
Japan Glyphosate Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Crop Type, GMO Adoption, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Glyphosate Market Summary:
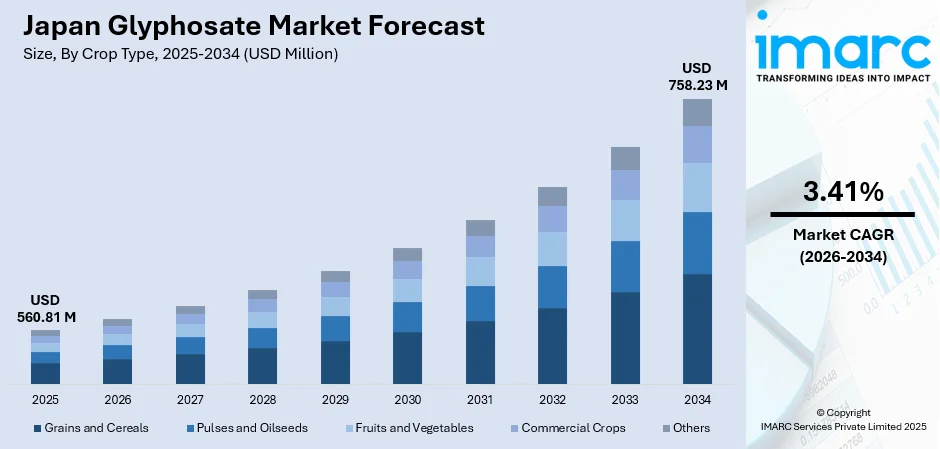
The Japan glyphosate market size was valued at USD 560.81 Million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 758.23 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 3.41% from 2026-2034.
The Japan glyphosate market is propelled by the critical need for efficient weed management solutions amid an aging agricultural workforce and persistent labor shortages in rural areas. The country's emphasis on maintaining crop productivity across its limited arable land necessitates reliable herbicide applications, particularly for staple grain cultivation. Furthermore, the integration of precision agriculture technologies and drone-based spraying systems is enhancing herbicide application efficiency, supporting sustained demand for glyphosate products and driving Japan glyphosate market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Crop Type: Grains and cereals dominate the market with a share of 46.5% in 2025, driven by Japan's focus on rice and wheat production, where glyphosate serves as an essential pre-emergence and post-harvest weed control solution across major cultivation regions.
-
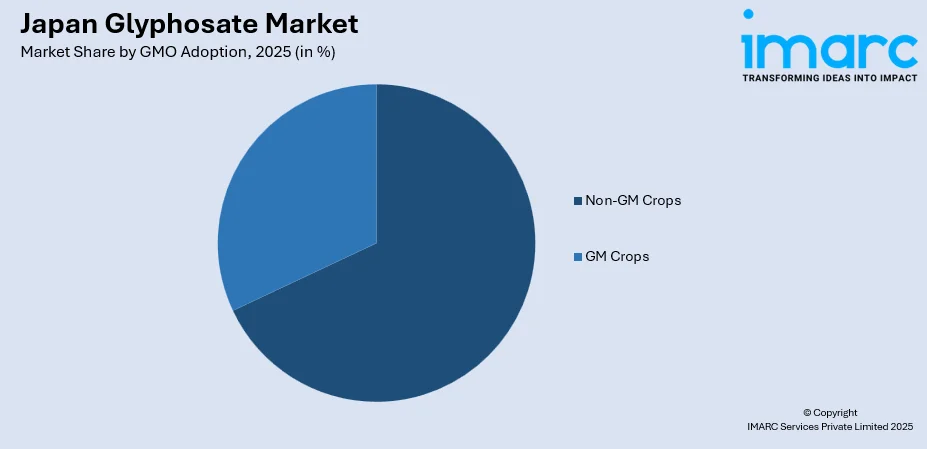
By GMO Adoption: Non-GM crops lead the market with a share of 68.9% in 2025, owing to Japan's stringent labeling regulations requiring zero detectable genetically modified content for non-GM certification and strong consumer preference for conventionally produced agricultural products.
