
Japan Isobutanol Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Isobutanol Market Summary:
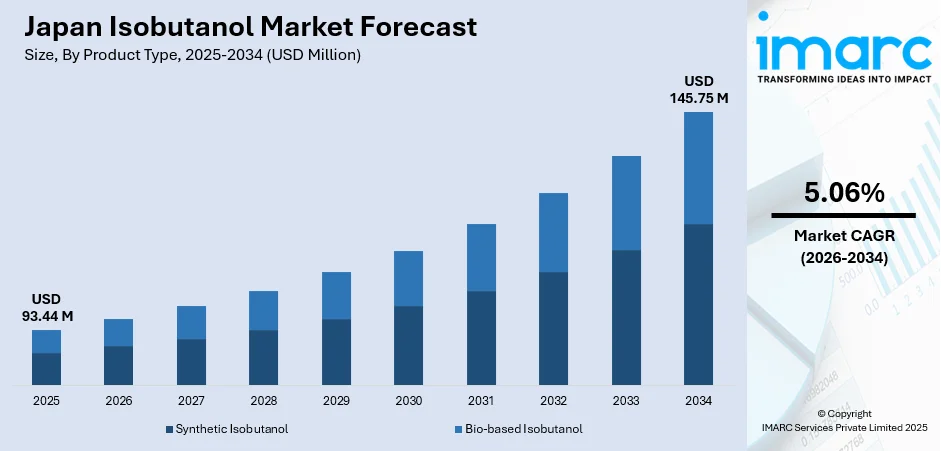
The Japan isobutanol market size was valued at USD 93.44 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 145.75 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.06% from 2026-2034.
The Japan isobutanol market is experiencing steady growth driven by expanding industrial applications across petrochemical, coatings, and chemical manufacturing sectors. Rising demand for high-performance solvents and chemical intermediates, coupled with Japan's advanced manufacturing infrastructure and stringent quality requirements, continues to support market development across diverse end-use industries.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Product Type: Synthetic isobutanol dominated the market with approximately 65.05% revenue share in 2025, driven by established petrochemical manufacturing capabilities, consistent product quality specifications, competitive pricing advantages, and reliable supply chain infrastructure supporting large-scale industrial consumption requirements.
-
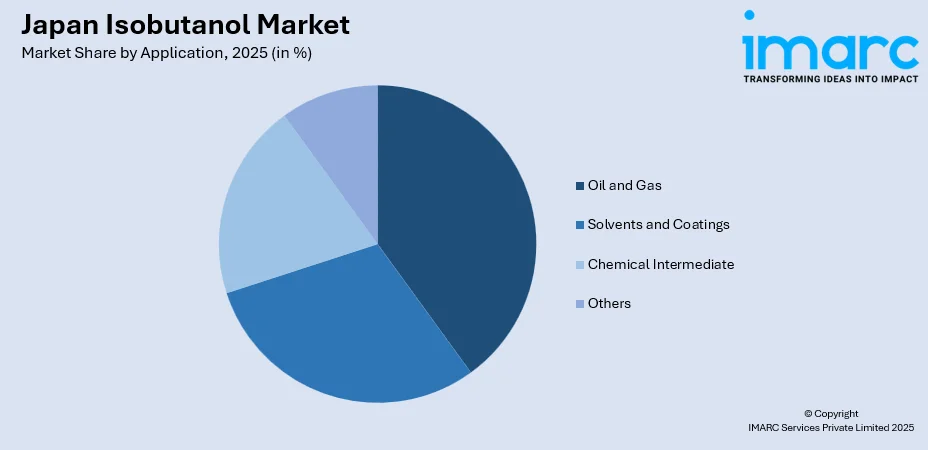
By Application: Oil and gas led the market with a share of approximately 35.12% in 2025, owing to extensive utilization as drilling fluid additives, corrosion inhibitors, and process solvents within Japan's refinery operations and offshore exploration activities requiring high-purity chemical inputs.
