
Indonesia Construction Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Sector and Region, 2026-2034
Indonesia Construction Market Summary:
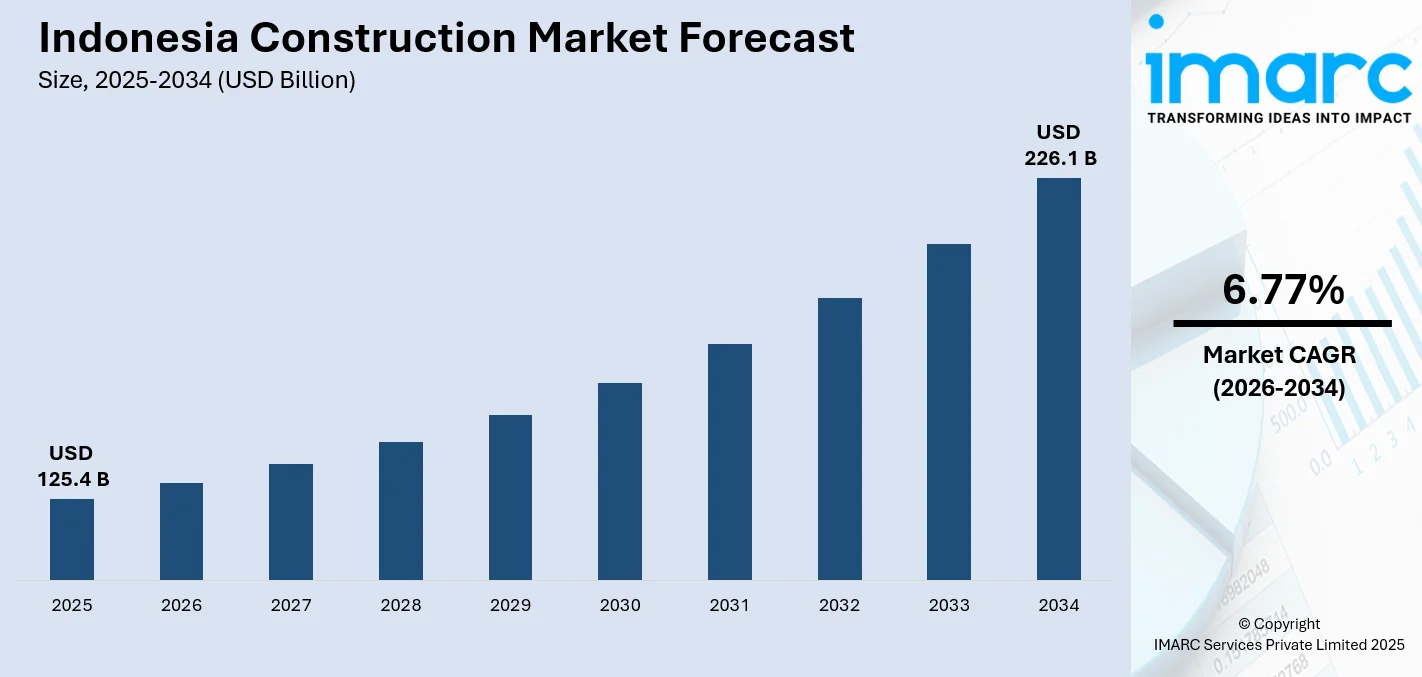
The Indonesia construction market size was valued at USD 125.4 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 226.1 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.77% from 2026-2034.
