Big Plans for Urea: Mexico Targets Tripling Fertilizer Production
_11zon.webp)
What is Urea?
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with the formula CO(NH2)2.
Key Applications Across Industries:
It is a highly versatile and widely used chemical, primarily known for its role in agriculture as a nitrogen fertilizer. Urea is available in various grades, including fertilizer grade, feed grade, and technical grade, and is used in a wide range of applications, such as nitrogenous fertilizers, stabilizing agents, keratolytic, and resins, among others. Key industries that utilize urea include agriculture, chemicals, automotive, and medical sectors.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
According to recent findings by IMARC Group, the global urea market reached a value of USD 52.7 Billion in 2024. Looking ahead, IMARC Group expects the market to grow to USD 60.2 Billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.5% during 2025-2033. Several factors are driving this growth, including the increasing demand for nitrogen-based fertilizers in India, ongoing advancements in urea production technology, the rising need for higher crop yields to meet growing food demand, and favourable government policies.
Mexico, a major global producer, and exporter of agricultural products, plays a significant role in the world’s agricultural exports. The country’s extensive agricultural activities, coupled with the need to increase crop yields, are fueling demand for urea. Mexican farmers rely on nitrogenous fertilizers like urea to boost the yields of crops such as wheat, canola, and corn. However, Mexico has experienced fertilizer shortages due to adverse weather conditions, supply chain disruptions, and rising energy and transportation costs, which have driven up the prices of ammonia and urea. In 2021, Mexico imported approximately 62% of its fertilizer needs.
In response to these challenges, the federal government announced plans in May 2022 to triple fertilizer production to support local farmers and curb consumer price inflation, with the aim of achieving fertilizer self-sufficiency by 2024. As part of this initiative, the government unveiled a US$ 500 million investment plan to reactivate national fertilizer production. Ammonia and urea production plants in Veracruz, Michoacán, and Baja California Sur will be revitalized to ensure a steady supply of fertilizer to small-scale farmers. With this investment, the Mexican government expects domestic production to reach 2,500 tons of urea per day. In addition to government efforts, several domestic and international companies have invested in fertilizer production in Mexico, further driving the growth of the urea market in the region, given its critical role as a raw material in fertilizer production.
Case Study on Cost Model of Urea:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a large-scale urea manufacturing plant in Mexico.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a detailed financial model for the setup and operation of the plant, which is planned to have an annual production capacity of 2,170 tons.
Manufacturing Process: The urea manufacturing process primarily involves the reaction between ammonia and carbon dioxide to produce urea and water. This process occurs through the Bosch-Meiser process, which includes two key steps: the formation of ammonium carbamate and its subsequent dehydration to urea. In the first step, liquid ammonia and gaseous carbon dioxide are reacted under high pressure (140-250 bar) and elevated temperatures (170-210°C) in a reactor, forming ammonium carbamate. The carbamate is then dehydrated to urea in a second reactor. Afterward, the urea solution is concentrated by evaporation and crystallized to form solid urea. The unreacted ammonia and carbon dioxide are recycled to minimize waste and improve process efficiency.
_11zon.webp)
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Mass Balance and Raw Material Required: The major raw materials used in a urea manufacturing plant are water, ammonia, and carbon dioxide. For a plant producing 1 ton of urea, approximately 1.25 tons of water, 0.58 ton of ammonia, and 0.75 ton of carbon-dioxide is required.
