
Japan Education Computing Devices Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Type, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Education Computing Devices Market Summary:
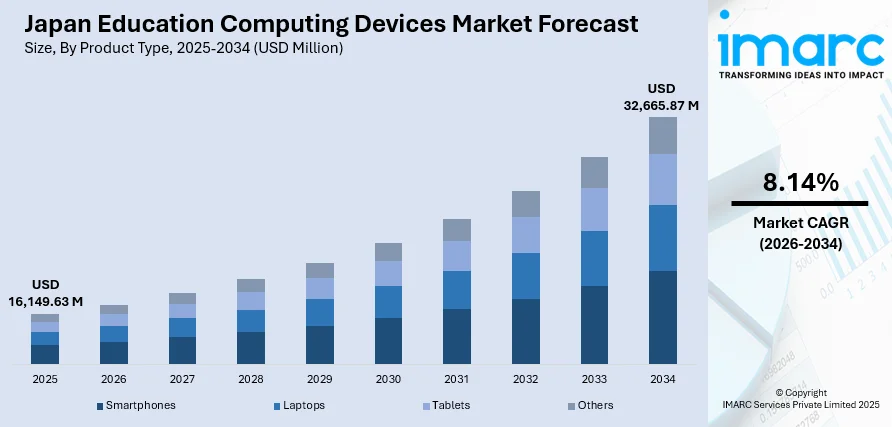
The Japan education computing devices market size was valued at USD 16,149.63 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 32,665.87 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.14% from 2026-2034.
The market is driven by strong government digitalization initiatives promoting technology integration in educational institutions nationwide. Rising adoption of personalized learning platforms, increasing emphasis on STEM education, and growing demand for interactive digital tools are accelerating device deployment across schools. The shift toward hybrid learning models and curriculum modernization continues to fuel procurement of advanced computing solutions. Enhanced connectivity infrastructure and collaborative efforts between public agencies and technology providers further support widespread adoption, strengthening the Japan education computing devices market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Product Type: Laptops dominate the market with a share of 40% in 2025, driven by versatile classroom use, compatibility with educational software, superior processing for complex learning programs, and preference in secondary and higher education institutions.
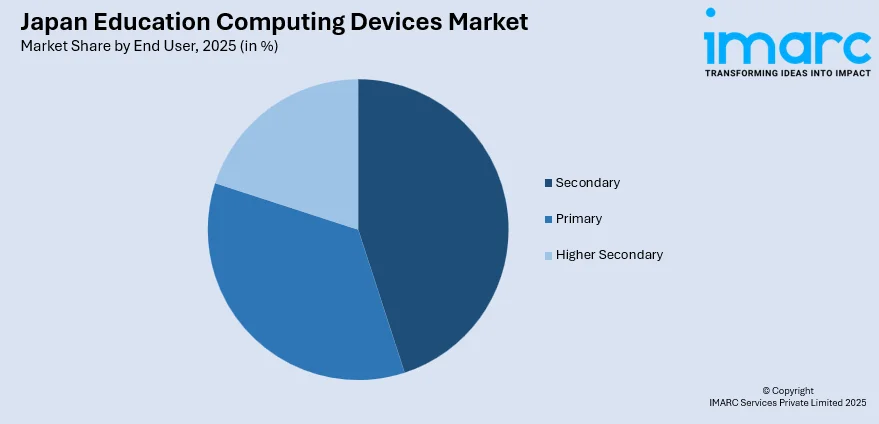
- By End User: Secondary leads the market with a share of 40% in 2025, fueled by digital literacy mandates, government device distribution programs, technology-focused curricula, and the need for robust computing to support advanced learning applications.
- By Region: Kanto Region dominates the market with a share of 35% in 2025, supported by Tokyo-area educational institutions, higher digital infrastructure budgets, advanced connectivity networks, and concentrated adoption of technology-driven learning solutions across schools and universities.
- Key Players: The Japan education computing devices market exhibits a well-established competitive structure, with multinational technology corporations competing alongside domestic manufacturers across various device categories and price segments, focusing on educational specifications and institutional requirements.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Japan education computing devices market is experiencing substantial expansion driven by comprehensive government initiatives aimed at digitizing the nation's educational infrastructure. As per sources, in January 2025, Japan’s Education Ministry began considering granting digital textbooks official schoolbook status, allowing local boards to choose paper or digital formats for primary education. The nationwide emphasis on integrating technology into classroom environments has created sustained demand for computing devices across all educational levels. Schools are increasingly adopting digital learning platforms that require advanced hardware capabilities, while curriculum modernization efforts prioritize technology literacy from primary education onwards. The growing recognition of personalized learning benefits, where devices enable individualized instruction tailored to student needs, further accelerates adoption. Additionally, the expansion of STEM education programs requiring computational tools, coupled with enhanced broadband connectivity across educational institutions, creates favorable conditions for market growth. Collaborative partnerships between educational authorities and technology providers ensure continuous innovation in device specifications designed specifically for academic environments.
