
Japan Farm Implements Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Farm Implements Market Summary:
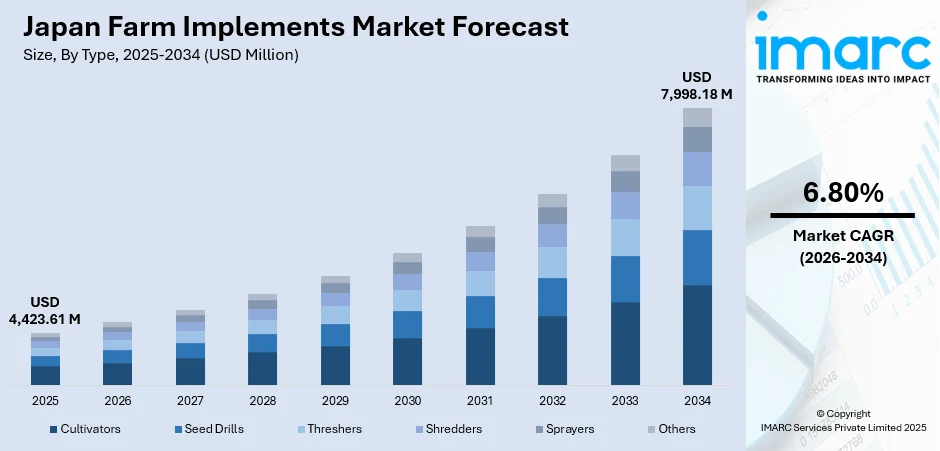
The Japan farm implements market size was valued at USD 4,423.61 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 7,998.18 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.80% from 2026-2034.
The Japan farm implements market is experiencing steady growth driven by the increasing adoption of advanced mechanization technologies, government initiatives promoting smart agriculture, and the pressing need to address critical labor shortages in the agricultural sector. Japan's aging farming population continues to accelerate demand for automated and efficient farming equipment. The government's strategic focus on agricultural modernization through subsidies and the promotion of precision farming techniques further strengthens market expansion across diverse regional farming landscapes.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Type: Cultivators dominate the market with a share of 24% in 2025, driven by their essential role in soil preparation activities across paddy fields and upland farming operations, supporting both traditional rice cultivation and diversified crop production throughout Japan's agricultural regions.
-
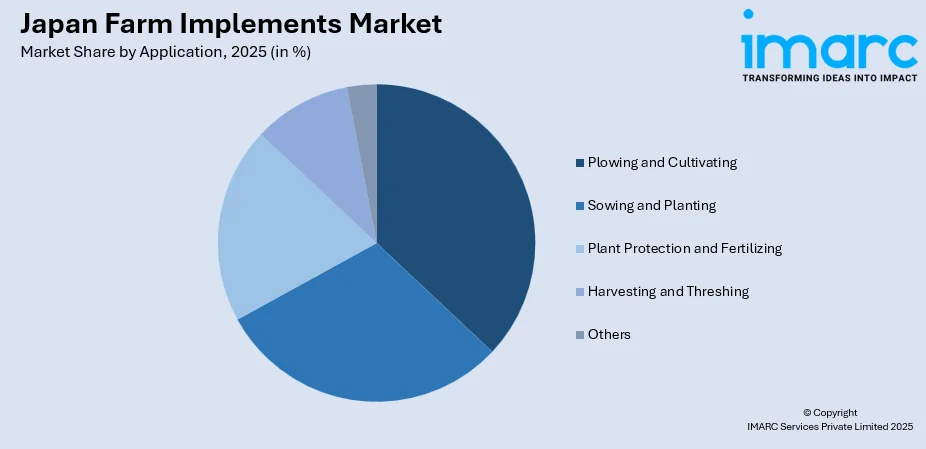
By Application: Plowing and cultivating leads the market with a share of 37% in 2025, reflecting the fundamental importance of soil preparation in Japanese agriculture where intensive cultivation practices and the need for efficient land management continue to drive demand for specialized implements.
-
By Region: Kanto Region represents the largest segment with a market share of 26% in 2025, attributed to its concentration of agricultural cooperatives, proximity to major urban markets, and strong adoption of precision farming technologies among farmers seeking to maximize productivity on limited available farmland.
-
Key Players: The Japan farm implements market exhibits moderate competitive intensity, with established domestic manufacturers dominating the landscape. Major players leverage technological expertise in developing compact, efficient equipment suited to Japan's unique agricultural requirements, including small landholdings and diverse terrain conditions.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Japanese farm implements industry is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological innovation and demographic pressures. The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) has launched comprehensive initiatives to promote smart agriculture adoption, including the Smart Agriculture Acceleration Demonstration Project with numerous pilot implementations across the country. In 2024, Kubota Group unveiled its New Agri Concept featuring an electric, autonomous agricultural machine at CES, emphasizing sustainability and AI integration for addressing global agricultural challenges. Similarly, Yanmar introduced its most powerful SM475 tractor and a fully electric concept tractor with Eleo battery technology in October 2024, demonstrating the industry's commitment to innovation.
