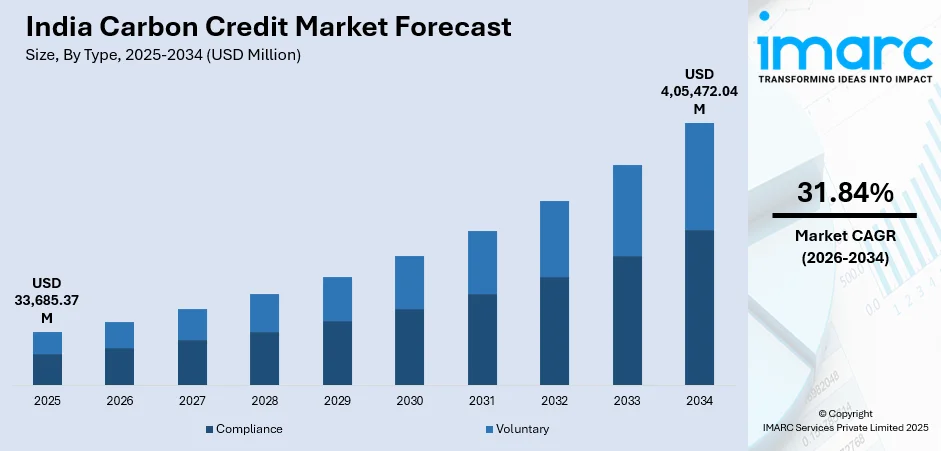
The India carbon credit market size was valued at USD 33,685.37 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 4,05,472.04 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 31.84% from 2026-2034.
The India carbon credit market is experiencing transformative growth as the country establishes comprehensive regulatory frameworks and accelerates corporate decarbonization efforts. Government initiatives are institutionalizing carbon trading mechanisms while industries adopt emissions reduction strategies. Expanding voluntary carbon markets through nature-based solutions, increasing participation in renewable energy projects, and rising corporate commitments to Net Zero targets are strengthening adoption across sectors, positioning India as a significant player in the global carbon credit ecosystem and expanding the India carbon credit market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: Voluntary dominates the market with a share of 58.04% in 2025, driven by strong corporate sustainability commitments and growing participation in nature-based offset projects.
- By Project Type: Avoidance/reduction projects lead the market with a share of 52.1% in 2025, reflecting the emphasis on renewable energy and industrial efficiency initiatives.
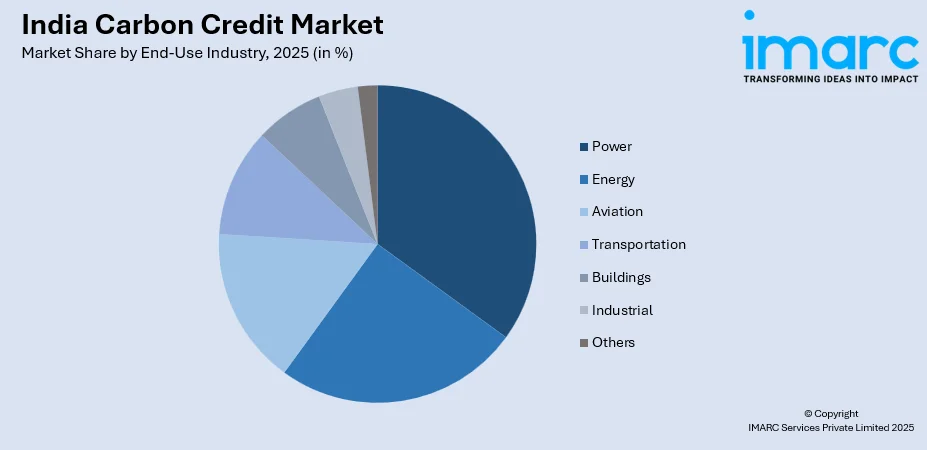
- By End-Use Industry: Power represents the largest segment with a market share of 20.05% in 2025, owing to aggressive decarbonization efforts and renewable energy transition mandates.
- By Region: North India dominates the market with a share of 31% in 2025, driven by the concentration of energy-intensive industries and manufacturing facilities in the region.
