
Japan Home Healthcare Monitoring Devices Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Home Healthcare Monitoring Devices Market Summary:
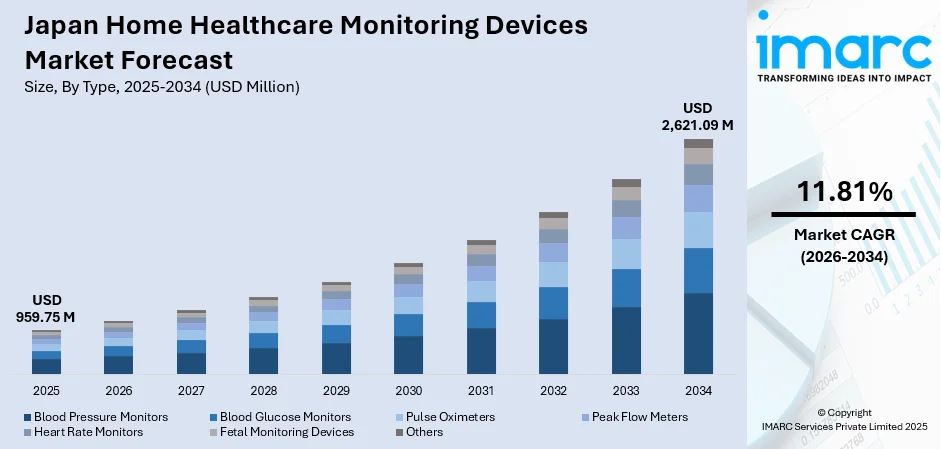
The Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market size was valued at USD 959.75 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2,621.09 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 11.81% from 2026-2034.
Japan’s aging population is driving growing demand for home-based health monitoring solutions. Cultural emphasis on independent living for seniors, coupled with government support for home healthcare services, encourages adoption of monitoring devices. Advanced technology infrastructure and widespread use of digital health platforms make non-invasive self-management tools increasingly accessible in both urban and rural areas. The need for continuous monitoring of chronic conditions among the elderly further supports this trend, prompting ongoing development and investment in home healthcare solutions. As a result, Japan is emerging as a significant market for innovative, patient-centered monitoring devices.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: Blood pressure monitors dominated the market with approximately 37.6% revenue share in 2025, driven by the high prevalence of hypertension among Japan's elderly population and the widespread adoption of digital monitoring solutions integrated with smartphone applications enabling convenient self-management.
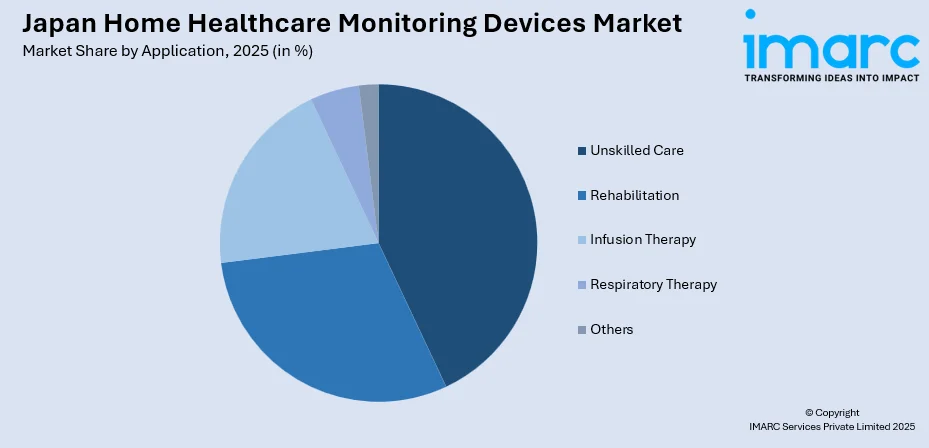
- By Application: Unskilled care segment led the market with a share of 43.2% in 2025, reflecting Japan's cultural preference for family-based caregiving and the government's promotion of community-based integrated care systems that empower non-professional caregivers with accessible monitoring tools.
