
India Semi-trailer Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Vehicle Type, Tonnage, Foot Length, End Use Industry, and Region, 2026-2034
India Semi-trailer Market Summary:
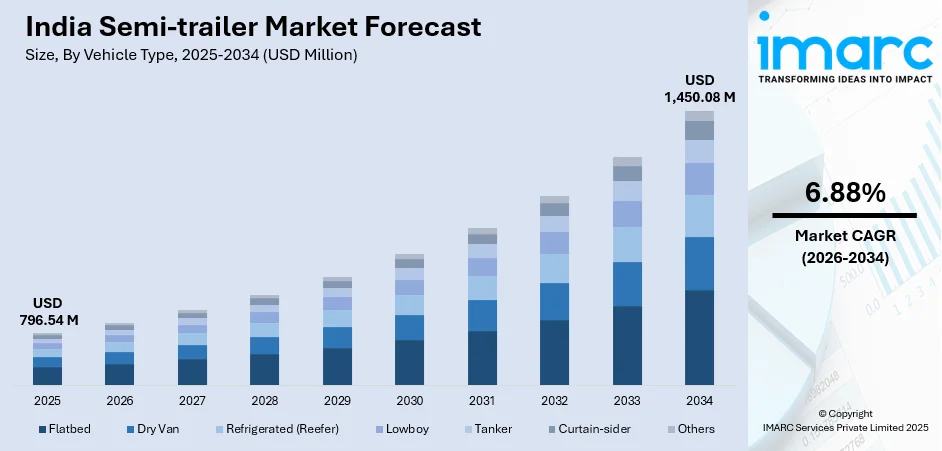
The India semi-trailer market size was valued at USD 796.54 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1,450.08 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.88% from 2026-2034.
The market growth is propelled by accelerating government infrastructure investments through the PM Gati Shakti initiative and Dedicated Freight Corridors and rapid e-commerce growth necessitating enhanced logistics capabilities. Apart from this, the increasing adoption of technologically advanced solutions, such as electric semi-trailers and road train configurations, for improving operational efficiencies and payload capacities are expanding the India semi-trailer market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Vehicle Type: Flatbed dominates the market with a share of 21% in 2025, driven by construction industry expansion and infrastructure development projects requiring transportation of heavy machinery.
- By Tonnage: 25 ton - 50 ton category the market with a share of 36% in 2025, representing optimal balance between payload capacity and operational efficiency while complying with legally permissible weight limits.
- By Foot Length: 28 - 45 ft represents the largest segment with a market share of 68% in 2025, offering ideal configuration balancing cargo capacity with maneuverability and regulatory compliance.
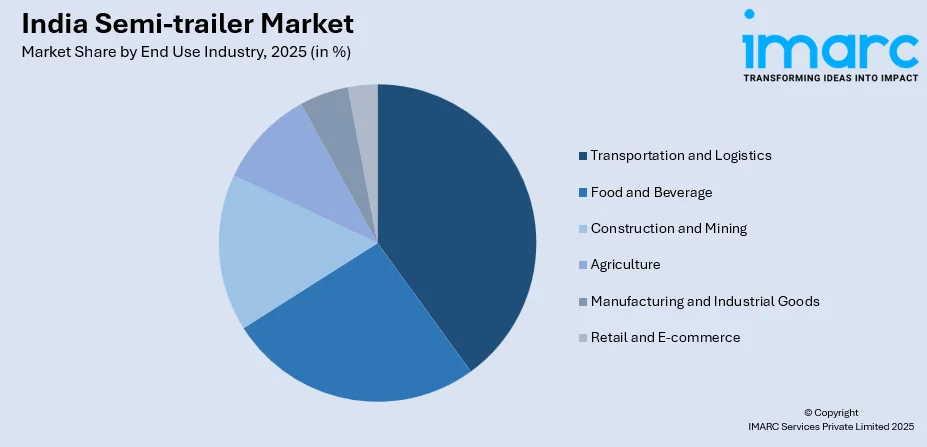
- By End Use Industry: Transportation and logistics leads the market with a share of 25% in 2025, propelled by exponential e-commerce growth with platforms establishing 650 additional delivery hubs and rapid manufacturing sector expansion.
