
India Fungicide Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Form, Crop Type, Mode of Action, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
India Fungicide Market Summary:
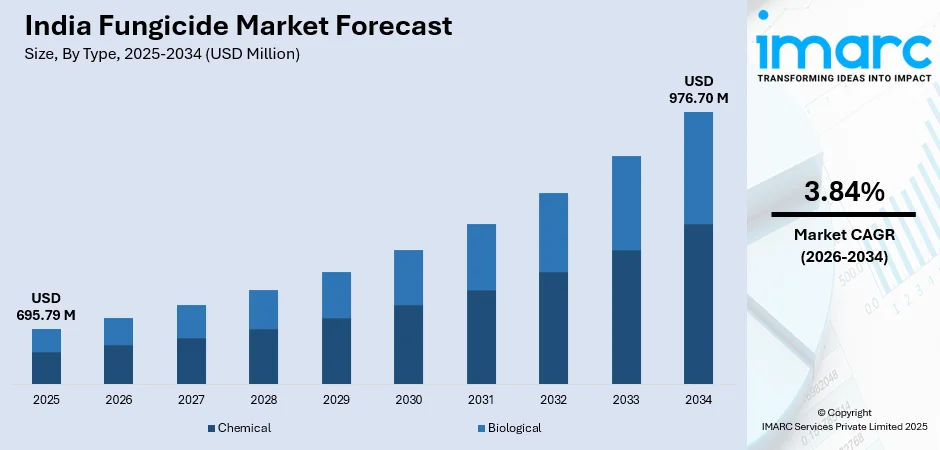
The India fungicide market size was valued at USD 695.79 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 976.70 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 3.84% from 2026-2034.
The market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing crop disease prevalence, government initiatives supporting modern agricultural practices, and rising food production demands to feed India's growing population. Apart from this, the integration of precision agriculture technologies and growing awareness among farmers about fungicide benefits are accelerating adoption rates across diverse agricultural regions. Moreover, enhanced distribution networks and introduction of innovative fungicide formulations are further expanding the India fungicide market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: Chemical dominates the market with a share of 76% in 2025, driven by farmers' preference for synthetic fungicides due to immediate efficacy and widespread availability across traditional agricultural distribution channels.
- By Form: Liquid leads the market with a share of 62% in 2025, benefiting from ease of application, superior mixing capabilities with water, and efficient coverage on plant surfaces compared to dry formulations.
- By Crop Type: Cereals and grains represent the largest segment with a market share of 40% in 2025, driven by extensive cultivation areas of rice and wheat and these crops' high susceptibility to fungal diseases requiring consistent fungicide protection.
- By Mode of Action: Contact dominates the market with a share of 54% in 2025, favored for their direct pathogen control and cost-effectiveness in managing foliar fungal diseases across diverse crop types.
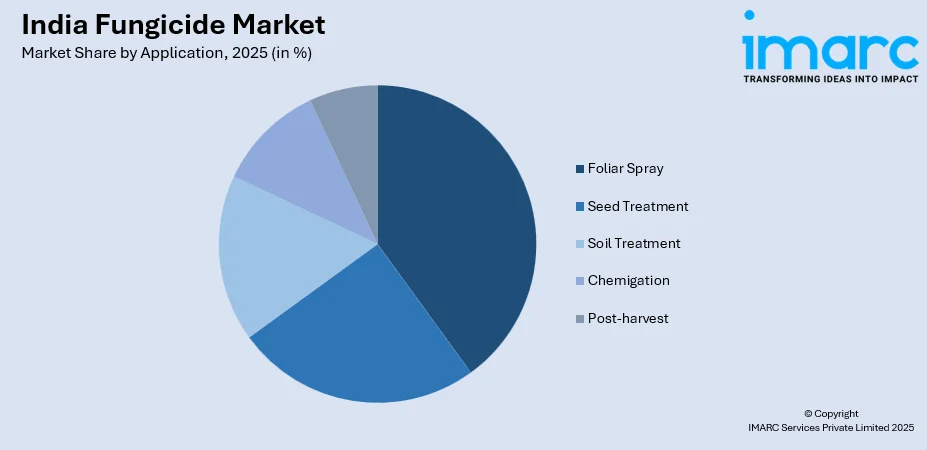
- By Application: Foliar spray leads the market with a share of 39% in 2025, preferred for efficient disease management by directly targeting pathogens on leaves and facilitating swift fungicide penetration into plant tissues.
