
Iran Seeds Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Seed Type, Traits, Availability, and Seed Treatment, and Region, 2025-2033
Iran Seeds Market Overview:
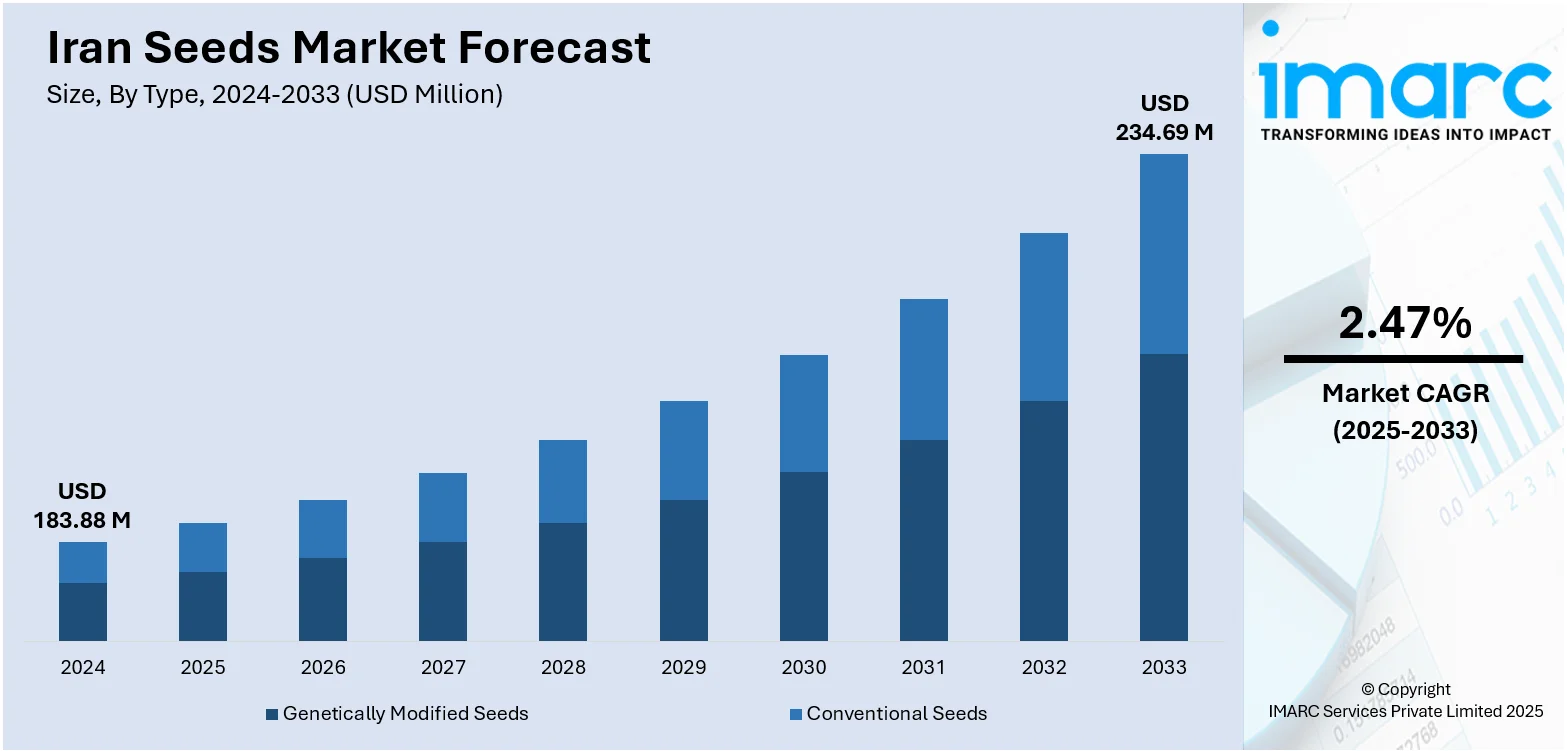
The Iran seeds market size reached USD 183.88 Million in 2024. The market is projected to reach USD 234.69 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 2.47% during 2025-2033. The market is experiencing steady development with increasing demand for high-yielding crops, advanced cultivation practices, and support initiatives by the government for developing agriculture. Rising awareness among farmers and supportive government policies are further driving innovation and adoption. Companies are investing in research to develop resilient and high-performing seed varieties, enhancing overall productivity and crop health. These factors collectively influence the growth of the Iran seeds market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 183.88 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 234.69 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 2.47% |
Iran Seeds Market Trends:
Expansion of Self‑Sufficient Seed Production
In January 2025, Iran achieved self‑sufficiency in seed and seedling production, meeting nearly all domestic requirements without relying on intermediate imports. Supported by the Ministry of Agriculture‑Jihad, infrastructure such as the Seed and Seedling Headquarters and Seed and Plant Improvement Institute supports continuous quality enhancement. Officials report that nearly all staple crop seeds from vegetables to grains are now produced locally, marking a major shift in agricultural input dynamics. Domestic hybrid seed development is advancing rapidly, and the National Program for Greenhouse and Aquaculture Development is facilitating commercialization plans for domestic hybrid seed lines, aligning public and private sector capacities alongside knowledge‑based firms. This blending of research, certification and production capabilities underlines a mature ecosystem for seed generation. As a result: farmers can increasingly access certified, locally adapted varieties, reducing dependency on foreign sources and strengthening resilience of national agriculture. This foundation sharply boosts the overall regional reliability and accessibility of seed supplies in the domestic system. This self-reliance is a key driver of Iran seeds market growth, supporting long-term sustainability and reducing exposure to external supply disruptions.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Hybrid Development Driving Domestic Innovation