Japan Education Computing Devices Market Trends:
Expansion of Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Learning Solutions
Educational institutions across Japan are increasingly incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities into their computing infrastructure to deliver personalized learning experiences. In June 2025, Fujitsu Japan and the University of Osaka launched a four-month (June to September) joint research project using generative AI to create individualized education plans for culturally and linguistically diverse students. Moreover, these advanced systems analyze individual student performance patterns and adapt content delivery, accordingly, enhancing educational outcomes. Schools are prioritizing devices capable of supporting sophisticated AI-powered applications that provide real-time feedback and customized lesson plans. The integration of machine learning algorithms into educational software requires computing devices with enhanced processing capabilities, driving demand for higher-specification hardware. This technological evolution reflects a broader commitment to leveraging innovative tools for improved academic achievement and student engagement throughout the educational journey.
Growing Emphasis on Collaborative Digital Learning Environments
Japanese schools are transitioning toward interconnected digital ecosystems where students engage in collaborative projects using cloud-based platforms and shared computing resources. In May 2025, NetOne Systems announced it had built a next-generation cloud-based ICT education infrastructure for the Aichi Prefectural Board of Education, set for full operation started January 2025, enhancing security and digital learning efficiency. This shift necessitates devices optimized for seamless connectivity and real-time collaboration across multiple users and locations. Educational institutions are deploying computing solutions that facilitate group learning activities, virtual classroom participation, and interactive content creation. The emphasis on developing teamwork and communication skills through digital platforms drives procurement of devices designed for enhanced connectivity and multimedia capabilities. This trend reflects evolving pedagogical approaches that prioritize collaborative learning as essential preparation for modern workforce requirements.
Integration of Immersive Educational Technologies
Schools across Japan are increasingly exploring immersive learning experiences through augmented and virtual reality applications that transform traditional educational content into interactive three-dimensional environments. In April 2024, NTT West and partners introduced a 3D Education Metaverse in Joyo City, Kyoto, providing remote learning support for non-attending students as part of MEXT’s nationwide COCOLO Plan formulated in 2023. Moreover, this adoption requires computing devices with advanced graphics processing capabilities and sufficient memory to support resource-intensive immersive applications. Educational institutions recognize the potential of experiential learning technologies to enhance student understanding of complex subjects including science, history, and technical disciplines. The growing availability of educational content designed for immersive platforms creates sustained demand for compatible computing hardware. This technological integration represents a significant shift toward experiential learning methodologies throughout Japanese educational institutions.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan education computing devices market is positioned for sustained revenue growth throughout the forecast period, supported by continued government investment in educational technology infrastructure. Revenue expansion will be driven by device replacement cycles, expansion of digital learning programs, and integration of advanced technologies across educational institutions. The market revenue trajectory reflects ongoing commitment to educational modernization, with institutions allocating substantial budgets for computing device procurement. Rising adoption of hybrid learning models, emphasis on technology-enabled personalized instruction, and expanding STEM curriculum requirements will generate consistent revenue streams across all market segments and regional territories. The market generated a revenue of USD 16,149.63 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 32,665.87 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.14% from 2026-2034.
Japan Education Computing Devices Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Laptops | 40% |
| End User | Secondary | 40% |
| Region | Kanto Region | 35% |
Product Type Insights:
- Smartphones
- Laptops
- Tablets
- Others
Laptops dominate with a market share of 40% of the total Japan education computing devices market in 2025.
Laptops represent the dominant product category within Japan education computing devices market, reflecting their comprehensive functionality for academic applications. These devices offer the processing power, keyboard functionality, and screen dimensions necessary for extended educational use, making them preferred choices for secondary and higher education institutions. Laptops support the full range of educational software applications, from word processing and research tools to complex programming environments and creative design platforms. Their versatility enables both classroom instruction and independent study activities.