List of Machinery:
The following equipment was required for the proposed plant:
- Ammonia Reactor
- Ammonia Converter
- Ammonia Condenser
- Ammonia Refrigeration System
- CO2 Compressor
- CO2 Absorber
- CO2 Scrubber
- Urea Reactor
- Urea Condenser
- Urea Stripper
- Urea Granulator
- High-Pressure Steam Generator
- High-Pressure Pumps
- High-Pressure Heat Exchangers
- Decomposer
- Flash Drums
- Evaporators
- Vacuum Pumps
- Condensers
- Granulator
- Drying Drum
- Cooling Drum
- Screening Machine
- Cyclones
- Bag Filters
- Storage Silos
- Bagging Machines
- Boiler
- Cooling Water System
- Instrumentation and Control Systems (PLC/DCS)
- Waste Heat Recovery Systems
- Ammonia Storage Tanks
- Air Compressors
- Nitrogen Generation Plant
- Installation, Piping, Instrumentation and Control - 40% of Equipment Cost
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
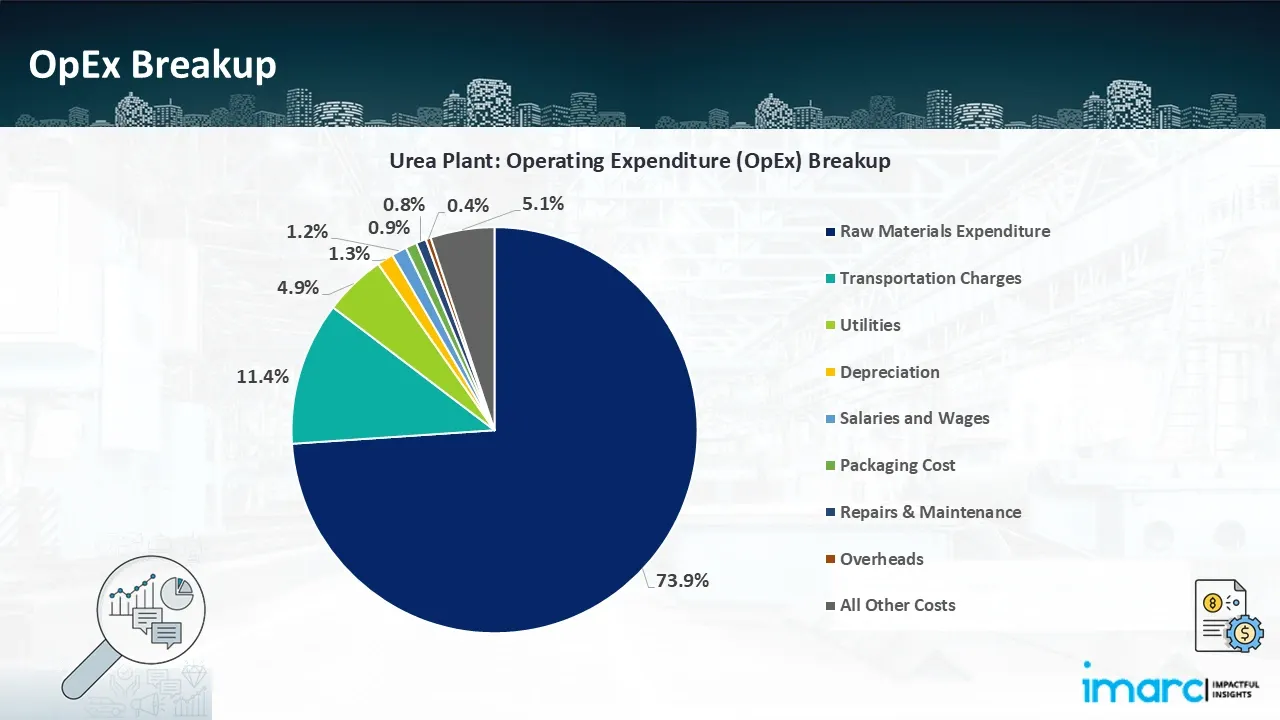
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth.
