Fiber Optic Cable Cost Optimization: Sourcing, Labor and Logistics
_11zon.webp)
What is Fiber Optic Cable?
Fiber optic cables are high-tech communications cables that carry information like bursts of light along extremely thin glass or plastic strands, providing high-speed, high-bandwidth connectivity with little loss of signal.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Fiber optic cables make up the foundation of contemporary telecommunications, carrying internet, cloud computing, 5G networks, and smart infrastructure. Fiber optics have better speed, reliability, and immunity to electromagnetic interference compared to traditional copper cables. The market for single-mode fibers (long-distance networks) and multi-mode fibers (short-range use) serves sectors such as telecom, data centers, healthcare, and defense. With the growth in data consumption and digitization, fiber optic networks are essential for future technologies, supporting global demand.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global fiber optics market reached USD 6.6 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 14.7 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 9.2% during 2025-2033. The market for fiber optic cables is growing fast, thanks to some of the core factors. First, 5G network rollout necessitates high capacity backhaul infrastructure, with telecommunication operators making extensive investments in fiber rollout. Second, increasing internet penetration and cloud computing necessitate low-latency, scalable networks, prompting data centers and ISPs to deploy fiber optics.
Governments across the globe are financing national broadband plans (e.g., U.S. BEAD Program, EU Digital Decade) to close the digital divide, ramping up fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) initiatives. Furthermore, smart city growth and IoT implementation depend on secure fiber infrastructure for timely data transfer. Advances in technology, including bend-insensitive cables and miniaturized cabling options, improve performance and lower installation expenses. Asia-Pacific and African emerging markets are experiencing high-speed urbanization, fueling requirements for advanced telecom infrastructure. In the meantime, submarine cable initiatives sustain data traffic expansion across the world, with tech titans Google and Meta investing in intercontinental connections. Lastly, the transition to renewable energy and light cables is compatible with sustainability objectives, further fueling market growth. These factors guarantee long-term growth, with the market set to cater to the needs of an interconnected world.
Case Study on Cost Model of Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a large-scale fiber optic cable manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed fiber optic cable manufacturing plant in Tamil Nadu, India. This plant is designed to produce 90 km of fiber optic cable per day.
Manufacturing Process: Fiber optic cable manufacturing starts with high-purity silica sand, which is then melted in a furnace to form glass preforms - cylindrical rods doped with highly accurate elements to manage optical characteristics. The preforms are subjected to thermal annealing to remove stresses prior to being drawn into very thin fibers. In the drawing tower, the preform is heated to 2,000°C and pulled into hair-thin strands (125-250μm diameter) with laser-measured accuracy. Each fiber is immediately given a double-layer protective coating (usually UV-cured acrylate) for strength. Groups of coated fibers are subsequently assembled into cable cores, usually with an interior strength member (aramid yarn or steel wire) for structural integrity. The assembly is buffered (with moisture-proof gels) and jacketed (with materials such as PVC or LSZH for fire-resistance). In specialized applications, armored cables are given extra metal shielding. During production, automated equipment performs intensive testing - testing attenuation (signal loss), bandwidth capacity, and tensile strength. Final cables are subjected to environmental stress testing (temperature cycling, crush resistance) prior to being wound onto reels with RFID-tagged quality records. State-of-the-art facilities feature Industry 4.0 technologies such as AI-driven defect detection and robotized packaging for uniform quality in 5G backhaul, FTTH networks, and submarine cable systems. The whole process stresses precision cleanliness since even micron-level contaminants can compromise optical performance.
_11zon.webp)
Mass Balance and Raw Material Required: The primary raw materials used in the fiber optic cable manufacturing plant include optical fibre, buffer tubes, core mass, cladding mass, buffer coating mass, strength members mass, inner sheath mass and outer jacket mass.
For a plant producing 1 km of UNI-TUBE (24F Single Sheath - Micro Nylon Sheath - 2.5mm) cable, 0.11 ton of core, 0.43 tons of cladding, 0.44 tons of buffer coating, 27.35 tons of strength members, 3.36 tons of inner sheath and 8.35 tons of outer jacket is required.
Additionally, a plant producing 1 km of MULTI TUBE (12F - 96F Single Sheath - Micro Duct - 200 Um)12 (12F/Tube) cable requires 0.19 ton of optical fiber, 0.60 tons of buffer tubes, 0.10 tons of strength members, 0.20 tons of outer sheath and 0.10 tons of material.
_11zon.webp)
For a plant producing 1 km of MULTI TUBE (12F - 96F Single Sheath - Micro Duct - 200 Um) 96 (12F/Tube) cable, 0.22 ton of optical fiber, 0.55 tons of buffer tubes, 0.12 tons of strength members, 0.20 tons of outer sheath and 0.11 material (aramid yarns) is required.
