How AI is Impacting Gonorrhea Risk Assessment, Prevention & Early Diagnosis?
.webp)
A Global Public Health Challenge of Growing Urgency:
Gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, is a major public health issue globally. Reports show that over one million new cases of curable STIs are contracted every day by individuals aged 15 to 49 years, with the majority being asymptomatic. Specifically, gonorrhea leads to approximately 82 Million new cases annually, further emphasizing the prevalence of the disease and the complexity of trying to contain its spread. While in some instances gonorrhea presents with minimal symptoms, infections, if not treated, lead to severe consequences, including infertility in both men and women, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease that is chronic, and transmission of HIV infection. The impact of gonorrhea extends beyond bodily health to social well-being, with related additional healthcare expenditure. This is a very notable cost burden in low- and middle-income countries.
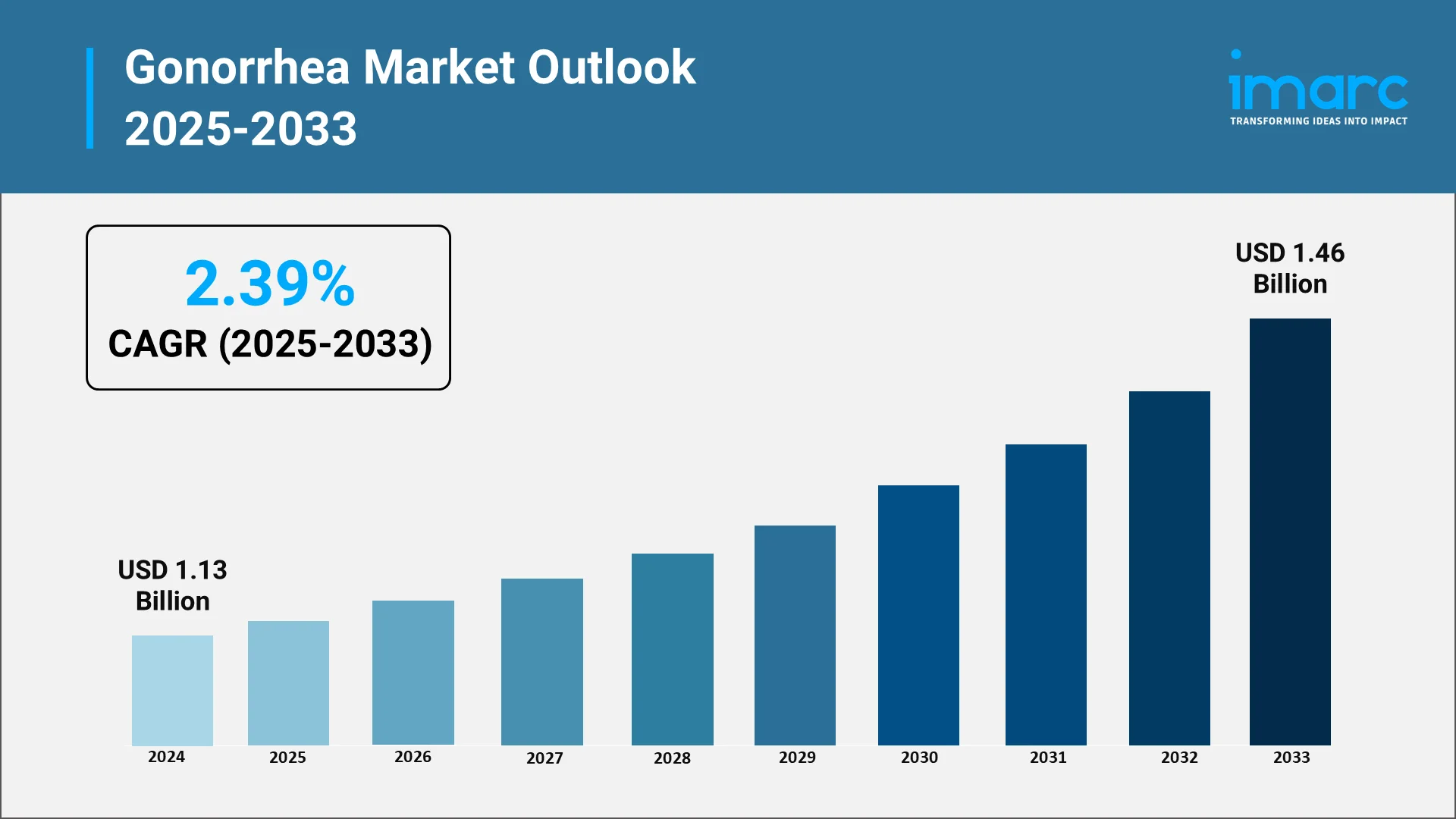
The global gonorrhea treatment market was valued at USD 1.13 Billion in 2024 across the top seven markets (United States, EU4, UK, and Japan). It is set to expand as healthcare professionals seek more sophisticated diagnostic and treatment options to meet the increasing problem of gonorrhea. Significantly, artificial intelligence (AI)-based solutions are not only as enhancements to current processes but also as leading instruments that are revolutionizing the future of preventing as well as treating gonorrhea. Artificial intelligence is utilized to examine large sets of data from clinical trials, medical records, and epidemiologic data to determine emerging trends and risk factors of the disease. AI algorithms can forecast impending outbreaks, enabling healthcare professionals to apply focused interventions in a timely manner. AI's ability to revolutionize risk evaluation, early diagnosis, and treatment approaches is an important opportunity in the battle against this chronic infection.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
The Dual Crisis: Rising Cases and Antibiotic Resistance