- By Region: North India represents the largest segment with a market share of 34% in 2025, driven by concentrated agricultural activities in Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan, where intensive cereal cultivation drives substantial fungicide consumption.
- Key Players: Top companies in the India fungicide market are expanding distribution, updating product lines with safer, effective chemistries, investing in local manufacturing, offering farmer training programs, and partnering with agri‑tech firms for better field support. Many are improving supply chains and digital sales channels to reach smaller growers faster and cheaper.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India fungicide market is positioned for sustained expansion as agricultural sector contributes approximately 17-18% to the country's GDP with over 58% of the population relying on agriculture for livelihoods. The growing emphasis on crop protection solutions stems from the critical need to mitigate yield losses caused by fungal diseases, which can reduce agricultural output by 20-50% depending on disease severity and crop type. Government support through schemes like Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN), which provided INR 6000 to farmers, is facilitating access to quality fungicides and modern agricultural inputs. The market is witnessing technological transformation with precision agriculture adoption, as by end of 2025, a majority of Indian farmers are expected to utilize precision technologies including targeted fungicide application systems optimized through data analytics and remote sensing.
India Fungicide Market Trends:
Rapid Adoption of Precision Agriculture Technologies
Precision agriculture is fundamentally transforming fungicide application practices across India's agricultural landscape, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions regarding crop disease management and fungicide deployment. Advanced technologies including remote sensing, GPS-guided equipment, drone-based surveillance, and predictive analytics platforms are being progressively integrated into farming operations to optimize fungicide application timing, dosage, and coverage. This technological shift results in enhanced crop health, improved disease control efficacy, reduced fungicide waste, and better economic returns for farmers. The government supports this transformation through initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana, which aims to improve agricultural efficiency and increase crop yields through technology adoption. In 2025, The Prime Minister unveiled two significant initiatives in the agricultural sector, with a budget of Rs 35,440 crore. He initiated the PM Dhan Dhaanya Krishi Yojana with a budget of Rs.24,000 crore. He also initiated the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses with a budget of Rs. 11,440 crores. The Prime Minister also launched and committed to the nation initiatives totaling over Rs 5,450 crore in the animal husbandry, fisheries, agriculture, and food processing fields, while also laying the groundwork for further projects estimated at about Rs 815 crore.
Rising Prominence of SDHI Fungicides with Multi-Site Activity
Succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) fungicides are experiencing rapid market expansion in India due to their unique mode of action, broad-spectrum efficacy, excellent translaminar and systemic activity, and ability to address fungicide resistance challenges. These advanced fungicides not only effectively control wide-ranging crop diseases but also tackle resistance issues posed by pathogens that have developed tolerance to older azole and strobilurin products. Major agrochemical companies including have intensified their focus on SDHI product registrations, recognizing substantial market potential for these innovative compounds. Syngenta India has unveiled two new crop protection products including Miravis®️ Duo and Reflect®️ Top, aimed at transforming crop protection and guaranteeing high-quality yields for farmers throughout India.