For a plant producing 1 km of FLAT DROP (1F-2F FRP-Embedded) 2F 3.0 X 6.5 mm cable, 0.13 ton of core, 0.66 of cladding, 0.42 tons of buffer coating, 32.30 tons of strength members, 3.30 tons of inner sheath and 10.32 tons outer jacket is required.
_11zon.webp)
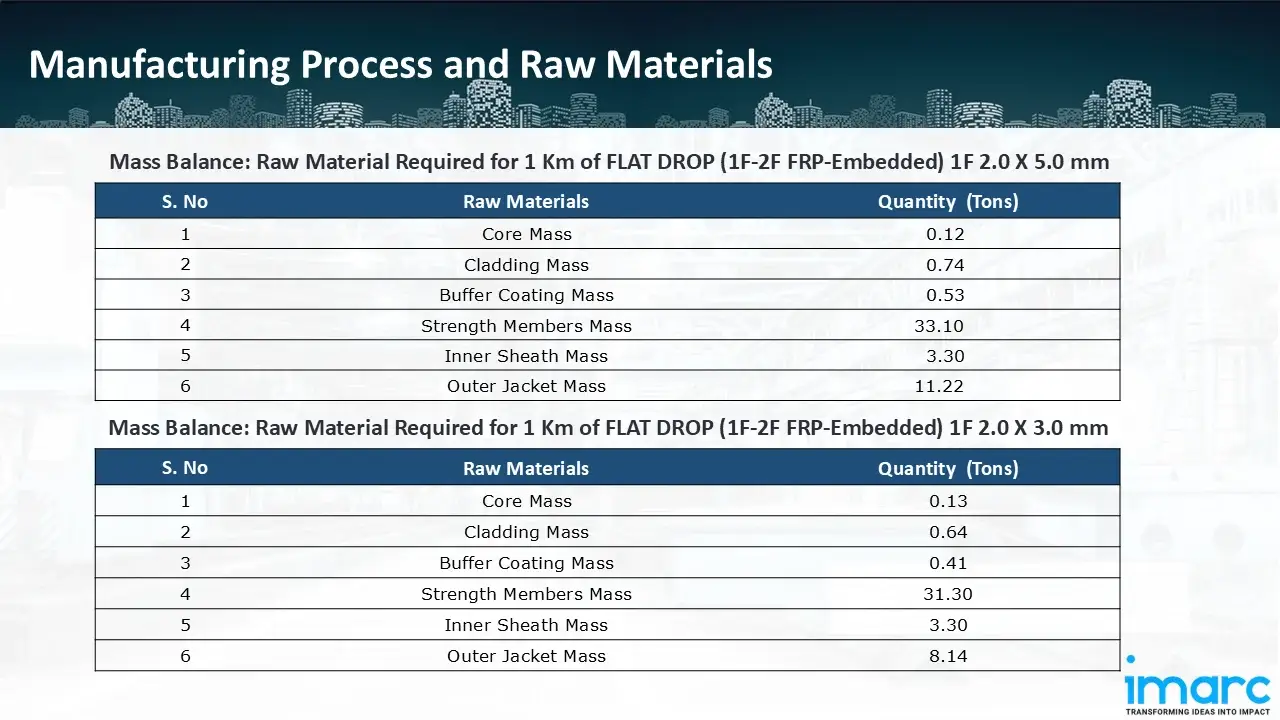
Similarly, for a plant producing 1 km of FLAT DROP (1F-2F FRP-Embedded) 1F 2.0 X 5.0 mm cable, 0.12 ton of core, 0.74 of cladding, 0.53 tons of buffer coating, 33.10 tons of strength members, 3.30 tons of inner sheath and 11.22 tons outer jacket is required.
For a plant producing 1 km of FLAT DROP (1F-2F FRP-Embedded) 1F 2.0 X 3.0 mm cable, 0.13 ton of core, 0.64 of cladding, 0.41 tons of buffer coating, 31.30 tons of strength members, 3.30 tons of inner sheath and 8.14 tons outer jacket is required.
