
India Hydroelectric Power Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type of Hydroelectric Plant, Component, End Use, and Region, 2026-2034
India Hydroelectric Power Market Size and Share:
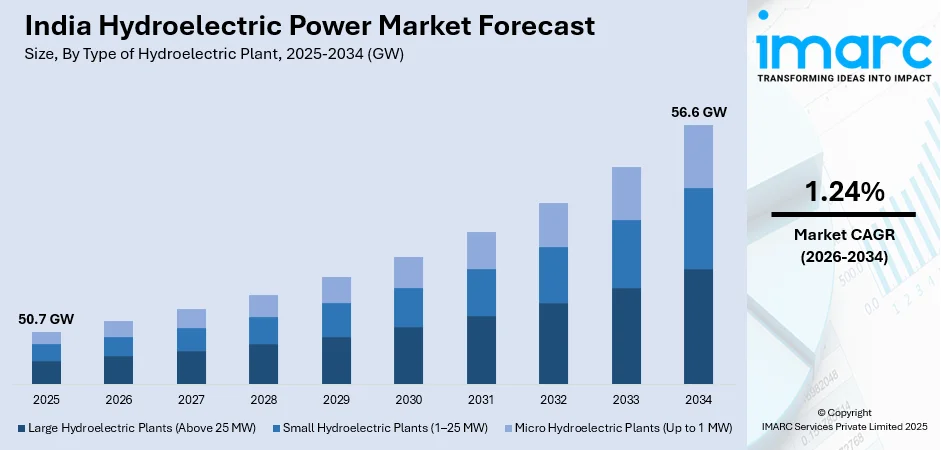
The India hydroelectric power market size reached 50.7 GW in 2025. The market is expected to reach 56.6 GW by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 1.24% during 2026-2034. The market growth is attributed to strong government support through policies offering financial incentives, streamlined approvals, and carbon reduction goals, alongside significant private sector investments and public-private partnerships (PPP) that provide capital, innovation, and operational efficiency for accelerated project development and energy transition.
Market Insights:
- On the basis of region, the market has been divided into North India, South India, East India, and West India.
- On the basis of type of hydroelectric plant, the market has been divided into large hydroelectric plants (above 25 MW), small hydroelectric plants (1–25 MW), and micro hydroelectric plants (up to 1 MW).
- On the basis of component, the market has been divided into turbines, generators, transformers, and control systems.
- On the basis of end use, the market has been divided into residential, commercial, and industrial.
Market Size and Forecast:
- 2025 Market Size: 50.7 GW
- 2034 Projected Market Size: 56.6 GW
- CAGR (2026-2034): 1.24%
India Hydroelectric Power Market Trends:
Government Policies and Initiatives
The hydroelectric power industry size in India is greatly influenced by the strong commitment of the governing body to renewable energy development, supported by various policies and initiatives. To achieve its ambitious renewable energy targets, the governing body is implementing incentives such as tax reductions, subsidies, and favorable tariff arrangements, which promote the development of hydropower projects. Moreover, the government provides financial assistance and is simplifying approval procedures, facilitating the rapid advancement of hydroelectric initiatives. This focus on renewable energy is further propelled by India's initiatives to lower carbon emissions and transition from fossil fuels towards cleaner energy alternatives. In accordance with this vision, the government is progressively aiming to improve the efficiency of hydropower initiatives. For instance, in 2024, state-operated hydroelectric power generation company SJVN announced India's launch of a tender for 6GW of renewable energy with storage to provide reliable power during peak hours. The initiative was part of India's effort to reach 500GW of non-fossil fuel power capacity, with plans to connect 35GW of solar and wind energy by March 2025. This project aimed to enhance the country's energy security and support its decarbonization goals.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Private Sector Investment and Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
Investment from the private sector and public-private partnerships (PPPs) are essential for the growth of the hydroelectric power industry in India. The focus of the government on infrastructure improvement is motivating private firms to engage in the hydropower industry, pursuing lucrative chances in renewable energy. Private investments provide crucial funding while also bringing technological advancements, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced project management techniques. PPPs offer a cooperative framework enabling the government and private companies to exchange resources, risks, and advantages, thus facilitating the swift execution of hydroelectric initiatives. This collaboration enables the government to utilize its regulatory and administrative skills while the private sector offers specialized technical expertise and quicker implementation. These collaborations reduce the financial and operational risks linked to extensive hydropower initiatives. According to the latest India hydroelectric power market statistics, in 2024, India sanctioned two major hydropower initiatives in Arunachal Pradesh, totaling a capacity of 426 MW and an investment of Rs 3,689 crore. The state, possessing a significant hydropower capacity of 58,000 MW, is positioned to emerge as a major hydropower center, with projects amounting to Rs 1 lakh crore planned. The government aimed for an ambitious goal of achieving 12,500 MW operational capacity in two years, backed by central public sector enterprises (CPSUs) such as NHPC and NEEPCO. These investments showcase the successful partnership between the public and private sectors in advancing hydropower development in India.
