
India Smart Power Transmission Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Technology, Voltage Level, End User, and Region, 2025-2033 2025-2033
India Smart Power Transmission Market Overview:
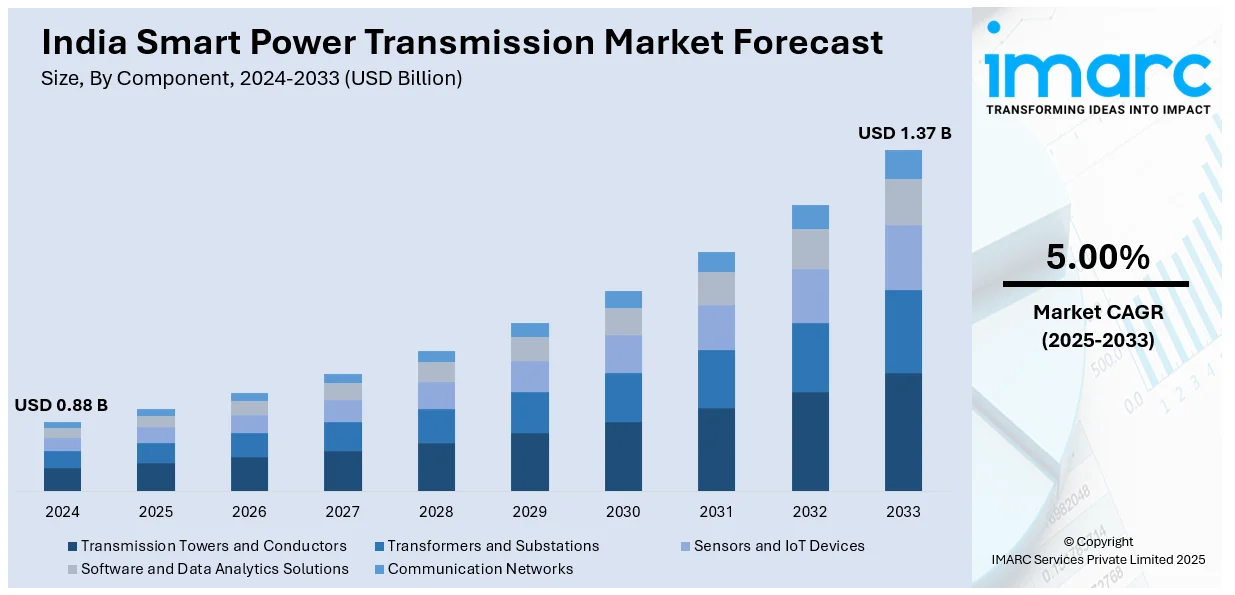
The India smart power transmission market size reached USD 0.88 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 1.37 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 5.00% during 2025-2033. The market is driven by the growing demand for efficient and reliable energy distribution systems, supported by government initiatives like the Smart Grid Mission and increased investments in renewable energy. In addition to this, the growing need to reduce power losses, improve grid resilience, and enhance automation capabilities in transmission systems are some of the major factors augmenting India smart power transmission market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 0.88 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 1.37 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 5.00% |
India Smart Power Transmission Market Trends:
Increased Adoption of Smart Grids and Automation Technologies
The market is experiencing a monumental shift with the increased use of automation technologies and intelligent grids. They enable real-time monitoring, fault detection, and control of electricity transmission, which leads to grid reliability and efficiency. Smart grids use advanced sensors, communication systems, and software to automate power distribution, and this enables support for integrating the use of renewable sources of power, like solar and wind. This ensures adequate energy distribution and saves expenditure. Additionally, grid automation systems enhance the responsiveness of the grid through predictive maintenance and automated fault isolation. Other than this, the Indian government's push towards digitalization via initiatives like the National Smart Grid Mission (NSGM) is pushing the growth of these technologies ahead. Also, the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in grid management further enhances energy efficiency and reliability for both utilities and customers.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Government Policy and Regulatory Framework
The government of India plays a major role in developing and expanding smart power transmission with continual policy implementation as well as policy and regulatory drives. Initiatives like the National Smart Grid Mission (NSGM) and UDAY scheme (Ujwal DISCOM Assurance Yojana) create an environment conducive to the upgradation of the transmission system. The government is investing in the upgrading of transmission networks and promoting the adoption of smart technologies to improve efficiency and reduce losses. Moreover, policy implementation to stimulate private sector participation, such as the tariff-based competitive bidding (TBCB) approach, further promotes investments in smart power transmission projects. Regulation systems are tailored to incentivize utilities to adopt advanced technologies, such as dynamic line rating systems and real-time monitoring. Government measures to streamline the approval process for such projects, along with financial incentives and subsidies, are likely to keep propelling the growth of smart transmission solutions across India.
