
India Exotic Vegetables Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Variety, Sector, Distribution Channel, and Region, 2026-2034
India Exotic Vegetables Market Summary:
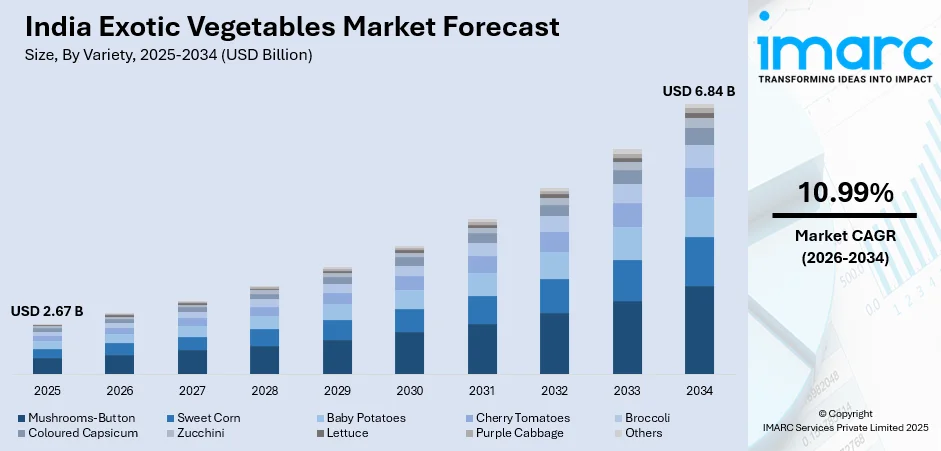
The India exotic vegetables market size was valued at USD 2.67 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 6.84 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 10.99% from 2026-2034.
The market for exotic veggies in the Indian market is expanding rapidly due to increasing awareness about health, increasing disposable incomes, and the need for foreign cuisine. The factors that are increasing the demand for these veggies include urbanization, supermarket creations, and online shopping. Some of the key veggies that are in high demand in the market are broccoli, mushrooms, and lettuce.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Variety: Mushrooms-button leads the market with a share of 18% in 2025, driven by their year-round availability, versatile culinary applications, established domestic cultivation infrastructure, high nutritional value, and growing consumer acceptance as a protein-rich meat alternative across vegetarian households.
- By Sector: Organised sector dominates the market with a share of 55% in 2025, attributed to superior quality control mechanisms, standardized packaging, reliable supply chains, enhanced cold storage capabilities, and the ability to maintain consistent product freshness and traceability standards demanded by modern consumers.
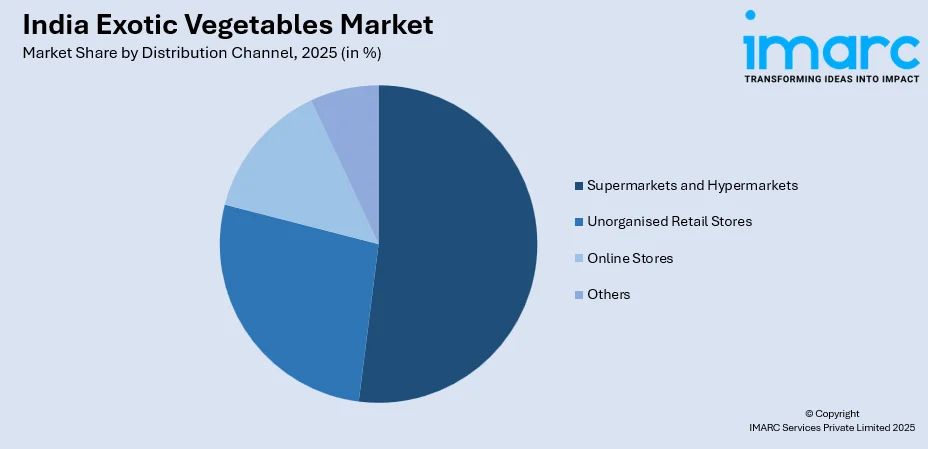
- By Distribution Channel: Supermarkets and hypermarkets lead the market with a share of 52% in 2025, supported by their organized retail environment, wide product assortment, refrigerated storage facilities, consumer preference for one-stop shopping convenience, and the ability to maintain product quality through controlled temperature displays.
- By Region: North India dominates the market with a share of 30% in 2025, supported by favorable climatic conditions for exotic vegetable cultivation in states like Punjab, Haryana, and Himachal Pradesh, high urbanization in the National Capital Region, greater disposable incomes, and well-developed modern retail infrastructure.