Growing Shift Toward Biological and Eco-Friendly Fungicides
Environmental consciousness and consumer demand for chemical-free agricultural produce are driving a significant transition toward bio-based and environmentally sustainable fungicides across India's agricultural sector. These biological fungicides, derived from natural materials including plant extracts, bacteria, and fungi, provide targeted disease control with minimal residues affecting human health or environmental ecosystems, making them ideal for both domestic consumption and export-oriented agriculture. Regulatory support includes quicker clearance procedures for biopesticides, encouraging manufacturers to expand product offerings in this sustainable segment. In 2025, BASF India has revealed the introduction of two innovative crop protection products, Valexio Insecticide and Mibelya Fungicide, aimed at assisting rice farmers in India. These worldwide advancements are designed for one of the nation's most essential crops and seek to boost productivity while tackling significant pest and disease issues. The initiative supports India’s national food security objectives and aims to enhance yields via efficient control of rice hoppers and diseases like sheath blight.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The increasing agricultural intensification and rising crop protection needs is supporting the growth of the market. This growth will be underpinned by expanding agricultural land under commercial cultivation, government initiatives promoting modern farming practices, technological advancements in fungicide formulations, and heightened farmer awareness regarding disease management importance. The market generated a revenue of USD 695.79 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 976.70 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 3.84% from 2026-2034. The market will witness intensified competition as domestic and multinational players introduce innovative products targeting specific crop-disease combinations while adhering to environmental sustainability standards. Regional expansion into untapped eastern and northeastern states will create additional growth opportunities beyond traditional agricultural belts.
India Fungicide Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Type |
Chemical |
76% |
|
Form |
Liquid |
62% |
|
Crop Type |
Cereals and Grains |
40% |
|
Mode of Action |
Contact |
54% |
|
Application |
Foliar Spray |
39% |
|
Region |
North India |
34% |
Type Insights:
- Chemical
- Triazoles
- Strobilurins
- Dithiocarbamates
- Chloronitriles
- Phenylamides
- Others
- Biological
- Microbials
- Microchemical
- Macrobials
Chemical dominates with a market share of 76% of the total India fungicide market in 2025.
Chemical fungicides dominate the India fungicide market with approximately 76% share due to their rapid disease control efficacy, broad-spectrum pathogen coverage, and cost-effectiveness compared to biological alternatives. These synthetic compounds have undergone extensive validation across India's diverse agro-climatic zones, providing farmers with proven disease management reliability. The segment benefits from well-established manufacturing infrastructure, comprehensive distribution networks penetrating remote agricultural regions, and robust technical support from agrochemical companies. Major chemical fungicide classes including triazoles, strobilurins, and SDHI compounds maintain strong market dominance through systemic action and multi-site protective capabilities against fungal pathogens.
The chemical fungicide segment's sustained leadership reflects continuous innovation in formulation technologies, including improved adjuvants, surfactants, and delivery-enhancing systems that optimize fungicide adhesion, rain fastness, and plant tissue penetration. The segment's competitive pricing structure, established farmer trust built over decades of field performance, and compatibility with integrated disease management programs ensure continued market dominance despite growing environmental consciousness and regulatory scrutiny surrounding synthetic pesticide usage in agricultural production systems.
Form Insights:
- Liquid
- Suspension Concentrates (SC)
- Emulsifiable Concentrates (EC)
- Soluble Liquid Flowables (SLC)
- Dry
- Water Dispersible Granules (WDG)
- Wettable Powder (WP)
Liquid leads with a share of 62% of the total India fungicide market in 2025.
Liquid fungicides command the largest market share due to their practical advantages in application technology, mixing characteristics, and distribution logistics across India's diverse agricultural landscape. These formulations offer farmers convenient preparation processes, consistent spray solutions, and effective coverage on plant foliage and soil surfaces. Furthermore, liquid fungicides facilitate precise dosing, reduce dust exposure during handling, and enable efficient tank-mixing with other crop protection products for integrated disease management programs.
The segment encompasses various formulation types including emulsifiable concentrates, suspension concentrates, and soluble liquids, each designed for specific application requirements and crop-disease scenarios. Apart from this, major agrochemical companies invest heavily in developing advanced liquid formulations incorporating adjuvants, surfactants, and delivery-enhancing technologies that improve fungicide adhesion, rainfastness, and penetration into plant tissues. Distribution networks for liquid fungicides are well-established across urban and rural markets, ensuring consistent product availability during critical application periods.