-
By Region: Hokkaido Region represents the largest segment with a market share of 27.7% in 2025, due to its large-scale commercial farms, extensive crop acreage, and higher weed pressure from cooler, wetter conditions. Farm consolidation and labor shortages further increase reliance on chemical weed control for efficient land management.
-
Key Players: Key players are fueling the market expansion through product innovations, improved formulations, and strong distribution networks. They provide farmer training, technical support, and customized solutions, while ensuring regulatory compliance and supply reliability, strengthening user confidence and encouraging long-term adoption across agricultural and non-agricultural segments.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Japan glyphosate market continues to evolve alongside agricultural modernization efforts addressing the country's pressing labor shortage challenges. Farm consolidation and expansion of commercial agriculture support steady herbicide consumption across larger land areas. Urban infrastructure maintenance and non-agricultural applications further strengthen demand beyond farming. In 2024, the Japanese government set aside approximately 100 Billion Yen (€700 Million) for research and the incorporation of robotics in agriculture. These technological advancements, combined with the expansion of large-scale farming operations in key agricultural regions, are sustaining steady market growth while addressing efficiency requirements across diverse cropping systems. As productivity remains crucial in a land-constrained farming system, growers will continue to seek reliable solutions that ensure cleaner fields and stable yields across the country.
Japan Glyphosate Market Trends:
Expansion of Smart Agricultural Equipment Integration
The integration of glyphosate application with smart agricultural equipment continues to accelerate, as manufacturers develop compatible spraying solutions. In October 2024, Yanmar, based in Japan, introduced cutting-edge agricultural machinery, such as the exclusive SA223 Kuro and electric prototype tractors, highlighting the industry's dedication to enhancing herbicide application systems. This equipment evolution supports efficient glyphosate utilization while addressing the mechanization needs of Japan's consolidating farming operations.
Broadening of Large-Scale and Commercial Farming
Japan is gradually shifting from fragmented small farms to more organized commercial farming models. Larger farms require cost-effective and time-saving weed control methods to maintain productivity. Glyphosate fits this need by offering broad-spectrum weed control with fewer applications. It supports mechanized farming and bulk spraying practices, which are essential for handling expanded crop areas efficiently. As farm consolidation is increasing, the demand for reliable herbicides like glyphosate continues to rise.
Growth in Horticulture and Specialty Crops
Japan has a strong market for high-value crops like fruits, vegetables, tea, and flowers. As per OEC, in 2024, Japan shipped ¥1.64B worth of cut flowers, ranking as the 717th most exported item (among 1,177) from Japan. These crops are especially sensitive to weed competition and require precise field management. Glyphosate is widely used in non-crop areas and between rows in plantations where manual control is difficult. As the demand is rising for premium produce, farms are investing more in chemical weed control to maintain product quality and appearance, indirectly boosting glyphosate consumption.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan glyphosate market is projected to experience steady revenue growth, supported by continuous agricultural modernization and the sustained need for effective weed control solutions. The market generated a revenue of USD 560.81 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 758.23 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 3.41% from 2026-2034. The market is driven by the adoption of precision application technologies and expansion of large-scale farming operations. Glyphosate's established position as a cost-effective, broad-spectrum herbicide ensures continued demand across Japan's primary grain and cereal cultivation regions throughout the forecast period.
Japan Glyphosate Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Crop Type | Grains and Cereals | 46.5% |
| GMO Adoption | Non-GM Crops | 68.9% |
| Region | Hokkaido Region | 27.7% |
Crop Type Insights:
- Grains and Cereals
- Pulses and Oilseeds
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Commercial Crops
- Others
Grains and cereals dominate with a market share of 46.5% of the total Japan glyphosate market in 2025.
The grains and cereals segment dominates the Japan glyphosate market, primarily driven by the country's extensive rice and wheat cultivation requiring effective weed management throughout production cycles. Glyphosate applications in this segment serve critical functions, including pre-plant burndown, stubble treatment, and harvest preparation, across Japan's primary agricultural regions.
