
India IoT Connectivity Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Application, Enterprise Size, End Use Industry, and Region, 2025-2033
India IoT Connectivity Market Size and Share:
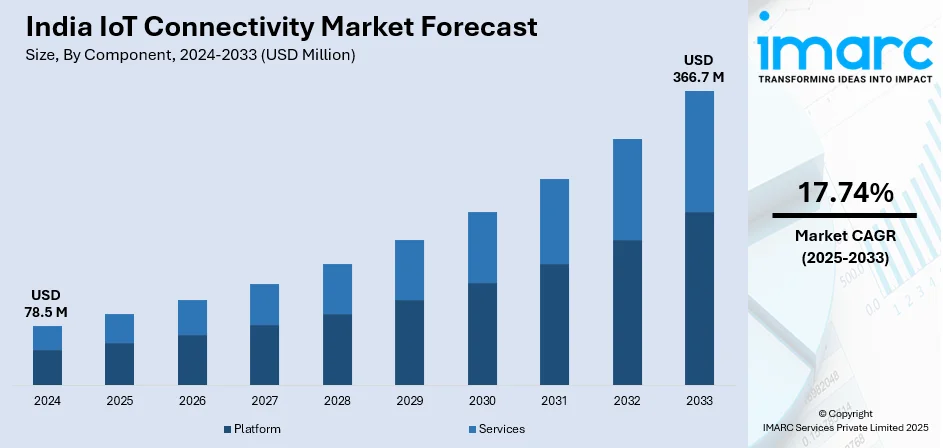
The India IoT connectivity market size reached USD 78.5 Million in 2024. The market is expected to reach USD 366.7 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 17.74% during 2025-2033. The market growth is attributed to the emerging automation trend in industrial processes, the increasing sales of connected cars, and the widespread adoption of IoT-enabled devices in the healthcare industry.
Market Insights:
- Based on region, West and Central India dominated the market in 2024.
- On the basis of component, platform leads the market in 2024.
- Based on the application, buildings and home automation accounted for the largest market share in 2024.
- On the basis of enterprise size, large enterprises represented the largest segment in 2024.
- Based on end use industry, transportation accounted for the largest market share in 2024.
Market Size and Forecast:
- 2024 Market Size: USD 78.5 Million
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 366.7 Million
- CAGR (2025-2033): 17.74%
- West and Central India: Largest Region in 2024
Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity refers to a network solution that provides a communication platform and infrastructure for connecting IoT devices, including sensors, trackers, gateways, routers, etc. IoT projects vary in their requirements, and many of them use various connectivity options depending on their needs, such as power consumption, range, bandwidth, etc. Numerous communication technologies are used for connecting the IoT devices, such as low-power WAN, satellite, cellular, short-range wireless, etc. Ethernet connections are a viable choice for large machines that are stationary and don't need to move. LPWAN IoT protocols are used to send limited amounts of data wirelessly from specialized base stations to sensors and devices. Satellites provide ubiquitous coverage for IoT devices as they can connect to them with limited to no ground-based IoT connection. Wi-Fi aids in linking IoT devices, including sensors, security cameras, etc., for homes and businesses. As a result, IoT connectivity is widely employed across various sectors, including retail, healthcare, transportation and logistics, manufacturing, etc.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
The rising dependence of several organizations on IoT-based solutions for boosting their productivity and creating new business models and revenue streams is primarily driving the India IoT connectivity market growth. In addition to this, the emerging automation trend in industrial processes is further propelling the need for IoT connectivity to monitor products continuously, streamline processes, reduce time-to-market, and address quality defects in real-time. Moreover, the widespread adoption of IoT-enabled devices in the healthcare industry for remote monitoring and improving patient care is also augmenting the product demand in the country. Besides this, the increasing sales of connected cars owing to rising preferences for luxurious driving experiences are further bolstering the requirement for IoT connectivity to aid device-to-device communication. Additionally, the inflating investments by numerous government bodies in the development of smart cities are also augmenting the India IoT connectivity market share. It assists in reducing energy consumption, improving building performance, enhancing urban space management, etc. Apart from this, the increasing deployment of 5G networks and multi-access edge computing (MEC) to enhance device connectivity is acting as a significant growth-inducing factor. Furthermore, numerous medium and large-scale organizations across the country are adopting long-term evolution for machines (LTE-M) solutions to provide enhanced end-to-end security, device-level access, encrypted data transfer, etc., which is expected to fuel the India IoT connectivity market during the forecasted period.