Crop Type Insights:
- Cereals and Grains
- Corn
- Wheat
- Rice
- Others
- Oilseeds and Pulses
- Soybean
- Cotton
- Others
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Apple
- Pears
- Cucumber
- Potatoes
- Grapes
- Others
- Others
Cereals and grains exhibit a clear dominance with a 40% share of the total India fungicide market in 2025.
Cereals and grains face severe disease pressure from fungal pathogens including rice blast, sheath blight, wheat rusts, and various leaf spot diseases capable of devastating yields without effective fungicide intervention. The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) documents that disease outbreaks in cereal crops can reduce yields by up to 50% when left unmanaged, creating compelling economic justification for preventive and curative fungicide applications throughout growing seasons. Government procurement programs guaranteeing minimum support prices for wheat and rice incentivize farmers to invest substantially in crop protection measures including fungicides to maximize production volume and grain quality standards.
The cereals and grains segment's market dominance is reinforced by government initiatives supporting food security objectives and agricultural modernization across India's vast cereal-producing regions. Climate change amplifies disease management challenges through altered rainfall patterns and extended humidity periods creating favorable conditions for fungal pathogen proliferation, with warming trends along India's west coast, central regions, and interior peninsula fostering conducive environments for diseases including maize sorghum downy mildew and turcicum leaf blight.
Mode of Action Insights:
- Contact
- Systemic
Contact leads with a share of 54% of the total India fungicide market in 2025.
Contact fungicides maintain market dominance through straightforward mode of action, broad-spectrum disease control capabilities, cost-effectiveness, and well-established efficacy across diverse crop-disease combinations throughout India's agricultural regions. These protectant fungicides form chemical barriers on plant surfaces that directly inhibit fungal spore germination and mycelial growth upon contact, providing preventive protection against multiple fungal pathogens without requiring absorption into plant tissues. Contact fungicides including sulfur, mancozeb, copper-based compounds, and chlorothalonil are extensively deployed for managing diseases in cereals, vegetables, fruits, and plantation crops.
The segment benefits from decades of accumulated farmer experience, extensive distributor networks ensuring rural availability, competitive pricing structures accessible to smallholder farmers, and proven performance under varied environmental conditions across India's diverse agro-climatic zones. Major advantages include significantly lower resistance development risk compared to single-site systemic fungicides, rainfast properties in specific formulations maintaining efficacy under monsoon conditions, and compatibility with integrated disease management programs enabling tank-mixing with other crop protection products.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Seed Treatment
- Soil Treatment
- Foliar Spray
- Chemigation
- Post-harvest
Foliar spray exhibits a clear dominance with a 39% share of the total India fungicide market in 2025.
Foliar spray applications dominate the market as the predominant fungicide deployment method across India's agricultural sector, accounting for the majority of fungicide volume applied across diverse crops and agro-climatic regions. This application method provides efficient protection against foliar fungal diseases by directly targeting pathogens on leaves, stems, and reproductive structures, ensuring swift penetration and absorption into plant tissues for both contact and systemic fungicides. Technological advancements including improved spray equipment with adjustable nozzles, proprietary adjuvants enhancing coverage and adhesion, and weather-based disease forecasting systems optimize foliar fungicide applications for maximum efficacy while minimizing off-target movement and environmental impacts.
The foliar spray segment's market dominance is reinforced by comprehensive farmer training programs conducted by government extension services and agrochemical companies emphasizing proper application techniques, equipment calibration, safety precautions, and environmental stewardship practices. Foliar applications remain essential for high-value horticultural crops including grapes, tomatoes, chilies, and potatoes where diseases like downy mildew and late blight require frequent protective and curative treatments throughout growing seasons to maintain premium quality standards demanded by domestic and export markets.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
North India leads with a share of 34% of the total India fungicide market in 2025.