- Key Players: The India carbon credit market exhibits a fragmented competitive landscape, with carbon credit developers, verification agencies, trading platforms, and industrial conglomerates collaborating to expand offset generation, enhance credit quality standards, and build robust market infrastructure.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India carbon credit market is advancing through government-led regulatory reforms and private sector engagement. The Bureau of Energy Efficiency adopted detailed regulations for the compliance carbon market in July 2024, implementing an intensity-based baseline-and-credit system that assigns mandatory greenhouse gas emissions intensity targets to obligated entities. The framework establishes structured compliance pathways where entities exceeding targets must surrender Carbon Credit Certificates representing one tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent. The Ministry of Power approved eight methodologies for voluntary carbon credit generation in March 2025, including mangrove afforestation, green hydrogen production, renewable energy, and industrial energy efficiency. The National Dairy Development Board enabled India's first carbon credit payments to dairy farmers in November 2024, where over one thousand farmers received payments for household-level biogas plants that generate tradable credits through sustainable manure management practices.
India Carbon Credit Market Trends:
Institutionalization of Compliance Carbon Market Through Regulatory Framework
The Indian government is establishing a comprehensive institutional infrastructure to operationalize the country's carbon market. The Carbon Credit Trading Scheme transitions the existing Perform, Achieve and Trade program to a credit-based system aligned with international standards, supporting India's carbon credit market growth. The Bureau of Energy Efficiency implemented regulations covering nine energy-intensive industrial sectors, including aluminum, cement, iron and steel, and petroleum refining. Baseline emissions levels are determined using 2023-2024 data, enabling full operationalization by fiscal year 2026.
Expansion of Voluntary Carbon Markets Through Community-Based Projects
India's voluntary carbon market is experiencing substantial growth through nature-based solutions and community development projects delivering environmental benefits alongside social co-benefits. The number of registered projects under the Verra and Gold Standard programs increased from 921 in January 2022 to 1,451 by June 2023. The Green Credit Programme announced in October 2023 under the Environment Protection Act encourages tree planting in degraded forest areas and grants digital credits to participants maintaining plants over extended periods.
Innovation in Carbon Credit Generation Through Diverse Methodologies
Innovative carbon credit generation approaches are emerging across sectors, creating diversified offset opportunities. The world's first floating solar project accredited under the Verified Carbon Standard was registered in October 2024, featuring a 24.7 megawatt floating solar photovoltaic plant in Tamil Nadu, anticipated to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 38,376 tons annually. These innovative efforts highlight the potential for scaling technology-driven carbon initiatives throughout India’s renewable energy sector, showcasing how advanced solutions can support broader sustainability goals and accelerate the country’s transition to low-carbon energy.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The outlook for India’s carbon credit market remains optimistic, supported by evolving regulatory frameworks and increasing corporate engagement. The formal rollout of the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme is expected to drive growth in the compliance segment, while the voluntary market continues to expand through nature-based solutions and technology-driven initiatives. These developments attract buyers seeking high-quality credits and encourage broader participation across industries. Overall, the market is poised for sustained growth, underpinned by both regulatory support and rising demand for credible, environmentally focused carbon offsets. The market generated a revenue of USD 33,685.37 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 4,05,472.04 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 31.84% from 2026-2034.
India Carbon Credit Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Type |
Voluntary |
58.04% |
|
Project Type |
Avoidance/Reduction Projects |
52.1% |
|
End-Use Industry |
Power |
20.05% |
|
Region |
North India |
31% |
Type Insights:
- Compliance
- Voluntary
Voluntary dominates the market with a share of 58.04% of the total India carbon credit market in 2025.
The voluntary carbon credit segment leads market share due to strong corporate sustainability initiatives and growing participation in offset projects. Companies across sectors are proactively purchasing voluntary credits to achieve Net Zero commitments and demonstrate environmental responsibility to stakeholders. The voluntary market offers flexibility in project selection, enabling businesses to support nature-based solutions, renewable energy installations, and community development initiatives aligned with corporate sustainability strategies.
Rising international demand for high-quality Indian carbon credits is boosting the voluntary market. Projects certified under leading standards, such as Verra and Gold Standard, have expanded significantly, offering buyers credible offset options. The introduction of new voluntary crediting methodologies, including initiatives like mangrove afforestation and green hydrogen production, has further broadened opportunities for carbon offset generation. These developments are diversifying the voluntary credit portfolio, attracting a wider range of domestic and international buyers, and strengthening the overall dynamics and growth potential of India’s voluntary carbon market.