-
Key Players: The Japan isobutanol market exhibits moderate competitive intensity, characterized by established chemical manufacturers with integrated production facilities competing alongside specialized distributors. Market participants differentiate through product purity grades, technical support services, supply reliability, and customized formulation capabilities addressing specific industrial requirements.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Japan isobutanol market benefits from the nation's sophisticated chemical manufacturing ecosystem and strong industrial demand base. Isobutanol serves as a versatile chemical compound utilized across multiple applications including solvent formulations, chemical synthesis intermediates, and fuel additives. In November 2025, Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Company, a major Japanese chemical producer, signed a long-term purchase agreement with U.S.-based Transition Industries to offtake approximately 1 million tons per year of ultra-low-carbon methanol, underscoring Japanese chemical firms’ strategic moves toward low-carbon feedstocks and sustainable chemical value chains. Japan's advanced petrochemical infrastructure supports efficient synthetic isobutanol production while emerging bio-based alternatives gain attention amid sustainability initiatives. The market landscape reflects balanced demand across oil and gas processing, coatings manufacturing, and specialty chemical production sectors that value isobutanol's favorable solvent properties and chemical reactivity characteristics.
Japan Isobutanol Market Trends:
Growing Interest in Bio-based Isobutanol Alternatives
The Japanese chemical industry demonstrates increasing interest in bio-based isobutanol production pathways aligned with national sustainability objectives. Sojitz Corporation has been investing in the development and commercialization of biomass-derived chemicals, including bio-isobutanol, through its stake in the Tokyo-based Green Earth Institute, an effort to leverage microbial fermentation technologies for low-cost green chemical production from non-food biomass. Fermentation-derived isobutanol offers renewable sourcing advantages appealing to environmentally-conscious industrial consumers. Research initiatives explore advanced biotechnology approaches enhancing bio-isobutanol yield efficiency while manufacturers evaluate integration opportunities within existing supply chains.
Expansion of High-Purity Grade Applications
Demand growth for high-purity isobutanol grades reflects expanding applications in electronics manufacturing, pharmaceutical synthesis, and specialty coatings requiring stringent quality specifications. According to reports, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, a key player in the isobutanol industry, is leveraging cutting-edge Oxo process technology to produce high-purity isobutanol with an elevated normal-to-iso isomer ratio that enhances product quality and lowers purification costs for downstream users. Japanese manufacturers invest in purification technologies delivering ultra-high purity products commanding premium positioning. This trend supports value-added market development beyond commodity chemical applications.
Integration into Advanced Fuel Formulations
Isobutanol is attracting growing interest as a biofuel blending component due to its higher energy density and better compatibility with existing engines and fuel systems compared to conventional bioethanol. In Japan, energy sector stakeholders are increasingly assessing the feasibility of incorporating isobutanol into next-generation fuel formulations. This approach aligns with national transportation decarbonization goals while enabling the use of existing fuel distribution and storage infrastructure, reducing transition costs and operational challenges for refiners and fuel retailers.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan isobutanol market is positioned for moderate growth throughout the forecast period, supported by sustained industrial demand across established application segments and emerging opportunities in bio-based production and advanced fuel applications. Revenue generation will benefit from premiumization trends favoring high-purity specialty grades while conventional synthetic isobutanol maintains volume leadership through cost competitiveness. The market outlook reflects balanced development combining traditional petrochemical production with gradual bio-based capacity expansion aligned with Japan's carbon neutrality commitments and circular economy initiatives. The market generated a revenue of USD 93.44 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 145.75 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.06% from 2026-2034.
Japan Isobutanol Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Synthetic Isobutanol | 65.05% |
| Application | Oil and Gas | 35.12% |
Product Type Insights:
- Synthetic Isobutanol
- Bio-based Isobutanol
The synthetic isobutanol dominates with a market share of 65.05% of the total Japan isobutanol market in 2025.
Synthetic isobutanol maintains market leadership through established production infrastructure leveraging Japan's advanced petrochemical capabilities. In March 2025, JFE Engineering Corporation completed its acquisition of a 66.6% stake in Sumitomo Chemical Engineering, now renamed JFE Plant Technology, to enhance engineering and construction capabilities for advanced chemical plants supporting petrochemicals and semiconductor materials production in Japan. The oxo synthesis process delivers consistent product quality meeting stringent industrial specifications required by downstream manufacturers. Economies of scale achieved through integrated production facilities enable competitive pricing supporting broad industrial adoption across diverse application segments.