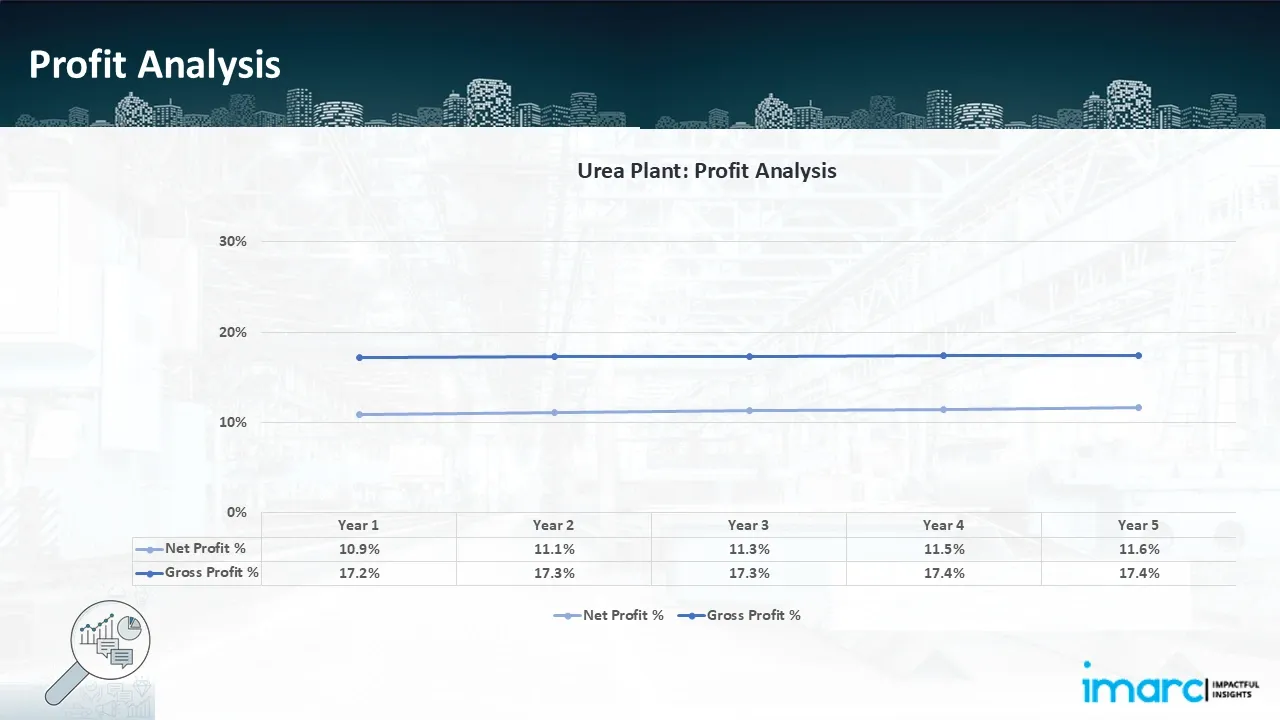
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: The proposed urea plant, with an annual capacity of 2,170 tons of urea, achieved an impressive revenue of US$ 170.8 million in its first year. We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins improve from 17.2% to 17.4%, and net profit rises from 10.9% to 11.6%, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the urea production plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of producing 2,170 tons urea annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights for strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In July 2025, PEMEX starts building the fertiliser factory in Poza Rica. According to PEMEX, Mexico's peak yearly urea demand is approximately 150,000 metric tonnes, which the new facility will supply.
- In August 2024, Casale entered into a contract with Duro Felguera SA, a subsidiary of Mota-Engil, to deliver licensing and preliminary engineering services for a new fertilizer complex for Pemex in Escolin, Veracruz, Mexico. This state-of-the-art facility will include a 1,200 MTD ammonia production plant using Casale's N-ELEVA™ process and a 2,125 MTD granular urea melting plant that features the advanced Split Flow Loop® and Casale Green Granulation® technologies.
- In July 2024, Mota-Engil entered into a partnership with PEMEX to construct a fertilizer plant in Veracruz, with an investment of US$1.2 billion. This initiative aims to enhance agricultural productivity in Mexico while reducing reliance on fertilizer imports. The project also emphasizes environmental benefits through the production of AdBlue. The agreement with PEMEX encompasses the engineering, construction, financing, and operation of a facility for the production of ammonia, urea, and AdBlue in Veracruz.
- In June 2023, the Indian firm Fermachem announced plans to invest US$ 1.5 billion in an ammonia and urea manufacturing facility in Armería, Colima, aimed at addressing Mexico's fertilizer needs. The plant is designed to produce 3,500 metric tons of ammonia daily, along with 2,860 metric tons of urea. Additionally, it will include a fertilizer granulation plant with a daily capacity of 2,860 metric tons.
- In April 2023, PEMEX announced plans to invest approximately US$ 750 million to enhance Mexico's fertilizer production facilities, aiming to support small farmers. This investment will be allocated to upgrading two urea plants and four ammonia plants across the country, as well as comprehensively refurbishing the fertilizer plant in Lazaro Cardenas and the phosphate rock mine in Baja California. Additionally, the company aims for Mexico to achieve self-sufficiency in fertilizer production.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104