While awareness campaigns and sexual health programs have expanded in recent years, gonorrhea case numbers continue to climb. This trend is complicated by the bacterium’s exceptional ability to develop resistance against widely used antibiotics, including penicillin, tetracyclines, and fluoroquinolones. The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified gonorrhea as a ‘high-priority pathogen’—a designation reserved for infectious agents that pose severe risks to global health security due to their resistance profiles.
The challenge lies in gonorrhea’s genetic adaptability. Even small-scale misuse of antibiotics—whether through incorrect dosing, incomplete treatment courses, or self-medication—can accelerate resistance development. This creates a vicious cycle where ineffective treatment not only prolongs infection but also promotes the spread of resistant strains. Artificial intelligence algorithms match patient-level bacterial resistance information with international resistance patterns, assisting clinicians in writing down antibiotics most likely to be effective. This not only enhances patient treatment but also decreases the potential for prescribing ineffective medications, slowing down the development of resistance.
AI is providing a critical countermeasure through:
- Genomic Surveillance: AI-based systems scan N. gonorrhoeae genome sequences from around the world, identifying mutations that are drug-resistant.
- Real-Time Tracking: Resistance information is overlaid on global patterns of incidence, allowing for localized containment before resistance is fixed in an area.
- Policy Guidance: AI insights are guiding revisions to treatment guidelines and stimulating investment in future-proofed antibiotics.
Notably, in September 2024, researchers reported the identification of novel antimicrobial compounds targeting the Neisseria gonorrhoeae enzymes L,D-carboxypeptidase LdcA and lytic transglycosylase LtgD through the application of AtomNet virtual high-throughput screening and comprehensive computational modeling. The leading compounds exhibited significant inhibitory activity against gonococcal strains, demonstrating specificity and negligible cytotoxicity to human epithelial cells. These results represent a promising advancement in the development of targeted therapeutics to combat the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea.