Project Type Insights:
- Avoidance/Reduction Projects
- Removal/Sequestration Projects
- Nature-based
- Technology-based
Avoidance/reduction projects lead the market with a share of 52.1% of the total India carbon credit market in 2025.
Avoidance and reduction projects lead the India carbon credit market because they directly prevent or minimize greenhouse gas emissions at the source, offering measurable and verifiable environmental benefits. Renewable energy initiatives such as wind, solar, and hydro power replace fossil fuel–based generation, while energy efficiency and industrial process improvements reduce emissions in key sectors. These projects provide high-quality, reliable carbon credits that appeal to both domestic and international buyers seeking tangible climate impact, making them a dominant segment within India’s growing carbon credit ecosystem.
The scalability and technological innovation associated with avoidance and reduction projects further strengthen their market leadership. Initiatives like floating solar plants, green hydrogen production, and mangrove afforestation showcase advanced methods of emission avoidance, combining sustainability with economic viability. Regulatory support, standardized certification frameworks, and corporate demand for credible credits reinforce their attractiveness. By delivering both environmental and financial value, avoidance and reduction projects continue to drive India’s carbon credit market, shaping its development and expanding voluntary and compliance market participation.
End-Use Industry Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Power
- Energy
- Aviation
- Transportation
- Buildings
- Industrial
- Others
Power represents the largest share at 20.05% of the total India carbon credit market in 2025.
The power sector commands the largest market share driven by aggressive decarbonization mandates and renewable energy transition requirements. Thermal power generators are increasingly participating in carbon markets to offset emissions while transitioning toward cleaner generation sources. The sector's participation in the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme framework positions power companies as significant credit buyers and sellers.
Leading power utilities are implementing internal carbon accounting systems and conducting emissions assessments to prepare for compliance obligations. Companies are setting ambitious Net Zero targets, prompting increased investment in carbon credit initiatives and emission reduction technologies. Integrating carbon pricing into energy planning is influencing investment strategies and accelerating the shift toward cleaner, more sustainable power generation. These measures not only support corporate sustainability goals but also drive broader adoption of low-carbon technologies, positioning the power sector as a key contributor to the country’s carbon reduction efforts.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
North India lead the market with a share of 31% of the total India carbon credit market in 2025.
North India leads the carbon credit market due to its high concentration of energy-intensive industries, manufacturing facilities, and thermal power plants. States such as Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Punjab host major industrial clusters in sectors like iron and steel, cement, and textiles, which fall under compliance carbon market regulations. The region’s extensive agricultural base also supports the development of nature-based carbon projects. Together, industrial activity and agricultural potential make North India a key hub for both carbon credit generation and market participation.
The presence of large industrial conglomerates and manufacturing hubs positions North India as a major participant in the carbon credit market. Industries are preparing for the implementation of carbon trading schemes by establishing emissions monitoring systems, identifying opportunities for efficiency improvements, and adopting renewable energy solutions. These measures allow companies to generate credits through sustainable practices while meeting compliance obligations. This dual role strengthens North India’s influence in the market, supporting both credit supply and demand within the emerging carbon trading framework.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Carbon Credit Market Growing?
Establishment of Comprehensive Regulatory Framework for Carbon Trading
The Indian government’s structured approach to establishing carbon markets through the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme is creating a strong foundation for long-term market growth. Detailed regulations introduce an intensity-based baseline-and-credit framework with mandatory greenhouse gas emissions targets for energy-intensive industrial sectors such as cement, steel, fertilizers, and textiles. The scheme provides clear compliance pathways, enabling companies to plan and implement decarbonization strategies effectively. Transitioning from existing mechanisms, the framework allows businesses to monitor emissions, invest in reduction technologies, and integrate carbon pricing into strategic decision-making, fostering a predictable and robust market environment.
Accelerating Corporate Net Zero Commitments Across Industrial Sectors
Industrial and corporate entities in India are increasingly adopting ambitious Net Zero targets, driving investments in carbon reduction measures and credit mechanisms. Companies are establishing internal carbon accounting systems, conducting emissions inventories, and identifying cost-effective abatement opportunities. The availability of diverse voluntary crediting methodologies further encourages the development of offset projects across multiple sectors. By integrating carbon pricing and reduction strategies into corporate planning, organizations are reshaping investment decisions, advancing sustainability goals, and positioning themselves competitively while contributing to broader national efforts to reduce industrial emissions.
