
India Waste to Energy Solutions Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Waste Type, and Region, 2025-2033
India Waste to Energy Solutions Market Overview:
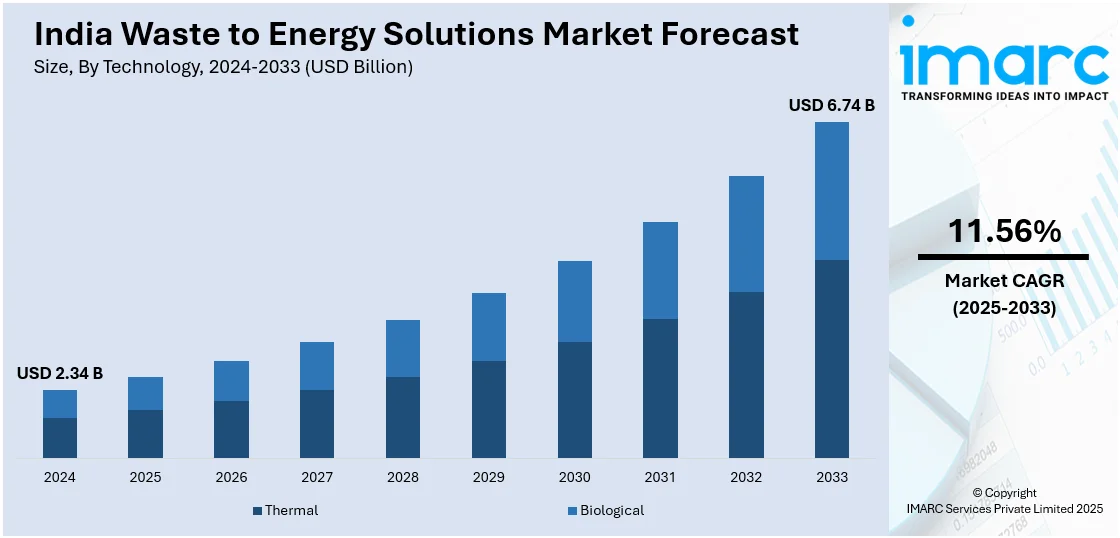
The India waste to energy solutions market size reached USD 2.34 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 6.74 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 11.56% during 2025-2033. Rapid urbanization, increasing municipal solid waste generation, and policy-backed decentralization of waste treatment infrastructure, along with capital subsidies, feed-in tariffs, and renewable energy obligations, are some of the factors positively impacting the market. Integration of gasification and biomethanation technologies, real-time waste segregation tools, and public-private collaborations are additional factors augmenting the India waste to energy solutions market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.34 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 6.74 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 11.56% |
India Waste to Energy Solutions Market Trends:
Urbanization and Municipal Solid Waste Management Pressure
India’s rapid urbanization has led to an exponential increase in municipal solid waste generation, placing unprecedented pressure on city administrations and public infrastructure. On April 1, 2025, Hasiru Dala Innovations (HDI), a Bengaluru-based waste management company, raised INR 6 Crore (USD 725,000) in a pre-series A funding round led by Rainmatter Fintech Investments and Next Bharat Ventures IFSC. The investment will drive the company’s expansion in plastics circularity and bio-energy solutions, further enhancing its waste-to-energy initiatives. HDI has already diverted over 100,000 tons of municipal solid waste from landfills, contributing to significant greenhouse gas emission reductions. With over 400 million urban residents and a growing number of metropolitan zones, managing waste sustainably has become a critical policy and operational challenge. Traditional landfill-based disposal methods are no longer viable, given land constraints, environmental hazards, and public health risks. In this context, energy recovery from waste is being prioritized as a dual-purpose strategy, addressing waste volume and meeting renewable energy goals. Urban local bodies are increasingly collaborating with private sector players to establish decentralized waste-to-energy (WTE) facilities that utilize combustion, biomethanation, and gasification technologies. These solutions help reduce the burden on landfills while simultaneously contributing to the country’s non-fossil energy capacity. Additionally, policy support through initiatives such as the Swachh Bharat Mission and the Smart Cities Mission is driving municipalities to explore viable, scalable alternatives to waste disposal. The growing integration of WTE facilities in urban planning and infrastructure development reflects the policy alignment and market response. The rise in city-level partnerships, infrastructure-linked implementation models, and the urgent need to divert waste from landfills have collectively contributed to India waste to energy solutions market growth.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Renewable Energy Policy Incentives and Technological Advancements
India’s commitment to achieving clean energy targets under national and international frameworks has led to a significant focus on alternative energy generation, including waste-to-energy initiatives. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has introduced various fiscal and regulatory incentives to encourage the deployment of WTE plants. These include viability gap funding, capital subsidies, and generation-based incentives that reduce the financial risks of adopting such technologies. In parallel, state-level energy regulators are implementing feed-in tariffs and mandatory procurement obligations, strengthening the commercial viability of WTE projects. On April 25, 2025, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) provided details on its Waste to Energy Programme, offering financial assistance for Waste to Energy projects aimed at generating Biogas, BioCNG, Power, or syngas from urban, industrial, and agricultural waste. The programme spans from FY 2021-22 to FY 2025-26 and includes Central Financial Assistance (CFA) for various energy-generation technologies, with higher support for plants in Special Category States. The initiative aims to promote sustainable waste management while reducing landfill dependence, offering incentives based on project performance and commissioning timelines. On the technological front, there is growing adoption of advanced anaerobic digestion, plasma arc gasification, and refuse-derived fuel systems that enhance energy recovery efficiency. Public-private partnerships are being leveraged to bridge the technological and operational gaps in legacy waste infrastructure. Additionally, India’s growing startup ecosystem is fostering innovation in real-time waste segregation, bio-reactor systems, and AI-powered waste sorting: tools that are being integrated into end-to-end WTE solutions. These advancements are not only improving conversion rates but also aligning with the broader sustainability goals of reducing carbon emissions and maximizing resource recovery.