North India represents the dominant regional market for fungicides, encompassing major agricultural states including Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan that collectively account for significant portions of India's wheat, rice, and sugarcane production. This region's agricultural significance stems from extensive irrigation infrastructure including canal networks fed by major river systems, favorable agro-climatic conditions supporting multiple cropping patterns, and well-developed agricultural input distribution networks reaching rural markets. The region benefits from government procurement programs providing minimum support prices for wheat and rice, incentivizing farmers to invest in crop protection measures including fungicides to maximize yields and grain quality.
Intensive cereal cultivation across millions of hectares creates substantial fungicide demand, with farmers applying multiple fungicide treatments throughout the growing season to manage diseases including rice blast, sheath blight, wheat rusts, and various leaf spot pathogens. Agricultural universities, research institutions, and extension services in this region actively promote scientific crop protection practices, contributing to higher fungicide adoption rates compared to other regions. The presence of major agrochemical manufacturing facilities, distributor headquarters, and retail networks further strengthens market infrastructure supporting fungicide distribution and farmer education programs.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Fungicide Market Growing?
Government Support and Agricultural Development Initiatives Driving Modernization
The Indian government's commitment to enhancing agricultural productivity and ensuring national food security serves as a fundamental driver propelling fungicide market growth through comprehensive policy support, financial assistance programs, and infrastructure development initiatives. Emphasizing the well-being of farmers and the advancement of the agriculture sector, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced on July 23 in her Union Budget for 2024-25 that the government will conduct a thorough evaluation of the agricultural research framework to enhance productivity and create climate-resilient crop varieties. The finance minister revealed that ₹1.52 lakh crore has been earmarked for agriculture and related sectors while presenting the Budget for the fiscal year 2024-25.
Increasing Prevalence of Crop Diseases Threatening Agricultural Production
The escalating occurrence of fungal diseases across India's diverse agricultural landscape presents a critical challenge adversely affecting crop output, quality, and farmer livelihoods, thereby necessitating expanded fungicide usage to protect agricultural investments and ensure food security. Alarming increases in diseases such as rice blast, wheat rusts, powdery mildew, downy mildew, and stem rot across major crop-producing regions drive farmers to seek reliable fungicide solutions for disease prevention and control. Climate change amplifies disease challenges through altered rainfall patterns, temperature fluctuations, and extended humidity periods that create favorable conditions for fungal pathogen survival, reproduction, and spread across agricultural landscapes. In 2025, India’s agricultural regions suffered from a triple crisis as Punjab, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh encounter extensive crop damage caused by floods, persistent monsoon rains, and a viral infection affecting soybeans. Millions of acres of kharif crops were devastated, prompting urgent demands for financial assistance. The extensive crop failures were severely jeopardizing farmer incomes and exerting considerable pressure on India’s food security.
Rising Food Production Demands to Feed Growing Population
India's demographic trajectory, with population expected to reach 1.51 billion by 2030, creates unprecedented pressure on agricultural systems to increase food production while operating under land and resource constraints. With over 58% of India's population relying directly on agriculture for livelihoods and the sector contributing to national GDP, ensuring agricultural productivity through effective crop protection becomes a matter of national economic and food security priority. The growing middle class with increasing purchasing power drives demand for diverse, high-quality food products including fresh fruits, vegetables, and processed foods that require consistent agricultural output uncompromised by disease losses. Government programs emphasizing crop intensification, multiple cropping patterns, and productivity enhancement all depend fundamentally on protecting crops from disease losses that would otherwise negate gains from improved seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation investments.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Fungicide Market is Facing?
Prevalence of Counterfeit and Substandard Products Undermining Market Integrity
The widespread circulation of counterfeit, spurious, and adulterated fungicides throughout India's fragmented distribution networks poses a severe challenge undermining farmer confidence, crop protection efficacy, and legitimate manufacturer revenues across the market. Counterfeit products are sold at artificially low prices that lure cost-conscious farmers into purchasing inferior products that fail to control diseases, ultimately resulting in crop damage, reduced yields, and higher overall costs when farmers must reapply legitimate fungicides or suffer harvest losses. Sustained use of counterfeit fungicides can permanently damage farmland fertility, contaminate food chains with hazardous residues causing foodborne diseases, and threaten India's agricultural export reputation when residue violations are detected on shipments to international markets.
