E-Rickshaw Cost Model: Sustainable Rides, Smart Costs

What is E-Rickshaw?
An e-rickshaw is an ele]ctric-powered three-wheeled vehicle designed to transport passengers and goods over a short distance. It is an efficient, low-cost, eco-friendly substitute for conventional fuel-based auto-rickshaws and cycle rickshaws. The general specification of an e-rickshaw involves an electrical motor ranging from 650W to 1500W powered by a rechargeable lead-acid or lithium-ion battery, a lightweight chassis manufactured from mild steel or reinforced metal, and a simple drivetrain system.
Key Applications Across Industries:
These vehicles are designed for urban and semi-urban mobility, capable of carrying 3–4 passengers with a range of 80–120 km depending upon the battery configuration and load. An e-rickshaw is designed to be simple, cheap, and easy to maintain. Its electric powertrain gains the extra virtue of zero tailpipe emissions and a drastic reduction in noise pollution. E-rickshaws have become a common means of last-mile connectivity, plugging the gap in transportation from main transit points to residential or commercial areas. The vehicles can also be charged via conventional power outlets, which extends their feasibility to regions with limited infrastructure. Besides, Original Equipment Manufacturers are increasingly opting for lithium-ion batteries, regenerative braking, and modular components to give efficiency and durability. From a socio-economic point of view, e-rickshaws have become a source of sustainable livelihoods for low-income drivers owing to their low operational cost and minimum maintenance requirements. Again, they help in energy diversification by reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels. As nations transition toward clean mobility solutions, e-rickshaws are increasingly finding themselves at the forefront as an enabler of affordable, inclusive, and sustainable urban transportation in developing economies across Asia and Africa.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global e-rickshaw market reached a value of USD 3.01 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 12.83 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 17.5% during 2025-2033. The growth of the global e-rickshaw market is driven by a combination of key environmental, economic, regulatory, and technological factors. The drivers include the growing shift globally toward sustainable transportation, where governments and consumers start to give more importance to zero-emission mobility options. Due to their electric propulsion and compact design, e-rickshaws represent a practical solution for reducing urban air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Their deployment aligns with global climate commitments and national e-mobility policies that incentivize EV adoption through subsidies, tax benefits, and infrastructure support.
Another critical growth factor is economic affordability. With much lower operating and maintenance costs due to electricity instead of using expensive fuels such as petrol or CNG, e-rickshaws prove to be much more economical compared to conventional auto-rickshaws. This attracts small-scale drivers and fleet operators, making it more viable for income generation, especially in developing countries where populations are dense, and public transport has poor coverage. The pace of urbanization and growing need for connectivity to the last mile provide a more robust demand for compact, energy-efficient mobility solutions that can navigate congested streets of cities while maintaining operational affordability. Advances in the technological aspects of battery technology, electric drivetrain, and lightweight materials have further propelled market expansion. The shift from lead-acid to lithium-ion batteries further extends the range of the vehicle, reduces charging time, and enhances overall durability. At the same time, support from governments in favor of local manufacturing and the electrification of public transport-in countries like India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and African economies-is boosting production capacities and infrastructural development. Globally, the e-rickshaw market benefits from aligning with socio-environmental goals, economic inclusion, and smart city mobility frameworks that position it as a cornerstone for sustainable urban transportation in the coming decade.
Case Study on Cost Model of E-Rickshaw Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale e-rickshaw manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed e-rickshaw manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 15,000 units of e-rickshaw annually.
Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process of an e-rickshaw is a well-coordinated sequence of mechanical, electrical, and assembly operations that will result in safe, efficient, and durable vehicles for urban mobility. The production of an e-rickshaw starts with product design and engineering, where CAD design software is used to plan the chassis layout, body structure, and component integration. That stage aims at optimization in weight distribution, passenger capacity, and battery placement, which provides vehicle stability and energy efficiency. After the design is accomplished, the production shifts to the chassis fabrication stage, where mild steel or tubular frames are cut, bent, and welded using precision tools and jigs to form the skeletal structure of the vehicle. It is then coated with anti-rust paint or powder coating for better corrosion resistance. This is followed by the electrical integration stage, where the main units, comprising the electric motor, controller, wiring harness, battery pack, and throttle system, are fitted. The batteries can be lead-acid or lithium-ion-based on specific market requirements and the intended pricing. It is at this stage that drivetrain, suspension, and braking systems are fitted and aligned properly to provide efficiency and comfort. Putting up body panels, a roof, and a passenger cabin involves lighter materials such as fiberglass, sheet metal, or reinforced plastic. On-site assembly is followed by quality control tests for electrical safety, load capacity, brake efficiency, and road performance. Final inspections follow to ensure adherence to regulatory standards before painting, branding, and packaging the rickshaws for dispatch. This structured process ensures every e-rickshaw delivers reliability, energy efficiency, and long service life in urban and semi-urban transport environments.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for e-rickshaw manufacturing include:
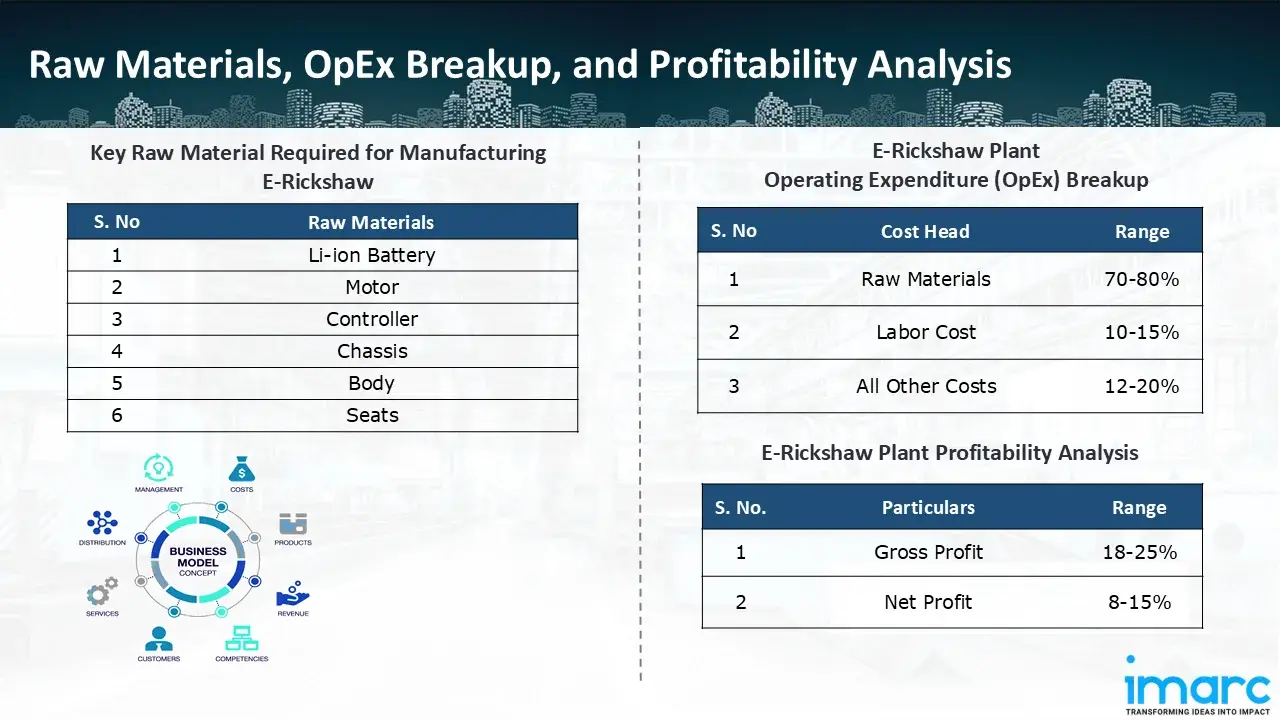
- Li-ion Battery
- Motor
- Controller
- Chassis
- Body
- Seats
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Chassis Fabrication
- Body Building
- Assembly Line
- Painting
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in e-rickshaw manufacturing plant ranges between 70-80%, labor cost ranges between 10% to 15%, and all other costs ranges between 12-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 18-25%, and net profit lie between the range of 8-15% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the e-rickshaw manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 15,000 units of e-rickshaw annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In August 2025, Zuperia Auto Pvt Ltd, earlier known under the Lohia brand, announced its foray into the electric L5 passenger vehicle category with the launch of its flagship Youdha EPOD, marking a strategic expansion beyond its core e-rickshaw business.
- In May 2025, Bajaj Auto Ltd. announced to launch an electric rickshaw under its recently unveiled brand, ‘GoGo’, by early July 2025. The action reflects the company's plan to take the lead in the expanding electric three-wheeler market in India.
- In May 2025, Terra Motors launched the Kyoro+ e-rickshaw in India, which can travel 200 kilometres. After the COVID-19 outbreak hindered exports to African countries like Ethiopia, Tanzania, and Nigeria, the corporation is concentrating on restoring such exports. Terra Motors claims to have sold more than 1,00,000 L3-category cars, mostly in East India, and it plans to grow.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104