- By Region: North India represents the largest segment with a market share of 30% in 2025, supported by robust industrial manufacturing clusters, extensive agricultural production requiring crop transportation infrastructure, and strategic geographic location with well-developed highway networks and proximity to Dedicated Freight Corridor routes enhancing logistics connectivity and operational efficiency.
- Key Players: Key players in India’s semi-trailer market are investing in lightweight designs, customized trailers, and safety features, adopting telematics and automation, expanding capacity, and partnering with logistics firms to serve growing freight, infrastructure, and e-commerce demand.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India semi-trailer market is experiencing transformative growth driven by comprehensive government infrastructure modernization programs and burgeoning e-commerce logistics requirements creating unprecedented freight transportation demand. The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan with Rs 100 lakh crore investment is fundamentally reshaping logistics infrastructure, coordinating 44 central ministries and 36 states to eliminate infrastructure redundancies while maximizing operational synergies across transport modes. The Eastern and Western Dedicated Freight Corridors, with 2,741 kilometers operational and handling over 130,000 freight trains in fiscal year 2024-2025, demonstrated 47% year-over-year growth in freight operations, exemplifying infrastructure development catalyzing semi-trailer deployment. E-commerce sector expansion in the country is also intensifying logistics network requirements, with major platforms establishing large number of additional festive delivery hubs in tier II and III cities necessitating extensive semi-trailer fleet expansion for first-mile, mid-mile, and last-mile distribution efficiency.
India Semi-trailer Market Trends:
E-commerce Expansion Driving Comprehensive Logistics Infrastructure Development
India's e-commerce sector is experiencing transformative growth fundamentally altering logistics demand patterns and necessitating substantial semi-trailer fleet expansion across distribution segments. The e-commerce industry valued at Rs 10,82,875 crore (USD 125 billion) in 2024 is projected to reach Rs 29,88,735 crore (USD 345 billion) by 2030, reflecting compound annual growth rate of 15%, creating unprecedented freight transportation requirements. E-commerce logistics market growth also demonstrates intensifying need for efficient semi-trailer deployments. Quick commerce services promising 10-minute deliveries are intensifying requirements for strategically positioned warehousing facilities and efficient transportation networks, with major platforms creating seasonal jobs and establishing additional festive delivery hubs in tier II and III cities during 2024, necessitating extensive semi-trailer fleet expansion.
Advanced Technology Integration Revolutionizing Semi-trailer Operational Capabilities
The semi-trailer market is witnessing significant technological transformation through integration of electric powertrains and innovative road train configurations enhancing operational efficiency and sustainability. January 2025 marked major milestone as EKA Mobility unveiled 55,000 Kg electric tractor-trailer at Bharat Mobility Global Expo representing significant advancement in India's transition toward zero-emission heavy-duty commercial vehicle transportation. February 2025 witnessed Volvo Trucks launching India's first Road Train solution in partnership with Delhivery Ltd., featuring Volvo FM 420 4×2 tractor with 44-ft semi-trailer and 24-ft intermediate trailer delivering combined cargo volume of 144 cubic meters, 50% higher than standard semi-trailers, certified by Ministry of Road Transport and Highways and Automotive Research Association of India for operations between Nagpur and Bhiwandi hubs.