India IoT Connectivity Market Trends:
Growth in 5G Deployment and Edge Computing Integration
India’s push toward widespread 5G rollout has been a critical enabler of the market. With spectrum auctions completed and commercial services launched in most major cities, telecom operators like Reliance Jio and Bharti Airtel are aggressively expanding 5G coverage to tier-2 and tier-3 regions. Moreover, the significant increase in bandwidth and reduction in latency provided by 5G make it viable for real-time applications across sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and utilities. In industrial IoT, for instance, factory automation, predictive maintenance, and digital twins rely heavily on the low latency and device density that only 5G can support. Alongside 5G, edge computing is being deployed to address bottlenecks in centralized data processing. Rather than routing all IoT-generated data to cloud servers, edge nodes now handle critical processing near the data source. This approach minimizes delays, cuts bandwidth use, and supports sensitive applications like surveillance, energy grid optimization, and connected vehicles. The pairing of edge computing with 5G is transforming how IoT networks are designed—favoring distributed, low-latency, and resilient architectures that suit India’s heterogeneous connectivity landscape.
Demand for Smart Devices Across Consumer and Industrial Segments
The rise in demand for smart devices driven by both consumer appetite and enterprise digitization is one of the prominent India IoT connectivity market trends. On the consumer side, affordable smart home products, ranging from plugs and lights to voice assistants and security systems, are gaining popularity in urban and semi-urban households. Moreover, the availability of low-cost sensors, improved internet penetration, and vernacular language support in connected apps are supporting adoption. Also, smartphone makers and appliance brands are embedding IoT features into entry- and mid-range products, which has helped scale the market beyond metro cities. In parallel, enterprise use cases for smart devices are expanding rapidly. Smart meters, environmental sensors, asset trackers, and industrial monitoring equipment are being widely deployed. Utilities and infrastructure providers are investing in smart grids and remote monitoring to reduce operational losses and improve energy efficiency. Logistics firms are integrating IoT-based telematics and condition monitoring into fleet operations to enhance reliability and route optimization. The growth in device volume is also prompting demand for scalable device management platforms and interoperability standards.
Focus on Cybersecurity in IoT Ecosystems
As the volume and complexity of IoT deployments increase across India, cybersecurity has become a central concern for enterprises, government bodies, and consumers. IoT devices often run on minimal computing power and usually don’t follow consistent security standards, leaving them open to attacks. Frequent issues include unauthorized access, data theft, and attackers using these unsecured devices to move laterally into larger corporate networks. Incidents of botnet-based DDoS attacks and sensor spoofing have prompted regulators to prioritize device and network security. Apart from this, the Indian government has issued advisories and proposed frameworks encouraging manufacturers to implement security-by-design, which is positively impacting the India IoT connectivity market outlook. Mandates for secure boot processes, encrypted firmware updates, and unique device credentials are becoming more common in procurement standards. Enterprises are increasingly deploying network segmentation, zero-trust architectures, and endpoint detection solutions to contain threats within IoT environments. Meanwhile, cybersecurity startups are offering anomaly detection tools using machine learning to monitor unusual behavior across IoT devices.
Government Support and Smart City Initiatives
Government initiatives have played a significant role in accelerating market growth, particularly through programs like Smart Cities Mission, Digital India, and Make in India. These efforts aim to create digitally integrated urban infrastructure by embedding IoT into services such as traffic management, waste disposal, water supply monitoring, and energy grids. The Smart Cities Mission alone, covering over 100 cities, has led to extensive deployment of connected streetlights, smart surveillance, and environmental sensors. State and municipal authorities are increasingly collaborating with private technology providers to implement scalable IoT frameworks. Additionally, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and Department of Telecommunications (DoT) have issued policy guidelines supporting machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN). Moreover, as per the India IoT connectivity market forecast, incentives for domestic IoT manufacturing, public-private partnerships, and the development of standards for data exchange and interoperability is expected to create a more structured environment. These policy measures are critical in addressing India’s diverse connectivity needs and infrastructure challenges.
Key Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the India IoT connectivity market, along with forecasts at the country level from 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on component, application, enterprise size, and end use industry.
Component Insights:
- Platform
- Services
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the India IoT connectivity market based on the component. This includes platform and services. According to the India IoT connectivity market analysis, platform represented the largest segment.
