
India Foreign Exchange Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Counterparty, Type, and Region, 2026-2034
India Foreign Exchange Market Summary:
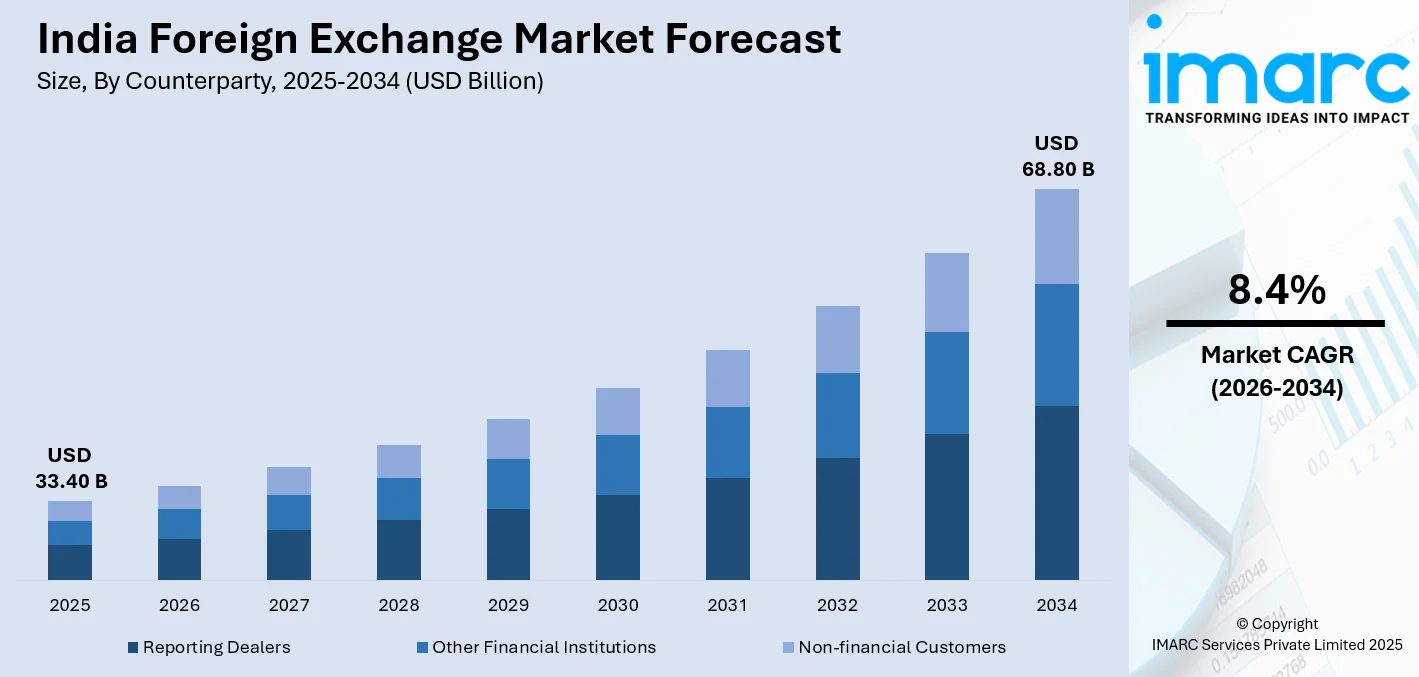
The India foreign exchange market size was valued at USD 33.40 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 68.80 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.4% from 2026-2034.
The India foreign exchange market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing cross-border trade activities, rising foreign direct investments (FDIs), and growing integration with global financial markets. Major commercial banks and authorized dealers facilitate currency trading while ensuring regulatory compliance with RBI guidelines. The expansion of digital forex platforms, growing outward FDIs by Indian corporations, and rising services exports are strengthening market dynamics. Additionally, strategic monetary policy interventions by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and expanding non-resident Indian (NRI) deposit inflows are supporting the market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Counterparty: Reporting dealers dominate the market with a share of 42.1% in 2025, owing to their central role in facilitating currency trading, ensuring market liquidity, and executing high-volume transactions for institutional and corporate clients across India's foreign exchange landscape.
