
India Hospital Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Ownership, Type, Bed Capacity, Regionality, Type of Services, and Region, 2026-2034
India Hospital Market Summary:
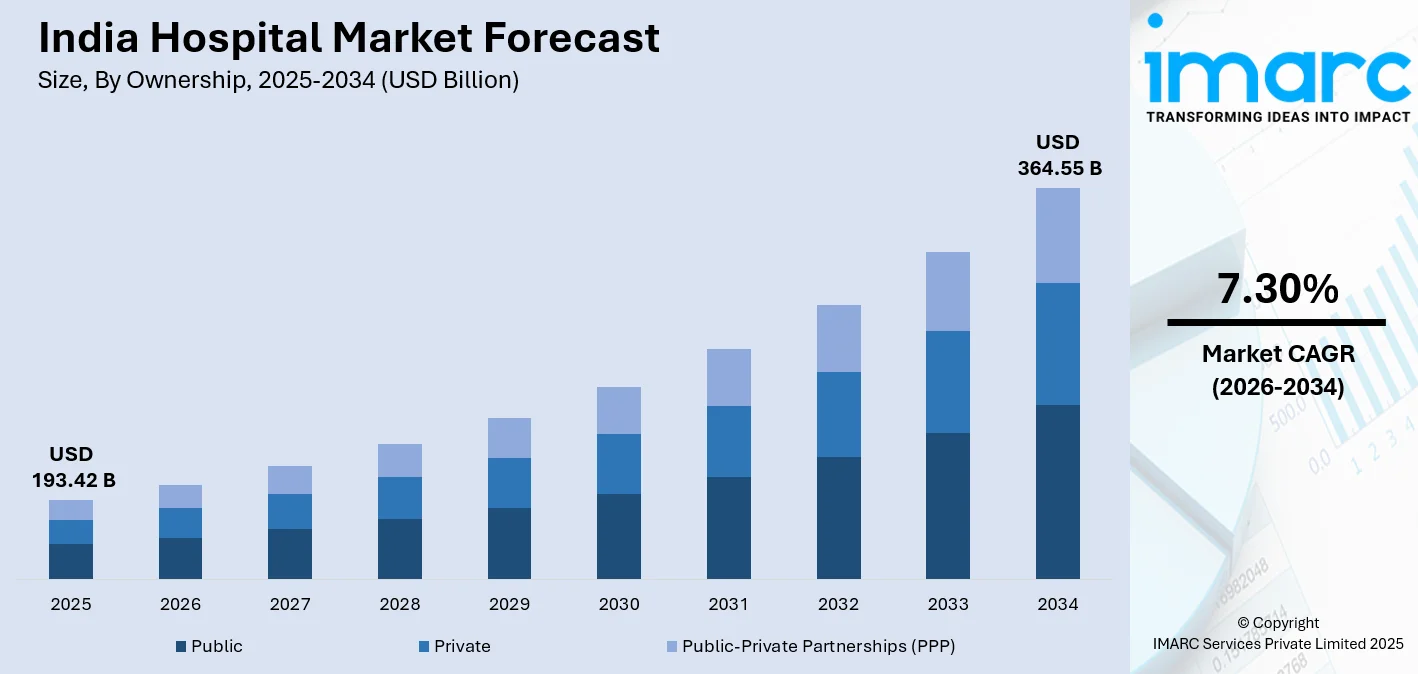
The India hospital market size was valued at USD 193.42 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 364.55 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 7.30% from 2026-2034.
The India hospital market is registering strong growth on account of enhanced healthcare investments, government initiatives, and rising demand for high-class healthcare facilities. Forays into tier 2 and tier 3 cities, technological improvements in the healthcare sector, and rising healthcare tourism are propelling the growth of the market. The rise in public-private collaborations, improved health insurance penetration, and the development of healthcare technology platforms are transforming the Indian healthcare market.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Ownership: Private dominate the market with a share of 59% in 2025, driven by superior infrastructure, advanced medical technology adoption, quality patient care services, and the growing preference among patients for personalized healthcare experiences and shorter waiting times.
