
Japan Electric Substation Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Electric Substation Market Overview:
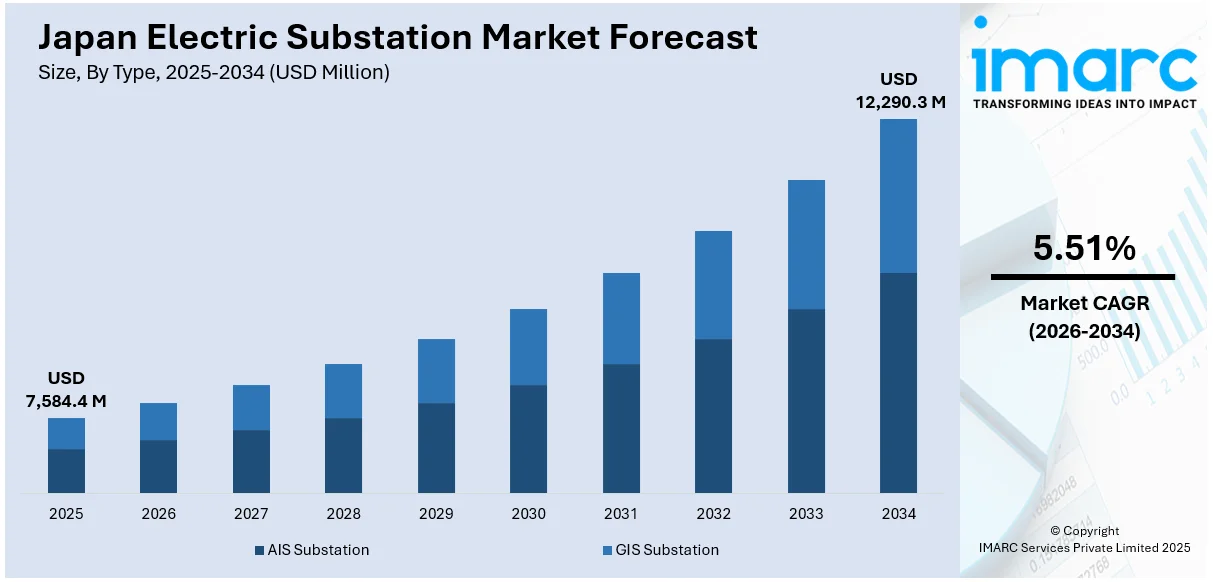
The Japan electric substation market size reached USD 7,584.4 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 12,290.3 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 5.51% during 2026-2034. The demand is also driven by the growing need to replace old infrastructure and integrate renewable energy sources like solar and offshore wind. Rising electricity demand driven by urbanization and expanding data centers is also propelling growth. Additionally, the emergence of digital technologies like smart grids and automation forces utilities to replace substations with higher reliability and efficiency. Clean energy and grid resilience policies of the government are also propelling the Japan electric substation market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 7,584.4 Million |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 12,290.3 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 5.51% |
Japan Electric Substation Market Trends:
Renewable Energy Integration and Infrastructure Modernization
With Japan’s growing shift toward renewable energy, substations are being modernized to manage variable sources like wind and solar. Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (TEPCO) intends to use its subsidiary Tepco Power Grid to invest more than $3 billion in transmission infrastructure by 2027 as part of this shift. This includes the construction of a major substation in Inzai, Chiba Prefecture, aimed at meeting rising electricity demands from both data centers and renewable projects. These upgrades are crucial for integrating clean energy sources like offshore wind farms into the grid while replacing aging infrastructure. The modernization enhances grid flexibility and ensures stable transmission across regions without sacrificing reliability. By supporting both energy sustainability and digital the Japan electric substation market growth is expected to surge, thus contributing to a more efficient, adaptive, and resilient power network ready to meet the country’s long-term climate and energy goals.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Digitalization and Smart Grid Integration
Japan is swiftly advancing digital substations to boost grid reliability and efficiency. By integrating artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and digital twins, utilities gain real-time monitoring and control over power systems. This enables predictive maintenance, significantly reducing outages and enhancing the grid’s resilience to natural disasters like earthquakes. Automated substations improve energy flow and streamline processes, which lowers costs and improves service quality. These smart grid innovations demonstrate Japan's commitment to creating a more resilient and flexible electrical system. The electricity network can effectively adapt to changing energy demands and environmental concerns thanks to this innovation. In general, the implementation of digital substations in Japan represents a significant step toward a resilient, sustainable, and future-ready power system.