The synthetic route offers reliable supply characteristics essential for industrial consumers requiring consistent material availability. Established quality control protocols ensure batch-to-batch consistency critical for applications in coatings, chemical synthesis, and specialty formulations. While bio-based alternatives gain development attention, synthetic isobutanol remains the practical choice for volume industrial applications prioritizing cost efficiency and supply security.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Oil and Gas
- Solvents and Coatings
- Chemical Intermediate
- Others
The oil and gas leads with a share of 35.12% of the total Japan isobutanol market in 2025.
The oil and gas application segment demonstrates strong market performance driven by isobutanol's essential role in refinery operations and petrochemical processing. Utilization as drilling fluid additives, process solvents, and extraction agents supports upstream and downstream petroleum industry requirements. Japan’s oil and gas market reached 3.08 BPD of oil and 6.93 Tcf of natural gas in 2024, and according to IMARC Group, is expected to rise to 4.43 BPD and 9.37 Tcf by 2033, reflecting sustained long-term activity across the energy value chain. Japan's refinery infrastructure generates consistent demand for high-quality isobutanol meeting operational specifications.
Isobutanol's favorable chemical properties including moderate volatility, water miscibility, and compatibility with hydrocarbons make it valuable across oil and gas processing applications. The compound serves as corrosion inhibitor components and gas treatment chemicals within refinery operations. Continued investment in refinery efficiency improvements and maintenance activities sustains demand for specialty chemical inputs including isobutanol.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto region represents Japan's largest isobutanol consumption center, driven by the concentration of chemical manufacturing facilities, petrochemical complexes, and industrial end-users in the Tokyo metropolitan area and surrounding prefectures. Advanced logistics infrastructure and proximity to major ports facilitate efficient raw material procurement and product distribution.
The Kansai/Kinki region serves as a significant isobutanol market, supported by established chemical and petrochemical industries centered around Osaka and surrounding industrial zones. The region's manufacturing heritage in coatings, specialty chemicals, and industrial processing generates consistent demand for high-quality solvent and chemical intermediate applications.
The Central/Chubu region demonstrates strong isobutanol consumption driven by Japan's automotive manufacturing hub requiring coatings, adhesives, and specialty chemicals. Nagoya's industrial corridor hosts numerous chemical processing facilities serving automotive supply chains and broader manufacturing sectors demanding consistent chemical input supply.
The Kyushu-Okinawa region contributes to isobutanol demand through its petrochemical processing facilities, semiconductor manufacturing operations, and industrial chemical consumers. Strategic port locations facilitate import access while regional chemical production supports local industrial requirements across diverse application segments.
The Tohoku region maintains moderate isobutanol consumption centered on chemical manufacturing, electronics production, and industrial processing operations. Post-reconstruction industrial development has strengthened regional manufacturing capabilities, generating stable demand for chemical inputs including solvents and processing aids.
The Chugoku region hosts significant petrochemical infrastructure along the Seto Inland Sea industrial corridor, supporting isobutanol production and consumption activities. Regional chemical complexes and manufacturing facilities generate demand for solvent applications, chemical intermediates, and specialty formulation requirements.
The Hokkaido region represents a smaller but growing isobutanol market, driven by regional industrial development, agricultural chemical applications, and energy sector activities. The region's expanding manufacturing base and natural resource industries create emerging demand for chemical inputs and specialty solvents.
The Shikoku region maintains specialized isobutanol consumption through its chemical manufacturing facilities and paper industry operations. Regional industrial clusters focused on specialty chemicals and materials processing generate targeted demand for high-purity solvents and chemical intermediate applications.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Isobutanol Market Growing?
Expanding Industrial Solvent Applications
Japan's advanced manufacturing sector generates sustained demand for high-performance solvents including isobutanol across diverse industrial applications. For example, in 2025, major domestic producers such as JNC Corporation and KH NeoChem implemented price increases for isobutanol in Japan, reflecting strong underlying industrial cost pressures and continued demand from local manufacturers. The compound's favorable solvent properties including appropriate evaporation rate, compatibility with various resins, and low toxicity profile make it valuable for coatings, inks, and adhesive formulations. Continued manufacturing activity in automotive, electronics, and general industrial sectors supports consistent isobutanol consumption. Quality-conscious Japanese manufacturers prioritize solvent performance characteristics, creating demand for premium-grade isobutanol meeting stringent specifications.
