Tire Economics: A Cost Modeling Framework for Manufacturing Efficiency

What is Tire?
A tire is a crucial component of a vehicle, serving as the outer covering of a wheel. Its main purposes are to support the vehicle's weight, provide traction for movement, and act as a flexible cushion that absorbs shocks from the road.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Usually composed of rubber, tires are strengthened with steel and cloth. Tires for cars, trucks, motorbikes, bicycles, and other vehicles have different designs and compositions depending on the vehicle type and its intended usage. To improve stability and grip, they have a tread pattern on the outside.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
According to an IMARC study, the global tire market reached USD 181.1 Billion in 2025. Looking ahead, the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4.33% from 2026 to 2034, reaching a projected size of USD 272.6 Billion by 2034.
The market for tires is influenced by numerous important aspects. Growth in the automotive sector, which includes both passenger and commercial vehicles, directly increases demand for tires. The market is expanding even faster due to rising car ownership rates, especially in emerging markets. Tire technology has advanced to include reduced rolling resistance and smart tires as a result of the growing demand for long-lasting and fuel-efficient tires. Additionally, increased car fleets and safety regulations are driving growth in the replacement tire industry. Increased vehicle usage leads to increased tire wear and replacement requirements, which are exacerbated by urbanisation and infrastructural development. Innovations in tires are also being impacted by the growth of electric vehicles (EVs), with an emphasis on high-durability and low-noise options. Furthermore, market dynamics are being shaped by government rules that support retreaded and environmentally friendly tires. Finally, growing customer demand for high-end, all-season tires is spurring manufacturer innovation and competitiveness.
Case Study on Cost Model of Tire Manufacturing Plant
Objective
One of our clients has approached us to conduct a feasibility study for establishing a mid to large-scale tire manufacturing plant in India.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We have developed a detailed financial model for the plant's setup and operations. The proposed facility is designed with an annual production capacity of 7,900,000 units of tires.
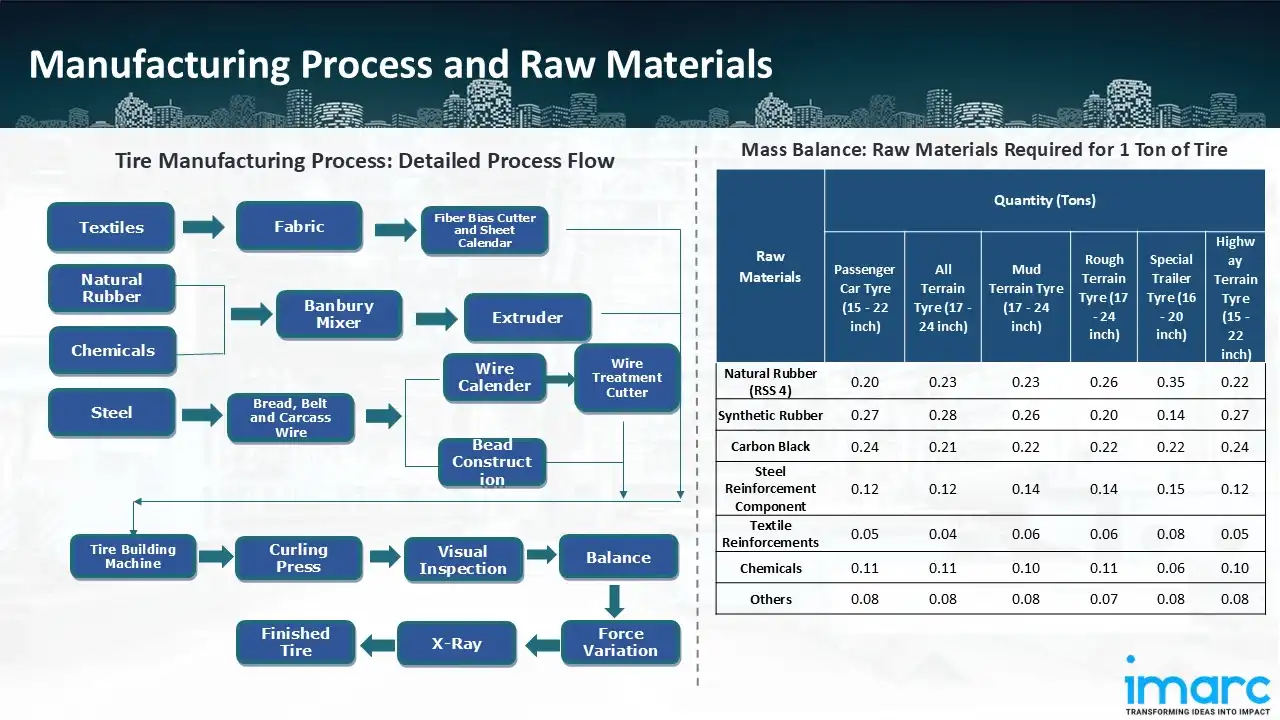
