
Indonesia Solar Energy Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Indonesia Solar Energy Market Size:
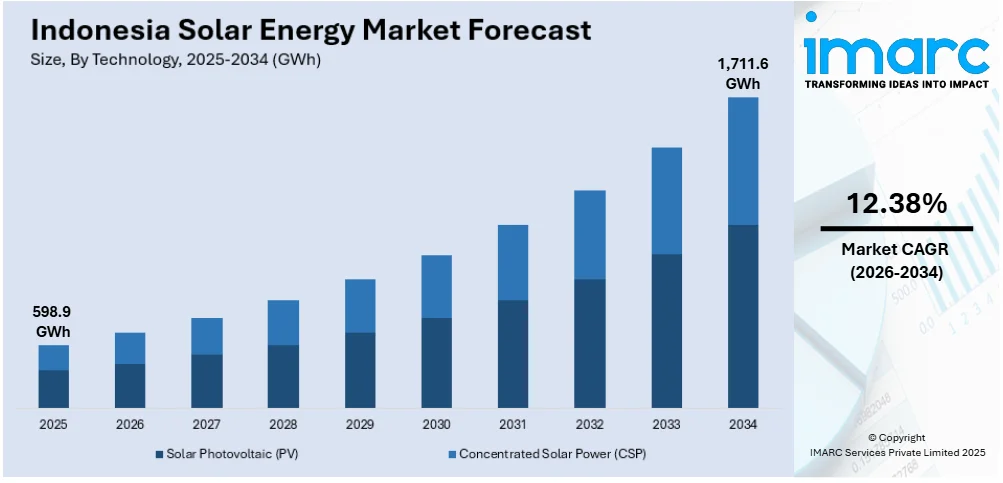
The Indonesia solar energy market size reached 598.9 GWh in 2025. The market is projected to reach 1,711.6 GWh by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 12.38% during 2026-2034. The market growth is attributed to the achievement of grid parity, increasing energy security and independence, rapid advancements in solar technology, rising climate change mitigation goals, and growing rural electrification initiatives.
Market Insights:
- The market is analyzed on the basis of region, which includes Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, and others.
- Based on technology, the market is divided into Solar Photovoltaic (PV) and Concentrated Solar Power (CSP).
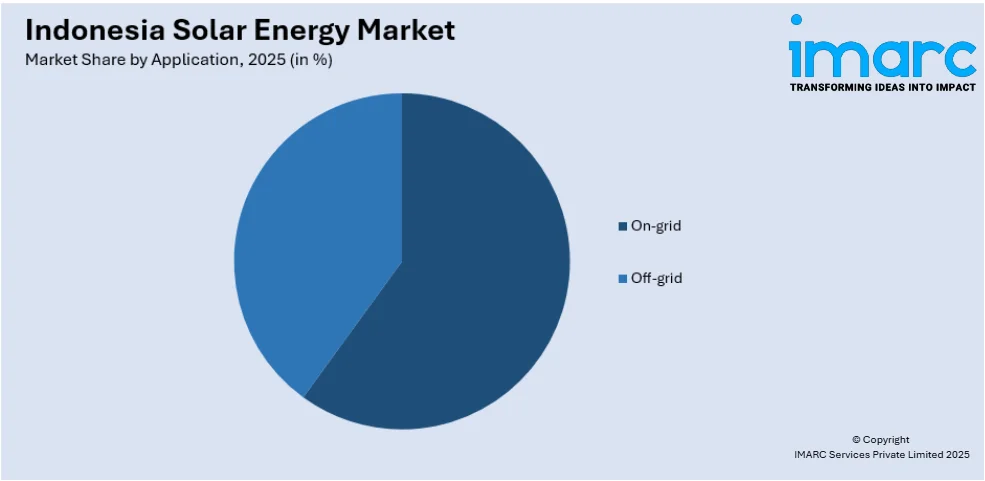
- On the basis of application, the market is divided into on-grid and off-grid solutions.
Market Size and Forecast:
- 2025 Market Size: 598.9 GWh
- 2034 Projected Market Size: 1,711.6 GWh
- CAGR (2026-2034): 12.38%
Indonesia Solar Energy Market Analysis:
- Major Market Drivers: The rising implementation of supportive policies and incentives by government across the country, decreasing costs of solar technology, and increasing electricity demand are some of the major factors augmenting the Indonesia solar energy market share. The country’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and diversifying its energy mix is accelerating investments in solar projects. The growing awareness of renewable energy’s environmental benefits and the push for energy security also contribute significantly to the market growth.