- By Region: Kanto Region represented the largest market with 33.8% share in 2025, attributable to the concentration of Japan's population in the Tokyo metropolitan area, superior healthcare infrastructure, and higher disposable incomes enabling premium device adoption.
- Key Players: The Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market demonstrates moderate competitive intensity, with established domestic manufacturers competing alongside global medical device corporations across diverse product categories and price segments.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The market is undergoing transformation driven by technological integration, demographic pressures, and evolving healthcare delivery models. Japan’s expertise in precision manufacturing and electronics engineering gives domestic companies a competitive edge in developing innovative monitoring solutions. In October 2025, Fujitsu completed an AI‑driven pilot project with Genshukai in Iki City, Nagasaki, aimed at improving hospital and home‑care management with data‑integration and AI, and the company estimates the solution could boost annual revenues by about 10%. Government initiatives emphasizing preventive care and home-based health management create supportive policy conditions for market growth. Rising digital literacy and smartphone penetration among older populations facilitate adoption of connected health devices. Combined with cultural preferences for independent living and non-invasive self-care, these factors are accelerating demand for advanced home healthcare monitoring solutions, positioning Japan as a leading market for patient-centered, technology-driven healthcare innovation.
Japan Home Healthcare Monitoring Devices Market Trends:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Remote Monitoring Capabilities
Healthcare providers and device manufacturers are increasingly incorporating artificial intelligence algorithms into monitoring systems, enabling real-time health assessments and predictive analytics for chronic disease management. Connected devices equipped with cloud connectivity and smartphone applications allow healthcare professionals to remotely track patient vitals, facilitating timely interventions and reducing unnecessary hospital visits. For example, in March 2023 Fujitsu launched a cloud-based platform in Japan that enables secure aggregation and analysis of health-related data (vital signs, step counts, calorie consumption etc.), paving the way for IoT + AI-based preventive care and individualized health management. This technological convergence aligns with Japan's digital healthcare transformation objectives.
Rising Demand for Compact and Wearable Monitoring Solutions
Consumer preferences are shifting toward miniaturized, wearable devices that enable continuous health monitoring without disrupting daily activities. Wrist-type blood pressure monitors, smart rings, and patch-based sensors are gaining popularity due to their convenience and discreet design. In 2024, the market for medical-grade wearables in Japan was valued at about USD 1,985.96 million, showing significant demand for compact, everyday health-monitoring devices. Japanese manufacturers are leveraging expertise in precision engineering to develop medical-grade wearable devices that meet stringent accuracy requirements while maintaining user comfort and aesthetic appeal.
Expansion of Telemedicine and Digital Health Ecosystems
The proliferation of telemedicine services is driving demand for home monitoring devices that seamlessly integrate with virtual consultation platforms. Healthcare systems are establishing digital ecosystems connecting monitoring devices, electronic health records, and telehealth applications to enable comprehensive remote patient management. For example, in April 2024, the government of Japan began a pilot program delivering telemedicine services through post offices, enabling online doctor consultations and home delivery of prescriptions, simplifying access to remote care and encouraging the integration of remote monitoring and telehealth. Government policy revisions expanding reimbursement coverage for telemedicine services further accelerate the adoption of connected home monitoring solutions.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market is positioned for sustained expansion, supported by demographic imperatives, technological innovation, and supportive government policies. Aging population dynamics will continue driving demand for accessible self-monitoring solutions enabling independent living. Integration of advanced technologies including artificial intelligence, continuous monitoring capabilities, and cloud connectivity will enhance device functionality and clinical utility. Healthcare system reforms emphasizing preventive care and home-based management will create favorable reimbursement conditions. The market generated a revenue of USD 959.75 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 2,621.09 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 11.81% from 2026-2034.
Japan Home Healthcare Monitoring Devices Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Blood Pressure Monitors | 37.6% |
| Application | Unskilled Care | 43.2% |
| Region | Kanto Region | 33.8% |
Type Insights:
- Blood Pressure Monitors
- Blood Glucose Monitors
- Pulse Oximeters
- Peak Flow Meters
- Heart Rate Monitors
- Fetal Monitoring Devices
- Others
The blood pressure monitors dominate with a market share of 37.6% of the total Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market in 2025.