Japan Farm Implements Market Trends:
Accelerating Adoption of Autonomous and Electric Farm Implements
Japanese manufacturers are pioneering autonomous and electric farming equipment to address labor shortages and environmental concerns. In 2024, Kubota introduced the world's first combine harvester capable of unmanned automatic operation for tractors and rice transplanters, completing its full lineup of autonomous agricultural machinery. The company will also unveil a hydrogen fuel cell tractor with self-driving capabilities at Expo 2025 Osaka, combining AI-driven autonomous driving with zero-emission hydrogen power. This technological advancement reflects the industry's strategic direction toward sustainable, labor-saving agricultural solutions.
Integration of IoT and Precision Agriculture Technologies
Farm implements are increasingly equipped with IoT sensors, GPS guidance systems, and data analytics capabilities enabling precision agriculture practices. The government's WAGRI agricultural data collaboration platform facilitates the integration of weather, soil, and production prediction data, enhancing decision-making for farmers. As an example of the industry's transition to interconnected farming ecosystems, agricultural cooperatives have adopted equipment sharing models with digital platforms that enable equipment booking and maintenance scheduling. These technologies enable optimized resource utilization and improved crop yields.
Rising Focus on Compact and Multi-Functional Equipment
Given Japan's characteristic small landholdings and fragmented farm structures, manufacturers continue developing compact, versatile implements capable of performing multiple functions efficiently. These machines are specifically designed to navigate narrow field layouts and irregular terrain while delivering reliable performance across various agricultural tasks. Technology development centers in Osaka and Kagoshima serve as important testing grounds for agricultural robotics startups, enabling rapid development of region-specific solutions that address diverse geographical conditions, varying soil types, and unique farm structures across Japan's agricultural regions.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan farm implements market demonstrates resilient growth prospects underpinned by sustained government support for agricultural modernization and the imperative to address critical workforce challenges facing the sector. The declining availability of agricultural labor combined with an aging farming population creates compelling demand for mechanized solutions that reduce manual labor requirements while maintaining productivity levels. Strategic investments in smart agriculture technologies, including robotics, AI-powered implements, and precision farming systems, are expected to drive market expansion throughout the forecast period. Additionally, the growing emphasis on sustainable farming practices and environmental responsibility encourages adoption of fuel-efficient and electric-powered equipment. Collaborative efforts between government agencies, research institutions, and private manufacturers continue fostering innovation ecosystems that accelerate development and commercialization of advanced farm implements suited to Japanese agricultural conditions. The market generated a revenue of USD 4,423.61 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 7,998.18 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.80% from 2026-2034.
Japan Farm Implements Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Type |
Cultivators |
24% |
|
Application |
Plowing and Cultivating |
37% |
|
Region |
Kanto Region |
26% |
Type Insights:
- Cultivators
- Seed Drills
- Threshers
- Shredders
- Sprayers
- Others
The cultivators dominate with a market share of 24% of the total Japan farm implements market in 2025.
Cultivators remain fundamental to Japanese agriculture given the predominance of rice cultivation requiring thorough soil preparation in paddy fields. These implements facilitate efficient seedbed preparation, weed control, and soil aeration across both wet and dry field conditions. The segment benefits from continuous technological improvements including GPS-guided systems and automated depth adjustment capabilities that enhance precision while reducing operator fatigue.
Japanese manufacturers have pioneered compact cultivator designs suited to the nation's characteristic small and fragmented landholdings. Modern cultivators increasingly incorporate smart features including real-time soil condition monitoring and variable tillage depth control. The emphasis on reduced tillage practices supported by government soil conservation programs has driven innovation in lightweight, fuel-efficient cultivator models that minimize soil compaction while maintaining optimal seedbed conditions for diverse crop types.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Plowing and Cultivating
- Sowing and Planting
- Plant Protection and Fertilizing
- Harvesting and Threshing
- Others
The plowing and cultivating leads with a share of 37% of the total Japan farm implements market in 2025.
Plowing and cultivating applications dominate the market reflecting the critical importance of soil preparation in Japan's intensive agricultural practices. The country's focus on rice production, which occupies most cultivated farmland, requires thorough land preparation including puddling operations for paddy fields. Advanced plowing equipment featuring GPS guidance and automatic steering functions has gained significant traction, enabling aged farmers to maintain productivity while reducing physical labor requirements.
The segment has witnessed substantial innovation in direct seeding technology adoption, driven by labor shortages and the need for efficient cultivation practices. Kubota's AgriRobo autonomous agricultural machinery enables unmanned automatic puddling operations with high precision, addressing the challenge of declining farm worker availability. Government depreciation policies supporting regular fleet updates have maintained strong demand for modern plowing and cultivating equipment incorporating the latest technological advancements.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto Region exhibits a clear dominance with a 26% share of the total Japan farm implements market in 2025.