Resilience and Disaster Preparedness in Substation Design
Given Japan’s exposure to frequent natural disasters like earthquakes, tsunamis, and typhoons, there is a strong nationwide push to improve the resilience of its electric substations. Utilities are incorporating disaster-resistant designs, such as seismic-proof foundations, elevated structures to prevent flooding, and fire-retardant materials. Remote monitoring and automation technologies are also being used to ensure uninterrupted operations during emergencies. Notably, a poll revealed that 84.8% of Japanese towns and all prefectures had made progress in constructing emergency power sources, highlighting the country's readiness efforts. Backup systems and redundant connections are becoming standard to uphold grid stability in crisis scenarios. These efforts are part of a broader national energy strategy aimed at long-term infrastructure resilience. By reinforcing substations with advanced design and emergency-ready capabilities, Japan is creating a more secure, sustainable, and disaster-resilient power infrastructure to meet evolving environmental and energy demands.
Japan Electric Substation Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on type and application.
Type Insights:
- AIS Substation
- GIS Substation
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes AIS substation and GIS substation.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
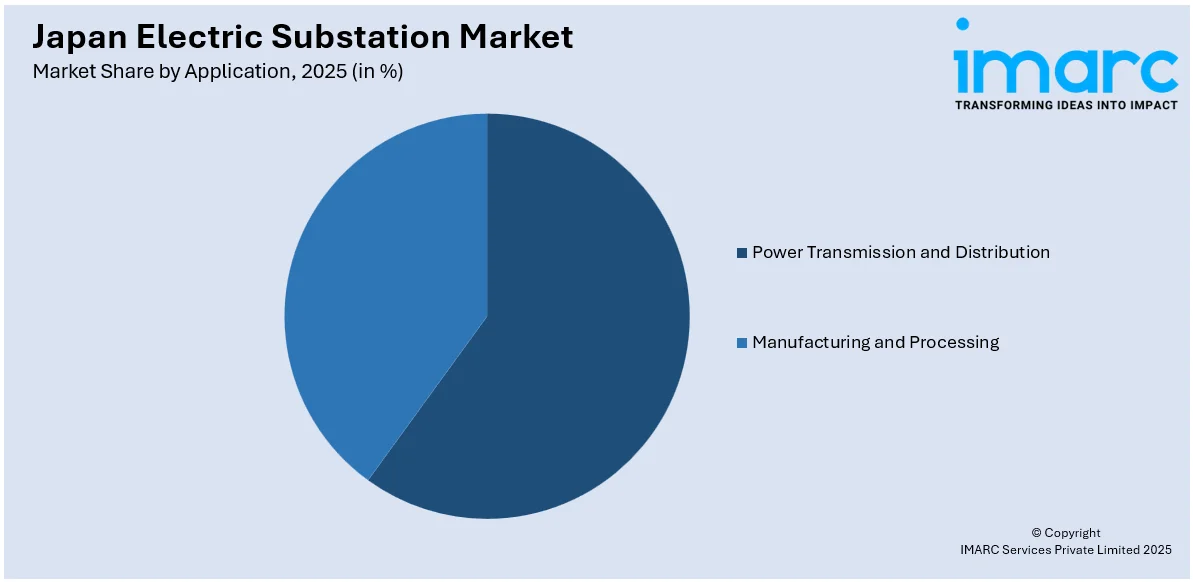
- Power Transmission and Distribution
- Manufacturing and Processing
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application have also been provided in the report. This includes power transmission and distribution and manufacturing and processing.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Kanto, Kansai/Kinki, Central/ Chubu, Kyushu-Okinawa, Tohoku, Chugoku, Hokkaido, and Shikoku Region.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Japan electric substation Market News:
- In September 2024, India's first Micro Substation utilizing Power Voltage Transformer (PVT) technology was introduced through a demonstration project initiated by Tata Power-DDL and Nissin Electric of Japan. Aimed at delivering stable electricity to areas lacking grid access, the project is part of Japan’s International Demonstration Program for Energy Efficiency Technologies, backed by NEDO. The partnership was formalized with a Project Agreement signed on August 21, 2024, marking a key step in cross-border energy innovation.
- In July 2024, Japan's largest power producer, JERA, will launch a new 2.34 GW gas-fired power plant in Goi, Chiba, on August 1 to address peak summer electricity demand. The facility, comprising three 0.78 GW units, replaces an older 1.886 GW plant closed in 2018. While Japan aims to reduce emissions, challenges in restarting nuclear plants and slow renewable adoption have led to continued investment in thermal power, including new gas and coal-fired stations.
Japan electric substation Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | AIS Substation, GIS Substation |
| Applications Covered | Power Transmission and Distribution, Manufacturing and Processing |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Japan electric substation market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Japan electric substation market on the basis of type?
- What is the breakup of the Japan electric substation market on the basis of application?
- What is the breakup of the Japan electric substation market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Japan electric substation market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Japan electric substation?
- What is the structure of the Japan electric substation market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Japan electric substation market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Japan electric substation market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Japan electric substation market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Japan electric substation industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