Japan has one of the highest hypertension prevalence rates globally, with an estimated 43 million individuals affected by the condition. The aging demographic profile, characterized by elevated susceptibility to cardiovascular disorders, creates substantial demand for accessible blood pressure monitoring solutions. Cultural emphasis on preventive healthcare and regular self-monitoring has established home blood pressure measurement as a standard health management practice among Japanese households.
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced the functionality and user experience of blood pressure monitors in Japan. Modern devices feature Bluetooth connectivity enabling automatic data synchronization with smartphone applications, facilitating trend tracking and physician sharing. Wrist-type and upper-arm monitors with cuffless measurement capabilities are gaining traction among consumers seeking convenient monitoring options. Domestic manufacturers continue investing in sensor accuracy improvements and artificial intelligence integration to detect irregular heartbeats and potential cardiovascular risks.
Application Insights:
Access the Comprehensive Market Breakdown Request Sample
- Rehabilitation
- Infusion Therapy
- Unskilled Care
- Respiratory Therapy
- Others
The unskilled care leads with a share of 43.2% of the total Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market in 2025.
Japan's healthcare system prioritizes community-based integrated care that enables elderly individuals to receive support within familiar home environments. Under the revised Long‑Term Care Insurance (LTCI) framework updated in 2024, care-service providers can now combine home-visit nursing and small-scale in-home care support, and home-care support businesses are allowed to handle care-prevention and support planning tasks previously handled only by community support centers. Cultural traditions emphasizing filial responsibility motivate family members to actively participate in health management for aging relatives.
Device manufacturers have responded to unskilled care requirements by developing intuitive interfaces with large displays, voice guidance features, and simplified operation procedures. Automated measurement capabilities minimize technical expertise requirements while maintaining clinical accuracy. Connected devices enable remote oversight by healthcare professionals, providing expert guidance to family caregivers managing chronic conditions. The expansion of certified home nursing services and government-authorized foreign caregivers further supports unskilled care segment growth.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto Region exhibits a clear dominance with a 33.8% share of the total Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market in 2025.
The Kanto Region, encompassing the Tokyo metropolitan area and surrounding prefectures, concentrates approximately one-third of Japan's total population and significant healthcare infrastructure. Higher income levels in metropolitan areas enable greater adoption of premium monitoring devices with advanced features. Dense urban environments facilitate efficient distribution networks and after-sales service accessibility.
Healthcare technology innovation clusters centered in Tokyo drive product development and early adoption of emerging monitoring solutions. Leading medical device companies maintain headquarters and research facilities in the region, fostering close collaboration between manufacturers and healthcare providers. Government digital health initiatives and smart city programs create favorable conditions for connected health technology deployment across Kanto communities.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Home Healthcare Monitoring Devices Market Growing?
Rapidly Aging Population and Rising Chronic Disease Burden
Japan has one of the world’s most aged populations, with a large proportion of elderly citizens. Indeed, as of 2024 the number of people aged 65 or older reached a record high of 36.25 million — about 29.3% of the total population. This demographic trend drives significant demand for healthcare solutions that support independent living and management of chronic illnesses at home. Conditions common among older adults, such as hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders, require ongoing monitoring to prevent complications and enable timely medical intervention. Emphasis on community-based integrated care encourages home-based health management, boosting adoption of monitoring devices among aging households.
Government Initiatives Promoting Home Healthcare Services
Healthcare policy in Japan increasingly focuses on preventive care and home-based health management to ensure sustainable healthcare delivery. Reforms aim to expand access to telemedicine services and remote monitoring technologies. National initiatives envision a shift toward prevention-oriented, home-centered care models. For example, under the Medical Digital Transformation (DX) Promotion Plan, the Japanese government is actively promoting nationwide adoption of cloud-based electronic medical records (EMRs) and enabling interoperable medical information sharing across institutions, facilitating telemedicine, remote monitoring, and data-driven care. Policy support includes incentives for digital health adoption, streamlined regulatory pathways for innovative devices, and awareness campaigns promoting self-monitoring practices. These measures create favorable conditions that encourage both consumer adoption of home healthcare solutions and investment from manufacturers.