Government Infrastructure Development Initiatives Accelerating Market Expansion
Comprehensive government infrastructure programs are fundamentally transforming India's logistics landscape and creating substantial opportunities for semi-trailer deployment across freight corridors. Three Economic Railway Corridor Programs covering high-traffic routes, port connection corridors, and energy-mineral-cement routes total roughly 40,900 kilometers, with investments amounting to INR 11.16 lakh crore. The Eastern and Western freight corridors have collectively noted a 47% rise in freight train activities, with train trips escalating from 88,225 in 2023-24 to 1,30,116 in 2024-25.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The India semi-trailer market is poised for robust expansion through 2034, driven by sustained government infrastructure investments, exponential e-commerce growth, and technological innovations transforming freight transportation capabilities. The market generated a revenue of USD 796.54 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 1,450.08 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.88% from 2026-2034. Infrastructure development programs including PM Gati Shakti initiative and Dedicated Freight Corridor expansion creating enhanced logistics networks facilitating increased semi-trailer adoption across industries. E-commerce sector projected growth from Rs 10,82,875 crore to Rs 29,88,735 crore by 2030 necessitating substantial fleet expansions, while technological advancements including electric semi-trailers and road train configurations offering improved operational efficiencies positioning market for sustained growth trajectory.
India Semi-trailer Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Vehicle Type |
Flatbed |
21% |
|
Tonnage |
25 Ton - 50 Ton |
36% |
|
Foot Length |
28 - 45 ft |
68% |
|
End Use Industry |
Transportation and Logistics |
25% |
|
Region |
North India |
30% |
Vehicle Type Insights:
- Flatbed
- Dry Van
- Refrigerated (Reefer)
- Lowboy
- Tanker
- Curtain-sider
- Others
Flatbed dominates with a market share of 21% of the total India semi-trailer market in 2025.
Flatbed trailers dominate the India semi-trailer market segment owing to their versatility in transporting oversized and heavy loads essential for construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure development sectors. These trailers feature flat, level design allowing heavy, large, bulky, or oversized consignments to be loaded and offloaded efficiently, finding extensive applicability in construction, manufacturing, and logistics businesses. December 2024 marked significant development as Indian Ministry of Defense awarded contracts to state-owned BEML Ltd. to produce 8×8 high-mobility vehicles and heavy-duty trailers for Indian Army with USD 9.8 million investment, with heavy-duty trailers featuring up to 50 tons carrying capacity designed to withstand hostile environments delivering tactical flexibility to logistics operations. Growing construction industry across developed and emerging economies anticipated to fuel segment growth as flatbed trailers transport heavy cargo including machinery, construction materials, and equipment.
Flatbed configuration proving cost-effective and adaptable enough to cater to varied cargo needs, contributing significantly to segment's popularity across automotive, agricultural, retail, and industrial sectors depending on them for transportation of commodities including machinery, steel products, timber, agricultural equipment, and manufactured goods. Being durable and rugged enough to bear rough loads makes them preference for heavy-duty applications, establishing their position as prime segment within trailer industry serving diverse transportation requirements. Rising demand for lower-cost freight shipment combined with accelerating infrastructure development projects including highways, bridges, ports, and industrial facilities further intensifying flatbed trailer adoption as businesses seek efficient solutions for transporting construction materials and heavy equipment across expanding project sites.
Tonnage Insights:
- Below 25 Ton
- 25 Ton - 50 Ton
- 51 Ton - 100 Ton
- Above 100 Ton
25 ton - 50 ton leads with a share of 36% of the total India semi-trailer market in 2025.
The 25 Ton - 50 Ton tonnage segment accounts for dominant market position owing to optimal balance between payload capacity, operational versatility, and regulatory compliance across diverse industry applications nationwide. This category represents most commonly used semi-trailers for transportation requirements including dry vans, refrigerated semi-trailers, and tankers, offering lower cost of transportation while maintaining considerable freight capacity meeting logistics efficiency requirements for majority of commercial operations. These trailers largely used in flatbed and lowboy applications prove essential for industries requiring reliable and robust transport solutions for diverse cargo types while complying with legally permissible limits across most Indian jurisdictions, making them preferred choice for general freight operations balancing operational efficiency with regulatory adherence.