Hydroelectric Power as a Comprehensive Clean Energy Solution with Advanced Integration Capabilities
Hydroelectric power represents a cornerstone of clean energy generation, utilizing water-driven turbine systems to produce sustainable electricity with minimal environmental impact and exceptional operational longevity. As per the India hydroelectric power market analysis, the sector's expansion is primarily driven by India's ambitious sustainability goals, comprehensive carbon reduction strategies, and critical energy security imperatives that position hydropower as an essential component of the national energy mix. Government initiatives have been instrumental in sector development, encompassing targeted subsidies for project development, streamlined regulatory approvals, and strategic project tenders that facilitate large-scale capacity additions while ensuring competitive pricing structures. Private sector investments and PPP models have emerged as vital funding mechanisms, enabling effective risk-sharing arrangements between public and private entities while accelerating project timelines and operational efficiency, which contributes to the India hydroelectric power market growth. However, the industry faces technological gaps, particularly in AI-based optimization systems for predictive maintenance and digital twin technologies that could enhance operational performance and reduce maintenance costs. Environmental considerations have become increasingly prominent, with biodiversity protection measures and climate adaptation strategies being integrated into project planning to minimize ecological disruption and ensure long-term sustainability. Social concerns regarding community relocation programs and workforce training initiatives require comprehensive management frameworks to address local impacts while creating employment opportunities. The sector's future growth increasingly depends on storage synergies, particularly the integration of pumped hydro storage with battery technologies, creating hybrid systems that enhance grid stability and provide flexible energy storage solutions for renewable energy integration.
Growth, Opportunities, and Challenges in the India Hydroelectric Power Market:
Growth Drivers of the India Hydroelectric Power Market
The market is primarily driven by strong government support through comprehensive policies offering financial incentives, streamlined approval processes, and alignment with national carbon reduction targets. Significant private sector investments and public-private partnerships provide essential capital infusion, technological innovation, and operational efficiency improvements. The increasing focus on energy security and India's ambitious renewable energy targets of 500GW non-fossil fuel capacity creates substantial demand for hydroelectric power generation and a positive India hydroelectric power industry outlook.
Opportunities in the India Hydroelectric Power Market
Substantial opportunities exist in developing small and micro hydroelectric plants in remote and hilly regions, addressing decentralized energy needs while supporting rural electrification initiatives. The integration of advanced technologies including AI-based optimization and digital twin systems presents significant potential for operational efficiency improvements and predictive maintenance capabilities. Pumped hydro storage combined with battery technologies offers lucrative prospects for grid stability enhancement and renewable energy storage solutions.
Challenges in the India Hydroelectric Power Market
The industry faces environmental and social challenges including biodiversity protection requirements, community relocation concerns, and the need for comprehensive workforce training programs. Regulatory complexities and lengthy approval processes despite government initiatives continue to delay project implementation timelines. Climate change impacts on water availability and seasonal variations pose operational risks that require adaptive management strategies and resilient infrastructure development.
India Hydroelectric Power Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the regional level for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on type of hydroelectric plant, component, and end use.
Type of Hydroelectric Plant Insights:
- Large Hydroelectric Plants (Above 25 MW)
- Small Hydroelectric Plants (1–25 MW)
- Micro Hydroelectric Plants (Up to 1 MW)
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type of hydroelectric plant. This includes large hydroelectric plants (above 25 MW), small hydroelectric plants (1–25 MW), and micro hydroelectric plants (up to 1 MW).