Expansion of Voluntary Carbon Markets Through Nature-Based Solutions
India’s voluntary carbon market is expanding through participation in nature-based and community-driven projects. Initiatives such as tree planting on degraded lands and household-level biogas generation are creating tradable carbon credits while supporting sustainable development and local livelihoods. Increased recognition of carbon finance as a tool for environmental and social impact is encouraging more projects to seek certification under recognized standards. These initiatives demonstrate the scalability of community-based and nature-focused solutions, strengthening the voluntary carbon market and providing businesses with diversified options for offset generation while promoting sustainable practices across agricultural and rural sectors.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Carbon Credit Market is Facing?
Limited Market Infrastructure and Trading Mechanisms
The India carbon credit market faces infrastructure limitations as trading platforms, verification systems, and market mechanisms remain under development. The absence of established price discovery mechanisms and limited liquidity in early market stages may create volatility and uncertainty for participants. Building a robust market infrastructure requires continued investment in trading platforms, registry systems, and verification capabilities.
Technical Capacity Constraints for Monitoring and Verification
Many entities face technical capacity constraints for emissions monitoring, reporting, and verification required under the compliance framework. Smaller industrial units may lack resources and expertise to implement carbon accounting systems meeting regulatory requirements. Building technical capacity across sectors necessitates training programs, technology transfer, and support mechanisms for widespread compliance participation.
Quality Assurance Concerns in Voluntary Credit Markets
Ensuring credit quality and environmental integrity in voluntary markets remains challenging as project methodologies and verification standards vary. Concerns about additionality and permanence of carbon offsets may affect buyer confidence and credit pricing. Establishing standardized quality assurance frameworks and enhancing verification protocols are essential for maintaining market credibility and attracting sustained investment.
Competitive Landscape:
The India carbon credit market exhibits a diverse competitive landscape encompassing carbon credit developers, verification agencies, trading platforms, and industrial participants. Market players are focusing on expanding project portfolios, enhancing credit quality standards, and building strategic partnerships to strengthen market positioning. Companies are investing in technology platforms for emissions monitoring, credit tracking, and trading facilitation. Competition is intensifying as domestic entities collaborate with international standards bodies and global carbon market participants. Strategic alliances between project developers, verification agencies, and industrial conglomerates are accelerating market development and credit generation capabilities across multiple sectors.
Recent Developments:
- December 2025: IIT-Roorkee, in collaboration with the Uttar Pradesh government, launched a program that will allow farmers to generate carbon credits. The initiative is expected to provide farmers with supplementary earnings ranging from Rs 5,000 to Rs 8,000 per hectare each year. Previously, the facilitation of carbon credits for agricultural activities was limited to private companies, making this government-supported program a pioneering effort to broaden farmer participation in the carbon credit market.
- October 2025: The Government of India announced the final greenhouse gas (GHG) emission intensity targets for the first industrial sectors included in the compliance framework of the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS). This notification marks a key milestone in establishing the country’s domestic carbon market, providing a clear regulatory foundation for industries to monitor, reduce, and trade emissions, and paving the way for the operationalization of India’s compliance carbon credit system.
India Carbon Credit Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Compliance, Voluntary |
| Project Types Covered |
|
| End Use Industries Covered | Power, Energy, Aviation, Transportation, Buildings, Industrial, Others |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India carbon credit market size was valued at USD 33,685.37 Million in 2025.
The India carbon credit market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 31.84% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 4,05,472.04 Million by 2034.
Voluntary carbon credits dominate with the largest revenue share of 58.04% in 2025, driven by strong corporate sustainability commitments, growing participation in nature-based offset projects, and increasing demand from businesses seeking high-quality credits to meet Net Zero targets.
Key factors driving the India carbon credit market include the establishment of comprehensive regulatory frameworks through the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, accelerating corporate Net Zero commitments, expanding voluntary carbon markets through nature-based solutions, government approval of multiple crediting methodologies, and the transition of energy-intensive industries to compliance mechanisms.
Major challenges include limited market infrastructure and trading mechanisms in early stages, technical capacity constraints for emissions monitoring and verification among smaller entities, quality assurance concerns in voluntary credit markets, and the need for standardized verification protocols to maintain market credibility.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.

 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