Growing adoption of 25-50 ton semi-trailers driven by their versatility across multiple applications including containerized cargo, bulk materials, refrigerated goods, and general merchandise transportation serving diverse end-use industries from manufacturing to retail distribution networks. This tonnage category offers optimal payload utilization without requiring specialized road permits or infrastructure modifications, enabling fleet operators to maximize operational flexibility while maintaining compliance with national and state-level weight regulations governing commercial vehicle operations. Rising e-commerce sector expansion necessitating efficient mid-mile transportation solutions between distribution centers and regional hubs particularly favoring 25-50 ton configurations offering adequate capacity for consolidated shipments while maintaining fuel efficiency and operational cost-effectiveness.
Foot Length Insights:
- 28 - 45 ft
- Above 45 ft
28 - 45 ft exhibits a clear dominance with a 68% share of the total India semi-trailer market in 2025.
The 28 - 45 ft foot length segment represents dominant market configuration offering optimal balance between cargo capacity, maneuverability, and regulatory compliance across diverse transportation applications serving India's complex logistics requirements. This length category accommodates majority of freight transportation requirements across industries, proving versatile for both regional and long-haul transport operations while meeting governmental regulations and infrastructure limitations including loading dock standards, highway clearances, and urban access restrictions. New governmental regulations permitting longer vehicle configurations under specified conditions and expansion of manufacturing industry positively impacting market growth as these length configurations optimize payload utilization while maintaining operational flexibility across varied route conditions, toll plaza clearances, and loading dock facilities nationwide.
Versatility of 28-45 ft semi-trailers enabling fleet operators to accommodate diverse cargo types ranging from palletized goods and containerized shipments to bulk materials and specialized equipment, making this length range preferred choice for full truckload operations and inter-city freight movements. Growing standardization of logistics infrastructure including warehouse loading docks, container freight stations, and multi-modal terminals designed to accommodate semi-trailers in this length range further reinforcing segment dominance as businesses invest in compatible equipment maximizing operational efficiency across integrated supply chain networks.
End Use Industry Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Transportation and Logistics
- Food and Beverage
- Construction and Mining
- Agriculture
- Manufacturing and Industrial Goods
- Retail and E-commerce
Transportation and logistics lead with a share of 25% of the total India semi-trailer market in 2025.
Transportation and Logistics sector represents largest end-use industry segment driven by rapid development in manufacturing, e-commerce, and retail industries creating intensified demand for efficient freight transit solutions supporting India's evolving supply chain requirements. Rising logistics requirements positioned at forefront of driving semi-trailer demand as businesses compete to exceed burgeoning consumers' expectations of faster and on-time delivery, with trailers proving key in enhancing supply chain maximization enabling products to travel with ease from region to region across expanding distribution networks.
Third-party logistics providers and organized fleet operators increasingly investing in modern semi-trailer fleets equipped with advanced tracking systems, temperature control capabilities, and specialized cargo handling features addressing diverse client requirements across industries from retail to pharmaceuticals. Improved highway infrastructure including expanded expressway networks, upgraded national highways, and enhanced road surfaces enabling faster transit times and increased payload utilizations, making semi-trailer investments more attractive for logistics companies seeking competitive advantages through operational efficiency improvements and superior customer service delivery capabilities supporting India's transformation into global manufacturing and consumption powerhouse.
Region Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
North India exhibits a clear dominance with a 30% share of the total India semi-trailer market in 2025.
North India acquires highest market share in India semi-trailer market due to robust industrial and agricultural sectors coupled with abundant transport infrastructure and strategic geographic location facilitating uninterrupted movement of goods supporting sustained trailer demand across diverse economic activities. Region's industrial strength encompassing manufacturing hubs across automotive, engineering, textiles, consumer goods, and electronics sectors generates substantial freight transportation requirements, while agricultural production from states including Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh necessitates extensive semi-trailer deployments for crop transportation to agricultural produce markets, processing facilities, and export terminals.