Regulatory Complexities and Approval Delays Hindering Innovation
Stringent regulatory frameworks, complex approval processes, and lengthy registration timelines create significant barriers to introducing innovative fungicide formulations, advanced active ingredients, and improved disease management technologies in India's agricultural market. These extended approval timelines increase development costs, delay return on research investments, and potentially allow disease resistance to develop against existing fungicides before superior alternatives receive market approval. Fragmented regulatory oversight involving multiple government agencies at central and state levels creates coordination challenges, inconsistent enforcement standards, and bureaucratic inefficiencies that frustrate both domestic and multinational manufacturers seeking to commercialize new products.
Environmental Concerns and Shift Toward Alternative Farming Practices
Growing public awareness regarding pesticide environmental impacts, residue concerns in food chains, and ecological sustainability is driving farmers toward alternative crop protection approaches including organic farming, integrated pest management, and biological controls that may limit conventional fungicide adoption. Environmental advocacy groups, consumer organizations, and media coverage highlighting pesticide-related environmental contamination, biodiversity impacts, and potential health effects create negative perceptions that influence farmer purchasing decisions and government policy formulations. The adoption of alternative farming methods including crop rotation, mechanical pest controls, predatory insect introduction, and biopesticide applications provides farmers with non-chemical disease management options that may reduce conventional fungicide demand, particularly among educated, environmentally conscious farming communities.
Competitive Landscape:
The India fungicide market exhibits moderate competitive intensity characterized by the presence of established multinational agrochemical corporations, prominent domestic manufacturers, and emerging regional players competing across technology innovation, product portfolio breadth, distribution network reach, and pricing strategies. Major global companies maintain significant market positions through continuous research and development investments, introduction of patented fungicide molecules, extensive field trial networks, and comprehensive technical support services to farming communities. These multinational players leverage their global research capabilities to introduce advanced fungicide technologies including SDHI compounds, novel formulations, and integrated disease management solutions that address evolving pathogen resistance challenges and farmer productivity requirements. Prominent domestic manufacturers compete effectively through localized product portfolios, competitive pricing structures, extensive rural distribution networks, and deep understanding of regional crop-disease dynamics and farmer preferences. The competitive landscape is further shaped by strategic partnerships between seed companies and fungicide manufacturers, collaborations with agricultural universities for field research, and investments in digital agriculture platforms providing disease forecasting and application advisory services.
Recent Developments:
- In September 2025, Corteva Agriscience has introduced Zorvec Entecta, a fungicide designed for grapes and potatoes in India. Utilizing Zorvec technology, the product is claimed to offer defense against Downy Mildew (Plasmopara viticola) in grapes and Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) in potatoes.
India Fungicide Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered |
|
| Forms Covered |
|
| Crop Types Covered |
|
| Modes of Action Covered | Contact, Systemic |
| Applications Covered | Seed Treatment, Soil Treatment, Foliar Spray, Chemigation, Post-harvest |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India fungicide market size was valued at USD 695.79 Million in 2025.
The India fungicide market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 3.84% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 976.70 Million by 2034.
Chemical dominated the market with approximately 76% market share in 2025, driven by widespread farmer preference for synthetic fungicides offering immediate efficacy, proven performance, and established availability through traditional distribution channels across rural and urban agricultural markets.
Key factors driving the India fungicide market include government support providing farmer assistance, increasing crop disease prevalence reducing yields by 20-50%, rising food production demands the masses, precision agriculture adoption reaching majority of the farmers by 2025, and climate change intensifying fungal pathogen proliferation.
Major challenges include counterfeit products causing annual food losses, complex regulatory approval delays extending several years, environmental concerns over pesticide contamination affecting Indian rivers, and farmers shifting toward organic farming and integrated pest management alternatives.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.

 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