- Key Market Trends: The rapid expansion of solar photovoltaic (PV) installations, widespread adoption of rooftop solar systems, and the increasing investment in large-scale solar projects are some of the key trends in the market. Significant advances in solar technology and the rising government focus on renewable energy targets and regulatory support are encouraging the development and adoption of solar energy.
- Competitive Landscape: Some of the major market players in the Indonesia solar energy industry include PT. Solardex Energy Indonesia, PT. Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur, PT. Sumber Energi Surya Nusantara, SUN Energy, Trina Solar Co. Ltd., among many others.
- Challenges and Opportunities: The market is facing several challenges such as regulatory hurdles, limited grid infrastructure, and high initial investment costs. However, the market also faces various opportunities including the government’s commitment to renewable energy targets and international support for green initiatives, along with technological advancements and decreasing solar panel costs.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Indonesia Solar Energy Market Trends:
Rising Government Policies and Support
The increasing implementation of various supportive policies and incentives by the Government of Indonesia to promote renewable energy including solar power as a part of its commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increasing energy security is contributing to the growth of the solar energy market in Indonesia. For instance, in early 2024, the Indonesian government amended the Energy and Mineral Resources Ministerial Regulation No. 26/2021 to boost the household sector transition to renewable energy, eliminating the previous solar PV installation limit of 10 to 15% out of the total electricity capacity installed by PLN. Similarly, in November 2023, President Joko Widodo inaugurated the Cirata Floating Solar Power Plant (PLTS) with a capacity of 192 MW peak in Purwakarta Regency, West Java Province. The president emphasized that the PLTS primarily serves the green energy industry’s demands, as there is a significant desire for premium products derived from green energy. This is expected to boost Indonesia solar energy market share during the forecast year.
Decreasing Costs of Solar Technology
The declining costs of solar panels and related equipment, along with significant advances in solar technology are making solar energy more affordable and attractive for both residential installations and large-scale projects which are influencing the market growth. For instance, in September 2023, Lazada Indonesia announced plans to install solar panels at its largest logistics facility in an ongoing effort to operate more sustainably. The company marked this clean energy commitment by signing a solar release agreement with renewable energy company Inecosolar. Through its collaboration with Inecosolar, Lazada will install solar panels with the capacity to generate more than 5,55,000 kWh of electricity per year at Lazada Logistics’ facility in Cimanggis, West Java. The solar panels are projected to reduce up to 400 tonnes of carbon emissions annually while meeting approximately 13% of Lazada’s warehouse electricity needs. This is likely to fuel Indonesia solar energy market revenue over the coming years.
Increasing Demand for Electricity
The growing population of Indonesia and the rising economic development are leading to the increasing electricity demand which is further driving the need for alternative and sustainable energy sources such as solar power. According to the data from Enerdata, electricity subsidies increased in 2018, from US$0.9bn to US$7.6bn and from US$4.4bn to US$9.1bn for industries and households, respectively. Since then, they have remained stable at around US$16BN total, increasing slightly to US$17.1bn in 2023. Total consumption per capita is 0.93 toe, while electricity consumption per capita increase by nearly 13% in 2023, reaching 1.3 MWh. Total energy consumption increased in 2022 (+ 16% vs 2021), after a decline of around 5% in 2020 and 2021. It increased by 3.4%/year from 2013 to 2019. This is further influencing Indonesia solar energy market statistics significantly.
Increasing Number of Investment Projects in Solar Energy
Besides government subsidies, increasing private investments are propelling the expansion of solar power projects and assisting in the Indonesia solar energy market growth. In January 2025, for instance, PT Sembcorp Renewables Indonesia and PT PLN Nusantara Renewables commissioned the Nusantara Sembcorp Solar Energi (NSSE) Power Plant, Indonesia's first utility-scale integrated solar and energy storage project. The NSSE campus, covering an area of 87 hectares, hosts a 50 MW solar farm and a 14.2 MWh battery energy storage system. Beyond this, Indonesian public-private sector strategic partnership mirrors a broad trend of cross-sector partnership fueling the drive towards a greener and cleaner tomorrow, encouraging an optimistic Indonesia solar energy market outlook. In addition, technological improvements and reducing prices are rendering solar power more competitive relative to traditional sources of power, further encouraging private capital. Further, Indonesia is also experiencing the trend for hybrid power plants where solar power is blended with other renewable forms such as wind or hydro and also using smart grid technology. With private sector companies offering the finance, technical knowledge, and innovation, while the government provides the regulation and policy environment, the combined endeavor is making way for a cleaner, greener future.