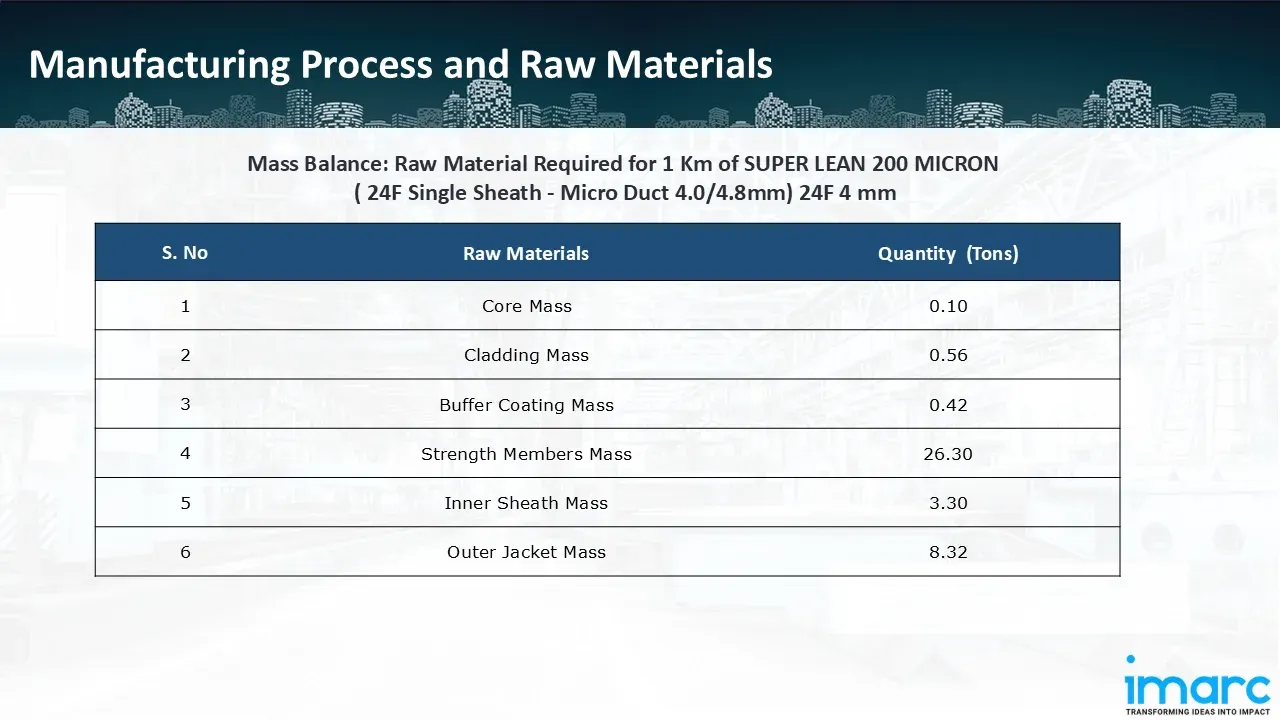
Furthermore, for a plant producing 1 km of SUPER LEAN 200 MICRON (24F Single Sheath - Micro Duct 4.0/4.8mm) 24F 4 mm cable, 0.10 ton of core, 0.56 of cladding, 0.42 tons of buffer coating, 26.30 tons of strength members, 3.30 tons of inner sheath and 8.32 tons outer jacket is required.
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Investment (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
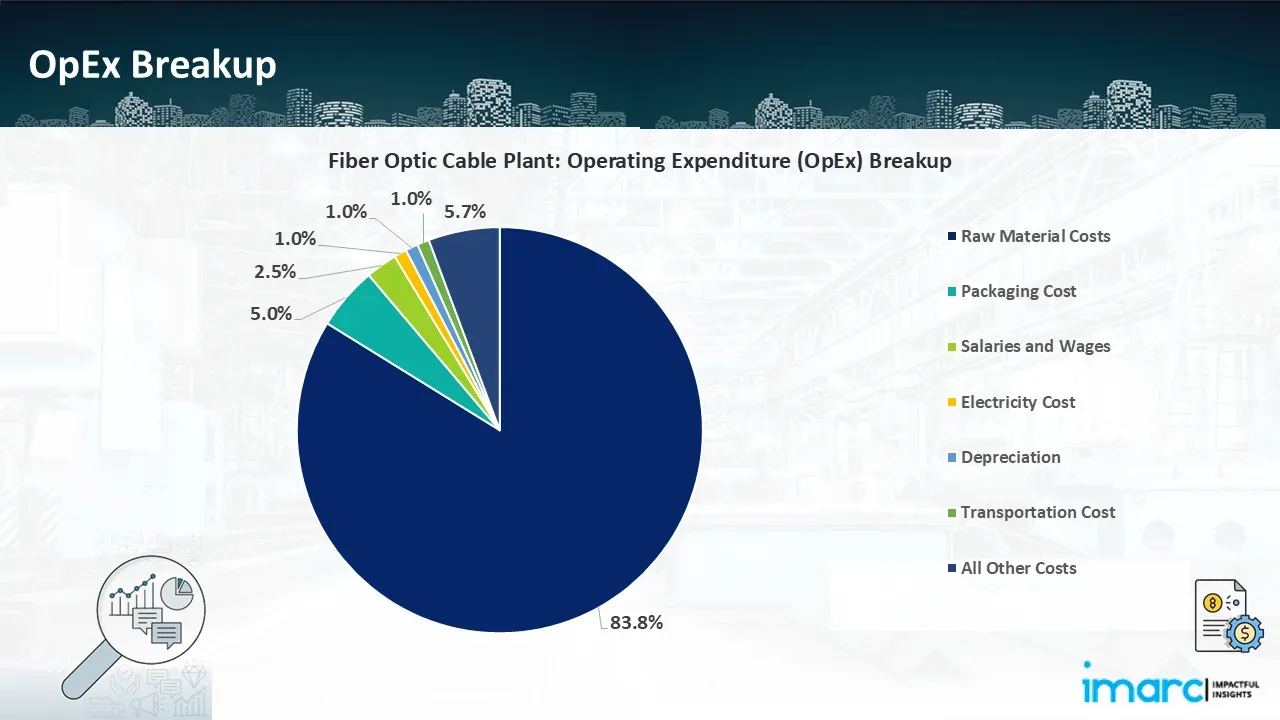
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth.