Manufacturing Process: A number of crucial procedures are included in the tire manufacturing process to guarantee performance and longevity. The process starts with compounding and Banbury mixing, which produces a homogenous rubber compound by blending rubber, carbon black, and chemicals under regulated heat and pressure. During the milling stage, rollers are used to form the rubber into flat strips. The rubber is then refined into sheets, covered with layers of fabric, and formed into treads and sides by extrusion and calendering. These components are assembled and built by placing them onto a revolving drum to form a "green tire," which is secured in place with solvents and adhesives. After that, the tire goes through vulcanisation and curing, which turns the rubber into a strong, flexible material using pressure and heat. Lastly, quality is guaranteed by trimming, testing, and packaging during the inspection and finishing phase. This methodical procedure guarantees tire longevity and safety while enabling producers to satisfy consumer demand.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Mass Balance and Raw Material Required: The primary raw materials utilized in the Tire manufacturing plant include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, carbon black, steel reinforcement component, textile reinforcements, chemicals, and others. To produce 1 ton of passenger car tire, we require 0.20 tons of natural rubber, 0.27 tons of synthetic rubber, 0.24 tons of carbon black, 0.12 tons of steel reinforcement component, 0.05 tons of textile reinforcements, 0.11 tons of chemicals, and 0.08 tons of other raw materials. To produce 1 ton of all terrain tire, we require 0.23 tons of natural rubber, 0.28 tons of synthetic rubber, 0.21 tons of carbon black, 0.12 tons of steel reinforcement component, 0.04 tons of textile reinforcements, 0.11 tons of chemicals, and 0.08 tons of other raw materials. To produce 1 ton of mud terrain tire, we require 0.23 tons of natural rubber, 0.26 tons of synthetic rubber, 0.22 tons of carbon black, 0.14 tons of steel reinforcement component, 0.06 tons of textile reinforcements, 0.10 tons of chemicals, and 0.08 tons of other raw materials. To produce 1 ton of rough terrain tire, we require 0.26 tons of natural rubber, 0.20 tons of synthetic rubber, 0.22 tons of carbon black, 0.14 tons of steel reinforcement component, 0.06 tons of textile reinforcements, 0.11 tons of chemicals, and 0.07 tons of other raw materials. To produce 1 ton of special trailer tire, we require 0.35 tons of natural rubber, 0.14 tons of synthetic rubber, 0.22 tons of carbon black, 0.15 tons of steel reinforcement component, 0.08 tons of textile reinforcements, 0.06 tons of chemicals, and 0.08 tons of other raw materials. To produce 1 ton of highway terrain tire, we require 0.22 tons of natural rubber, 0.27 tons of synthetic rubber, 0.24 tons of carbon black, 0.12 tons of steel reinforcement component, 0.05 tons of textile reinforcements, 0.10 tons of chemicals, and 0.08 tons of other raw materials.