India Waste to Energy Solutions Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on technology and waste type.
Technology Insights:
- Thermal
- Biological
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology. This includes thermal and biological.
Waste Type Insights:
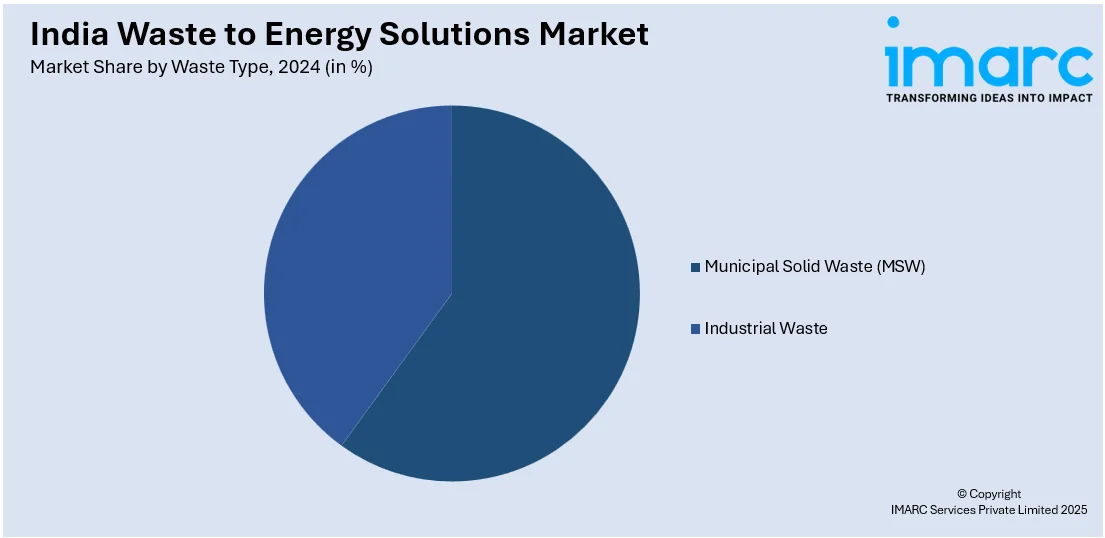
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
- Industrial Waste
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the waste type. This includes municipal solid waste (MSW) and industrial waste.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
The report has provided a comprehensive analysis of all major regional markets, which include North India, South India, East India, and West India.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
India Waste to Energy Solutions Market News:
- On February 16, 2024, Re Sustainability Limited (ReSL) launched a new Waste-to-Energy (WTE) facility in Rewa, Madhya Pradesh, as part of its Integrated Solid Waste Management (ISWM) project, which serves the Rewa, Satna, and Sidhi districts. The facility includes a 6 MW WTE plant capable of processing 350-380 metric tons of waste daily and will serve approximately 235,000 households, contributing to cleaner waste disposal and renewable energy generation. With a total project cost of INR 220 crore (USD 26.5 million) and plans for future expansion, the project emphasizes ReSL’s commitment to sustainability and circular economy principles in the region.
- On February 13, 2025, Oswal Energies showcased its clean energy innovations, including green hydrogen, waste-to-energy, and carbon capture technologies, at India Energy Week 2025. The company introduced its Plasma-Enhanced Gasification System (PEGS®) for waste-to-energy conversion, which addresses environmental challenges while generating clean energy.
India Waste to Energy Solutions Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Thermal, Biological |
| Waste Types Covered | Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), Industrial Waste |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the India waste to energy solutions market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the India waste to energy solutions market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the India waste to energy solutions industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India waste to energy solutions market was valued at USD 2.34 Billion in 2024.
The India waste to energy solutions market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 11.56% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 6.74 Billion by 2033.
The India waste-to-energy solutions market is driven by the growing urgency to manage municipal and industrial waste sustainably, government policies promoting circular economy practices, and investments in renewable energy infrastructure. Rising urbanization increases waste volumes while clean energy targets prioritize converting refuse into electricity and heat, boosting India waste to energy solutions market momentum.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