- Key Players: India’s exotic vegetables market include organized retail chains, large importers, and distribution firms focusing on quality and supply efficiency. Companies differentiate through cold-chain logistics, year-round availability, and partnerships with greenhouse growers. Competition centers on pricing, product variety, and distribution reach in urban and tier-II markets, with emerging startups boosting supply innovation and market penetration.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India exotic vegetables industry spans cultivation, distribution, and retail of non-native vegetables, supported by rising health awareness and increasing exposure to international cuisines. In December 2025, farmers in Uttar Pradesh’s trans-Yamuna region reported strong returns from lettuce, zucchini, parsley, asparagus, and broccoli cultivated in polyhouses and net houses, largely supplying premium hotels and modern retail outlets. This growth has been supported by state-backed subsidies that encourage protected cultivation for high-value crops, highlighting a structural shift toward controlled environment farming. Exotic vegetables are primarily grown in greenhouses, polyhouses, and net houses, enabling year-round production with consistent quality. Sold at premium prices, these vegetables reflect specialized cultivation practices and perceived nutritional benefits. Key products include mushrooms, broccoli, zucchini, lettuce, colored capsicum, and asparagus. Expanding domestic production is reducing import dependence, aided by organized farm-to-fork supply chains focused on urban markets.
India Exotic Vegetables Market Trends:
Rising Health Consciousness and Demand for Nutrient-Dense Foods
Indian consumers are increasingly prioritizing health and wellness, boosting demand for nutrient-rich exotic vegetables valued for their vitamin, mineral, and antioxidant content. In West Bengal, daily demand for locally grown broccoli rose from about 1.5 tonnes to nearly 5 tonnes in 2024, reflecting growing consumer focus on its nutritional benefits and encouraging farmers to expand production. This health-driven shift is most evident among urban middle-class and affluent households seeking dietary diversity and functional foods. Exotic vegetables such as broccoli, kale, and colored capsicum are associated with immunity support, anti-inflammatory benefits, and weight management, reinforcing their appeal amid rising lifestyle disease prevalence.
Expansion of Organized Retail and E-Commerce Channels
The proliferation of supermarkets, hypermarkets, and online grocery platforms is significantly enhancing exotic vegetable accessibility across Indian cities. This expansion aligns with the rapid growth of India’s e-commerce sector, which was valued at USD 129.72 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 651.10 billion by 2034, reflecting its growing influence on food retail and distribution. Modern retail formats provide controlled temperature environments, quality assurance, and convenient shopping experiences suited to premium produce. At the same time, e-commerce platforms are extending reach beyond metropolitan areas into tier-two and tier-three cities, while quick commerce models with rapid delivery capabilities are accelerating adoption by addressing freshness concerns and lowering purchase barriers for perishable exotic vegetables.
Growth in Domestic Cultivation and Greenhouse Farming
Domestic exotic vegetable cultivation is expanding as farmers increasingly adopt advanced practices such as greenhouse, polyhouse, and controlled environment farming. Under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) and state schemes, farmers in Uttar Pradesh and Shravasti received up to 50% subsidies on polyhouse and protected farming structures in 2025, boosting off-season production of capsicum, cucumbers, and other high-value vegetables. States like Maharashtra, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh, and Haryana have become major production hubs, supported by government initiatives in technology adoption, protected cultivation, and cold chain infrastructure, enhancing supply reliability, freshness, and reducing import dependence.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Indian exotic vegetable industry is projected to offer continued growth in the coming years due to changes in eating habits, organized retailing, and progress made in farmland. Increasing urbanization and middle-class growth create demands for high-quality health-oriented vegetables. Recovery in the institutional segment, such as QSR restaurants, coffee shops, and cloud kitchens, contributes to institutional demand. Investments in cold supply chain infrastructure, farm-to-retail supply systems, and product standardization enhance availability. Online or quick commerce growth extends product availability beyond metros, thereby creating new consumer segments in smaller cities. The market generated a revenue of USD 2.67 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 6.84 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 10.99% from 2026-2034.
India Exotic Vegetables Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Variety | Mushrooms-Button | 18% |
| Sector | Organised Sector | 55% |
| Distribution Channel | Supermarkets and Hypermarkets | 52% |
| Region | North India | 30% |
Variety Insights:
- Mushrooms-Button
- Sweet Corn
- Baby Potatoes
- Cherry Tomatoes
- Broccoli
- Coloured Capsicum
- Zucchini
- Lettuce
- Purple Cabbage
- Others
The mushrooms-button dominates with a market share of 18% of the total India exotic vegetables market in 2025.