List of Machinery:
The following equipment was required for the proposed plant:
- Banbury Mixer (that includes internal mixer also)
- 6" Hot feed Extruder (with flat head and strainer head)
- 8" Hot Feed Extruder (with flat head and strainer head)
- 3 Roll Calendar
- 26” x 84” Mixing Mill (including Component feeder, stock blender)
- Belt building machine
- Belt building drum
- Automatic belt server with customized let off station
- Let off station belt
- Automatic ply server for assembled innerliner (PA) and one or two carcass plies (BP)
- PA let off station
- BP1 let off station
- BP2 let off station
- Transfer station with transfer ring
- Bead setting & pushing device
- Tire building unit
- Tire building drum
- Reel tread server
- Automatic reel tread & Dynamic stitcher
- Main switch cabinet & Operator`s panel
- Industrial PC
- JLB server /let-off station
- Chafer server
- Curing press (including dual-mode vulcanizing machine)
- automatic cutter
- Tire Testing Machine (X-ray machine, uniformity testing machine and dynamic balance testing machine)
- Banbury Mixer (including internal mixer)
- Hot feed Extruder (with flat head and strainer head)
- 24" X 76 4 Roll Calendar
- Mixing Mill (including Component feeder, stock blender)
- Belt building machine
- Belt building drum
- Automatic belt server with customized let off station
- Let off station belt
- Automatic ply server for assembled innerliner (PA) and one or two carcass plies (BP)
- PA let off station
- BP1 let off station
- BP2 let off station
- Transfer station with transfer ring
- Bead setting & pushing device
- Tire building unit
- Tire building drum & Reel tread server
- Automatic reel tread & Dynamic stitcher
- Main switch cabinet & Operator`s panel
- Industrial PC & Chafer server
- JLB server /let-off station
- Curing Press (including Dual-mode vulcanizing machine)
- Automatic Cutter
- Tire Testing Machine (X-ray machine, Uniformity testing machine and Dynamic balance testing machine)
- Banbury Mixer (including internal mixer)
- Mixing Mills (including Component feeder, stock blender)
- Hot feed Extruders (with flat head and strainer head)
- 4 Roll Calendar
- Tire Building Machine
- Curing Press (including Dual-mode vulcanizing machine)