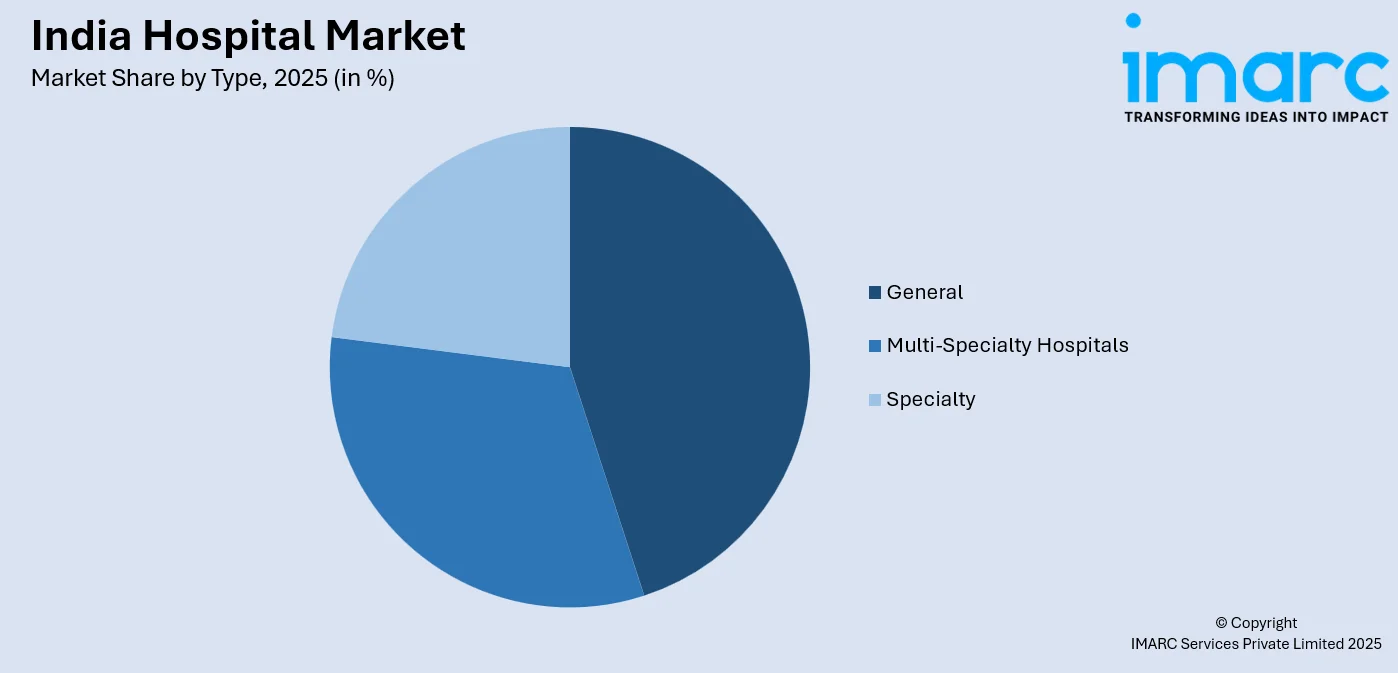
- By Type: General lead the market with a share of 41% in 2025, owing to their comprehensive healthcare service offerings, widespread geographic presence, accessibility to broader patient demographics, and ability to address diverse medical conditions under single facility settings.
- By Bed Capacity: The 101-300 beds represents the largest segment with a market share of 35% in 2025, attributable to optimal operational efficiency, balanced capital investment requirements, suitability for tier-two and tier-three city deployments, and capacity to serve substantial patient volumes effectively.
- By Regionality: Regional/district dominate with a share of 40% in 2025, driven by government focus on decentralized healthcare delivery, district-level health infrastructure expansion, and growing emphasis on bringing quality medical services closer to underserved populations.
- By Type of Services: In-patient services lead with a share of 60% in 2025, owing to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases requiring prolonged care, increasing surgical procedures, growing demand for specialized treatments, and enhanced facilities for post-operative recovery and monitoring.
