
Indonesia Textile Manufacturing Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Process Type, Textile Type, Equipment and Machinery, and Region, 2026-2034
Indonesia Textile Manufacturing Market Size and Share:
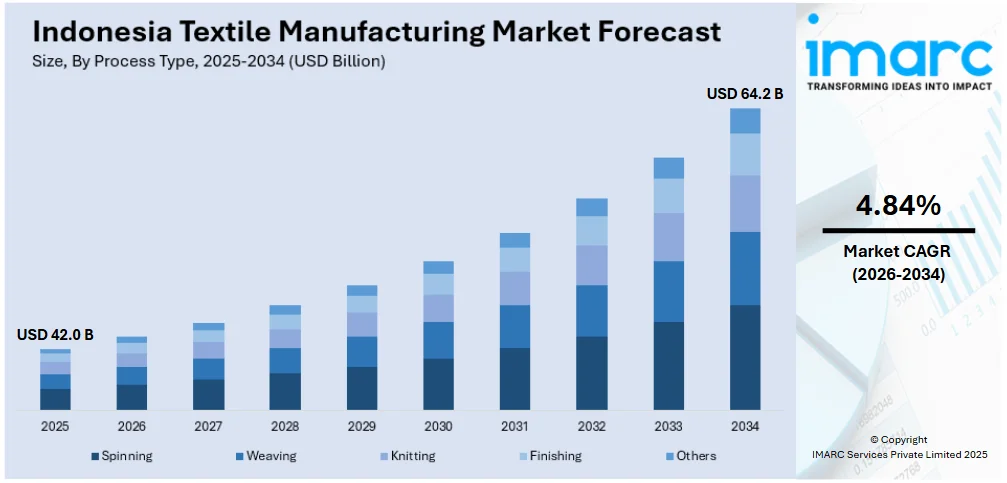
The Indonesia textile manufacturing market size was valued at USD 42.0 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 64.2 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.84% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by the nation's robust reputation as a leading worldwide textile exporter due to competitive labor prices and a well-developed manufacturing base. The rising need for both domestic and global markets, especially in apparel and home textiles, further enhances production capacities. Moreover, the adoption of government policies to promote the competitiveness and sustainability of the textile industry and raise consumer demand for environmentally friendly products are further augmenting the Indonesia textile manufacturing market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 42.0 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 64.2 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 4.84% |
The market is propelled by the implementation of government policies that support the textile industry through incentives, subsidies, and ease of doing business. According to industry reports, in 2024, 43% of Indonesian consumers have begun purchasing sustainable products, reflecting a significant shift in consumer preferences. This growing awareness toward sustainability is reshaping market dynamics, with an increasing number of manufacturers adapting to the rising demand for eco-friendly solutions. Furthermore, the growth of the middle-class population in Indonesia and neighboring countries has boosted domestic consumption of textile goods. The country's strategic location in Southeast Asia allows manufacturers to tap into regional and international markets with ease. Additionally, investments in technological innovations, such as automation and digitalization, have enhanced productivity and competitiveness.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
In addition to this, the rising domestic demand for apparel, fueled by a large and youthful population with increasing fashion consciousness. Indonesia, the world's fourth most populated country, has about 270 million residents with a median age of 30 years, offers a vast base of young consumers actively shaping fashion trends and preferences. The constant shift in fashion trends further drives innovation within the textile industry, encouraging manufacturers to improve production techniques and diversify their product offerings to meet consumer expectations. Moreover, Indonesia's well-established infrastructure, including a robust supply chain and efficient transportation networks, enables smoother operations and quick access to global markets. Besides this, the country's large, skilled workforce contributes significantly to maintaining high production standards.