Component Insights:
- Turbines
- Generators
- Transformers
- Control Systems
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the component have also been provided in the report. This includes turbines, generators, transformers, and control systems.
End Use Insights:
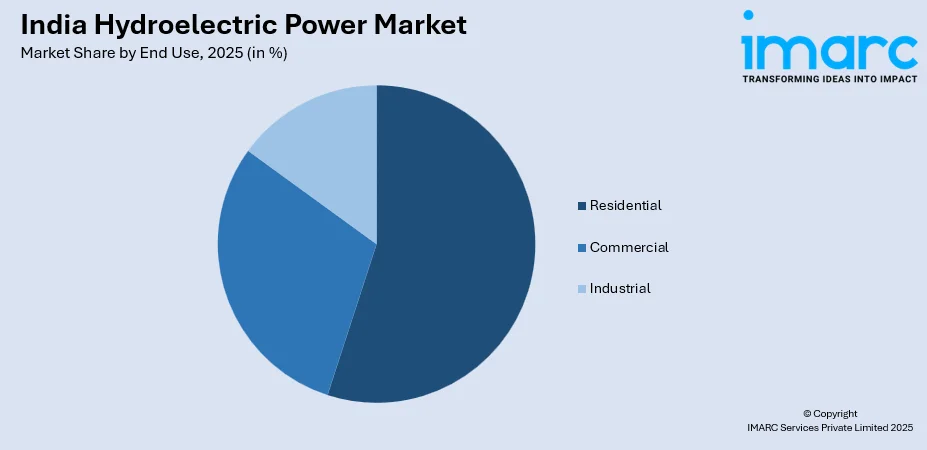
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end use. This includes residential, commercial, and industrial.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include North India, South India, East India, and West India.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
India Hydroelectric Power Market News:
- September 2025: Adani Power and Druk Green Power signed an MoU to develop a 570 MW Wangchhu hydro project in Bhutan, marking cross-border collaborations in regional hydropower development. This project advances India’s strategic renewable energy partnerships.
- June 2025: GE Vernova commissioned India’s first variable speed pumped storage unit at Tehri Hydropower Complex, enhancing the plant’s capacity to 2,400 MW and supporting rapid grid balancing. This advanced technology is key for integrating large-scale renewables efficiently.
- In March 2025, Himachal Pradesh signed MoUs with Telangana to establish the 400 MW Seli and 120 MW Miar hydroelectric power projects in Lahaul-Spiti. The projects, estimated at Rs 6,200 crore, will create employment for 5,000 youth and generate power for both states.
- January 2025: NHPC Ltd expanded India’s hydropower portfolio by commissioning Parbati-II (3×200 MW) and Uhl-III (3×33.33 MW) units, increasing total large hydro capacity to 54,480 MW by mid-2025. Major state utilities also added new plants in Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- October 2024: The Indian government allocated INR 12,461 Crore for hydroelectric and pumped storage projects aiming to add over 31 GW capacity by 2031–32. This move supports infrastructure expansion and renewable energy integration across states.
- In August 2024, Union Minister Manohar Lal launched the JAL VIDYUT DPR portal and a comprehensive CEA regulations compendium to enhance transparency and efficiency in India’s hydropower and electricity sector. The portal monitored survey and investigation activities for hydroelectric and pumped storage projects, while the compendium consolidated key regulations under the Electricity Act, 2003. These initiatives aimed to streamline project development and improve grid stability.
India Hydroelectric Power Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | GW |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Type of Hydroelectric Plants Covered | Large hydroelectric plants (above 25 MW), Small hydroelectric plants (1–25 MW), Micro hydroelectric plants (up to 1 MW) |
| Components Covered | Turbines, Generators, Transformers, Control Systems |
| End Uses Covered | Residential, Commercial, Industrial |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the India hydroelectric power market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the India hydroelectric power market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the India hydroelectric power industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The hydroelectric power market in India was reached at 50.7 GW in 2025.
The India hydroelectric power market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 1.24% during 2026-2034, reaching a volume of 56.6 GW by 2034.
India’s hydroelectric power market is growing due to rising demand for clean energy and long-term sustainability goals. The country’s vast water resources, favorable government support, and focus on reducing fossil fuel dependency drive expansion. Technological advancements and improved grid infrastructure also support capacity development and reliability.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