- Banbury Mixer (including internal mixer)
- Mixing Mills (including Component feeder, stock blender)
- 4 Roll Calendar
- Tire Building Machine
- Curing Press (including Dual-mode vulcanizing machine)
- Automatic Cutter
- Tire Testing Machine (X-ray machine, Uniformity testing machine and Dynamic balance testing machine)
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Investment (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
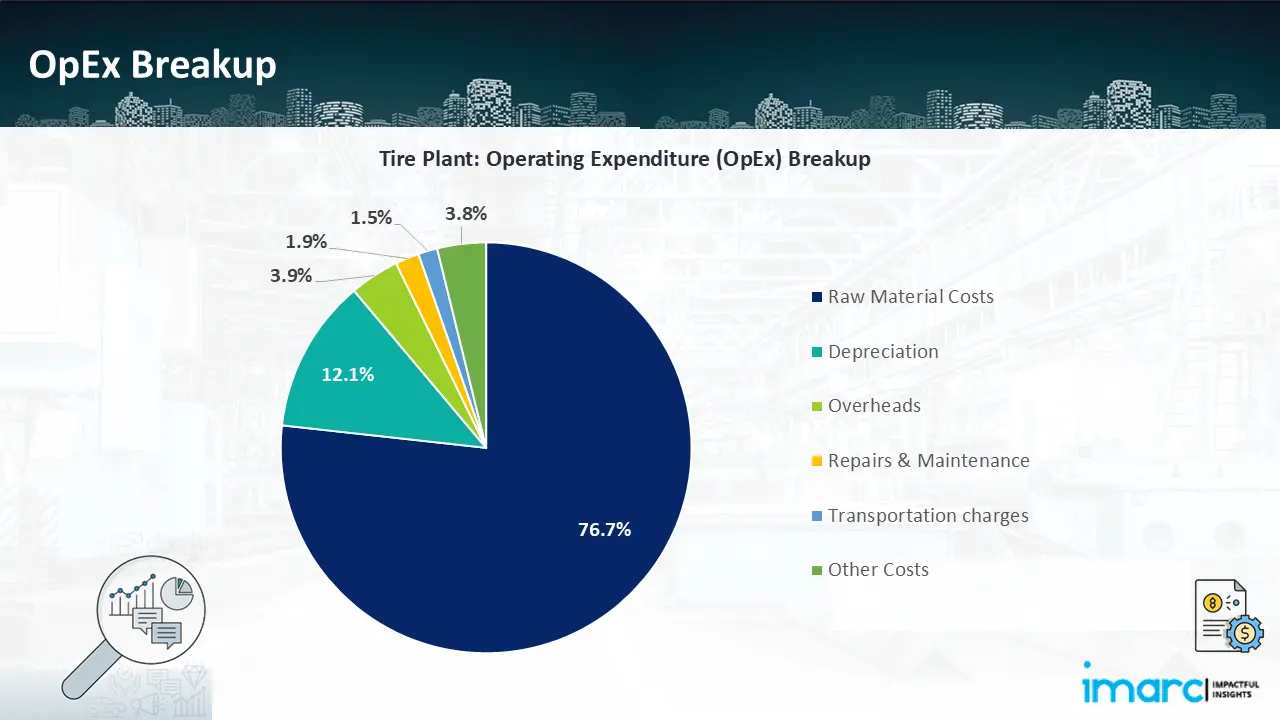
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth.
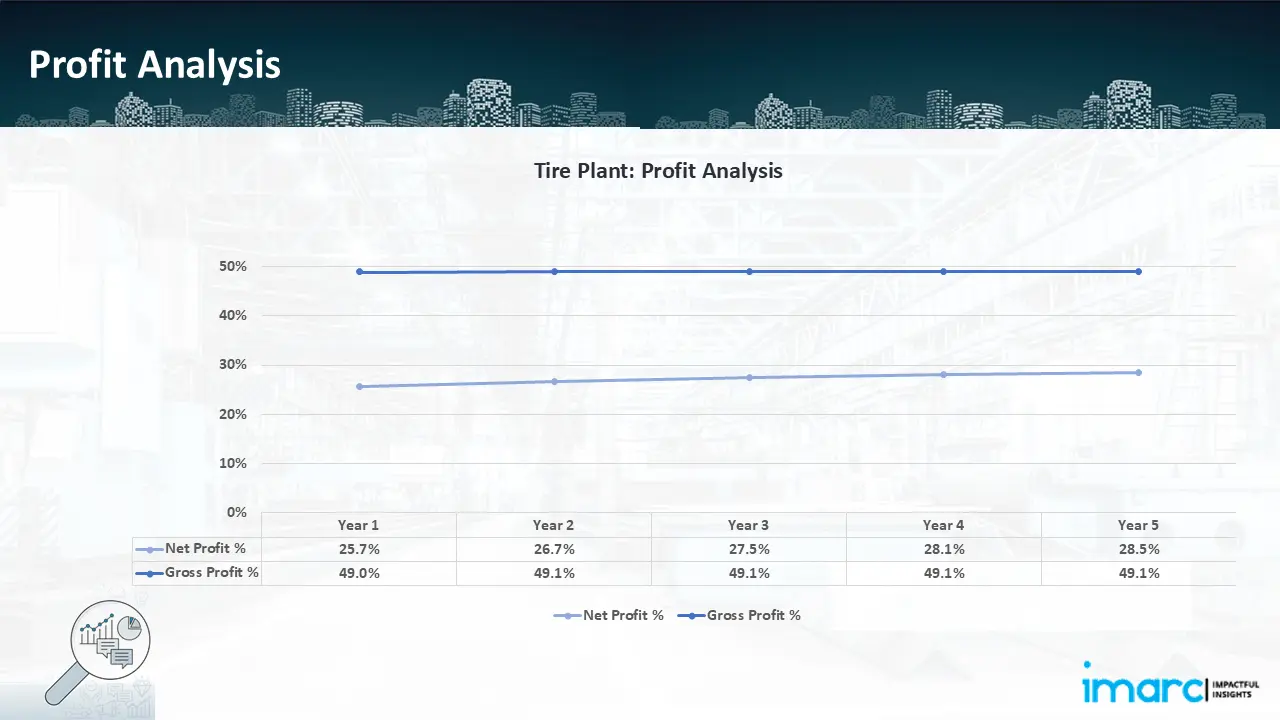
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: The proposed tire plant, with an annual capacity of 7,900,000 units of tire, achieved an impressive revenue of US$ 630.8 million in its first year. We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Gross profit margins slightly improved from 49.0% to 49.1% during the period, and net profit margins rise from 25.7% to 28.5%, highlighting strong financial viability and operational efficiency.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our tire manufacturing plant's financial model was meticulously modelled to satisfy the client's requirements. It provided a thorough analysis of production costs including capital expenditures, manufacturing processes, raw materials, and operating costs. The model predicts profitability while accounting for market trends, inflation, and any shifts in the price of raw materials. It was created especially to satisfy the demand of producing 7,900,000 units of tire annually. Our commitment to offering precise, client-cantered solutions that ensure the long-term success of significant industrial projects by giving the client useful data for strategic decision-making is demonstrated by this comprehensive financial model.
Latest News and Developments:
- In February 2025, Yokohama India has expanded its local production capabilities by manufacturing 20-inch tires at its Indian facility. This action lessens reliance on imports and promotes the nation's rising need for high-end, high-performance tires. The program seeks to increase supply chain efficiency while meeting the growing demand from the SUV and luxury automobile segments, which is in line with the government's "Make in India" agenda.