Indonesia Textile Manufacturing Market Trends:
Abundant Availability of Raw Materials
The sector benefits significantly from its rich endowment of natural resources, particularly cotton, rayon, and other fibers used in textile production. According to the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service, production of cotton in Indonesia for 2023-24 reached 2,000 sales. The country possesses extensive agricultural land that supports the cultivation of various fiber-producing plants, including kapok and bamboo, which are increasingly gaining commercial interest. Moreover, Indonesia is one of the largest producers of viscose rayon, supported by domestic wood pulp industries, making it a key player in the global supply chain. The consistent availability of raw materials ensures production continuity and reduces dependency on volatile global markets. Additionally, the government is promoting vertical integration within the textile industry to improve raw material self-sufficiency, attract foreign investment, and enhance overall competitiveness. This trend enables manufacturers to reduce operational risks and cost volatility, which is creating a positive Indonesia textile manufacturing market outlook.
Increasing Demand for Textile Products
The growing domestic and international demand for textile products, driven by population growth, rising middle-class income, is significantly expanding the market development. According to the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service, the Indonesian textile industry sells 30% of its products to export markets and 70% to the domestic market. Domestically, fashion-conscious consumers are fueling demand for a wide range of textile products, including apparel, home furnishings, and functional fabrics. The rise of e-commerce and digital retail platforms is further enabling access to these products, especially among younger demographics. Internationally, Indonesia has become a strategic supplier to countries in Asia, Europe, and North America, bolstered by competitive labor costs and improving manufacturing capabilities. The government's participation in trade agreements also expands market access and export potential. Furthermore, the country's efforts to modernize its textile sector through technology adoption and workforce upskilling are enabling manufacturers to meet diverse and high-quality product demands. This sustained increase in both domestic and international demand contributes to robust growth in textile manufacturing activities.
Growing Eco-Friendly Production Methods
The country's focus on sustainable and eco-friendly practices is an emerging Indonesia textile manufacturing market trends. The increasing awareness regarding environmental issues and the demand for sustainable textiles are driving manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly production methods, including the use of organic materials and environmentally conscious processes. For instance, South Korea-based Win Textile, a fabric manufacturing company, successfully replaced coal with biomass fuel at its manufacturing facility in Indonesia in April 2025 as part of the company's 'Coal Zero' initiative. Now, the Indonesian plant is run using palm kernel shells (PKS), a byproduct of the palm oil industry that has a high combustion rate and lower emissions. Apart from this, the government, in collaboration with international organizations, has introduced green certification programs and incentives for sustainable manufacturing practices. Additionally, collaboration with fashion brands that demand traceability and low-carbon supply chains has accelerated the shift toward sustainable operations. This trend not only enhances environmental performance but also strengthens the global marketability and resilience of Indonesian textile manufacturers.
Indonesia Textile Manufacturing Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Indonesia textile manufacturing market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on process type, textile type, and equipment and machinery.
Analysis by Process Type:
- Spinning
- Weaving
- Knitting
- Finishing
- Others
Spinning is a foundational process in textile manufacturing, playing a critical role in the market. The process involves converting raw fibers into yarn, which is essential for further textile production processes like weaving and knitting. Indonesia benefits from a strong supply of natural fibers such as cotton and rayon, often imported and blended with synthetic fibers to increase versatility. Spinning mills across Java and Sumatra support the country's large-scale textile production by ensuring a consistent yarn supply. As the first value-adding step in the textile chain, spinning also supports upstream industries and contributes significantly to employment. Investment in modern spinning technologies is helping Indonesia stay competitive in the global market by improving efficiency and output quality.
Weaving holds substantial importance in the market as it produces woven fabrics used in apparel, home textiles, and industrial applications. The country's weaving sector is diverse, ranging from traditional handwoven techniques like ikat and songket to modern mechanized looms. The presence of major industrial weaving centers in West Java and Central Java produces high volumes of fabrics for export and domestic use. Weaving adds economic value and reflects Indonesia's deep-rooted cultural heritage in textiles. The integration of advanced weaving machinery allows for mass production with consistent quality. This sector supports downstream industries and enhances Indonesia's positioning in the international textile supply chain.