AI in Risk Prediction: Targeting High-Risk Populations with Precision
AI's ability to predict and target high-risk population is enhancing efforts to prevent gonorrhea transmission. By analyzing vast amounts of demographic, behavioral, and clinical data, AI models can identify individuals most likely to contract the disease. Moreover, with patterns in patient data, AI can foresee likely clusters of outbreaks and facilitate the rapid use of mobile clinics, targeted educational programs, and prevention campaigns. AI is increasingly being used to integrate data from social media, electronic health records (EHR), and mobile health applications to provide real-time risk assessments. Machine learning algorithms assist in classifying people according to different characteristics like sexual practices, age, geographical location, and past STI history.
Notably, in January 2024, scientists reported on the MySTIRisk AI-powered risk estimation tool, which uses machine learning algorithms to well identify people at high risk for HIV and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) based on extensive clinical data from the period between 2008 and 2022. The research set optimal risk score cut points that showed robust sensitivity and specificity for the identification of high-risk groups, allowing targeted screening and prevention. The high-risk populations identified with such thresholds represented 78% of syphilis, 78% of gonorrhea, and 69% of chlamydia infections, validating the increased public health interventions with precision risk stratification. These predictive models facilitate health practitioners to institute precision public health measures, including targeted testing, campaigns for health education, and preventive healthcare, specifically for high-risk populations.
Early Diagnosis Through AI-Driven Tools: Enhancing Detection Accuracy
Early diagnosis of gonorrhea is critical to preventing complications and controlling the spread of infection. AI-enhanced equipment is being used in laboratories and point-of-care tools to provide quicker, more precise diagnostics than standard culture procedures. Such equipment can detect infection patterns from microscopic images or test results within seconds, minimizing the time window between diagnosis and initiation of treatment. AI is playing a pivotal role in enhancing diagnostic capabilities for gonorrhea by improving both speed and accuracy. AI-powered tools are now able to analyze laboratory test results, such as urine samples or swabs from infected areas, using deep learning algorithms to automatically identify Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria in microscopic images. This approach provides faster and more reliable results than traditional culture methods. Moreover, AI can integrate various diagnostic techniques like PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and molecular testing, allowing for the detection of gonorrhea at its earliest stages, even before symptoms become visible. This increased sensitivity of AI-driven diagnostic tools reduces the likelihood of false negatives, ensuring patients receive timely treatment and preventing further complications and transmission.
A recent systematic review and meta-analysis, published in August 2025, evaluated the effectiveness of deep learning algorithms in detecting sexually transmitted infections (STIs) from skin lesions. The analysis, which examined 101 studies, found that deep learning models exhibited high sensitivity and specificity, with mpox achieving 97% sensitivity and 99% specificity. These findings reinforce the growing potential of AI in the early detection of STIs, including gonorrhea, highlighting its ability to improve diagnostic accuracy and streamline healthcare responses. With such capabilities, AI is positioned to significantly enhance the early detection of gonorrhea and other STIs, contributing to more efficient and effective healthcare practices.
AI in Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring: Real-Time Surveillance
AI is becoming a vital tool in the fight against antimicrobial resistance (AMR), a growing concern in gonorrhea treatment. AI-based systems monitor the resistance patterns of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, enabling real-time surveillance of antibiotic efficacy. By integrating data from diagnostic tests, medical prescriptions, and genomic sequencing, AI tools can track resistance trends across various regions. This real-time data provides invaluable insights into which antibiotics remain effective and where new resistance patterns are emerging.
Moreover, AI helps researchers develop new treatment strategies by analyzing large datasets to identify potential new antibiotics or alternative therapies. A recent study, published in 2025, addresses the growing challenge of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The study developed a hybrid machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) framework to predict resistance profiles of N. gonorrhoeae isolates, achieving significant improvements in prediction accuracy over traditional methods. The CatBoost ML model, combined with SHAP analysis, successfully identified key resistance markers, offering a promising tool for enhancing real-time AMR detection and supporting antibiotic stewardship programs.
