
India E-Waste Recycling Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Material, Source, and Region, 2025-2033
India E-Waste Recycling Market Size and Share:
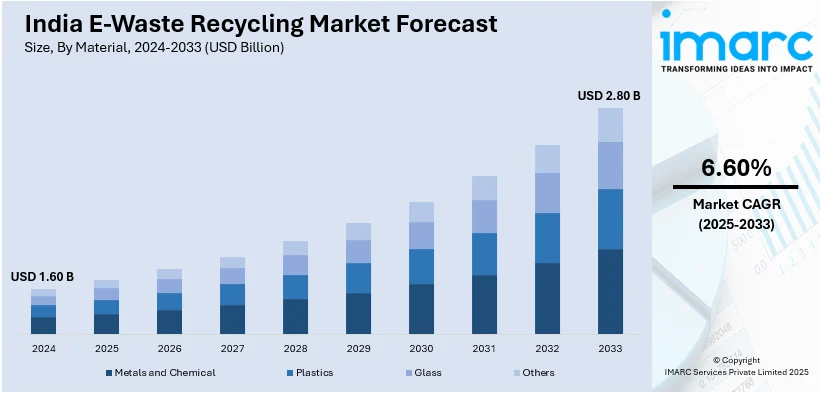
The India e-waste recycling market size was valued at USD 1.60 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 2.80 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.60% from 2025-2033. The market is driven by the supportive government policies, growing consumer awareness, and advancements in recycling infrastructure. Regulations like Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) mandate responsible e-waste handling, while awareness campaigns promote eco-friendly disposal. Improved collection and processing systems enable efficient resource recovery and reduce environmental harm. These developments foster a shift toward sustainable practices, minimizing landfill use and pollution. Together, these drivers support a circular economy by encouraging reuse, recycling, and responsible consumption of electronic products further aiding the India e-waste recycling market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.60 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 2.80 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 6.60% |
India’s surging demand for electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and appliances is driven by rapid economic growth, urbanization, and digitization. This has significantly increased the generation of e-waste across the country. With over 820 million internet users, of which approximately 54% are from rural areas, digital adoption is no longer limited to cities. The rapid technological evolution is shortening the life cycle of gadgets, especially among urban youth and professionals who frequently upgrade to newer models. This consumer behavior leads to the early obsolescence of devices and the accumulation of vast quantities of discarded electronics every year. Simultaneously, the growing digital footprint in rural areas is expanding the base of electronic consumers. Together, these trends are creating a massive and continuous influx of e-waste, driving demand for formal collection, dismantling, and recycling infrastructure, and propelling the India’s organized e-waste recycling market growth.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Government intervention through policy frameworks like the e-waste (Management) Rules, 2016 and subsequent amendments has played a pivotal role in shaping India’s e-waste recycling landscape. A key aspect of these regulations is extended producer responsibility (EPR), which mandates manufacturers to collect and responsibly recycle a specified percentage of e-waste generated from their products. This compels brands to establish take-back channels, partner with recyclers, and ensure safe disposal practices. Additionally, the government is promoting formalization of the informal sector, incentivizing recycling startups, and raising awareness about environmental hazards of improper e-waste disposal. These measures create a more structured, regulated market environment, encouraging private investment and innovation in recycling technologies. Consequently, compliance-driven demand and regulatory pressure act as powerful market drivers.
India E-Waste Recycling Market Trends:
Growing Government Initiatives and Regulations
The Indian recycling industry of e-waste is witnessing a large-scale growth fueled by stringent regulation from the government and heightened policy support. As of February 9, 2025, there are 322 registered recyclers and 72 registered refurbishers with the CPCB, providing services for recycling and refurbishing e-waste. Implementation of the E-Waste (Management) Rules has obligated manufacturers to adopt extended producer responsibility (EPR) and ensure responsible collection and recycling of electronic waste. The rule structure has favored the setup of authorized recycling plants and legalized channels of waste management. Alongside, government initiatives to create awareness regarding responsible disposal of e-waste are also picking up speed. As per the sources, in October 2023, the TDB-sponsored "Recycling on Wheels Smart-ER" was launched by Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh in Delhi improving e-waste management, the cause of sustainability, and the Swachhata Hi Seva campaign. Furthermore, cooperation from urban local bodies and private sector players has also further consolidated the collection and processing chain. Incentives by way of financial support and subsidies for development of recycling infrastructure are further India e-waste recycling market demand. With more stringent enforcement and monitoring mechanisms, the regulatory environment is further encouraging eco-friendly e-waste management practices. As the amount of electronic waste increases, initiatives from the government will be essential in providing for responsible recycling and mitigating the environmental footprint of e-waste in India.