Application Insights:
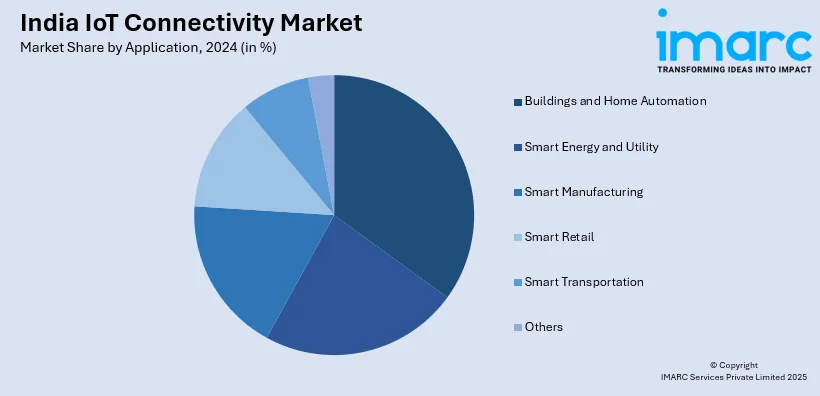
- Buildings and Home Automation
- Smart Energy and Utility
- Smart Manufacturing
- Smart Retail
- Smart Transportation
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the India IoT connectivity market based on the application has also been provided in the report. This includes buildings and home automation, smart energy and utility, smart manufacturing, smart retail, smart transportation, and others. According to the report, buildings and home automation accounted for the largest market share.
Enterprise Size Insights:
- Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
- Large Enterprises
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the India IoT connectivity market based on the enterprise size. This includes small and medium-sized enterprises and large enterprises. According to the report, large enterprises represented the largest segment.
End Use Industry Insights:
- Transportation
- Manufacturing
- Energy and Utilities
- Healthcare
- Retail
- Residential
- Government
- Insurance
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the India IoT connectivity market based on the end use industry has also been provided in the report. This includes transportation, manufacturing, energy and utilities, healthcare, retail, residential, government, insurance, and others. According to the report, transportation accounted for the largest market share.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- West and Central India
- South India
- East India
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets that include North India, West and Central India, South India, and East India. According to the report, West and Central India was the largest market for IoT connectivity. Some of the factors driving the West and Central India IoT connectivity market included the rising dependence on IoT-based solutions, the development of smart cities, the increasing deployment of 5G networks, etc.
Competitive Landscape:
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the India IoT connectivity market. Detailed profiles of all major companies have also been provided. Some of the companies covered include Ericsson, Cisco Systems, Inc., Orange Business Services, Bharti Airtel Limited, Vodafone, etc. Kindly note that this only represents a partial list of companies, and the complete list has been provided in the report.
Latest News and Developments:
- June 2025: APM Group, branded as India’s first fully integrated AI‑powered IoT company, formally unveiled its rebranding initiative emphasizing end‑to‑end in‑house capabilities spanning hardware design, software engineering, testing, and manufacturing. Its newly launched suite of smart vehicle modules includes 4G Wi‑Fi connectivity, real‑time load sensors, and auto‑dipper lighting systems, supported by AI‑driven analytics on vehicle health, fuel usage, and driver behavior to enhance operational efficiency and safety.
- July 2024: Dhruva Space announced a strategic partnership with France-based satellite operator Kinéis to introduce space-based IoT connectivity in India. As part of the collaboration, Dhruva Space will integrate a Kinéis IoT payload into its P-30 nanosatellite platform and develop end-user terminals customized for Kinéis’s upcoming 25-satellite constellation. The initiative aims to support low-data-rate applications such as environmental monitoring, logistics, agriculture, and infrastructure, providing a cost-effective and scalable solution to expand satellite IoT access across India’s public and private sectors.
Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Segment Coverage | Component, Application, Enterprise size, End Use Industry, Region |
| Region Covered | North India, West and Central India, East India, South India |
| Companies Covered | Ericsson, Cisco Systems, Inc., Orange Business Services, Bharti Airtel Limited, Vodafone, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the India IoT connectivity market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What are the drivers, restraints, and opportunities in the India IoT connectivity market?
- What are the key regional markets?
- What is the breakup of the market based on the component?
- What is the breakup of the market based on the application?
- What is the breakup of the market based on the enterprise size?
- What is the breakup of the market based on the end use industry?
- What is the competitive structure of the India IoT connectivity market?
- Who are the key players/companies in the India IoT connectivity market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the India IoT connectivity market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the India IoT connectivity market.
- The study maps the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's five forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the India IoT connectivity industry and its attractiveness.
- The competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