The Kanto Region prioritizes precision farming to maximize output on limited farmland surrounding Japan's largest metropolitan area. Agricultural cooperatives in Saitama and Chiba have implemented innovative equipment sharing models, enabling cost-effective access to advanced machinery for smaller farm operations. Kubota Corporation, headquartered in Tokyo, develops GPS-enabled implements that enhance soil preparation, planting, and harvesting efficiency while reducing fuel consumption. This demonstrates the region's commitment to sustainable agriculture solutions addressing land constraints and environmental responsibility.
The Kanto Region benefits from strong agricultural cooperative networks facilitating technology adoption and equipment modernization among member farmers. The concentration of research institutions and agricultural technology companies drives continuous innovation in farm implements suited to the region's intensive cultivation practices. Digital platforms optimize the use of costly machinery across various farming operations by making equipment booking and maintenance scheduling easier.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Farm Implements Market Growing?
Accelerating Labor Shortages and Aging Agricultural Workforce
Japan faces a critical agricultural labor shortage with the number of core agricultural workers declining significantly over recent years. This dramatic demographic shift creates compelling demand for mechanized solutions that reduce manual labor requirements while maintaining agricultural productivity. The aging farmer population, with a substantial majority aged 65 years and above, accelerates adoption of automated implements featuring user-friendly interfaces and labor-saving technologies. Government initiatives actively promote smart agriculture to address workforce challenges and ensure the long-term sustainability of Japan's agricultural sector.
Government Support and Smart Agriculture Promotion Initiatives
The Japanese government provides substantial support for agricultural mechanization through subsidies, tax incentives, and strategic programs designed to accelerate technology adoption across farming operations. The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries received an allocation of 818 Billion Yen (approximately $ 5.5 Billion) in the fiscal year 2023 supplementary budget, underscoring commitment to enhancing agricultural productivity through technological integration. These initiatives provide financial assistance for farmers adopting precision farming equipment, autonomous machinery, and sustainable technologies while supporting research and development efforts advancing smart agriculture solutions nationwide.
Technological Advancements in Autonomous and Electric Equipment
Rapid technological innovation drives market growth as manufacturers develop increasingly sophisticated farm implements featuring advanced automation and electrification capabilities. Yanmar introduced the YANMAR PRODUCT VISION in November 2024, a forward-looking initiative standardizing components, enhancing automation, and integrating electrification across agricultural equipment. These technological developments address environmental sustainability goals while improving operational efficiency for farmers seeking to reduce carbon footprints and operational costs. The emphasis on cleaner energy sources reflects broader industry commitment to eco-friendly agricultural practices.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Japan Farm Implements Market is Facing?
High Initial Investment Costs for Advanced Equipment
The substantial capital requirements for modern farm implements present significant barriers, particularly for small-scale and part-time farmers who comprise a significant portion of Japan's agricultural sector. Advanced autonomous and precision farming equipment commands premium prices that may not align with the economic realities of fragmented farm operations with limited production volumes.
Declining and Fragmented Agricultural Landholdings
Japan's cultivated land area continues to shrink as farmland is converted for housing and infrastructure development. The average farm size remains extremely small compared to international standards, limiting the economic viability of large-scale equipment investments and requiring specialized compact implements that may not achieve economies of scale in manufacturing.
Technical Complexity and Training Requirements
The increasing sophistication of smart agriculture equipment creates adoption barriers for aging farmers unfamiliar with digital technologies. Effective utilization of GPS-guided systems, IoT sensors, and data analytics platforms requires technical competencies that may exceed the capabilities of traditional farmers without adequate training and support infrastructure.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan farm implements market demonstrates moderate concentration with established domestic manufacturers maintaining dominant positions through technological leadership and comprehensive distribution networks. Major players are leveraging decades of experience in developing equipment specifically suited to Japanese agricultural conditions. These manufacturers emphasize research and development investments in autonomous technologies, electric powertrains, and precision farming systems to address evolving farmer requirements. Strategic partnerships between domestic manufacturers and international technology companies enhance innovation capabilities, while strong relationships with agricultural cooperatives ensure market access across diverse regional markets.
Japan Farm Implements Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Cultivators, Seed Drills, Threshers, Shredders, Sprayers, Others |
| Applications Covered | Plowing and Cultivating, Sowing and Planting, Plant Protection and Fertilizing, Harvesting and Threshing, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan farm implements market size was valued at USD 4,423.61 Million in 2025.
The Japan farm implements market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.80% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 7,998.18 Million by 2034.
Cultivators dominated the market with a share of 24% in 2025, driven by their essential role in soil preparation for rice cultivation and diversified crop production across Japan's agricultural regions.
Key factors driving the Japan farm implements market include accelerating labor shortages and aging agricultural workforce, government support through smart agriculture promotion initiatives, and technological advancements in autonomous and electric equipment.
Major challenges include high initial investment costs for advanced equipment, declining and fragmented agricultural landholdings, technical complexity requiring specialized training, and the need for infrastructure to support smart agriculture adoption across diverse regional farming operations.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