Increasing Adoption of Formal Recycling Facilities
Another significant India e-waste recycling market trend is the transition to formal recycling facilities. With the long history of informal sector predominance in managing waste, worries about environmental pollution and unsafe recycling have motivated campaigns to encourage formal operations. These units with state-of-the-art facilities ensure safe disassembly, processing of valuable elements, and harmless disposal of dangerous elements. The formal economy also aids resource optimization by retrieving valuable metals such as gold, silver, and palladium from e-waste. Companies are also working together with certified recyclers to comply with compliance requirements under the e-waste management rules. Public awareness campaigns and corporate social responsibility initiatives are inspiring consumers to responsibly dispose of electronic waste through sanctioned channels. For instance, in July 2024, Attero launched Selsmart, a doorstep e-waste recycling platform for consumers. It provides doorstep collections to avoid data leakage and damage to the environment, broadening Attero's D2C footprint. Moreover, as investments in recycling facilities increase and informal sector integration programs expand, it is anticipated that the dependence on formal recycling units will rise, adding to a more effective and sustainable e-waste management system.
Rising Consumer Awareness and Participation
Consumer consciousness of the need for e-waste management responsibility is intensifying gradually in India. Education drives by government, non-profits, and green groups are informing consumers of the environmental and health risks caused by the unsafe disposal of e-waste. With forecasts indicating that India could generate more than 161 Million Tons of e‑waste by 2050, heightened consumer participation is critical to diverting electronics from landfills and reducing health risks. Consumers are turning to returning end-of-life electronic items to proper collection facilities or enrolling in take-back services by manufacturers. The accelerating number of e-waste collection points within urban and semi-urban locales has also eased responsible disposal further. The easy availability of mobile recycling apps and online platforms further facilitates the task of arranging for e-waste pickups for consumers. School and college awareness campaigns, as well as corporate offices, are further promoting responsible handling of e-waste. With changing consumer patterns towards environmentally friendly habits, enhanced involvement in institutional recycling streams should help minimize the amount of e-waste finding its way to landfills and lead to a healthier and cleaner environment.
India E-Waste Recycling Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the India e-waste recycling market, along with forecast at the regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on material and source.
Analysis by Material:
- Metals and Chemical
- Plastics
- Glass
- Others
Metals like copper, aluminum, gold, and hazardous chemicals form the most valuable and sensitive part of e-waste. Efficient recycling enables resource recovery and reduces environmental risks. This segment drives the economics of e-waste management, making metal extraction a primary focus for recyclers and a key component of sustainability efforts.
Additionally, the plastics from electronic casings and components are abundant in e-waste. While less valuable than metals, they present environmental challenges due to non-biodegradability. Recycling helps reduce landfill burden and pollution. Innovations in plastic separation and reuse are enhancing the viability of this segment within India’s growing circular economy framework.
Moreover, the glass is mainly found in screens, monitors, and bulbs. Though not hazardous, improper handling can lead to injury and waste. Specialized recycling processes are needed for cathode ray tubes and display glass. This segment holds limited commercial value but remains important for complete and safe e-waste dismantling.
Also, the other segment includes rubber, ceramics, and circuit board composites. These materials often require complex separation and have limited recycling options. However, advancements in technology are improving their recovery. Though small in volume, managing this category is essential for reducing landfill use and ensuring holistic, environmentally sound e-waste processing.
Analysis by Source:
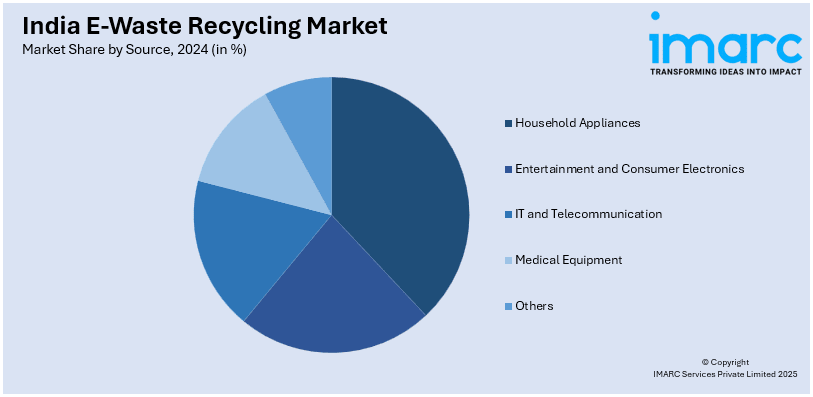
- Household Appliances
- Entertainment and Consumer Electronics
- IT and Telecommunication
- Medical Equipment
- Others
Household appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners contribute significantly to e-waste. With increasing consumerism and rapid appliance upgrades, this segment generates high waste volumes. Many appliances contain valuable metals and hazardous components, making proper recycling crucial for resource recovery, safety, and reducing environmental impact.
In line with this, the entertainment and consumer electronics includes TVs, music systems, and personal gadgets. Frequent product launches and consumer demand for newer technologies lead to high turnover and disposal. These devices contain reusable materials like plastics and metals, creating strong incentives for recycling while addressing growing concerns over electronic pollution and sustainable disposal practices.