In November 2024, Iran's Ministry of Agriculture-Jihad announced the successful development of several hybrid lettuce varieties, including romaine, iceberg, little gem, frisée, and oakleaf types. This marked a significant step in hybrid vegetable seed innovation, which is becoming central to Iran’s agricultural modernization. A total of 67 domestic hybrid seed varieties including greenhouse cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, watermelons, and melons were also commercialized around the same time, offering growers more consistent, climate-adapted options. These hybrids are the result of investment in genetic research, double haploid breeding, and collaboration between research universities and knowledge-based firms. With certification and quality control frameworks strengthening across the board, farmers now have access to improved varieties that offer higher yields, better pest resistance, and more predictable growth cycles. These technical improvements are not only increasing productivity but also reducing costs by decreasing reliance on imported seed. The rapid rise in hybrid seed availability reflects one of the most important Iran seeds market trends, pointing to a future shaped by domestic innovation and sustainable agricultural inputs.
Knowledge-Based Ecosystem Accelerating Seed Advancement
In March 2025, the Iranian government announced that more than 300 knowledge-based enterprises are currently working on agricultural innovation, with a high emphasis placed on seed genetics, quality enhancement, and local hybrid production. This growing ecosystem indicates the way science and technology are being used to enhance Iran's seed self-sufficiency and supply resilience. Most of these companies are directly collaborating with academic institutions and agricultural research institutes to create high-performance seed varieties especially for vegetables, oilseeds, and summer crops. One such example is the establishment of a 10-hectare smart greenhouse by Islamic Azad University, constructed specially for breeding and testing vegetable seed varieties under controlled environments. These initiatives are increasing germination levels, enhancing responsiveness to local climate conditions, and strengthening seed quality consistency for farmers. Synergy between knowledge-intensive firms, public sector institutions, and research centers is changing the seeds development paradigm from a commodity import-based model to a strategic, innovation-focused industry. These developments are paving the way for an improved, more secure, and scalable seed supply chain in response to Iran's long-term agriculture objectives.
Iran Seeds Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on type, seed type, traits, availability, and seed treatment.
Type Insights:
- Genetically Modified Seeds
- Conventional Seeds
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes genetically modified seeds and conventional seeds.
Seed Type Insights:
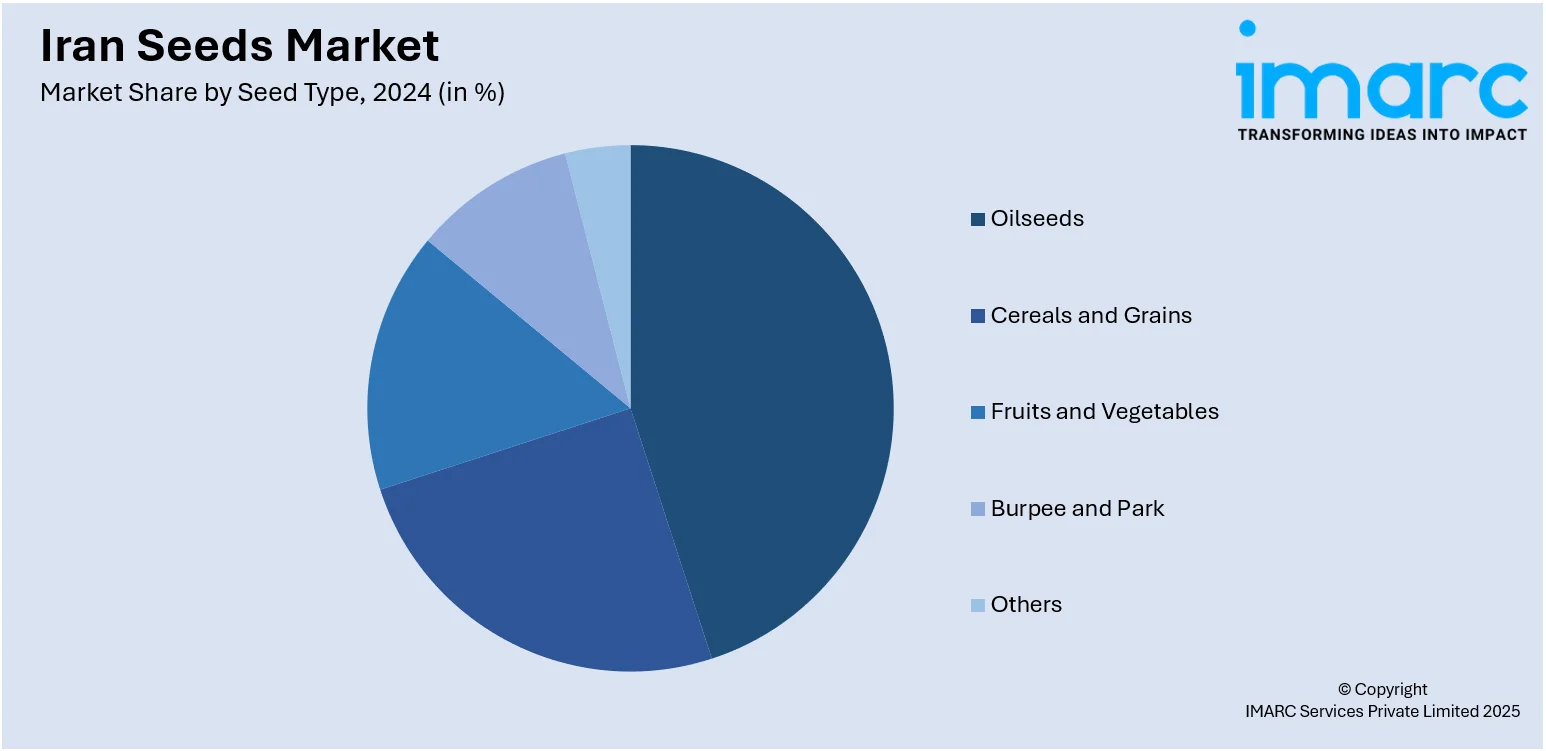
- Oilseeds
- Soybean