Indonesia's construction market is recording strong growth buoyed by significant government infrastructure investments, rapid urbanization, and strong inflows of foreign direct investment. Ambitious national development projects-like a new capital city, Nusantara; a network of transport reaching every nook and corner; and renewable energy projects-reshape not just the nation's built environment but the economic landscape and stimulate demand across all residential, commercial, and industrial construction segments nationwide.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
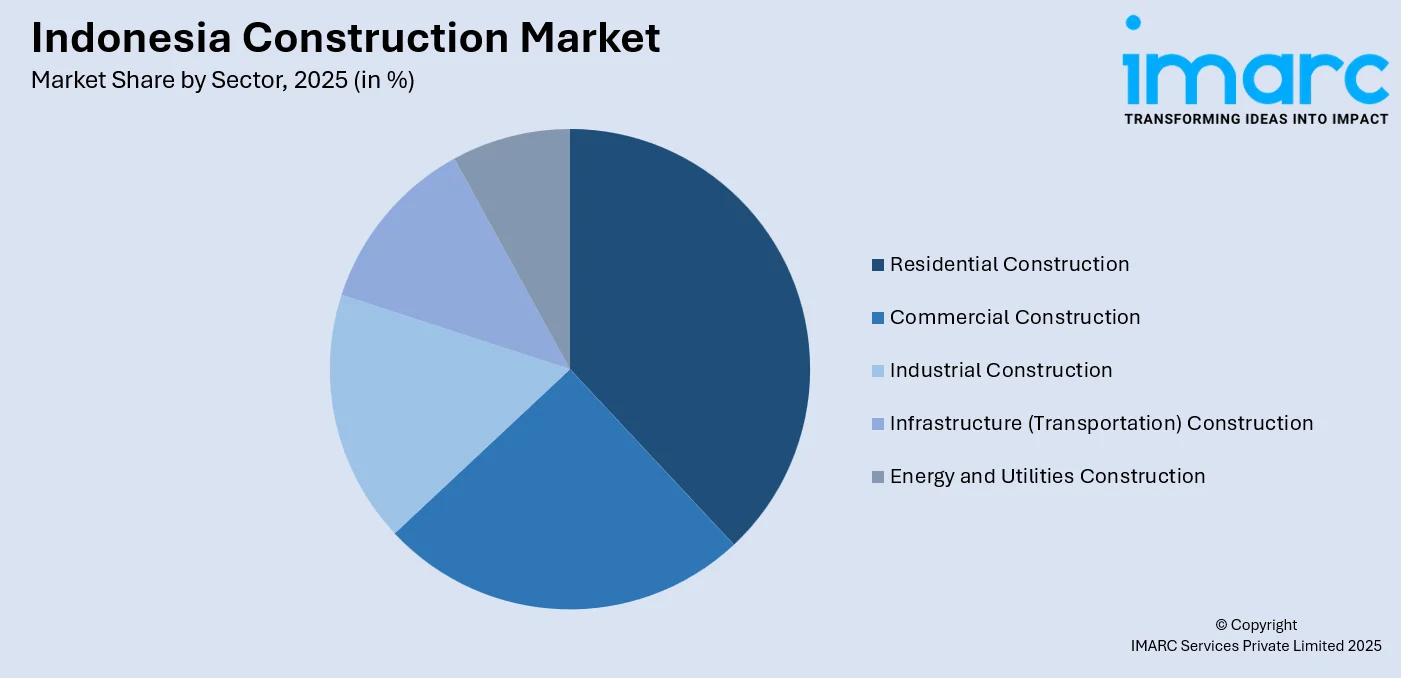
- By Sector: Residential construction dominates the market with a share of 38.06% in 2025, driven by persistent housing demand from a growing population, government stimulus measures including VAT incentives, and urbanization trends accelerating housing development across metropolitan and emerging urban areas.
- By Region: Java leads the market with a share of 34% in 2025, supported by concentrated economic activity, established infrastructure networks, dense urban population centers including Jakarta, and substantial commercial and residential development pipelines.
- Key Players: The Indonesia construction market features a competitive landscape comprising major domestic contractors, state-owned enterprises, and international construction firms. Industry participants are leveraging government partnerships, infrastructure expertise, and sustainable construction capabilities to capture growth opportunities across diverse project segments.
The Indonesian construction industry is a key driver of economic growth, contributing significantly to GDP and employment. In October 2025, the Nusantara Capital Authority began construction on legislative and judicial complexes as part of Phase II of the new capital city project, with multiple major road and infrastructure contracts signed to support development through 2027. Government-led infrastructure programs focus on connectivity, regional development, and industrialization, with major investments in roads, railways, ports, and airports improving logistics nationwide. The Nusantara capital city project attracts substantial domestic and international investment, while regulatory reforms like the Omnibus Law streamline permits and boost foreign investment. Sustainable construction practices are increasingly emphasized to meet national carbon reduction goals, positioning the sector as a strategic pillar for long-term economic and environmental development.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Indonesia Construction Market Trends:
Accelerating Infrastructure Development Through National Strategic Projects
Indonesia's construction landscape is being transformed by unprecedented government commitment to infrastructure development through the National Long-Term Development Plan. In November 2025, President Prabowo Subianto directed the expansion of the national railway network to Sumatra, Kalimantan, Java, and Sulawesi to support both passenger travel and freight distribution, aiming to cut logistics costs and boost competitiveness as part of broader connectivity and industrialization goals. Major transportation projects including the Trans-Sumatra toll road corridor, Jakarta-Bandung high-speed rail, and extensive port modernization initiatives are enhancing connectivity across the archipelago.