The segment's leadership reflects established agricultural practices where glyphosate provides reliable broad-spectrum weed control essential for maintaining competitive yields in staple grain production. The integration of glyphosate into mechanized grain production systems supports labor efficiency critical for Japan's aging farming population. Furthermore, the use of glyphosate for pre-harvest desiccation and post-harvest weed management in rice paddies and upland cereal fields ensures continued segment dominance, as farmers prioritize productivity amid workforce constraints.
GMO Adoption Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- GM Crops
- Non-GM Crops
Non-GM crops lead with a share of 68.9% of the total Japan glyphosate market in 2025.
The non-GM crops segment commands substantial market share, reflecting Japan's unique regulatory environment and consumer preferences regarding genetically modified agricultural products. The stringent framework shapes glyphosate application patterns towards conventional cropping systems where identity-preserved production practices dominate domestic cultivation.
Japanese consumers demonstrate strong preferences for conventionally produced agricultural products, with consumer surveys indicating significant awareness regarding production methods and food safety considerations. There is no commercial production of genetically engineered (GE) food crops in Japan, ensuring domestic cultivation relies entirely on conventional varieties requiring traditional herbicide management approaches. The segment's dominance is further reinforced by Japan's position as a major importer of non-segregated commodities for processing while maintaining strict domestic production standards, sustaining glyphosate demand in conventional farming systems.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
Hokkaido Region exhibits a clear dominance with a 27.7% share of the total Japan glyphosate market in 2025.
Hokkaido Region dominates the market in Japan as the nation's largest agricultural producer with approximately JPY 1.3 Trillion in agricultural output value in 2023. The region accounts for major portion of Japan's domestic wheat production and maintains extensive large-scale farming operations ideal for mechanized herbicide application.
The area supports large-scale cultivation of crops, such as potatoes, sugar beet, and corn, which require effective weed control over wide areas. Its cooler climate and longer growing season encourage faster weed spread, increasing herbicide usage. Farms in Hokkaido are more mechanized and commercially operated, making chemical weed management the most practical solution. Labor shortages further increase dependence on herbicides. In addition, organized farming structures and better access to agri-input suppliers support higher and consistent glyphosate adoption.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Glyphosate Market Growing?
Expansion of Large-Scale Farming Operations
The consolidation of Japanese agricultural operations into larger farming enterprises is driving increased glyphosate consumption, as mechanized herbicide application becomes more economically viable. As smaller family farms retire without successors, remaining agricultural land concentrates among commercial operations capable of investing in precision application equipment. Hokkaido exemplifies this trend, with large-scale wheat and potato operations utilizing systematic glyphosate programs for pre-emergence weed control and harvest preparation. The government's promotion of farmland aggregation policies encourages efficient production methods where broad-spectrum herbicides provide cost-effective weed management across expanded cultivation areas. This structural transformation favors glyphosate adoption, as consolidated operations prioritize input efficiency and labor productivity over traditional cultivation practices.
Integration of Smart Agriculture and Precision Application Technologies
The rapid adoption of smart agriculture technologies in Japan is creating new demand channels for glyphosate through enhanced application precision and efficiency. As of November 2024, approximately 40% of Japanese farms employed robotic or automated technology, with drone-based spraying emerging as a particularly impactful application method for herbicide delivery. These technologies enable optimized glyphosate utilization through variable-rate application based on real-time weed pressure assessment, improving efficacy while reducing overall consumption per hectare. Government demonstration projects and subsidies supporting smart agriculture adoption ensure continued technology integration that sustains glyphosate demand within modernizing farming systems. As chemical usage becomes more efficient and controlled, farmers view glyphosate as a practical, manageable input rather than a broad chemical risk. This technological integration supports continued use while aligning with sustainability goals and regulatory expectations.