The sustained preference for laptops stems from their ability to accommodate diverse educational requirements across multiple subject areas and learning activities. Educational institutions value the durability and longevity of laptop devices compared to alternatives, while students benefit from portable yet powerful computing solutions. The availability of education-specific laptop configurations with enhanced battery life, reinforced construction, and simplified management features further supports adoption. In June 2025, ASUS JAPAN launched multiple Intel® N150-equipped laptops for businesses, educational institutions, and GIGA Schools, offering diverse configurations and six-year ASUS Anshin Warranty for reliable, long-term use. Furthermore, schools increasingly standardize on laptop devices to ensure consistent learning experiences and simplified technical support across their educational technology infrastructure.
End User Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Primary
- Secondary
- Higher Secondary
Secondary leads with a share of 40% of the total Japan education computing devices market in 2025.
Secondary education institutions represent the largest end-user segment for computing devices in Japan's educational technology market. According to sources, in 2025, Obunsha conducted its ninth nationwide survey on ICT use in high schools, reporting that 95.3% of students now use one device per student, with over 70% being school-designated. This dominance reflects the critical role of technology in preparing students for higher education and workforce entry, where digital literacy is essential. Secondary schools integrate computing devices across virtually all subject areas, from humanities research to scientific analysis and technical skills development. The comprehensive curriculum requirements at this educational level necessitate robust computing capabilities that support diverse learning activities.
The concentration of device adoption within secondary education reflects both government policy priorities and practical educational requirements. Mandatory digital literacy standards require schools to provide adequate computing resources for all students, driving institutional procurement. Secondary education represents the transition point where students develop advanced technology skills necessary for academic and professional success. Educational authorities prioritize this segment for technology investment, recognizing its pivotal role in preparing students for increasingly digital higher education environments and employment opportunities requiring sophisticated technical competencies.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
Kanto Region dominates with a market share of 35% of the total Japan education computing devices market in 2025.
Kanto Region maintains its position as the largest geographic market for education computing devices in Japan, encompassing the Tokyo metropolitan area and surrounding prefectures. This regional dominance reflects the concentration of educational institutions, population density, and economic resources that drive technology adoption. Schools within this region benefit from advanced infrastructure, including high-speed connectivity and established technology support networks. The substantial student population across primary, secondary, and higher education levels generates consistent demand for computing devices.
The region's market leadership extends beyond population factors to include pioneering adoption of educational technology initiatives. Schools within this region often serve as testing grounds for new digital learning programs before nationwide implementation. Higher regional tax revenues enable more substantial education technology budgets, while proximity to technology providers facilitates rapid device deployment and support. The competitive educational environment within the metropolitan area encourages institutions to invest in advanced computing infrastructure, establishing adoption patterns that subsequently influence technology procurement across other Japanese regions.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Education Computing Devices Market Growing?
Government Digital Education Initiatives and Policy Support
The Japanese government's comprehensive commitment to educational technology transformation serves as a primary catalyst for computing device market expansion. National programs prioritizing digital infrastructure deployment in schools create sustained institutional demand for computing hardware across all educational levels. These initiatives provide funding mechanisms that enable schools to procure devices that might otherwise exceed their operational budgets. In February 2025, Japan’s Digital Agency announced a public invitation for business operators to participate in empirical research enabling fully digital handling of public highschool entrance exams, supporting education data linkage. Moreover, government policy establishes standardized technology requirements that ensure consistent device deployment throughout the public education system. The regulatory framework supporting educational digitalization includes connectivity mandates, curriculum integration requirements, and teacher training programs that collectively drive computing device adoption. Continued policy emphasis on preparing students for technology-driven economic participation ensures sustained governmental support for educational computing infrastructure investment.
Rising Demand for Personalized and Adaptive Learning Solutions
Educational institutions increasingly recognize the pedagogical benefits of technology-enabled personalized learning, driving demand for computing devices capable of supporting adaptive educational platforms. These systems analyze individual student performance and customize content delivery to address specific learning needs, requiring devices with sufficient processing capabilities. The shift toward individualized instruction represents a fundamental transformation in educational methodology that necessitates one-to-one device access for students. In April 2025, MediaTek and HP launched the HP Fortis Flip G1m 11 Chromebook at EDIX Tokyo, featuring the Kompanio 520 processor, enhanced battery life, and versatile performance for K–12 digital learning. Furthermore, schools implementing personalized learning programs report improved academic outcomes, encouraging broader adoption across the educational system. The growing availability of adaptive learning software designed for Japanese curriculum standards increases institutional motivation to invest in compatible computing hardware. This pedagogical evolution creates sustained market demand as schools transition from traditional instruction toward technology-mediated personalized learning approaches.