New Capital City Development Driving Long-Term Investment
The development of Nusantara in East Kalimantan is Indonesia’s most ambitious urban initiative, envisioned as a smart, sustainable city with net-zero carbon targets. In November 2025, the Nusantara Capital City Authority began building a Rp900 billion solar power plant to support clean energy in the capital region. The phased construction covers government complexes, residential communities, commercial facilities, and infrastructure for nearly two million residents. This multi-decade project is drawing both public funding and private investment, offering long-term opportunities for contractors and materials suppliers.
Emphasis on Sustainable and Resilient Construction Practices
Environmental sustainability and disaster resilience are increasingly shaping Indonesia’s construction sector as the country advances renewable energy targets and addresses natural disaster risks. In February 2025, IFC and PT Bank OCBC NISP issued Indonesia’s first major sustainability‑linked loan to PT Nirvana Wastu Pratama (NWP) to decarbonize commercial and logistics properties and expand green building certifications. Growing investments in solar and wind infrastructure are boosting construction demand, while developers increasingly adopt disaster‑resistant designs, sustainable materials, and green building standards in response to market and regulatory pressures.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
"The outlook in the construction industry in Indonesia is very positive as fundamental growth factors such as urbanization, infrastructure gaps, and industrialization remain to drive the growth. Budgetary expenditures on infrastructure development projects continue to remain at historical highs. Foreign direct investments in the country, especially in manufacturing plant projects, continue to increase, thus providing more diversity to the projects being developed, apart from the government-initiated residential projects to boost the residential construction industry. Development of the new capital of Nusantara and the overall development of the country’s transportation infrastructure will provide the long-term anchor to the growth of the industry. Adoption of innovative construction technologies will improve productivity to overcome the issue of talent deficiency in the industry. The market generated a revenue of USD 125.4 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 226.1 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.77% from 2026-2034.
Indonesia Construction Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Sector |
Residential Construction |
38.06% |
|
Region |
Java |
34% |
Sector Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Commercial Construction
- Residential Construction
- Industrial Construction
- Infrastructure (Transportation) Construction
- Energy and Utilities Construction
The residential construction dominates with a market share of 38.06% of the total Indonesia construction market in 2025.
The residential construction sector maintains market leadership driven by Indonesia's substantial housing demand stemming from population growth, urbanization, and rising middle-class aspirations. To sustain housing market activity, the government has extended the full value‑added tax (VAT) incentive (PPN DTP) on home purchases through the end of 2027, providing long‑term certainty for buyers and developers and reinforcing demand in the middle‑income segment. Government stimulus measures including VAT incentives for properties and favorable loan-to-value policies are supporting housing market activity.
Residential development extends beyond primary urban centers as improved transportation connectivity opens new suburban and satellite city opportunities. The apartment and condominium segment is experiencing growth in major cities including Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung, while landed housing remains popular in expanding suburban areas. Developer investment in integrated township developments combining residential, commercial, and recreational facilities reflects evolving consumer preferences for comprehensive lifestyle offerings.
Regional Insights:
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
- Others
Java exhibits a clear dominance with a 34% share of the total Indonesia construction market in 2025.
The market for Java remains nucleus to the entire Indonesian construction industry, being a representation of where it is for the economies of this largest Pacific archipelago. Jakarta and the surrounding metropolitan area are key to this demand for commercial, residential, and infrastructure developments, while secondary centers of Surabaya, Bandung, and Semarang are significant to development activity. This region has well-established supply chains, an available skilled workforce, and sophisticated contractors.
However, the outer island regions have been experiencing faster growth as a result of the government's efforts to ensure equitable regional development. Kalimantan is proving to be a promising market in the construction industry due to the development of Nusantara and natural resource industries. Sumatra derives its strength from the Trans-Sumatra toll road and the related industry. Sulawesi and the eastern regions of Indonesia are proving attractive to investment in infrastructure.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Indonesia Construction Market Growing?
Substantial Government Infrastructure Investment Programs
The Indonesian government has committed unprecedented budget allocations to infrastructure development as a cornerstone of national economic strategy. In August 2024, the government proposed a Rp400.3 trillion (about $25.5 billion) infrastructure budget for 2025 covering major connectivity projects and development of the Nusantara new capital, underscoring sustained high‑level fiscal prioritization of construction and public works. Annual infrastructure spending has reached historically high levels with substantial investments directed toward transportation networks, public facilities, and regional development initiatives. The National Long-Term Development Plan establishes ambitious targets for renewable energy expansion, transportation network enhancement, and digital infrastructure deployment that will sustain construction demand over the coming decades.