- By Region: North India represents the largest segment with a market share of 31% revenue share in 2025, supported by advanced healthcare infrastructure, concentration of premier medical institutions, high population density, and significant medical tourism inflows from neighboring regions and countries.
- Key Players: The India hospital market exhibits a competitive landscape comprising large multi-specialty hospital chains, regional healthcare providers, and government-operated facilities. Market participants are pursuing expansion strategies, technology investments, and service diversification to strengthen their competitive positioning in the evolving healthcare ecosystem.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India hospital market is undergoing transformative expansion propelled by fundamental shifts in healthcare demand patterns and delivery mechanisms. The rising burden of chronic and lifestyle diseases is driving sustained demand for institutional healthcare services across the country. For example, Manipal Hospitals recently agreed to acquire an 87% stake in Kolkata‑based Medica Synergie, increasing its bed count to over 10,500 and strengthening its presence in Eastern India as part of broader consolidation and expansion efforts. Government initiatives aimed at universal healthcare coverage are expanding access to hospital services for previously underserved populations. The emergence of organized healthcare delivery through corporate hospital chains is raising quality standards and operational efficiency across the sector. Digital transformation is enabling enhanced patient engagement, improved clinical outcomes, and streamlined operational workflows. Medical tourism continues to strengthen as international patients seek cost-effective quality treatment, contributing significantly to revenue growth for major hospital networks.
India Hospital Market Trends:
Rapid Expansion of Digital Health and Telemedicine Integration
The India hospital market is witnessing significant integration of digital health technologies that are transforming patient care delivery and operational efficiency. Hospitals are increasingly deploying telemedicine platforms, artificial intelligence-powered diagnostics, and electronic health record systems to enhance service quality and accessibility. For instance, India’s national telehealth platform eSanjeevani has facilitated over 350 million patient consultations by connecting more than 232,291 providers across thousands of hubs and spokes, dramatically extending remote care reach. Remote patient monitoring through wearable devices is enabling continuous health tracking and proactive intervention for chronic disease management.
Growth of Public-Private Partnerships in Healthcare Infrastructure
Public-private partnerships are emerging as a critical mechanism for expanding healthcare infrastructure and improving service delivery across India. The government is actively promoting collaborative models that leverage private sector expertise and investment to establish multi-specialty hospitals, diagnostic centers, and telemedicine services in underserved regions. For example, in December 2025, the Delhi government is planning to develop 11 under‑construction hospitals through the Public‑Private Partnership (PPP) model to expedite the functioning of key healthcare infrastructure projects in the national capital. These partnerships are facilitating the establishment of critical care units, emergency services, and specialized treatment facilities in areas with limited healthcare access. PPP initiatives under programs like Ayushman Bharat and Health Infrastructure Mission are accelerating the development of district-level hospitals and strengthening primary healthcare networks across states.
Rising Focus on Tier-Two and Tier-Three City Expansion
Hospital chains are increasingly focusing expansion strategies on tier-two and tier-three cities to capture growing healthcare demand in these emerging markets. Rising income levels, improving health awareness, and increasing health insurance penetration in smaller cities are creating attractive opportunities for organized healthcare delivery. For example, following its merger with Quality Care India, Aster DM Healthcare plans to add around 3,300 beds and strengthen its presence in tier‑2 cities such as Indore, Raipur, Aurangabad, and Bhubaneswar as part of its strategy to challenge larger rivals. The development of multi-specialty and super-specialty hospitals in these regions is reducing patient migration to metropolitan centers for advanced treatments.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The India hospital industry offers a strong outlook for growth over the coming years, fortified by the presence of positively developing demographics, increasing health expenditure, and the growing demands and expectations of patients. A growing demand for care due to the increasing presence of chronic ailments, an aging demography, and an awareness about health are contributing to the growing demand for institutionalized health care. A commitment to increasing health care coverage, under Ayushman Bharat, from the Indian Government, would continue to fuel patient numbers. The market generated a revenue of USD 193.42 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 364.55 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 7.30% from 2026-2034.