Knitting is an increasingly vital segment of the market, especially in producing fabrics for casualwear, sportswear, and undergarments. With growing global demand for stretchy, breathable textiles, knitted fabric production has expanded significantly in areas like Bandung and Tangerang. Unlike weaving, knitting offers flexibility, comfort, and faster production cycles, making it attractive for fashion-forward markets. The rise of knitwear manufacturing supports the country's shift toward value-added products in its textile exports. It also drives innovation in fabric design and functional textiles. As the country enhances its infrastructure and machinery for circular and flatbed knitting, knitting continues to grow as a competitive edge in both domestic and international markets.
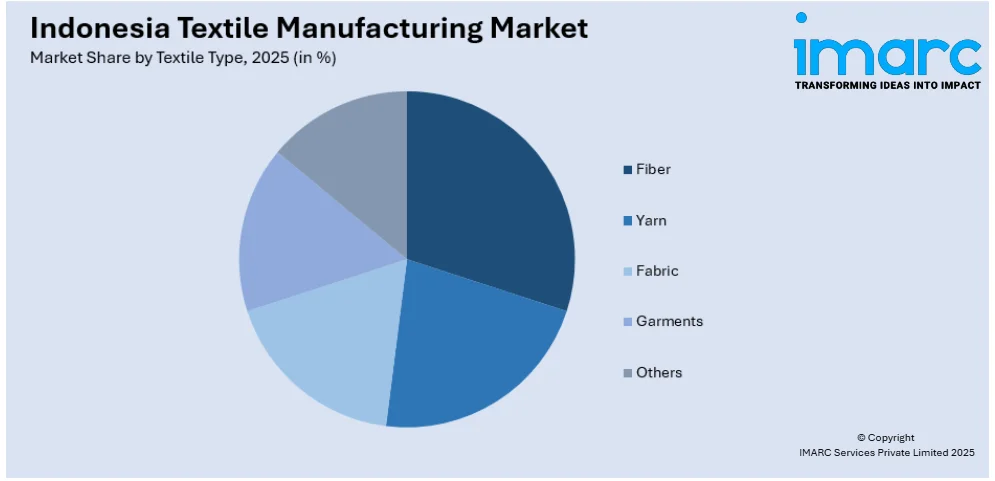
Analysis by Textile Type:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Fiber
- Yarn
- Fabric
- Garments
- Others
Fiber serves as the fundamental raw material in the market, forming the base for all downstream textile processes. Indonesia utilizes both natural fibers, like cotton and rayon, and synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon. While cotton is often imported, the country is one of the world's largest producers of viscose rayon, thanks to abundant forest resources. The fiber sector supports upstream integration and allows flexibility in producing a wide range of textile products. Investments in sustainable fiber production, such as eco-friendly viscose, position Indonesia as a responsible sourcing destination. The quality and availability of fiber significantly impact yarn and fabric output, making it a vital component of Indonesia's textile competitiveness.
Yarn represents a critical intermediary product in the country's textile value chain, linking raw fibers with finished fabrics. The spinning industry transforms various fibers into yarns of different thicknesses, textures, and strengths to meet the diverse needs of the weaving and knitting sectors. Indonesia's yarn production is robust, supported by both domestic and imported fiber inputs, and includes both natural and synthetic variants. Yarn is not only used domestically but also exported, especially to countries with large textile manufacturing bases. The strength of the yarn sector ensures supply chain efficiency, supports job creation, and enables Indonesia to cater to global demands for specific textile types.
Fabric is the most visible and value-added textile type in the market, produced through weaving, knitting, or non-woven processes. Indonesian fabrics cater to various industries, from fashion and upholstery to technical textiles. Traditional fabrics like batik, ikat, and songket highlight the cultural dimension, while industrial fabric production meets export demand. Fabric production integrates upstream (fiber and yarn) and downstream (garment) sectors, making it central to the overall textile ecosystem. With improved dyeing, finishing, and printing capabilities, the versatility and scalability of fabric production underscores the country's ambition to move beyond raw material exports toward more profitable, finished textile goods.