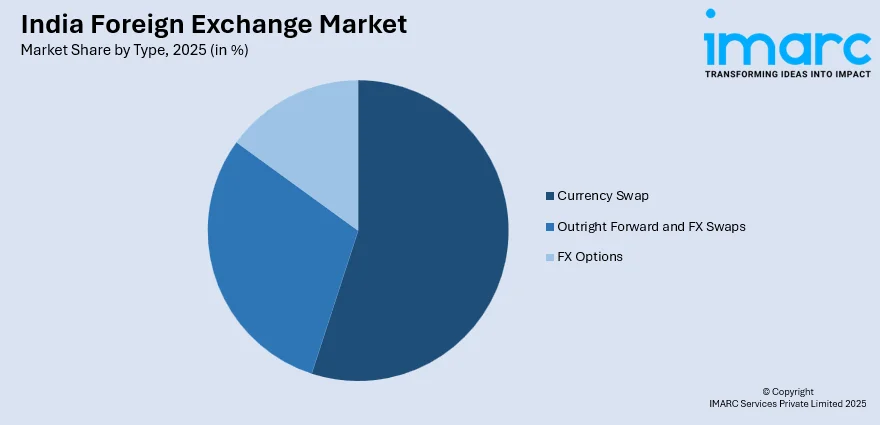
- By Type: Currency swap leads the market with a share of 40.28% in 2025, driven by growing demand for hedging instruments among corporates, rising cross-border financing activities, and strategic RBI interventions to manage rupee liquidity and exchange rate stability.
- By Region: North India comprises the largest region with 34% share in 2025, driven by the concentration of corporate headquarters, financial institutions, and authorized dealers in the National Capital Region (NCR), along with robust trade and investment activities.
- Key Players: Major commercial banks and financial institutions drive the India foreign exchange market by expanding digital platforms, enhancing currency hedging solutions, and strengthening nationwide branch networks. Their investments in technology infrastructure and strategic partnerships accelerate market participation.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India foreign exchange market is advancing, as businesses, financial institutions, and regulatory bodies embrace modernized trading infrastructure and digital solutions. Growing awareness about currency hedging instruments among corporates and rising adoption of multi-currency financial solutions continue to expand market participation significantly. The liberalization of forex regulations by the RBI and government initiatives promoting financial inclusion are encouraging broader participation from diverse market segments across the country. As of April 2025, India's outward FDI commitments nearly doubled to USD 6.8 Billion compared to USD 3.58 Billion in April 2024, demonstrating robust growth in global venture activities by Indian companies. The increasing integration of India's financial markets with the global economy, combined with the country's improving position in international competitiveness rankings, further supports sustained market expansion and technological innovations.
India Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
Rising Digital Forex Platform Adoption
The proliferation of digital platforms and increased awareness among retail investors have significantly democratized forex trading in India. User-friendly mobile applications, seamless onboarding processes, and live price feeds have lowered entry barriers for individual participants. A younger, tech-savvy investor base is actively trading major currency pairs using advanced broker-provided learning modules and analytical tools. This surge in retail involvement is adding depth and liquidity to the market, representing a notable shift from its traditionally institutional dominance, which is driving the market growth.
Expansion of NRI Remittances and Deposits
A prominent trend in the market is the continued rise in remittances from Non-Resident Indians, reflecting growing confidence in the Indian economy. According to the RBI, NRI deposits increased significantly, reaching USD 7.8 Billion from April to August 2024, compared to USD 3.7 Billion in the same period in 2023. Total outstanding NRI deposits reached USD 153 Billion by the end of August 2024. As the world's largest recipient of remittances, India benefits substantially from these inflows that strengthen forex reserves and support domestic economic stability.
Growing Internationalization of Indian Corporations
Indian companies are scaling operations beyond domestic borders by opening overseas offices, acquiring global assets, and billing in foreign currencies. This expansion significantly increases the need for currency conversions, hedging contracts, and offshore fund management solutions. From information technology (IT) services to pharmaceuticals and manufacturing, firms are embedding sophisticated forex management into their treasury strategies. India was expected to export approximately USD 210 Billion worth of IT services by FY25, resulting in significant cross-currency needs as these companies cater to their expanding global clientele base.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The India foreign exchange market outlook remains highly positive, underpinned by structural economic growth, increasing global trade integration, and proactive regulatory frameworks. The market generated a revenue of USD 33.40 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 68.80 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.4% from 2026-2034. Continued liberalization of forex regulations, expanding digital trading infrastructure, and rising corporate demand for hedging solutions will drive sustained growth. The RBI's commitment to maintaining orderly market conditions and adequate liquidity will further strengthen investor confidence. Additionally, growing FDI inflows, broadening services exports, and rising NRI remittances will contribute to market expansion throughout the forecast period.