- In January 2025, leading tire maker Ralson tires has entered the commercial and automotive tire markets in an attempt to take advantage of the rapidly expanding home market. At the Bharat Mobility Global Expo, the business declared its foray into the Indian market for premium commercial tires.
- In December 2024, CEAT has acquired Camso’s off-highway tires and tracks business from Michelin in a USD 225 Million deal. Through this transaction, CEAT's global reach is increased and its position in the material handling, construction, and agriculture tire markets is strengthened. The change supports CEAT's growth plan in the off-highway tire market by improving its product portfolio, manufacturing capacity, and technological capabilities.
- In March 2024, Titan International purchased Carlstar Group in a USD 296 Million transaction, increasing its line of industrial applications, speciality tires, and wheels. By utilising Carlstar's well-established brand, the acquisition enhances Titan's standing in the powersports, construction, and agriculture industries. This move is anticipated to expand Titan's product range and improve its production capabilities and global market reach.
- In January 2023, Nokian tire moved forward with the expansion of its Dayton, Tennessee factory as the facility nears full production capacity. The expansion will help meet the company's increasing demand in North America and generate 75 new employments. Nokia's aim to improve local manufacturing, lower supply chain risks, and increase production efficiency is in line with this action.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Brief List of Our Services: Market Entry and Expansion
- Market Entry and Opportunity Assessment
- Competitive Intelligence and Benchmarking
- Procurement Research
- Pricing and Cost Research
- Sourcing
- Distribution Partner Identification
- Contract Manufacturer Identification
- Regulatory Approvals, and Licensing
- Factory Setup
- Factory Auditing
- Company Incorporation
- Incubation Services
- Recruitment Services
- Marketing and Sales
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104