Besides this, the IT and telecom equipment, including computers, servers, and mobile phones, form a major share of India’s e-waste. Driven by digital transformation and device obsolescence, this segment offers high recycling potential due to precious metals content. Corporate e-waste policies and bulk disposal further boost structured recycling in this category.
Furthermore, the obsolete or broken medical devices such as monitors, scanners, and diagnostic machines contribute to e-waste from hospitals and clinics. Although smaller in volume, this category requires specialized handling due to safety and contamination risks. Proper disposal and recycling are essential to prevent biohazards and recover valuable electronic components.
Apart from this, the other category includes industrial electronics, lighting equipment, and electric tools. These items, though varied and less frequently replaced, contribute meaningfully to total e-waste. Often overlooked, they contain complex components that need specialized recycling processes. Growing industrial activity and infrastructure development are gradually increasing waste volumes from this diverse segment.
Analysis by Region:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
North India, including Delhi and surrounding areas, is a major hub for e-waste generation due to dense urbanization and high-tech consumption. Delhi leads in informal recycling activities, but formal recycling infrastructure is gradually improving, driven by regulatory efforts and rising awareness about safe and sustainable e-waste management.
Concurrently, South India, particularly Bengaluru and Hyderabad, is a key region due to its strong IT and electronics sectors. These cities generate substantial e-waste, encouraging organized recycling initiatives. Government support, active startups, and high digital penetration contribute to South India’s growing role in structured e-waste collection and environmentally responsible processing.
Likewise, the East India, including Kolkata and Bhubaneswar, is witnessing rising e-waste volumes due to growing urbanization and tech adoption. While the region has a smaller recycling footprint compared to others, efforts to formalize recycling operations are increasing, supported by public-private partnerships, awareness drives, and state-level implementation of waste management rules.
Along with this, the West India, led by Mumbai and Pune, plays a crucial role in India’s e-waste landscape. Mumbai, being a commercial hub, generates large e-waste volumes. The region boasts a growing network of formal recyclers and collection centers, aided by corporate participation, strict regulatory enforcement, and increasing focus on sustainability and circular economy.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape is dynamic and evolving, marked by a mix of formal and informal players. The formal sector is growing steadily, driven by regulatory compliance, technological advancements, and increasing environmental awareness. These players focus on organized collection, eco-friendly recycling processes, and adherence to government standards. However, the informal sector still handles a significant portion of e-waste, often using unsafe and unregulated methods. Competition is intensifying as more licensed recyclers enter the market, supported by government incentives and rising investor interest. Differentiation is emerging through innovation in logistics, recycling efficiency, and integrated digital solutions. Despite challenges like low collection rates and lack of public awareness, the market shows strong potential for growth and consolidation.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the India e-waste recycling market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
Latest News and Developments:
- June 2025: Recyclekaro launched ReLoop on World Environment Day 2025 to simplify e-waste recycling across India. The digital platform enabled users to schedule pickups for old electronics, earn rewards, and track recycling habits. Initially rolled out in major cities, it aimed to mainstream responsible e-waste disposal and support corporate sustainability initiatives.
- May 2025: Envision Energy unveiled India’s first Recover-E car recycled entirely from e-waste at an event in Colaba, Mumbai, in partnership with earthday.org. Valued at ₹20 lakh, the car symbolized circularity and sustainability, using discarded electronics to raise awareness about e-waste. It marked India’s entry into global e-waste innovation efforts.
- April 2025: Andhra Pradesh MedTech Zone (AMTZ) inaugurated its integrated e-waste recycling facility in Visakhapatnam, using advanced technologies to recover high-purity metals under a zero-waste model. Launched with government collaboration, the facility offered digital traceability, doorstep pickup, and monetary incentives, promoting sustainable practices and public participation in e-waste management.
- January 2025: Attero launched Metal Mandi, a digital scrap metal marketplace, aiming to process 1,000 tonnes daily and achieve a 10-fold revenue increase by FY26. It onboarded 15,000 scrap collectors, introduced AI-based pricing, and leveraged logistics across 1,400 cities to formalize the market and reduce emissions using proprietary recycling technology.
India E-Waste Recycling Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Materials Covered | Metals and Chemical, Plastics, Glass, Others |
| Sources Covered | Household Appliances, Entertainment and Consumer Electronics, IT and Telecommunication, Medical Equipment, Others |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the India e-waste recycling market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the India e-waste recycling market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the India e-waste recycling industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India e-waste recycling market was valued at USD 1.60 Billion in 2024.
The India e-waste recycling market is projected to reach USD 2.80 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.60% during 2025-2033.
Growth in the e-waste recycling market is driven by increasing electronic device consumption, rising awareness of environmental sustainability, and stricter government regulations on electronic waste disposal. The expanding IT and telecom sectors, coupled with shorter product life cycles, are generating large volumes of e-waste. Additionally, advancements in recycling technologies and rising investments in waste management infrastructure are fostering organized sector growth and improving collection, dismantling, and recovery efficiency.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