Analysis by Equipment and Machinery:
- Simple Machines
- Automated Machines
- Console/Assembly Line Installations
Simple machines are an important component of small-scale and traditional textile manufacturing in Indonesia, especially in rural and cottage industries. Handlooms, spinning wheels, and manually operated dyeing equipment are still utilized in the production of heritage textiles. This equipment is crucial for maintaining cultural heritage, sustaining artisan communities, and facilitating handmade textile exports. While less productive than contemporary machinery, basic machines involve lower capital outlays and are more within reach of small enterprises. They contribute to maintaining local economies and provide jobs in areas where industrial infrastructure is not well developed. Their function in specialty markets and high-value handmade products provides support for market growth.
Automated machines play a vital role in the market, enhancing productivity, quality, and consistency. Machinery like computer looms, spinning frames, and automatic knitting machines makes mass production for both the domestic and export markets possible. These machines minimize the need for human labor, decrease the cost of production in the long run, and provide consistency in fabric and garment production. Automation helps Indonesian producers achieve international specifications and meet supply requirements with quicker turnaround times. With the modernization of the textile sector in Indonesia, there is a rising investment in automation, aided by state and private investments. Adoption of automated systems fortifies Indonesia's position as an efficient, effective, and innovative textile player on the world stage.
Console and assembly line installations represent the highest level of industrial sophistication in the industry, particularly garment manufacturing and composite textile mills. These systems automate the whole production process, cutting and sewing, finishing and packaging, via centralized controls and synchronized workflows. It is utilized extensively in big factories across areas such as West Java and Central Java, where it maximizes efficiency, reduces human error, and enables real-time monitoring of output and quality. These installations enable the mass production of standardized clothing for global brands and fast-fashion consumers. Their incorporation with digital systems and AI-based analysis further boosts competitiveness, making Indonesia a leading player in high-volume, technology-driven textile manufacturing.
Regional Analysis:
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
- Others
Java is the country's textile production base, housing the greatest majority of production units, labor, and infrastructure. Provinces such as West Java (Bandung and Bekasi) and Central Java (Semarang and Solo) are textile centers with extensive operations ranging from spinning and weaving to garmenting. Java enjoys a qualified workforce, well-developed industrial estates, and access to key ports, positioning it well for both local distribution and exports. The areas' widespread road networks and availability of energy resources also further boost the efficiency of operation. Java facilitates innovation and higher-value production, hosts foreign investment, thereby contributing to the Indonesia textile manufacturing market growth.
Sumatra is an important contributor to textile production in the country, especially in its upstream capacity as a fiber and raw material processor. The region is host to large rayon and pulp manufacturers, complementing the manufacture of viscose fibers utilized in spinning and fabric production. Although less industrialized than Java, Sumatra's areas, such as North Sumatra and Riau, are emerging textile hubs, assisted by their natural resource endowment and increasing infrastructure. Its proximity to the Strait of Malacca makes it convenient for raw material trade and export logistics. Sumatra is significant in terms of resource availability and nascent industrial growth, which supplements the central manufacturing activity in Java and facilitates Indonesia's vision to establish a more geographically diversified textile industry.
The contribution of Kalimantan to the market is limited at present but increasing, mainly due to its potential future growth and supporting resources. Recognized for its enormous territory and proximity to natural resources, Kalimantan is considered a location for new textile and garment plants, particularly in light of the decentralization of industry from Java. With the establishment of the new capital city, Nusantara, infrastructure development is anticipated to draw textile investment. Kalimantan can sustain the industry through energy generation and environmental activities, including biomass and renewable energy sources for textile factories. Not yet a major textile center, Kalimantan is strategically positioned for long-term market diversification.