Public Health and Commercial Opportunities
AI is unlocking transformative opportunities in public health for gonorrhea prevention and treatment. By integrating AI into health surveillance systems, public health agencies can enhance their ability to detect and respond to gonorrhea outbreaks rapidly. AI’s predictive capabilities also support targeted prevention efforts, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to populations most at risk. Moreover, AI helps streamline contact tracing and facilitates personalized treatment plans by analyzing patient data in real time. On a broader scale, AI-driven tools help governments and organizations monitor trends, track resistance patterns, and forecast future outbreaks, making it a critical tool for global health organizations in their efforts to combat gonorrhea.
AI offers substantial commercial potential in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment optimization of gonorrhea. Advanced algorithms facilitate rapid detection from clinical images or molecular data, improving diagnostic precision and reducing laboratory costs. Predictive analytics enable the development of targeted prevention strategies, while AI-driven monitoring of drug resistance enhances therapeutic decision-making. These capabilities pave the way for cost-effective healthcare solutions, digital diagnostic tools, and global telemedicine integration. Key developments in the AI-driven gonorrhea treatment include:
- AI-powered diagnostic devices for faster, more accurate gonorrhea testing, improving detection efficiency and accuracy.
- AI-based platforms for monitoring antimicrobial resistance, providing valuable data to pharmaceutical companies for better drug development.
- Mobile apps for personalized risk assessment and prevention strategies, offering tailored guidance to individuals based on real-time data.
- AI-based decision-support tools for clinicians managing gonorrhea cases, aiding in better treatment planning and therapeutic decisions.
- AI-driven treatment planning systems that optimize drug efficacy, improving patient outcomes and overall healthcare effectiveness.
Conclusion: AI as a Frontline Force in Gonorrhea Control
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping the landscape of gonorrhea management, offering a powerful tool to combat the rising cases and the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance. From enhancing early diagnosis to providing real-time surveillance and predictive insights, AI-driven solutions enable healthcare providers to act swiftly and more accurately, significantly improving patient outcomes. The ability of AI to optimize antibiotic use, identify resistance patterns, and ensure prompt treatment is crucial in addressing the global challenge of gonorrhea. As AI technologies continue to evolve, they will remain at the forefront of strategies aimed at reducing the prevalence of gonorrhea, improving treatment efficacy, and combating antimicrobial resistance on a global scale.
- Competitive Imperative: Healthcare providers and organizations adopting AI technologies in gonorrhea management are gaining enhanced diagnostic capabilities, improved treatment precision, and better patient outcomes.
- Future-Ready Public Health Systems: AI-powered tools will drive innovation in the prevention, detection, and treatment of gonorrhea, helping to safeguard public health in the face of rising antimicrobial resistance.
- Path Forward: With continuous advancements in AI, ongoing research, and increased collaboration between public and private sectors, AI will play a pivotal role in transforming not only the treatment of gonorrhea but also the broader landscape of infectious disease management.
Empowering Stakeholders: IMARC’s Strategic Insights into the AI-Driven Gonorrhea Market
As AI continues to transform the gonorrhea treatment and prevention landscape, IMARC Group provides the insights needed for stakeholders to make informed decisions. Through comprehensive market analysis, IMARC offers in-depth understanding of key AI-driven trends shaping the future of gonorrhea management.
How IMARC Supports Industry Players:
- AI Adoption Monitoring: Tracks the integration of AI technologies in the treatment and diagnosis of gonorrhea, highlighting advancements in antimicrobial resistance (AMR) monitoring and risk prediction tools.
- Vendor and Startup Intelligence: Identifies key AI-powered vendors and startups in the gonorrhea space, facilitating strategic partnerships and collaborations.
- Policy Landscape Mapping: Assesses evolving regulatory frameworks surrounding AI technologies in healthcare, offering guidance on compliance and industry standards.
- Investment Insights: Highlights high-growth segments, funding trends, and potential investment opportunities within AI-driven solutions for gonorrhea treatment and prevention.
- Forecast and Strategy: Delivers granular forecasts by region, treatment approach, and AI technology, helping businesses and public health organizations navigate emerging opportunities.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