Delhi NCR region serving as major consumption market and commercial hub generating significant inbound and outbound freight movements requiring extensive semi-trailer deployments for servicing organized retail chains, e-commerce fulfillment centers, and wholesale distribution networks. Punjab and Haryana states representing agricultural powerhouses producing substantial wheat, rice, cotton, and dairy output necessitating seasonal semi-trailer capacity expansions during harvest periods for transporting agricultural commodities to government procurement centers, private traders, and food processing industries. Uttar Pradesh's emerging manufacturing sector under government's One District One Product initiative and industrial corridor developments along Dedicated Freight Corridor routes creating new demand pockets for semi-trailer deployments connecting production facilities with national distribution networks.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Semi-trailer Market Growing?
Cold Chain Infrastructure Expansion and Temperature-Controlled Logistics Growth
India's expanding cold chain infrastructure driven by pharmaceutical distribution requirements and perishable goods transportation is creating substantial demand for specialized refrigerated semi-trailers across healthcare and food sectors. As per the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), access to cold chain facilities can greatly enhance the earnings achieved by farmers. The rise is projected to be around 15-20%. Rising demand for fresh produce, frozen foods, dairy products, pharmaceutical supplies, and vaccines requiring strict temperature maintenance throughout supply chain necessitating increased adoption of refrigerated semi-trailers equipped with advanced cooling systems and temperature monitoring technologies. Food and beverage sector growth coupled with expanding organized retail chains, quick service restaurants, and increasing consumer preference for fresh and frozen food products driving substantial investments in cold chain logistics infrastructure.
Manufacturing Sector Expansion and Make in India Initiative
India's ambitious Make in India initiative launched to transform the country into global manufacturing hub is generating substantial freight transportation demand across automotive, electronics, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and engineering sectors requiring diverse semi-trailer configurations. Manufacturing output expansion across automotive clusters in Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Haryana creating intensive demand for specialized semi-trailers transporting raw materials, components, and finished vehicles between production facilities, suppliers, and distribution networks. Electronics manufacturing growth under Production Linked Incentive schemes attracting major global brands establishing production facilities in India necessitating efficient logistics solutions for component procurement and finished goods distribution requiring flatbed and dry van semi-trailers. Manufacturing is becoming a key pillar of India’s economic progress, accounting for approximately 16-17% of GDP and providing jobs for more than 27 million people. Private sector investments in manufacturing capacities responding to domestic consumption growth and export opportunities necessitating expanded logistics infrastructure including semi-trailer fleets supporting supply chain efficiency and just-in-time delivery requirements across manufacturing value chains.
Urbanization and Construction Industry Boom Fueling Heavy-Duty Transportation Demand
Rapid urbanization driving India's construction industry expansion across residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects is creating intensive demand for flatbed and lowboy semi-trailers transporting heavy construction equipment, building materials, and oversized structural components. India's urban population projected to reach 600 million by 2031 from current levels necessitating massive housing construction, commercial real estate development, and urban infrastructure projects including metro rail systems, flyovers, and utilities requiring extensive semi-trailer deployments for material logistics. Real estate sector recovery post-pandemic with residential launches increasing across tier I and tier II cities driving demand for construction material transportation including ready-mix concrete, steel reinforcement bars, precast elements, and finishing materials requiring reliable semi-trailer services connecting manufacturing facilities, batching plants, and construction sites ensuring timely project delivery and construction schedule adherence.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Semi-trailer Market is Facing?
Fluctuating Fuel Prices and Rising Operational Costs Pressuring Profit Margins
Volatility in diesel fuel prices creating significant challenges for semi-trailer operations as operating costs rise substantially impacting fleet profitability and investment decisions. Operating costs including driver wages, fuel expenses, tax payments, and toll charges constitute approximately two-thirds of total ownership cost, with fuel price fluctuations directly affecting transportation economics and pricing strategies across logistics sector. Increased total cost of ownership driven by rising input costs, higher interest rates, and elevated maintenance expenses resulting in many small fleet operators opting for pre-owned vehicles instead of purchasing new semi-trailers, potentially slowing market growth trajectory.