Sulawesi has a small but growing role in the industry, mostly in traditional textiles and new manufacturing areas. Regions like South Sulawesi, home to the famed silk production in Wajo and Sengkang, contribute to Indonesia's heritage textile exports. The local silk industry supports artisan livelihoods and cultural preservation. At the same time, industrial development in cities like Makassar is encouraging investment in garment and textile production facilities. Sulawesi's position along key maritime routes and its growing infrastructure network offers strategic advantages for regional trade. While still developing, Sulawesi's dual role in cultural textile production and industrial expansion adds depth to Indonesia's diversified textile economy.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the market is characterized by a combination of established players and modernizing companies, all competing to gain share in a dynamic marketplace. Domestic manufacturers enjoy the advantages of government assistance but are under growing pressure to modernize processes to remain competitive. There is fierce competition in segments like spinning, weaving, dyeing, and garment manufacturing. A lot of companies are currently concentrating on vertical integration to make operations leaner and more efficient. Sustainability is also becoming one of the competitive drivers, with increased demand for environmentally friendly and ethically sourced textiles. Export-oriented producers are increasingly investing in technology and compliance to qualify for international standards. Concurrently, home-market-oriented companies are taking advantage of the country's sizeable population and growing middle class to fuel sales. According to the Indonesia textile manufacturing market forecast, sustained growth in domestic demand is expected to propel exports and attract additional investment in the industry.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Indonesia textile manufacturing market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- April 2025: PT Xinfung Industry Indonesia, a subsidiary of China's Jiangsu Xinfang Technology Group, commenced the construction of a USD 30 million textile manufacturing facility in Subang Smartpolitan. The plant will produce dyed fibers, tops, and luxury fancy yarns from natural and sustainable fibers, aiming to serve Southeast Asian markets.
- March 2025: Nanshan Fashion announced that it would be establishing a new apparel production facility in Indonesia's Galang Batang SEZ, aiming to produce 160,000 units annually of suits, workwear, and shirts. This expansion leverages Nanshan's vertically integrated textile supply chain and targets markets in the US, EU, Japan, and Russia, enhancing global competitiveness and supply chain efficiency.
- April 2024: DBS Bank Indonesia partnered with PT Indo-Rama Synthetics Tbk to advance sustainability in textile manufacturing. The collaboration includes a USD 10 million credit facility to connect Indorama's Purwakarta factory to the national grid, transitioning from coal-based power and enhancing energy efficiency. Additionally, a USD 20 million Sustainability-Linked Trade Finance facility ties financing terms to ESG targets, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and water usage. These initiatives aim to decarbonize operations and promote sustainable practices in the textile industry.
- September 2023: The Lenzing Group revealed intentions to expand its manufacturing of premium, ethical viscose fibers in Asia-Pacific for its nonwoven Veocel and textile Lenzing Ecovero brands. The viscose fibers, which are manufactured at Lenzing's Purwakarta facility in Indonesia and have EU Ecolabel certification, will assist Lenzing in fulfilling the rising demand from eco-aware customers for textiles and nonwoven goods that have a smaller environmental impact.
Indonesia Textile Manufacturing Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Process Types Covered | Spinning, Weaving, Knitting, Finishing, Others |
| Textile Types Covered | Fiber, Yarn, Fabric, Garments, Others |
| Equipment and Machineries Covered | Simple Machines, Automated Machines, Console/Assembly Line Installations |
| Regions Covered | Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Indonesia textile manufacturing market from 2020-2034.
- The Indonesia textile manufacturing market research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the regional market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Indonesia textile manufacturing industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The textile manufacturing market in Indonesia was valued at USD 42.0 Billion in 2025.
The growth of the Indonesia textile manufacturing market is driven by rising domestic and global demand, government support through favorable policies, expanding e-commerce, and increasing foreign investment. Additionally, technological advancements, improved infrastructure, and Indonesia’s participation in trade agreements enhance export opportunities, making the country a competitive player in the global textile industry.
The textile manufacturing market in Indonesia is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 4.84% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 64.2 Billion by 2034.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