Button mushrooms are the most widely consumed exotic vegetable in India, supported by strong domestic cultivation and year-round availability. Their versatility in both Indian and continental dishes, affordable price compared to other exotic vegetables, and recognized high protein content and health benefits have driven broad acceptance among households and the foodservice sector, while increasing awareness of their antioxidant properties and potential role in a balanced diet has further boosted demand.
India has become a major mushroom-generating nation, with large-scale mushroom farming taking place in states such as Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, and Maharashtra. Button mushrooms represent an entry point or introduction to exotic vegetables for consumers in that they possess a familiar texture as well as a relatively simple flavor profile. An increase in investments in spawn production facilities, advancements in mushroom-growing methods, as well as an interest expressed in mushroom-growing amongst farmers as a highly rewarding agricultural practice, are enhancing this supply side.
Sector Insights:
- Organised Sector
- Unorganised Sector
The organised sector leads with a share of 55% of the total India exotic vegetables market in 2025.
The dominance of the organized sector in the distribution of exotic vegetables is indicative of the premium nature of such products and consumer expectations regarding quality assurance. Organized players, like supermarket chains, hypermarkets, and branded online platforms, therefore, are able to provide standardized packaging, temperature-controlled storage, traceability systems, and consistent product quality that merits premium pricing. These retailers invest in backward integration with contracted farmers and aggregators to guarantee reliable supply chains and freshness standards that are crucial to perishable exotic produce.
The organized sector gets benefitted by the infrastructure developments that are carried out by them in cold storage, cold logistics, and modern retailing formats that help preserve the quality of produce from farms to consumers. The consumer trust that exists for branded retailing formats to buy quality produce through them, besides the convenience of one-stop shopping assisted by electronic payments, has continued to help the sector by adopting food safety measures, quality certifications, and grading systems that are aligned to the consumer demands for trustworthy produce.
Distribution Channel Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Supermarkets and Hypermarkets
- Unorganised Retail Stores
- Online Stores
- Others
The supermarkets and hypermarkets dominate with a market share of 52% of the total India exotic vegetables market in 2025.
Supermarkets and hypermarkets are the preferred retail channel for exotic vegetables, providing convenient, quality-assured shopping for premium produce. According to reports, upscale Bengaluru supermarkets reported higher sales of imported and premium local vegetables, highlighting rising urban demand through modern retail. These stores offer refrigerated displays to maintain freshness, wide product variety for one-stop shopping, and consistent availability that builds consumer trust. Major chains have invested in dedicated exotic vegetable sections, trained staff, and quality management systems, setting them apart from traditional retail.
Organized retail chains are gradually expanding across major and second-tier urban cities, thus improving the reach of exotic veggies beyond the major urban centers. Supermarkets and hypermarkets capitalize on their size to reach out to direct suppliers and suppliers of exotic veggies, thus offering favorable pricing and segmentation. This segment has benefited from consumer spending habits that include making weekend stocking trips and allowing customers to see the veggies physically before making purchases, thus focusing on freshness issues pertaining to exotic veggies that are perishable in nature.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- West and Central India
- South India
- East India
North India exhibits a clear dominance with a 30% share of the total India exotic vegetables market in 2025.
North India is the leading market for exotic vegetables, thanks to optimum agro-climatic conditions for growth, a higher level of urbanization in the National Capital Region, and established modern retailing systems. Provinces such as Punjab, Haryana, Himachal, and Uttarakhand have come forward as major growth centers for the cultivation of exotic vegetables like broccoli, colored capsicum, and zucchini. Also, the winter season in this region allows cultivation of exotic veggies in the fields, and greenhouse cultivation is done for continuous supplies to urban centers.
The DelhiNCR market represents the principal consumption center, which is fueled by the upscaling consumer base, exposure to international cuisine, and the high penetration of hotels, restaurants, and modern retail establishments. The northern regions are supported by robust cold chain infrastructure that links the production areas to the principal consumption centers. The agricultural extension network and training of farmers in the region have accelerated the use of protected cultivation practices, thus supporting the regions ability to meet the expanding consumer base.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Exotic Vegetables Market Growing?
Rising Health Consciousness and Demand for Nutritious Foods
Growing health awareness among Indian consumers is boosting demand for nutrient-dense exotic vegetables rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. A 2025 survey in major metros found over a third of urban shoppers choose produce like broccoli, asparagus, and colored capsicum for their health benefits and are willing to pay a premium. Rising lifestyle diseases, including diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular conditions, are driving shifts toward plant-based, low-calorie foods. Exotic vegetables are increasingly valued as functional foods supporting immunity, wellness, and preventive health, particularly among urban middle-class and affluent households.