Indonesia Solar Energy Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on technology and application.
Breakup by Technology:
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV)
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology. This includes solar photovoltaic (PV) and concentrated solar power (CSP).
The demand for solar photovoltaic (PV) technology in Indonesia is driven by government incentives and supportive policies for renewable energy, decreasing costs of PV technology, and increasing electricity demand. According to an article by Business Indonesia published in May 2024, one of the major potentials is presented by the utilization of rooftop solar PV for households in Indonesia. With a potential capacity of 32.5 GW, Indonesia's rooftop solar PV, as of June 2023, produces up to 95 MW, with the household sector accounting for 72% of the share. Advancements in PV technology improve efficiency and reliability, making solar PV a viable and attractive option for energy generation.
The demand for concentrated solar power technology in Indonesia is driven by governments' renewable energy targets and supportive policies. Indonesia's high solar irradiance makes CSP viable, while technological advancements and decreasing costs enhance feasibility. CSP’s ability to provide stable dispatchable power by storing thermal energy addresses grid reliability issues. Furthermore, environmental concerns and the drive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions further encourage CSP adoption, promoting sustainable energy solutions and diversifying the country's energy mix.
Breakup by Application:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- On-grid
- Off-grid
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application have also been provided in the report. This includes on-grid and off-grid.
Government incentives and policies supporting renewable energy integration into the National Grid are driving the demand for on-grid applications in the market. Industrial growth and rapid urbanization increase electricity demand which makes on-grid solar solutions attractive. The increasing environmental concerns and rising push to reduce greenhouse gas emissions encourage the shift to cleaner energy sources. Moreover, improving grid infrastructure and reliability further promotes the adoption of on-grid solar systems.
The rising need for reliable electricity in remote and rural areas, where grid access is limited or non-existent is driving the demand for off-grid applications in the market across Indonesia. In line with this, the push for energy independence and reducing reliance on diesel generators promote solar solutions. Government support and incentives for rural electrification projects encourage solar adoption.
Breakup by Region:
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major markets in the region, which include Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, and Others.
High electricity demand due to dense population and rapid urbanization is driving the market growth in Java. The growing government incentives and supportive policies are encouraging solar adoption in the region. The decreasing solar technological costs, coupled with the improved efficiency are making solar power more viable. In line with this, the region's abandoned sunlight enhances solar potential while increasing environmental awareness and push for sustainable energy solutions which is further propelling the growth of the market in Java.
Abandoned sunlight, which provides high solar energy potential is driving the market growth in Sumatra. According to an article, Indonesia, with its Equatorial location, boasts significant solar energy potential, and South Sumatra is no exception. The province possesses a remarkable 17,233 MWp (Megawatt-peak) of solar power potential, yet a large portion of this potential remains untapped. The increasing electricity demand, especially in remote areas, is boosting the need for off-grid solar solutions. In line with this, environmental awareness, and initiatives to reduce carbon emissions further encourage the transition of solar energy in Sumatra, fostering sustainable development and energy security across the region.
Significant solar radiation which makes the region ideal for solar power generation is thriving the market growth across Kalimantan. The rising government incentives and policies supporting renewable energy initiatives are contributing to the growth of the market. For instance, in 2024, the central government plans to set up a solar power plant with a capacity of 50 megawatts this year to supply electricity to the new national capital Nusantara in east Kalimantan. In addition to this decreasing the costs of solar technology are enhancing feasibility and affordability which is driving the market demand.
High solar irradiance which provides excellent potential for solar power generation is driving the market growth across Sulawesi. In addition to this, the increasing environmental concerns, and initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are driving the shift toward sustainable energy sources which enhances solar energy market growth in the region. Moreover, the increasing electricity demand, especially in remote and rural areas is encouraging the use of off-grid solar solutions.
Competitive Landscape:
- The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the market. Detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided. Some of the major market players in the Indonesia solar energy industry include PT. Solardex Energy Indonesia, PT. Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur, PT. Sumber Energi Surya Nusantara, SUN Energy, Trina Solar Co. Ltd., among many others.