India Hospital Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Ownership |
Private |
59% |
|
Type |
General Hospitals |
41% |
|
Bed Capacity |
101-300 Beds |
35% |
|
Regionality |
Regional/District |
40% |
|
Type of Services |
In-Patient Services |
60% |
|
Region |
North India |
31% |
Ownership Insights:
- Public
- Private
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
The private dominates with a market share of 59% of the total India hospital market in 2025.
Private hospitals maintain commanding market leadership in India due to their superior infrastructure, advanced medical technology adoption, and enhanced patient experience delivery. The private sector has consistently invested in state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment, modern surgical facilities, and comfortable patient amenities that differentiate their service offerings from public alternatives. For example, Sancheti Hospital in Pune recently inaugurated a new 150‑bed Advanced OrthoCare Facility along with an AI Innovation Lab featuring state‑of‑the‑art operating suites, robotic rehabilitation systems, and AI‑enabled diagnostic tools to improve precision and clinical outcomes. Private hospitals attract patients through shorter waiting times, personalized care approaches, and comprehensive service portfolios spanning primary through super-specialty care.
It benefits from substantial capital investments enabling continuous facility upgrades and technology modernization. Private healthcare providers have developed strong physician networks attracting specialist talent and enabling comprehensive clinical capabilities. The growing penetration of health insurance has improved affordability of private healthcare for middle-income segments, expanding the accessible patient base. Corporate hospital chains are driving professionalization of healthcare delivery through standardized protocols, quality certifications, and operational excellence initiatives.
Type Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- General
- Multi-Specialty Hospitals
- Specialty
The general leads with a share of 41% of the total India hospital market in 2025.
General hospitals dominate the India hospital market owing to their comprehensive healthcare service offerings and broad patient accessibility. These facilities provide integrated medical services addressing diverse health conditions ranging from primary care consultations to emergency services and basic surgical procedures. The widespread geographic distribution of general hospitals ensures healthcare accessibility across urban, semi-urban, and rural locations, serving as the primary point of contact for most patient populations seeking medical care.
The segment benefits from government healthcare programs that emphasize district hospital development and primary healthcare strengthening. General hospitals serve as referral centers for community health facilities, creating integrated care pathways for patient management. The versatility to address multiple medical disciplines within single facilities makes general hospitals cost-effective infrastructure investments for both public and private operators. These institutions also serve as training platforms for medical professionals, contributing to healthcare workforce development.
Bed Capacity Insights:
- Up to 100 Beds
- 101-300 Beds
- 301-700 Beds
- Above 700 Beds
The 101-300 beds dominate with a market share of 35% of the total India hospital market in 2025.
Mid-sized hospitals with bed capacities between one hundred and three hundred beds dominate the market due to their optimal balance between operational scale and capital investment requirements. This capacity range enables comprehensive service delivery including multiple specialty departments, adequate diagnostic facilities, and sufficient critical care capacity while maintaining manageable operational complexity. The segment is particularly well-suited for tier-two and tier-three city deployments where patient volumes support sustainable operations without requiring mega-hospital infrastructure.
Mid-capacity hospitals achieve favorable unit economics through efficient bed utilization and appropriate staffing ratios. The segment attracts both private healthcare chains expanding beyond metropolitan markets and government infrastructure investments targeting district-level healthcare strengthening. These facilities can support essential super-specialty services while remaining financially viable in markets with moderate patient density. The flexibility to scale services based on local demand patterns makes this capacity segment attractive for diverse market conditions.
Regionality Insights:
- Regional/District
- Rural
- Others
The regional/district leads with a share of 40% of the total India hospital market in 2025.
Regional and district hospitals command the largest market share driven by government emphasis on decentralized healthcare delivery and district-level infrastructure development. These facilities serve as critical healthcare access points for substantial population segments residing outside major metropolitan centers. Government programs including the Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission prioritize district hospital upgradation and capacity enhancement to improve healthcare accessibility across the nation.
Regional and district hospitals benefits from sustained public investment in healthcare infrastructure expansion at the district level. Regional hospitals function as referral centers within the healthcare delivery hierarchy, providing secondary and tertiary care services that reduce patient migration to overburdened metropolitan facilities. The development of specialty departments and critical care capabilities at district hospitals is enabling local management of complex medical conditions previously requiring transfers to distant medical centers.