India Foreign Exchange Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Counterparty |
Reporting Dealers |
42.1% |
|
Type |
Currency Swap |
40.28% |
|
Region |
North India |
34% |
Counterparty Insights:
- Reporting Dealers
- Other Financial Institutions
- Non-financial Customers
Reporting dealers dominate with a market share of 42.1% of the total India foreign exchange market in 2025.
Reporting dealers are significant intermediaries in the India foreign exchange market, acting as facilitators for currency trading, liquidity provision, and price discovery. These institutions, primarily comprising major commercial and investment banks, play a crucial role in executing high-volume forex transactions for institutional and corporate clients. According to RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra, the India forex market average daily turnover doubled from USD 32 Billion in 2020 to USD 60 Billion in 2024, demonstrating the enhanced operational capacity of reporting dealers.
The dominance of reporting dealers in the market is underpinned by their extensive branch networks, sophisticated trading platforms, and regulatory compliance frameworks. These institutions offer comprehensive forex services, including spot transactions, forward contracts, and derivative instruments, to meet diverse client requirements. The Foreign Exchange Dealers' Association of India coordinates industry practices and standards among authorized dealers to ensure market integrity and operational efficiency across the Indian forex ecosystem.
Type Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Currency Swap
- Outright Forward and FX Swaps
- FX Options
Currency swap leads with a share of 40.28% of the total India foreign exchange market in 2025.
Currency swaps have emerged as the preferred instrument for managing forex exposure and liquidity requirements among Indian corporates and financial institutions. These instruments enable counterparties to exchange currencies at predetermined rates while managing interest rate differentials effectively. In December 2025, the RBI announced a USD 10 Billion USD/INR buy-sell swap for a three-year tenor to inject rupee liquidity into the banking system, highlighting the strategic importance of currency swaps in monetary policy operations.
Beyond liquidity management, currency swaps help Indian corporates hedge long-term foreign currency borrowings and overseas investment exposures more efficiently than short-term spot or forward contracts. Banks use these instruments to balance balance-sheet mismatches and manage funding costs in volatile currency environments. The growing utilization of swaps reflects increasing sophistication in treasury operations and risk management practices. As cross-border trade, external commercial borrowings, and foreign portfolio flows expand, currency swaps are becoming integral to maintaining market stability, smoothing interest rate transmission, and supporting orderly functioning of the India foreign exchange market.
Regional Insights:
- South India
- North India
- West & Central India
- East India
North India exhibits a clear dominance with a 34% share of the total India foreign exchange market in 2025.
North India's leadership in the foreign exchange market is driven by the concentration of corporate headquarters, major financial institutions, and authorized dealers in NCR. Delhi-NCR serves as a prominent economic hub with extensive forex infrastructure supporting trade and investment activities. As per the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), the total FDI inflow in Delhi reached INR 3,45,375 Crore (USD 38.96 Billion) from October 2019 to June 2025. The region hosts numerous RBI-authorized dealers and full-fledged money changers catering to diverse forex requirements of businesses, travelers, and students.
The regional dominance is further supported by strong industrial activities, significant international trade flows, and growing outbound travel demand from northern states. Noida has emerged as a prominent financial services hub, with substantial investments in commercial infrastructure and data center facilities supporting banking and financial operations. The region's proximity to government institutions and regulatory bodies facilitates efficient forex operations and policy implementation, strengthening North India's position as the leading regional market.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Foreign Exchange Market Growing?
Rising FDI and Portfolio Investments
FDI inflows and portfolio investments are significantly affecting currency markets and driving forex demand in India. The decision of foreign investors to invest in Indian assets creates substantial demand for the rupee, stimulating forex trading activities across institutional and corporate segments. As of December 2024, India reached USD 1 Trillion in cumulative FDI since April 2000, with USD 42.1 Billion inflows recorded in the first half of fiscal year 2024-25 alone, marking a significant increase of 26% over the previous period. This sustained investment momentum reflects growing international confidence in India's economic fundamentals and regulatory environment. The inflows strengthen foreign exchange reserves while supporting rupee stability through enhanced forex market liquidity and depth. Increased foreign participation also raises demand for hedging instruments, such as forwards, swaps, and options, further deepening forex market activity and institutional engagement.
Expansion of Services Exports and IT Sector Growth
The country's expanding exports, particularly in the services sector, have significantly influenced the market demand by increasing foreign currency inflows. Strong performance in industries, such as IT, software development, and business services has bolstered foreign exchange supply, contributing to trade balance improvements and greater market stability. Software and IT services, in particular, continue to serve as major sources of inflows, attracting global clients and reinforcing India’s competitive position in international markets. This growth supports greater participation in the forex market by corporate entities, who actively engage in hedging and currency management to optimize cross-border transactions. Additionally, the rising prominence of service exports strengthens India’s integration into global value chains, encourages investments in technology and infrastructure, and enhances confidence in the economy.