Rapid Urbanization and Population Growth
Indonesia's demographic trajectory drives sustained construction demand across residential, commercial, and infrastructure sectors. The nation's large and growing population, combined with accelerating urbanization, creates persistent housing requirements and expanding needs for commercial facilities, public services, and urban infrastructure. In August 2025, Statistics Indonesia (BPS) reported that the construction sector employed over 8.7 million workers, about 5.97 % of the country’s total workforce, highlighting the industry’s significant role in job creation amid rising domestic demand. Metropolitan areas continue expanding while secondary cities experience growth that necessitates new construction across multiple building categories.
Rising Foreign Direct Investment and Industrial Expansion
Foreign direct investment inflows have strengthened substantially as Indonesia attracts manufacturing facilities, industrial estates, and commercial operations from international corporations. Regulatory reforms including full foreign ownership provisions and streamlined approval processes have enhanced investment attractiveness. In 2025, Indonesia’s industrial estates expanded to 175 sites nationwide, supported by a 9.26 % increase in realized investment as foreign investors focused on sectors such as battery and electric vehicle manufacturing, modern logistics, renewable energy, and data centers, highlighting diversified construction opportunities beyond traditional government‑led projects. The development of industrial parks, manufacturing facilities, data centers, and logistics infrastructure creates diverse construction opportunities beyond traditional government-led projects.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Indonesia Construction Market is Facing?
Land Acquisition and Regulatory Complexity
Securing land rights for major infrastructure projects remains a significant challenge that can delay project timelines and increase costs. Complex land title systems, community consultation requirements, and multi-agency coordination extend acquisition processes beyond initial planning assumptions. While electronic permitting has accelerated building approvals, obtaining rights-of-way for linear infrastructure including roads, railways, and power corridors involves extended negotiations that impact project schedules.
Skilled Labor Shortages and Productivity Challenges
The construction industry faces persistent skilled labor constraints that impact project execution capacity and quality standards. Demand for qualified engineers, technicians, and specialized tradespeople exceeds available supply, particularly for major infrastructure projects in remote locations. Labor productivity improvements are necessary to address these constraints, driving adoption of prefabrication and mechanized construction methods that require workforce training investments.
Construction Material Cost Volatility
Fluctuations in construction material prices including cement, steel, and other key inputs create cost management challenges for contractors and developers. Import dependence for certain specialized materials exposes projects to currency fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. While domestic production capacity has expanded, demand pressures from simultaneous large-scale projects can strain supply availability and influence pricing dynamics.
Competitive Landscape:
The Indonesia construction market features a diverse competitive landscape comprising major state-owned construction enterprises, established domestic private contractors, and international construction firms participating through joint ventures and direct operations. State-owned enterprises maintain prominent positions in large-scale infrastructure projects through established government relationships and execution capabilities. Domestic private contractors compete across commercial and residential segments while building infrastructure portfolios. International firms bring technical expertise, project management capabilities, and financing arrangements that complement domestic industry strengths. Competition increasingly emphasizes sustainable construction capabilities, technology adoption, and integrated project delivery approaches as clients prioritize efficiency and quality outcomes.
Recent Developments:
- In June 2025, PT Semen Indonesia Tbk (SMGR) increased its solar power capacity sixfold to 6.5 MWp, supporting sustainable construction. Its Tuban plant’s 6.4 MWp solar system generated 1.726 MWh in 2024, cutting about 1.450.260 kg of CO₂ and lowering reliance on conventional energy. This expansion aligns with SMGR’s 2030 Sustainability Roadmap promoting renewable energy.
Indonesia Construction Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Sectors Covered | Commercial Construction, Residential Construction, Industrial Construction, Infrastructure (Transportation) Construction, Energy and Utilities Construction |
| Regions Covered | Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Indonesia construction market size was valued at USD 125.4 Billion in 2025.
The Indonesia construction market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.77% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 226.1 Billion by 2034.
Residential construction held the largest share of 38.06%, driven by persistent housing demand from population growth and urbanization, government stimulus measures including VAT incentives, and favorable financing conditions supporting housing market development.
Key factors driving the Indonesia construction market include substantial government infrastructure investment programs, rapid urbanization and population growth creating sustained construction demand, rising foreign direct investment in industrial and commercial facilities, and the development of Nusantara as Indonesia's new capital city providing long-term project visibility.
Major challenges include land acquisition complexities and regulatory coordination requirements that can delay project timelines, skilled labor shortages impacting project execution capacity, construction material cost volatility affecting project economics, and the need for continued investment in modern construction technologies to enhance productivity and quality standards.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