Growing Need for Integration with Renewable Energy
The increasing focus on clean and renewable energy sources in India is a significant factor contributing to the India smart power transmission market growth. As per industry reports, India has made aggressive renewable energy goals, with an objective to have 175 GW of renewable capacity by 2022 and 500 GW by 2030. In order to align with the variable nature of renewable energy, including solar and wind power, the current power transmission infrastructure needs massive upgradation. In addition to this, smart transmission systems with state-of-the-art control technologies allow for improved control of these variable energy sources. Storing surplus renewable energy during peak production periods and distributing it economically when demand increases is crucial to grid stability. Also, smart grids allow for effortless integration of decentralized generation sources, lowering reliance on centralized fossil fuel-based power plants. Apart from this, India's path towards a low-carbon future is accelerating investments in advanced transmission technologies to manage the challenges of integrating renewables.
India Smart Power Transmission Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on component, technology, voltage level, and end user.
Component Insights:
- Transmission Towers and Conductors
- Transformers and Substations
- Sensors and IoT Devices
- Software and Data Analytics Solutions
- Communication Networks
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the component. This includes transmission towers and conductors, transformers and substations, sensors and IoT devices, software and data analytics solutions, and communication networks.
Technology Insights:
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems
- Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs)
- Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS)
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Smart Transformers
- High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission
- Wide-Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS)
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology have also been provided in the report. This includes supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, phasor measurement units (PMUs), flexible AC transmission systems (FACTS), advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), smart transformers, high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission, and wide-area monitoring systems (WAMS).
Voltage Level Insights:
- Extra High Voltage (EHV) Transmission (≥ 220 kV)
- High Voltage (HV) Transmission (66 kV - 220 kV)
- Medium Voltage (MV) Transmission (11 kV - 66 kV)
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the voltage level. This includes extra high voltage (EHV) transmission (≥ 220 kV), high voltage (HV) transmission (66 kV - 220 kV), and medium voltage (MV) transmission (11 kV - 66 kV).
End User Insights:
.webp)
- Utilities
- Industrial Sector
- Commercial Sector
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes utilities, industrial sector, and commercial sector.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include North India, South India, East India, and West India.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
India Smart Power Transmission Market News:
- On April 30, 2025, Larsen & Toubro's Power Transmission & Distribution (PT&D) business secured major contracts for power transmission projects both in India and internationally. The domestic orders include the construction of 765 kV transmission lines and substations to strengthen the national grid and integrate renewable energy.
India Smart Power Transmission Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Transmission Towers and Conductors, Transformers and Substations, Sensors and IoT Devices, Software and Data Analytics Solutions, Communication Networks |
| Technologies Covered | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems, Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs), Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS), Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), Smart Transformers, High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission, Wide-Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS) |
| Voltage Levels Covered | Extra High Voltage (EHV) Transmission (≥ 220 kV), High Voltage (HV) Transmission (66 kV - 220 kV), Medium Voltage (MV) Transmission (11 kV - 66 kV) |
| End Users Covered | Utilities, Industrial Sector, Commercial Sector |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the India smart power transmission market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the India smart power transmission market on the basis of component?
- What is the breakup of the India smart power transmission market on the basis of technology?
- What is the breakup of the India smart power transmission market on the basis of voltage level?
- What is the breakup of the India smart power transmission market on the basis of end user?
- What is the breakup of the India smart power transmission market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the India smart power transmission market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the India smart power transmission?
- What is the structure of the India smart power transmission market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the India smart power transmission market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the India smart power transmission market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the India smart power transmission market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the India smart power transmission industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