Increasing Use in Non-Agricultural Applications
Glyphosate demand in Japan is being driven not only by farming but also by urban and industrial usage. Local authorities and facility managers use glyphosate-based products to control weeds along highways, railway tracks, parks, factory compounds, and waterways. As infrastructure is expanding and urban maintenance requirements are rising, weed control is becoming an operational necessity. As per IMARC Group, the Japan transportation infrastructure construction market size reached USD 10.0 Billion in 2025. Manual removal in public spaces is inefficient, expensive, and time-consuming, encouraging the use of chemical solutions. Glyphosate’s ability to manage unwanted vegetation over large areas quickly makes it suitable for municipal and industrial maintenance. Railway operators and power utilities also use it to prevent plant overgrowth that could cause safety hazards or equipment damage. Japan’s emphasis on cleanliness and orderly landscapes further encourages routine chemical weed management. This expanding non-agricultural use base reduces dependence on farming cycles and broadens overall demand for glyphosate across sectors.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges is the Japan Glyphosate Market Facing?
Stringent Regulatory Environment
Japan’s strong focus on food safety and environmental protection results in tough regulations for herbicide approvals and usage limits. Glyphosate products undergo intensive testing and lengthy approval processes, delaying market entry for new formulations. Frequent reviews and tighter compliance requirements raise operational costs for suppliers. Any regulatory amendment can disrupt supply planning. This strict environment discourages smaller manufacturers from entering the market and slows innovations across the glyphosate product portfolio.
Declining Agricultural Workforce
Japan’s aging farming population limits demand growth for agricultural inputs like glyphosate. As small farms close and younger generations move to cities, cultivated land decreases. Lower farm activity reduces herbicide consumption volumes. At the same time, labor shortages push farms to look for automation and low-chemical solutions rather than increased herbicide use. This structural challenge reduces long-term market expansion potential.
Preference for Sustainable Farming Practices
Japanese consumers value clean food and eco-friendly production methods. This has increased the demand for organic farming and reduced chemical use in agriculture. Cooperatives and retailers push farmers toward lower-residue herbicides or natural alternatives. As public sensitivity to health issues increases, glyphosate usage faces social resistance. This shift is encouraging manufacturers to focus on reformulation and diversification, adding pressure on profit margins and market positioning.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan glyphosate market features a competitive environment, characterized by established domestic agrochemical manufacturers alongside global crop protection companies. Competition centers on product formulation innovation, application technology integration, and distribution network coverage across Japan's fragmented agricultural regions. Domestic players leverage long-standing relationships with agricultural cooperatives and regional distribution channels, while multinational companies bring global research capabilities and diverse product portfolios. Strategic alliances between chemical vendors and agricultural technology providers are proliferating, as companies are seeking comprehensive weed management solutions combining herbicides with precision application systems. Intellectual property protection remains stringent, with companies actively defending formulation patents and process innovations. Supply chain considerations, including local warehousing and dual-sourcing strategies, influence competitive positioning as market participants balance cost efficiency with reliable product availability for seasonal application windows.
Japan Glyphosate Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Crop Types Covered | Grains and Cereals, Pulses and Oilseeds, Fruits and Vegetables, Commercial Crops, Others |
| GMO Adoptions Covered | GM Crops, Non-GM Crops |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan glyphosate market size was valued at USD 560.81 Million in 2025.
The Japan glyphosate market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 3.41% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 758.23 Million by 2034.
Grains and cereals dominate the market with a 46.5% share, driven by Japan's extensive rice and wheat cultivation requiring effective pre-emergence and post-harvest weed control solutions across major agricultural regions.
Key factors driving the Japan glyphosate market include severe agricultural labor shortages with an aging farmer population, expansion of large-scale farming operations requiring efficient weed control, and integration of smart agriculture technologies enabling precision herbicide application.
Major challenges include government sustainability targets, growing consumer preference for organic products, development of alternative mechanical and robotic weed control technologies, and increasing regulatory scrutiny regarding environmental impact of chemical herbicides.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












