
Japan Ports Infrastructure Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Port Type, Construction Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Ports Infrastructure Market Overview:
The Japan Ports Infrastructure market size reached USD 12,453.0 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 18,029.9 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 4.20% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by rising global trade demands, government-led modernization initiatives, and the need for efficient logistics. Additionally, competition with regional hubs and stricter environmental regulations push advancements in sustainability and operational efficiency, ensuring long-term market expansion. Investments in smart technologies (IoT, AI, automation) and green port solutions (electrification, LNG bunkering) are further expanding the Japan ports infrastructure market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 12,453.0 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 18,029.9 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 4.20% |
Japan Ports Infrastructure Market Trends:
Rising Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) for Port Modernization
Japan is increasingly leveraging public-private partnerships (PPPs) to accelerate port infrastructure development and modernization. Japan is leveraging Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs), which include 1,071 Private Finance Initiative (PFI) projects (903 local and 107 national) as of March 2024, to upgrade its aging infrastructure, including ports, in response to fiscal constraints and a shrinking population. The 2024 PPP/PFI Action Plan will see ¥30 Trillion (approximately USD 206.94 Billion) spent on projects over a decade, highlighting increased efficiency throughout the industries and regional development, ports being set to benefit from the use of extended Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) and concession schemes. Recent changes in the PFI Act have eased risk-sharing and subsidy procedures, while new economic security regulations ensure the stable operation of infrastructure, such as port improvements, under tighter control. The government is collaborating with global logistics firms and domestic corporations to upgrade aging facilities, expand container terminals, and enhance connectivity. Therefore, this is also supporting the Japan ports infrastructure market growth. Projects, such as the expansion of the Port of Yokohama and the development of new deep-water ports in regional areas, rely on private investment for funding and expertise. These partnerships help mitigate financial risks while improving operational efficiency and competitiveness. Additionally, PPPs facilitate the adoption of advanced technologies, such as automated cargo systems and digital tracking platforms. With Japan aiming to strengthen its position as a key Asian trade hub, PPPs are becoming a critical strategy for sustaining growth in the ports infrastructure sector.

To get more information on this market Request Sample
Expansion of Green Port Initiatives to Meet Emission Targets
Japan's ports are increasingly adopting green infrastructure initiatives to comply with stricter environmental regulations and achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. Key strategies include electrification of port equipment, shore power systems for docked vessels, and the use of renewable energy sources, including solar and wind. Since 2013, Japan has recorded a 19% decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, yet it still relies on fossil fuels, with 30% of its power emanating from coal. Ports are gearing up to use renewable energy resources that make up 23% of the energy mix and circular economy schemes that aim at 20% waste recycling, all under the 2024 Green Transformation (GX) Policy. Over 60% of the local governments are targeting net-zero emissions by 2050, backed by 82 decarbonization pilot zones and 146 circular economy initiatives that improve port activity via agrivoltaics and tighter emissions rules to meet OECD standards. Major ports, including Tokyo and Kobe, are implementing LNG bunkering facilities and hydrogen fuel stations to support cleaner shipping alternatives. The government's "Green Growth Strategy" further incentivizes eco-friendly port upgrades through subsidies and tax benefits. Additionally, partnerships with global organizations are fostering the adoption of low-emission technologies, such as hybrid cranes and energy-efficient lighting. As international pressure for sustainable logistics grows, Japan's focus on green port infrastructure positions it as a leader in eco-conscious maritime operations, driving long-term market growth.
Japan Ports Infrastructure Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on port type, construction type, and application.
Port Type Insights:
- Sea Port
- Inland Port
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the port type. This includes sea port and inland port.