Type of Services Insights:
- In-Patient Services
- Out-Patient Services
The in-patient services dominate with a market share of 60% of the total India hospital market in 2025.
In-patient services dominate the India hospital market revenue generation owing to the higher average revenue per case and the growing prevalence of conditions requiring hospitalization. For example, Apollo Hospitals reported strong patient occupancy and plans to add thousands of beds over the coming years, highlighting continued demand for hospital admissions that underpin revenue growth. The rising burden of chronic diseases, increasing surgical intervention rates, and expanding critical care requirements are driving sustained demand for in-patient healthcare services.
The segment benefits from advances in medical technology enabling increasingly sophisticated treatment protocols that require institutional care settings. The development of dedicated intensive care units, specialized surgery facilities, and post-operative recovery services has enhanced hospital capabilities for managing complex medical conditions. Growing health insurance coverage has improved affordability of in-patient care for middle-income populations, expanding the accessible market for hospitalization services.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
North India exhibits a clear dominance with a 31% share of the total India hospital market in 2025.
North India represents the largest regional market for hospital services, supported by advanced healthcare infrastructure, concentration of premier medical institutions, and substantial population base. The region encompasses major metropolitan centers including Delhi NCR which serves as a significant healthcare hub attracting patients from across northern states and neighboring countries. The presence of renowned multi-specialty and super-specialty hospitals has established North India as a preferred destination for complex medical treatments.
The region benefits from strong medical tourism inflows with international patients seeking cardiac care, orthopedic procedures, oncology treatment, and organ transplantation services. Well-developed transport connectivity and hospitality infrastructure support patient travel from distant locations. The concentration of medical education institutions ensures robust talent availability for healthcare delivery. States in the region are actively investing in healthcare infrastructure expansion to address growing demand and reduce inter-regional healthcare migration.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Hospital Market Growing?
Rising Burden of Chronic and Lifestyle Diseases
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases including cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, cancer, and respiratory disorders is driving sustained demand for hospital services across India. Lifestyle modifications associated with urbanization, sedentary occupations, and dietary changes are accelerating the emergence of non-communicable diseases among younger population segments. According to a 2025 study, chronic non‑communicable diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancers and respiratory illnesses now account for nearly 63–65 % of all deaths in India, reflecting a major shift in the disease burden toward conditions that often require hospitalization and long‑term care. The management of chronic conditions typically requires repeated hospitalizations, specialized interventions, and ongoing medical supervision that generate substantial hospital service utilization. The aging demographic profile with expanding elderly population further intensifies demand for healthcare services as advanced age correlates with higher disease burden and care requirements.
Government Healthcare Initiatives and Insurance Expansion
Comprehensive government programs aimed at universal healthcare coverage are significantly expanding access to hospital services for economically disadvantaged populations. The Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana has become a cornerstone of this effort, with over 42.48 crore Ayushman cards issued and nearly 10.98 crore hospital admissions authorised under the scheme by late 2025, providing cashless treatment coverage to families across a network of empanelled hospitals nationwide The Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana provides health insurance coverage to substantial segments of the population previously unable to afford quality healthcare. Enhanced government budgetary allocation to the healthcare sector is enabling infrastructure development, equipment procurement, and service expansion at public hospitals. State-level health insurance schemes are supplementing central programs to broaden coverage reach.
Medical Tourism Growth and International Patient Inflows
India's emergence as a leading global destination for medical tourism is contributing significantly to hospital revenue growth and capacity utilization. The country attracts international patients seeking high-quality medical treatments at substantially lower costs compared to developed markets. For instance, India recorded 1,31,856 foreign tourist arrivals for medical treatment between January and April 2025, reflecting a continued rebound and growth in international patient inflows as connectivity and visa facilitation improve. Cardiac surgery, orthopedic procedures, oncology treatment, organ transplantation, and reproductive medicine are primary service categories drawing medical tourists. Hospitals are developing dedicated international patient services including visa facilitation, language support, and culturally appropriate care to enhance medical tourism appeal.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Hospital Market is Facing?