Chemical Intermediate Demand Growth
Isobutanol serves as an important chemical intermediate for synthesizing various downstream products including isobutyl acetate, isobutyl acrylate, and other specialty chemicals. In October 2025, Japan’s Mitsui Chemicals acquired co‑catalyst producer Nippon Aluminum Alkyls to strengthen its capabilities in catalysts and organometallic derivatives used in specialty chemicals and polymer production, a move reflecting Japanese manufacturers’ focus on securing advanced inputs for derivative supply chains. Japan's sophisticated chemical manufacturing ecosystem requires reliable intermediate supply supporting production of performance chemicals, plasticizers, and specialty formulations. Growing demand for these derivative products drives upstream isobutanol consumption. The integrated nature of Japanese chemical complexes facilitates efficient intermediate utilization across interconnected production processes.
Oil and Gas Sector Requirements
Japan's petroleum refining and gas processing operations maintain consistent isobutanol demand for various operational applications. The compound's utility as drilling additives, extraction solvents, and process chemicals supports upstream and downstream energy sector activities. Refinery maintenance programs and capacity optimization initiatives require specialty chemical inputs including isobutanol. Japan's strategic focus on energy security and refining efficiency sustains demand for high-quality chemical supplies supporting operational requirements.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Japan Isobutanol Market is Facing?
Feedstock Price Volatility
Synthetic isobutanol production costs remain sensitive to petrochemical feedstock price fluctuations affecting propylene and synthesis gas inputs. Global crude oil price volatility translates into feedstock cost uncertainty impacting manufacturer margins and pricing strategies. Market participants must manage commodity price exposure while maintaining competitive positioning.
Environmental Regulatory Pressures
Increasingly stringent environmental regulations governing volatile organic compound emissions affect isobutanol applications in coatings and solvent formulations. Regulatory compliance requirements may drive reformulation toward lower-VOC alternatives in certain applications. Manufacturers must balance performance requirements with environmental compliance obligations.
Competition from Alternative Solvents
Isobutanol faces competition from alternative solvent chemistries including other alcohols, esters, and bio-based options offering different performance profiles. Customer evaluation of solvent alternatives based on cost, performance, and environmental characteristics creates competitive pressure. Market participants must demonstrate isobutanol's value proposition across specific application requirements.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan isobutanol market features a competitive environment characterized by established chemical manufacturers with integrated production capabilities competing alongside specialized distributors and trading companies. Market participants differentiate through product quality specifications, technical service support, supply chain reliability, and customized packaging solutions. Domestic producers leverage local manufacturing presence and customer relationships while importers offer competitive pricing on commodity-grade materials. The competitive landscape increasingly reflects sustainability considerations as bio-based isobutanol alternatives gain development attention. Strategic partnerships between producers, distributors, and end-users facilitate market development and supply chain optimization. Technical expertise and application support capabilities serve as important competitive differentiators in serving sophisticated industrial customers requiring formulation assistance and quality assurance.
Recent Developments:
-
In December 2024, Researchers achieved a high‑yield bio‑isobutanol breakthrough, producing up to 94% of theoretical yield from lignocellulosic biomass via engineered microbes. Technoeconomic modeling indicated process improvements could cut production costs by ~46%, bringing bio‑isobutanol closer to commercial viability as a sustainable fuel and chemical feedstock.
Japan Isobutanol Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered | Synthetic Isobutanol, Bio-based Isobutanol |
| Applications Covered | Oil and Gas, Solvents and Coatings, Chemical Intermediate, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan isobutanol market size was valued at USD 93.44 Million in 2025.
The Japan isobutanol market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.06% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 145.75 Million by 2034.
Synthetic isobutanol dominated the market with approximately 65.05% share, driven by established petrochemical production infrastructure, consistent quality specifications, and competitive pricing advantages.
Key factors driving the Japan isobutanol market include expanding industrial solvent applications, chemical intermediate demand growth, and oil and gas sector requirements for specialty chemical inputs.
Major challenges include feedstock price volatility affecting production costs, environmental regulatory pressures on VOC emissions, and competition from alternative solvent chemistries in certain applications.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