Expanding Urbanization and Changing Consumer Lifestyles
India’s rapid urbanization is creating concentrated consumer markets with higher disposable incomes and evolving dietary preferences. A 2024 study in Bangalore and Hyderabad found over a third of urban shoppers actively choose exotic fruits and vegetables for health-focused purchases, reflecting growing awareness of global cuisines and nutritional benefits. Exposure to international travel and diverse cuisines, along with food media, social platforms, and cooking shows, is driving experimentation with exotic vegetables. Busy lifestyles and dual-income households are accelerating demand for ready-to-cook and pre-cut exotic produce.
Growth in Foodservice Industry and International Cuisine Adoption
The expanding foodservice sector, including hotels, restaurants, cafes, quick-service restaurants, and cloud kitchens, is driving strong institutional demand for exotic vegetables. In 2025, the Indian government encouraged hotel and restaurant chains to source produce directly from Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), promoting farm-to-hotel linkages and ensuring fresh, high-quality supply. Growing consumer interest in international cuisines and premium dining experiences is increasing the use of exotic vegetables. Corporate catering, airline catering, and institutional food services further expand demand, highlighting the need for reliable exotic vegetable supply chains.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Exotic Vegetables Market is Facing?
High Prices and Affordability Constraints
Exotic vegetables in India command premium prices because of specialized cultivations, imported seeds, and controlled environments. Thus, customers are mostly confined to the higher-income groups. Traditional or conventional buyers, who normally get vegetables at reasonable prices, are the ones sensitive to prices. Further, seasonal fluctuations and inconsistency in supply reinforce price disparity, thus limiting mainstream market penetration and category growth.
Cold Chain and Supply Chain Infrastructure Gaps
The perishable nature of exotic vegetables calls for a strong cold chain, which is yet to be developed in the infrastructure of India, right from cold storage to logistics. This affects the disposal, which in turn results in escalated supply chain costs. The rural, semi-urban, and urban areas are most adversely affected, thus confining the sale of exotic vegetables to the urban sector.
Limited Consumer Awareness in Non-Metro Markets
The consumer knowledge about the availability of such veggies, their usage, and the health benefits of the produce remains limited to the urban areas. The local recipes, preparation methods, and lack of acceptance of such produce prevent any adaptation. The produce has not been part of the local culinary and hence the need for constant marketing for their education and exposure.
Competitive Landscape:
The India exotic vegetables market consists of organized retailers, specialized fresh produce companies, agri-aggregators, online grocery companies, and individual farmers. It is becoming less fragmented into a more organized market structure due to modern retail growth and supply chain integration. Supermarkets implement contracted farmers and quality checks, while online platforms use technology to forecast and deliver. Agri-tech firms facilitate farm-to-consumer connectivity. Competition focuses on cold chain investment, backward integration, quality standardization, and brand reliability.
Recent Developments:
- In December 2025, BASF | Nunhems to acquire Noble Seeds Pvt. Ltd., strengthening its footprint in India’s vegetable seed market, has signed an agreement to buy New Delhi-based Noble Seeds, a leading hybrid seed breeder. The deal, expected to close by Q1 2026, expands BASF’s crop portfolio and market reach, reinforcing innovation and leadership in India’s vegetable seed sector.
Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Varieties Covered | Mushrooms-Button, Sweet Corn, Baby Potatoes, Cherry Tomatoes, Broccoli, Coloured Capsicum, Zucchini, Lettuce, Purple Cabbage, Others |
| Sectors Covered | Organised Sector, Unorganised Sector |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Supermarkets and Hypermarkets, Unorganised Retail Stores, Online Stores, Others |
| Regions Covered | North India, West and Central India, South India, East India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India exotic vegetables market size was valued at USD 2.67 Billion in 2025.
The India exotic vegetables market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 10.99% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 6.84 Billion by 2034.
Mushrooms-button leads the variety segment with an 18% market share, driven by year-round availability, established domestic cultivation infrastructure, versatile culinary applications, and growing consumer acceptance as a protein-rich vegetarian option.
Key factors driving the India exotic vegetables market include rising health consciousness and demand for nutritious foods, expanding urbanization and changing consumer lifestyles, growth in foodservice industry and international cuisine adoption, expansion of organized retail and e-commerce channels, and increasing domestic cultivation capacity.
Major challenges include high prices and affordability constraints limiting mass-market adoption, cold chain and supply chain infrastructure gaps causing product spoilage, limited consumer awareness in non-metro markets, seasonal supply variability, and the need for farmer education on specialized cultivation techniques.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.

 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