(Please note that this is only a partial list of the key players, and the complete list is provided in the report.)
- The competitive landscape of the market features both international and local players. The major companies are actively engaged in developing large-scale solar projects and rooftop installations. Strategic partnerships, technological innovations, and increasing investments. Government incentives and regulatory support further stimulate competition, bolstering a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry environment. For instance, in November 2023, Sojitz officially established ownership in the company PT Surya Nippon Nusantara “SNN” together with PT Mitra Investama (EMI), the holding company of the Sun Energy Group. The Sun Group has presented businesses that provide sustainable solutions such as rooftop solar PV in the residential sector as well as mobile applications, development of electric vehicle infrastructure, water treatment services in the industrial sector, and a Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) buying and selling platform based on blockchain technology.
Indonesia Solar Energy Market News:
- In July 2025, Indonesia's government revealed its efforts to create a new presidential regulation to boost solar power plant (PLTS) development in rural villages. The regulation, which is expected to be finalized next week, aims to build solar power plants in about 80,000 village cooperatives with an investment of approximately USD 100 billion. This initiative is aligned with the country's energy self-sufficiency goals and is expected to reduce energy subsidies by shifting funding to solar energy infrastructure.
- In June 2025, LONGi, a key player in solar photovoltaic solutions, launched a strategic solar panel manufacturing facility by collaborating with Pertamina New and Renewable Energy in Deltamas, West Java, Indonesia. The facility, with an annual production capacity of 1.6 GW, will utilize LONGi’s advanced Hybrid Passivated Back Contact (HPBC) 2.0 technology to produce high-efficiency solar modules.
- In June 2025, Indonesia inaugurated its largest solar panel manufacturing facility, PT Trina Mas Agra Indonesia, with a production capacity of 1 gigawatt (GW) annually and panels delivering 720 watts-peak per unit. This new plant supports Indonesia's renewable energy goals, contributing to the country's target of generating 17.1 GW of solar power by 2034. The establishment of this facility is a strategic move to reduce dependency on imported modules and boost local manufacturing capabilities in clean energy.
- In May 2025, RGE and TotalEnergies signed a Co-Investment Agreement to jointly develop a solar photovoltaic (PV) power plant with a battery energy storage system (BESS) in Riau Province, Indonesia. This utility-scale project, which will be constructed in phases, aims to provide green energy to both domestic markets and for export to Singapore, contributing to regional energy security.
- In March 2024, state electricity company PT. PLN, through its sub-holding PLN Indonesia Power, and China Energy Engineering Group Co., Ltd (CEEC) signed a Joint Development Study Agreement (JDSA) for the exploration of green energy development in Sulawesi.
- In November 2023, an Indonesian renewable energy form is set to commence the construction of solar power plants valued at $9 billion (equivalent to S$12.3 billion) on an island near Batam starting in 2024. Their goal is to supply Singapore with low-carbon electricity by 2027.
- In August 2023, Sinar Mas provided support for the accelerated development and use of new and renewable energy in Indonesia through PT Daya Sukses Makmur Selaras, an indirect subsidiary of PT Dian Swastatika Sentosa Tbk and PT Agra Surya Energi who partnered with Trina Solar to develop the first integrated solar cell and solar module manufacturing plant in Indonesia.
Indonesia Solar Energy Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | GWh |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Solar Photovoltaic (PV), Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) |
| Applications Covered | On-grid, Off-grid |
| Regions Covered | Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Others |
| Companies Covered | PT. Solardex Energy Indonesia, PT. Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur, PT. Sumber Energi Surya Nusantara, SUN Energy, Trina Solar Co. Ltd., etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Indonesia solar energy market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Indonesia solar energy market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Indonesia solar energy industry and its attractiveness.
- The competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Indonesia solar energy market size reached 598.9 GWh in 2025.
The Indonesia solar energy market is expected to reach 1,711.6 GWh by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.38% during 2026-2034.
Market growth is driven by increasing government support for renewable energy adoption, declining costs of solar photovoltaic (PV) technology, and rising demand for clean and sustainable energy sources. Additionally, growing electricity consumption, favorable solar radiation levels, and international commitments to reduce carbon emissions are accelerating solar energy deployment across Indonesia. The expansion of decentralized solar projects and off-grid solutions further boosts the market outlook.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