- Sunflower
- Cotton
- Canola/Rapeseed
- Cereals and Grains
- Corn
- Wheat
- Rice
- Sorghum
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Tomatoes
- Lemons
- Brassica
- Pepper
- Lettuce
- Onion
- Carrot
- Burpee and Park
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the seed type have also been provided in the report. This includes oilseeds (soybean, sunflower, cotton, and canola/rapeseed), cereals and grains (corn, wheat, rice, and sorghum), fruits and vegetables (tomatoes, lemons, brassica, pepper, lettuce, onion, and carrot), burpee and park, and others.
Traits Insights:
- Herbicide-Tolerant (HT)
- Insecticide-Resistant (IR)
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the traits. This includes herbicide-tolerant (HT), insecticide-resistant (IR), and others.
Availability Insights:
- Commercial Seeds
- Saved Seeds
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the availability have also been provided in the report. This includes commercial seeds and saved seeds.
Seed Treatment Insights:
- Treated
- Untreated
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the seed treatment. This includes treated and untreated.
Regional Insights:
- Tehran
- Khuzestan
- Bushehr
- Esfahan
- Khorasan
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include the Tehran, Khuzestan, Bushehr, Esfahan, Khorasan, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Iran Seeds Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Genetically Modified Seeds, Conventional Seeds |
| Seed Types Covered |
|
| Traits Covered | Herbicide-Tolerant (HT), Insecticide-Resistant (IR), Others |
| Availabilities Covered | Commercial Seeds, Saved Seeds |
| Seed Treatments Covered | Treated, Untreated |
| Regions Covered | Tehran, Khuzestan, Bushehr, Esfahan, Khorasan, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Iran seeds market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Iran seeds market on the basis of type?
- What is the breakup of the Iran seeds market on the basis of seed type?
- What is the breakup of the Iran seeds market on the basis of traits?
- What is the breakup of the Iran seeds market on the basis of availability?
- What is the breakup of the Iran seeds market on the basis of seed treatment?
- What is the breakup of the Iran seeds market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Iran seeds market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Iran seeds market?
- What is the structure of the Iran seeds market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Iran seeds market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Iran seeds market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Iran seeds market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Iran seeds industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