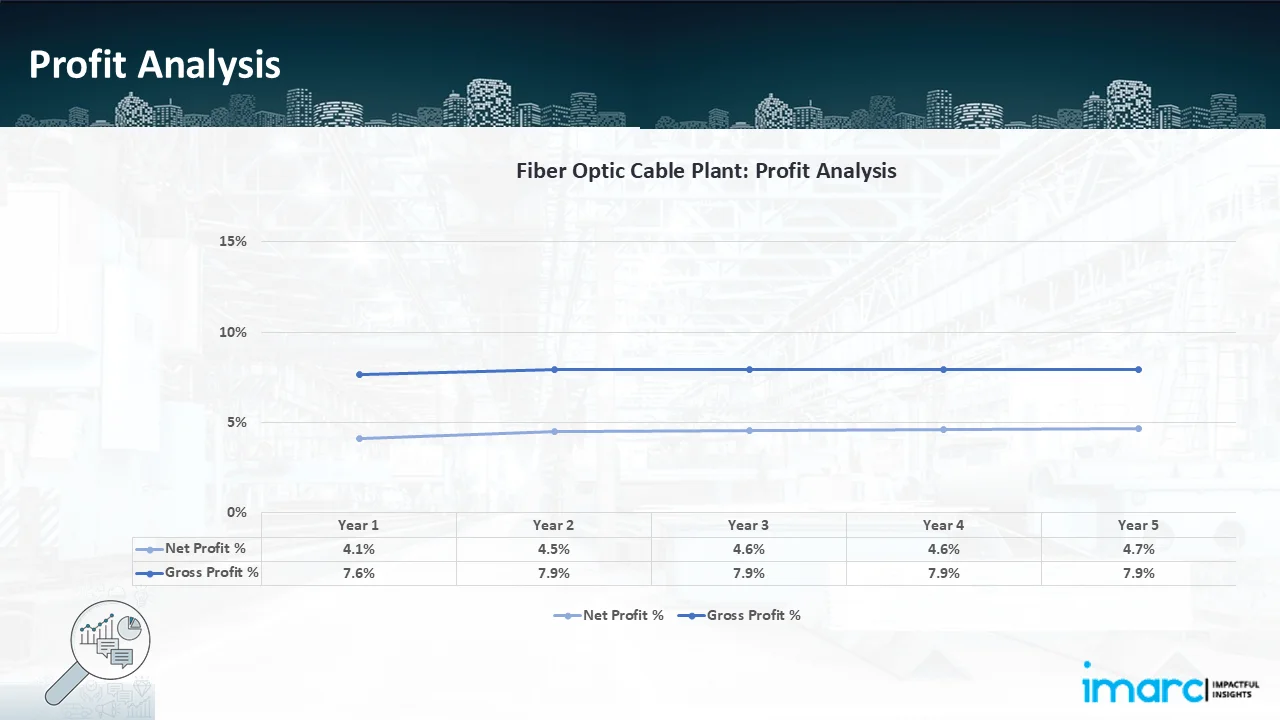
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: The proposed fiber optic cable plant, with a capacity of 90 km of fiber optic cable per day, achieved an impressive revenue of US$ 7.6 million in its first year. We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins improve from 7.6% to 7.9% by year 5, and net profit rises from 4.1% to 4.7%, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the fiber optic cable manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of producing 90 km of fiber optic cable per day, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In June 2025, Google and Chile have partnered to provide a quicker alternative to current US connections by installing the first submarine fibre optic cable connecting South America, Asia, and Oceania by 2027. According to reports, the Chilean government has contributed USD 25 million to the 14,800-kilometer cable project known as "Humboldt," while Google has invested between USD 300 million and USD 550 million.
- In April 2025, Ducab Group launched a High Voltage (HV) fiber optic cable marking an important step in the company’s global expansion and sustainable innovation.
- In May 2024, STL, a provider of digital and optical solutions, recently declared that its US-made fibre optic cable products comply with the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act's (IIJA) "Build America, Buy America" (BABA) requirements.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104