Expansion of STEM Education and Technical Curriculum Requirements
Japan's strategic emphasis on developing science, technology, engineering, and mathematics capabilities among students drives computing device demand across educational institutions. STEM curriculum implementation requires computing hardware capable of supporting programming environments, scientific simulation software, and engineering design applications. Schools expanding technical education programs must provide students with devices offering sufficient processing power and software compatibility for complex applications. As of May 2024, the Japan Society for Industrial Technology Education proposed restructuring junior high technical subjects into a new “Technology” course, emphasizing programming, digital manufacturing, robotics, and STEAM skills. Further, the recognition of technology skills as essential workforce preparation motivates educational authorities to prioritize computing device procurement. Coding education initiatives beginning at primary levels establish early requirements for computing device access that extend throughout the educational journey. This curriculum evolution toward technology-intensive subjects ensures sustained demand growth for computing devices supporting advanced educational applications.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Japan Education Computing Devices Market is Facing?
Budgetary Constraints and Funding Limitations
Educational institutions face persistent budgetary pressures that limit computing device procurement and replacement capabilities. Many schools struggle to allocate sufficient resources for technology infrastructure while maintaining other essential educational programs. The substantial capital investment required for comprehensive device deployment can delay implementation, particularly in regions with limited fiscal resources. Budget prioritization challenges require educational administrators to balance technology investments against competing educational needs.
Technical Infrastructure and Support Limitations
Many educational institutions lack adequate technical support infrastructure to manage comprehensive computing device deployments effectively. Schools in rural and remote areas particularly face challenges in maintaining devices, providing user support, and ensuring consistent functionality. The shortage of qualified technical personnel within educational environments creates operational difficulties that may delay technology adoption. Infrastructure limitations extend beyond devices to include connectivity gaps that reduce the effectiveness of deployed computing hardware.
Teacher Training and Technology Integration Challenges
Effective utilization of computing devices requires substantial teacher training and ongoing professional development that many institutions struggle to provide adequately. Educators may lack confidence in integrating technology into their instructional practices, reducing the return on device investments. The transition from traditional instruction to technology-enabled learning requires pedagogical shifts that demand significant time and institutional support. Professional development requirements create additional costs and logistical challenges that can slow technology adoption across educational institutions.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan education computing devices market features a mature competitive environment characterized by established relationships between educational institutions and technology providers. Market participants differentiate themselves through device specifications optimized for educational environments, including enhanced durability, extended battery performance, and simplified administrative management capabilities. Competition extends beyond hardware specifications to encompass comprehensive solutions including software integration, technical support services, and educational content partnerships. Vendors increasingly focus on addressing specific institutional requirements across different educational levels and learning environments. The competitive dynamics emphasize total cost of ownership considerations, where procurement decisions reflect device longevity, maintenance requirements, and support accessibility alongside initial acquisition costs. Strategic partnerships between technology providers and educational authorities facilitate large-scale deployment programs that influence competitive positioning throughout the market.
Recent Developments:
-
In February 2025, HP Japan unveiled new devices for the second phase of the GIGA School Initiative, designed to support remote and in-school learning. The lightweight, durable terminals feature high-capacity batteries, pen input with palm rejection, and LTE connectivity, ensuring equitable access to digital education even in schools with limited Wi-Fi infrastructure.
Japan Education Computing Devices Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered | Smartphones, Laptops, Tablets, Others |
| End Users Covered | Primary, Secondary, Higher Secondary |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan education computing devices market size was valued at USD 16,149.63 Million in 2025.
The Japan education computing devices market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.14% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 32,665.87 Million by 2034.
Laptops dominated the market with the largest share, driven by their comprehensive functionality, compatibility with educational software applications, processing capabilities for complex learning programs, and widespread preference among secondary and higher education institutions.
Key factors driving the Japan education computing devices market include government digitalization initiatives, rising demand for personalized learning solutions, expansion of STEM education programs, enhanced connectivity infrastructure, and growing emphasis on technology-enabled instruction.
Major challenges include budgetary constraints limiting device procurement, technical infrastructure gaps in remote areas, teacher training requirements for effective technology integration, device maintenance demands, and ensuring equitable access across diverse educational institutions.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