Healthcare Infrastructure Deficit and Bed Shortage
India faces a significant healthcare infrastructure deficit with bed-to-population ratios substantially below recommended standards. The shortfall constrains healthcare service delivery capacity and contributes to overcrowding at existing facilities. High capital requirements for hospital development, including land acquisition, construction, and equipment procurement, limit the pace of infrastructure expansion. Regulatory complexities and approval timelines extend project implementation periods, delaying capacity additions. The geographic concentration of quality healthcare infrastructure in metropolitan areas creates access disparities for populations in smaller cities and rural regions.
Healthcare Workforce Shortages and Talent Distribution Imbalances
The availability of qualified healthcare professionals remains a critical constraint for hospital sector expansion in India. Shortages exist across physician categories, nursing staff, and allied healthcare professionals relative to population requirements. Workforce distribution skews heavily toward urban areas, creating severe staffing challenges for hospitals in smaller cities and rural locations. Training capacity limitations in medical and nursing education constrain the pipeline of new healthcare workers entering the profession. Competition for specialist physicians intensifies operating costs and creates service delivery challenges for hospitals outside premier markets.
High Out-of-Pocket Expenditure and Affordability Concerns
Despite health insurance expansion, out-of-pocket healthcare expenditure remains substantially elevated in India, limiting affordability of hospital services for large population segments. Healthcare costs impose significant financial burden on households, particularly for expensive treatments, specialized procedures, and prolonged hospitalizations. The gap between healthcare costs and insurance coverage adequacy affects treatment seeking behavior and service utilization patterns. Price sensitivity among patients influences hospital selection decisions and treatment compliance. The relatively low public healthcare expenditure as a proportion of gross domestic product constrains government capacity to subsidize healthcare access for economically vulnerable populations.
Competitive Landscape:
The India hospital market exhibits an evolving competitive landscape characterized by the coexistence of large multi-specialty corporate hospital chains, regional healthcare providers, single-specialty centers, and government-operated facilities. Market consolidation is accelerating through mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships as larger players seek to expand geographic presence and service capabilities. Private equity investment is fueling expansion strategies and technology modernization across hospital networks. Competition centers on clinical excellence, patient experience, technology adoption, and geographic accessibility. Hospital chains are differentiating through center-of-excellence development in high-demand specialties including cardiac care, oncology, neurology, and orthopedics. Digital transformation initiatives are becoming competitive differentiators as hospitals invest in patient engagement platforms, telemedicine capabilities, and data-driven clinical decision support systems.
Recent Developments:
- In November 2025, Yashoda Hospital launched India’s first AI‑Driven Lung Nodule Clinic in collaboration with Qure.ai and AstraZeneca. The clinic aims to improve early detection and treatment of lung cancer using advanced artificial intelligence technology. This initiative marks a significant step in AI‑enabled healthcare in India.
India Hospital Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Ownerships Covered | Public, Private, Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) |
| Types Covered | General, Multi-Specialty Hospitals, Specialty |
| Bed Capacities Covered | Up to 100 Beds, 101-300 Beds, 301-700 Beds, Above 700 Beds |
| Regionalities Covered | Regional/District, Rural, Others |
| Type of Services Covered | In-Patient Services, Out-Patient Services |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India hospital market size was valued at USD 193.42 Billion in 2025.
The India hospital market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.30% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 364.55 Billion by 2034.
The private hospital dominated the market with a 59% share, driven by superior infrastructure, advanced technology adoption, quality patient care services, and growing consumer preference for personalized healthcare experiences.
Key factors driving the India hospital market include rising prevalence of chronic diseases, government healthcare initiatives and insurance expansion, medical tourism growth, increasing healthcare investments, technological advancements, and expanding health infrastructure in tier-two and tier-three cities.
The India hospital market faces challenges including inadequate infrastructure in rural areas, shortage of doctors and nurses, high out-of-pocket costs, low insurance coverage, regulatory inconsistencies, rising operational expenses, variable care quality, and increasing demand from non-communicable diseases. Addressing these requires investment, policy support, and digital adoption.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