Construction Type Insights:
- Terminal
- Equipment
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the construction type have also been provided in the report. This includes terminal and equipment.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
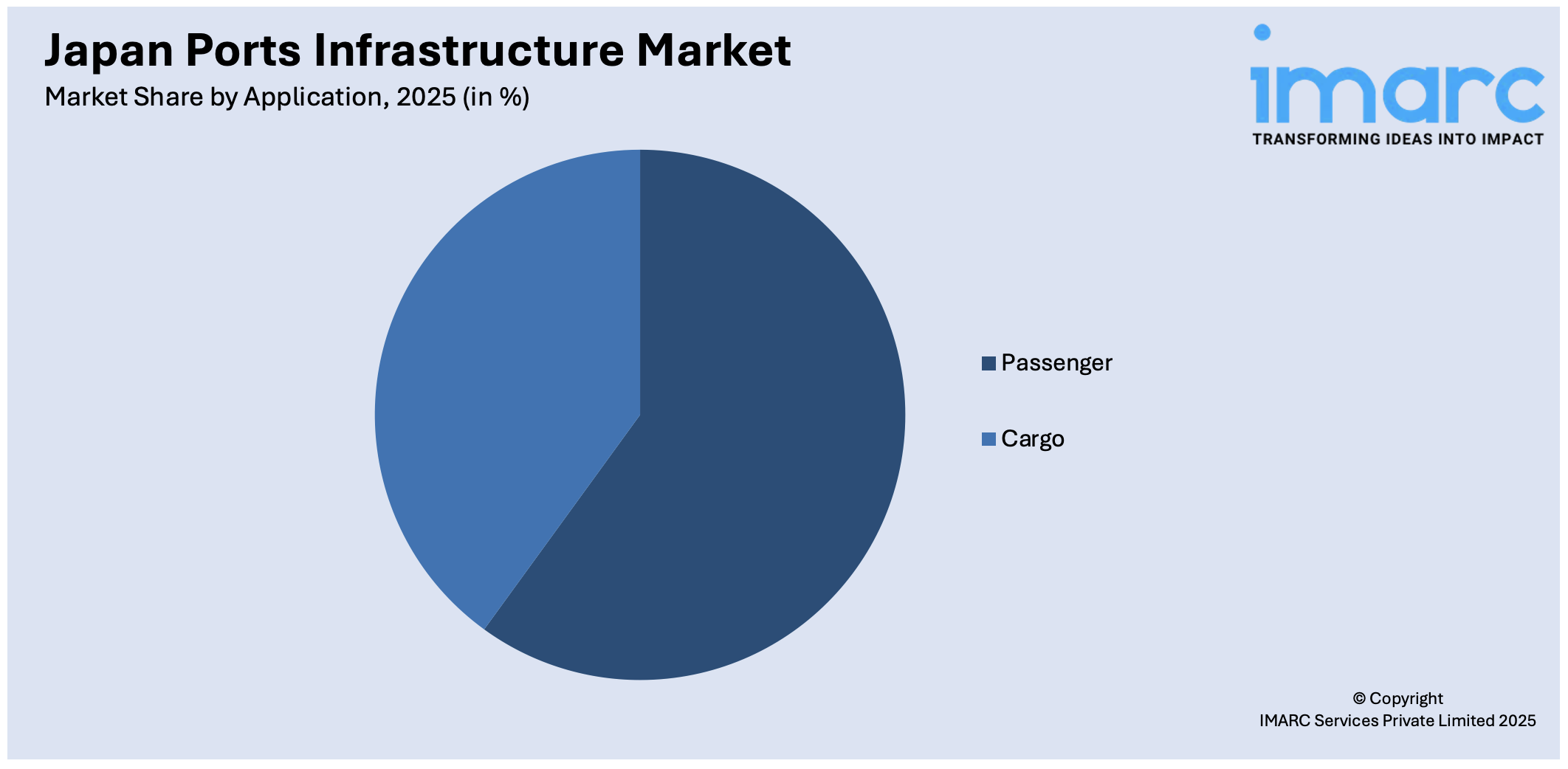
- Passenger
- Cargo
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application. This includes passenger and cargo.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, and Shikoku Region.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Japan Ports Infrastructure Market News:
- October 24, 2024: Japan has started its first operation of a hydrogen-fueled rubber-tired gantry (RTG) crane at Oi Container Terminal. This technology features fuel cells that were established through collaboration by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government, NYK Line, Uni-X NCT, Mitsui E&S, and Iwatani Corporation with the goal of minimizing carbon emissions in port operations. This project is a part of Japan's overall strategy towards carbon neutrality in port facilities. It aligns with earlier hydrogen-fueled cargo handling initiatives in Tokyo, Kobe, and Los Angeles, thus positioning Japan as a leader in sustainable maritime logistics.
- September 4, 2024: The Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Mitsui E&S and Yılport Holding A.Ş. to promote the export of port infrastructure, thus supporting Yılport's global terminal operations and development in regions such as Latin America and Africa. This collaboration is consistent with Japan's 2030 infrastructure vision and the G7-backed partnership for global infrastructure and investment (PGII) program, thus enhancing supply chain resilience and cementing Japan's position as a world leader in port machinery exports and economic security.
Japan Ports Infrastructure Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Port Types Covered | Sea Port, Inland Port |
| Construction Types Covered | Terminal, Equipment |
| Applications Covered | Passenger, Cargo |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Japan ports infrastructure market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Japan ports infrastructure market on the basis of port type?
- What is the breakup of the Japan ports infrastructure market on the basis of construction type?
- What is the breakup of the Japan ports infrastructure market on the basis of application?
- What is the breakup of the Japan ports infrastructure market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Japan ports infrastructure market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Japan ports infrastructure market?
- What is the structure of the Japan ports infrastructure market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Japan ports infrastructure market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Japan ports infrastructure market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Japan ports infrastructure market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Japan ports infrastructure industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