Technological Advancements in Connected Health Devices
Innovation in sensor technology, wireless connectivity, and artificial intelligence is enhancing home healthcare monitoring capabilities. Modern devices feature seamless data transmission to healthcare providers and cloud platforms. AI algorithms improve diagnostic accuracy, detect anomalies, and offer personalized health insights. For example, OMRON Healthcare has recently rolled out home‑use blood‑pressure monitors with integrated ECG functionality and AI‑based atrial‑fibrillation (AFib) detection, enabling not just BP readings but also early detection of irregular heart rhythm using everyday home devices. Advances in miniaturization allow wearable devices to integrate continuous monitoring into daily routines without disrupting lifestyles. Japan’s strength in precision electronics manufacturing gives domestic companies a competitive edge in producing sophisticated monitoring solutions that meet rigorous quality standards.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Japan Home Healthcare Monitoring Devices Market is Facing?
Limited Digital Literacy Among Elderly User Segments
Despite Japan's technological advancement, significant portions of the elderly population face challenges adopting connected health technologies due to limited familiarity with digital interfaces and smartphone applications. Complex device operation procedures and data synchronization requirements may deter adoption among primary target demographics, necessitating continued investment in intuitive design and user education initiatives.
High Product Costs and Reimbursement Limitations
Advanced monitoring devices incorporating connectivity features and artificial intelligence capabilities command premium pricing that may exceed affordability thresholds for fixed-income elderly consumers. While government insurance programs cover certain devices, reimbursement limitations for newer technologies and consumable supplies create financial barriers impacting adoption rates across income-sensitive market segments.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Connected health devices generate sensitive personal health information requiring robust protection against unauthorized access and data breaches. Consumer concerns regarding privacy and data security may inhibit adoption of connected monitoring solutions, particularly among demographics less comfortable with digital data sharing practices. Manufacturers must invest in comprehensive security measures and transparent data handling policies.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market exhibits moderately fragmented competitive dynamics, with established domestic manufacturers maintaining strong market positions alongside international medical device corporations. Japanese companies leverage deep understanding of local consumer preferences, distribution network advantages, and reputation for quality to compete effectively against global entrants. Key competitive strategies include continuous product innovation, strategic partnerships with healthcare providers and technology companies, and expansion of connected health ecosystems. Companies are investing in artificial intelligence integration, wearable device development, and telemedicine platform connectivity to differentiate product offerings. Distribution channel optimization through pharmacy networks, e-commerce platforms, and direct consumer relationships remains essential for market penetration.
Recent Developments:
- In June 2025: Fujitsu Limited rolled out its new “Millimeter‑Wave Monitoring System,” a privacy‑first, radar‑based solution for care homes, assisted‑living facilities, and accessible toilets. The system uses millimeter‑wave radar plus AI to detect breathing, muscle activity and subtle body vibrations, alerting for falls or irregular breathing without video or personal‑data capture, allowing safe 24/7 monitoring even in low‑light, privacy‑sensitive environments.
Japan Home Healthcare Monitoring Devices Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Blood Pressure Monitors, Blood Glucose Monitors, Pulse Oximeters, Peak Flow Meters, Heart Rate Monitors, Fetal Monitoring Devices, Others |
| Applications Covered | Rehabilitation, Infusion Therapy, Unskilled Care, Respiratory Therapy, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market size was valued at USD 959.75 Million in 2025.
The Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 11.81% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 2,621.09 Million by 2034.
Blood pressure monitors held the largest market share with 37.6%, driven by high hypertension prevalence among Japan's aging population and widespread adoption of digital self-monitoring practices.
Key factors driving the Japan home healthcare monitoring devices market include the rapidly aging population, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, government initiatives promoting home-based care, technological advancements in connected health devices, and expanding telemedicine adoption.
Major challenges include limited digital literacy among elderly users, high product costs for advanced connected devices, reimbursement limitations for newer technologies, data privacy and security concerns, and the need for interoperability across diverse healthcare platforms.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