Shortage of Skilled Drivers Limiting Effective Fleet Utilization
India's transportation industry facing persistent shortage of qualified commercial truck drivers limiting effective utilization of semi-trailer assets and constraining market growth potential. Industry reported deficit of skilled drivers, leading to operational delays, increased costs, and constraints on fleet expansion capabilities as trailers remaining idle generate no revenue impacting return on investment for fleet owners. Driver shortage exacerbated by demanding working conditions, low wage levels for taxi drivers, and challenging work-life balance considerations driving migration toward alternative employment opportunities in industrial and service sectors offering more comfortable working conditions.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements and Infrastructure Limitations
Implementation of stringent regulatory standards including Bharat Stage VI emission norms requiring significant investments in technology upgrades and cleaner technologies increasing manufacturing costs and operational complexities for fleet operators. Compliance with evolving emissions regulations, safety standards, and weight restrictions necessitating ongoing investments in fleet modernization and technology adoption, particularly challenging for small and medium fleet operators with limited capital access. Fragmented truck ownership structures, informal financing barriers for fleet upgrades, and varying regulatory standards across different states creating operational complexities, while infrastructure limitations including inadequate parking facilities, limited service networks, and congested urban routes constraining efficient semi-trailer operations across certain geographic corridors.
Competitive Landscape:
The India semi-trailer market exhibits moderately fragmented competitive landscape characterized by presence of established domestic manufacturers, international players, and numerous regional fabricators catering to diverse industry requirements across vehicle types and tonnage categories. Leading market participants focus on product innovation, manufacturing capacity expansion, technological integration, and strategic partnerships with logistics operators and fleet owners to strengthen market positions and capture growing demand across transportation and logistics sectors. Major players investing substantially in research and development activities to introduce advanced semi-trailer configurations incorporating lightweight materials, improved aerodynamics, and smart technologies including telematics systems and IoT sensors enhancing operational efficiencies and asset tracking capabilities. Competitive strategies encompass customization offerings tailored to specific industry applications, after-sales service network development, and financial solutions facilitating fleet acquisition for small and medium operators, while manufacturing capacity expansions addressing rising demand across e-commerce logistics and infrastructure development projects driving market growth.
Recent Developments:
- In January 2025, EKA Mobility revealed an electric trailer truck at Auto Expo 2025. EKA, having revealed the debut of a new electric truck, has ultimately unveiled a 55-ton electric tractor-trailer. The Brand offers clever and advanced features with its truck, providing a forward-thinking transportation option.
India Semi-trailer Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Vehicle Types Covered | Flatbed, Dry Van, Refrigerated (Reefer), Lowboy, Tanker, Curtain-sider, Others |
| Tonnages Covered | Below 25 Ton, 25 Ton - 50 Ton, 51 Ton - 100 Ton, Above 100 Ton |
| Foot Lengths Covered | 28 - 45 ft, Above 45 ft |
| End Use Industries Covered | Transportation and Logistics, Food and Beverage, Construction and Mining, Agriculture, Manufacturing and Industrial Goods, Retail and E-commerce |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India semi-trailer market size was valued at USD 796.54 Million in 2025.
The India semi-trailer market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.88% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 1,450.08 Million by 2034.
Flatbed trailers held the largest vehicle type segment share at 21%, driven by construction industry expansion and infrastructure development projects requiring transportation of heavy machinery, oversized equipment, steel, timber, and construction materials with their versatile flat design enabling efficient loading and unloading capabilities.
Key factors driving the India semi-trailer market include PM Gati Shakti infrastructure investments, e-commerce logistics expansion creating additional delivery hubs, GST implementation streamlining operations, cold chain infrastructure growth, Make in India manufacturing initiatives, and technological advancements including electric trailers and road train configurations.
Major challenges include fluctuating diesel fuel prices impacting operational costs constituting two-thirds of ownership expenses, shortage of skilled drivers limiting fleet utilization, Bharat Stage VI emission compliance requiring significant technology investments, and fragmented ownership structures with informal financing barriers constraining fleet modernization.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.

 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