Proactive RBI Monetary Policy and Market Interventions
Strategic monetary policy decisions by the RBI are playing a pivotal role in positively contributing to market growth and stability. Interest rate adjustments and targeted interventions help stabilize the rupee while managing market volatility effectively. The RBI has introduced several regulatory reforms to enhance forex market transparency and participant diversity, with the onshore and offshore markets becoming tightly integrated. The central bank’s proactive measures, including open market operations and liquidity management tools, ensure smooth functioning of currency and derivative markets. Forward guidance and policy communication strengthen investor confidence and reduce speculative pressures. RBI’s coordination with banks and financial institutions supports efficient hedging mechanisms for corporates and exporters. Overall, these interventions foster a resilient forex ecosystem, encouraging deeper market participation, improved pricing efficiency, and alignment with India’s broader economic and growth objectives.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Foreign Exchange Market is Facing?
Currency Volatility and Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Constant fluctuations in global oil prices affect the rupee significantly, as India is a major oil importer requiring substantial foreign currency for petroleum purchases. Rising geopolitical tensions and shifts in global monetary policy are creating unpredictable exchange rate movements that challenge forex market participants. The rupee faces pressure from dollar outflows and changing foreign investor sentiment, requiring active central bank intervention to maintain stability. These volatility concerns can discourage market participation and complicate hedging strategies for corporate treasury operations.
Regulatory Restrictions on Forex Trading Activities
The RBI and Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) enforce strict regulatory controls on forex trading to manage financial stability and limit excessive speculation. Retail participants are permitted to trade only a narrow set of exchange-traded, INR-linked currency pairs, restricting access to global forex markets. These limitations reduce diversification options and constrain advanced trading strategies commonly used internationally. While the framework prioritizes investor protection and capital account stability, it also slows market innovation and liquidity growth. Regulatory oversight increases compliance responsibilities for authorized intermediaries, adding procedural and operational complexity.
Global Geopolitical Uncertainties and Trade Tensions
Global geopolitical developments, including international trade tensions and regional conflicts, create uncertainty in forex markets worldwide, affecting Indian currency valuations. Policy decisions by major central banks influence capital flows and exchange rate dynamics significantly. The emergence of alternative payment mechanisms and potential shifts in global reserve currency composition add complexity to forex market operations. These external factors require market participants to continuously adapt their strategies while managing heightened risk exposure.
Competitive Landscape:
The India foreign exchange market is highly competitive, featuring major commercial banks that lead with extensive branch networks and customized service offerings. Fintech companies are driving innovations with digital platforms and mobile applications, enhancing accessibility and convenience for retail participants. Competition is intensifying, as market players expand their digital infrastructure, improve real-time pricing capabilities, and develop sophisticated hedging solutions. Strategic partnerships between banks and technology providers are fostering innovations while accelerating product launches and service enhancements. The market structure includes authorized dealers, forex brokers acting as intermediaries, and diverse customer segments, comprising individuals, corporates, and institutional investors seeking comprehensive forex solutions.
Recent Developments:
- In January 2025, the RBI revised regulations under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) to facilitate cross-border transactions, including allowing Indian exporters to open foreign currency accounts with overseas banks. Individuals residing outside India could utilize their funds in repatriable INR accounts for investments abroad, including FDI, in non-debt instruments.
India Foreign Exchange Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Counterparties Covered | Reporting Dealers, Other Financial Institutions, Non-Financial Customers |
| Types Covered | Currency Swap, Outright Forward and Fx Swaps, Fx Options |
| Regions Covered | South India, North India, West and Central India, East India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India foreign exchange market size was valued at USD 33.40 Billion in 2025.
The India foreign exchange market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.4% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 68.80 Billion by 2034.
Reporting dealers dominated the market with a share of 42.1%, driven by their central role in facilitating currency trading, providing market liquidity, and executing institutional transactions through extensive banking networks.
Key factors driving the India foreign exchange market include rising FDI inflows, expanding services exports, proactive RBI monetary interventions, growing digital forex platform adoption, and increasing corporate demand for hedging solutions.
Major challenges include currency volatility from global oil price fluctuations, regulatory restrictions limiting forex trading options, geopolitical uncertainties affecting capital flows, compliance complexities for market participants, and exchange rate pressures from shifting foreign investor sentiment.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












